IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
Archives
(PRELIMS + MAINS FOCUS)
PM-CARES for Children scheme
Part of: GS Prelims and GS -II – Policies and interventions
In news
- The Central government has announced the “PM-CARES for Children” scheme for all those children orphaned due to Covid-19.
- Also, the Supreme Court has ordered the district authorities to upload the details of children in need of care and protection on NCPCR (National Commission for Protection of Child Rights) portal Bal Swaraj.
Salient features of the Scheme

- Corpus of Rs. 10 Lakh:
- A corpus of Rs. 10 lakh will be allocated to each of these children from the PM CARES fund.
- It will provide monthly stipend from 18 years of age.
- On attaining 23 years, he/she will get the corpus amount.
- Education to the Children (under 10 years):
- Ensure admission to Kendriya Vidyalayas/ private schools.
- PM CARES will pay for the uniform text books and notebooks
- If the child is admitted in a private school the fees as per the RTE norms will be provided
- Education to the Children (11-18 years):
-
- The child will be given admission in any Central Government Residential School
-
- In case the child is to be continued under the care of guardian, he/she will be given admission in the nearest Kendriya Vidyalaya/private school
- Higher education:
-
- Provision of either a scholarship equivalent to the tuition fees/ educational loans.
- Interest on the loan will be paid by the PM-CARES fund.
- Health Insurance:
- All children will be enrolled as a beneficiary under Ayushman Bharat Scheme
- The premium amount will be paid by PM-CARES till a child turns 18.
Emergency Credit Line Guarantee Scheme (ECLGS) 4.0
Part of: GS Prelims and GS -III – Economy
In news
- Government has increased the scope of the Emergency Credit Line Guarantee Scheme (ECLGS) for three more months.
- Why was it extended?
- To help businesses across several sectors affected by the second wave of COVID 19.
About ECLGS 4.0

- 100% guarantee cover to be provided on loans, in hospitals/nursing clinics/medical colleges/homes, up to Rs.2 crore.
- Loan can be utilized to set up on-site oxygen generation plants.
- Additional ECLGS assistance up to 10% of outstanding as on February 2020 to borrowers who are covered under ECLGS 1.0.
- Ceiling of Rs. 500 Cr. of loan outstanding is removed. Assistance will be limited to 40% or Rs.200 crore, whichever is lower.
- Civil Aviation sector will be eligible under ECLGS 3.0.
- Validity of ECLGS extended to Sept 30 2021 or till guarantees for ₹3 trillion are issues
Significance of the move
- ECLGS 4.0 will enhance the utility and impact of ECLGS by providing additional support to MSMEs.
- It will safeguard livelihoods.
- It will help in the resumption of business activity.
- It will facilitate flow of institutional credit at reasonable terms.
Important value additions
Emergency Credit Line Guarantee Scheme (ECLGS)
- ECLGS was launched under Atmanirbhar Bharat Abhiyan in May 2020.
- Objective: To overcome the distress caused on economy due to lockdown.
- It helped different sectors by providing credit to them.
- Credit was provided to them for four years besides one year moratorium period on principled repayment.
Kerala retains top rank in SDG India Index 2020-21, Bihar worst performer
Part of: GS Prelims and GS -II – Development; Governance
In news
- Sustainable Development Goals (SDG) India Index 2020-21 was recently released.
- Launched by: NITI Aayog
- The SDG India Index was developed in collaboration with the Ministry of Statistics & Programme Implementation (MoSPI), Global Green Growth Institute and United Nations in India.
- Kerala has retained the top rank, while Bihar was ranked as the worst performer.

Key takeaways
- Second best performers: Himachal Pradesh and Tamil Nadu
- Worst performing States besides Bihar: Jharkhand and Assam
Why does the index matter?
- It is a primary tool for monitoring progress on the SDGs in India
- It fosters competitive spirit among the states and UTs
- It evaluates progress of states and UTs on social, economic and environmental parameters.
- The index has been successful as an advocacy tool to propagate sustainability, resilience, and partnerships.
Important value additions
The Sustainable Development Goals or Global Goals
- They are a collection of 17 interlinked global goals.
- They are designed to be a “blueprint to achieve a better and more sustainable future for all”.
- Set up in 2015
- Set up by United Nations General Assembly
- Target to achieve the goals: 2030.
Centre asks States to split wage payments under MGNREGA scheme into separate categories
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-III – Economy
In news
- The Centre has asked the States to split wage payments under the Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Act (MGNREGA) scheme into separate categories for Scheduled Castes, Scheduled Tribes and others from this financial year.
- Separate budget heads shall also be provided by the Government for SC and ST categories
- Funds shall be allocated according to job cards provided for SC and ST beneficiaries.
Issues with the order
- This will unnecessarily complicate the payment system,
- It may also lead to a reduction in scheme funding.
Important value additions
About MGNREGA

- Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Act (NREGA) was notified in 2005.
- Goal – To improve the livelihood security of people in rural areas.
- It is a universal scheme guaranteeing 100 days of wage employment in a year to every rural household that expresses a demand.
- It aims to guarantee the ‘Right to Work’.
- Every registered households receives a Job Card (JC) to track their work completed.
- The scheme is implemented by the gram panchayat.
- The failure of provision for employment within 15 days of the receipt of job application will result in the payment of unemployment allowance to the job seekers.
- Employment is to be provided within 5 km of an applicant’s residence
- Employment under MGNREGA is a legal entitlement.
Cabinet gives ex-post facto nod for SCO agreement on mass media cooperation
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-II – International Relations
In news
- The Union Cabinet has approved the ratification of an Agreement on “Cooperation in the field of Mass Media” between all the Member States of Shanghai Cooperation Organisation.
- The Agreement was signed in June, 2019.
About the Agreement on “Cooperation in the field of Mass Media”
- Aim: To promote equal and mutually beneficial cooperation among associations in the field of mass media.
- It would provide an opportunity to the member states to share best practices and new innovations
- The main area of cooperation is the creation of favorable conditions for wide and mutual distribution of information through mass media
- It will provide mutual assistance in training media professionals
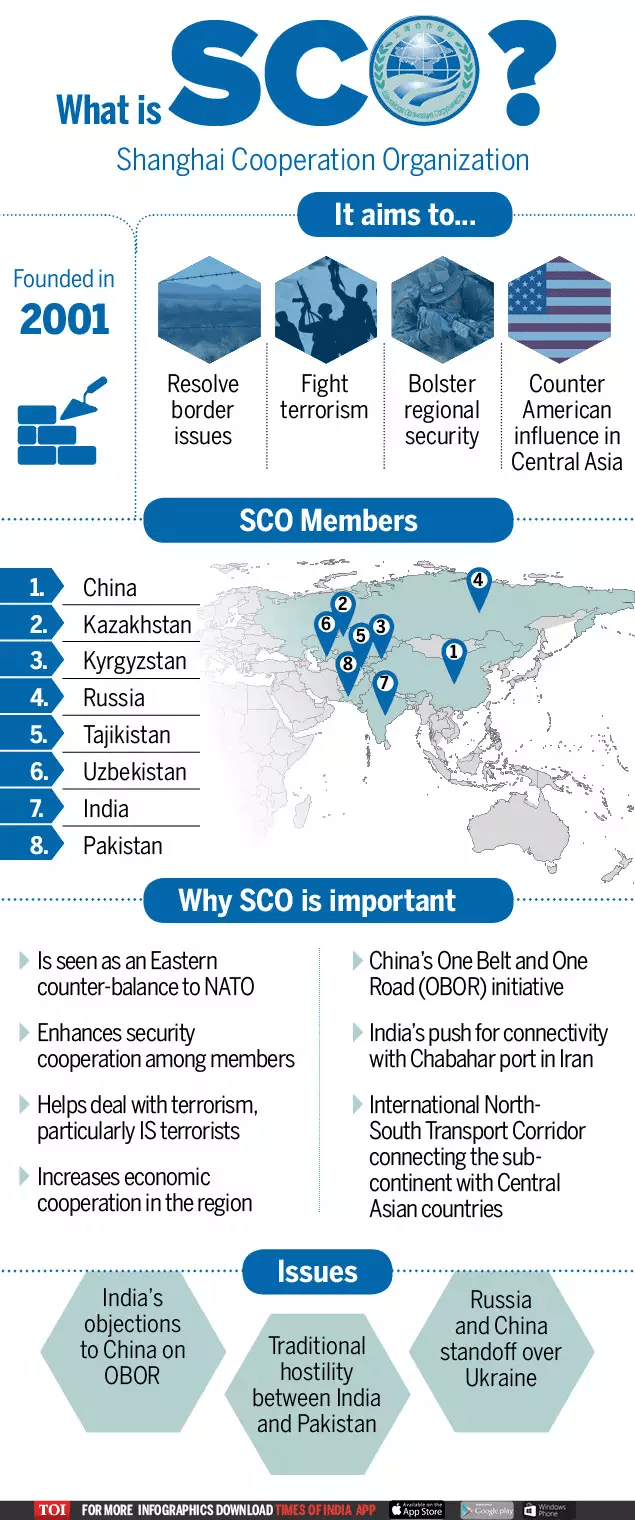
Why does the news matter?
- Mass media inform, educate and entertain people.
- They influence the way people look at the world and make them change their views.
- They help in organizing public opinion.
Important value additions
Shanghai Cooperation Organisation (SCO)
- The SCO is a permanent intergovernmental international organisation.
- It is a Eurasian political, economic, and security alliance
- Established in: 2001.
- Supreme decision-making body: Heads of State Council (HSC)
- It meets once a Year .
- Two permanent bodies:
- SCO Secretariat based in Beijing.
- Executive Committee of the Regional Anti-Terrorist Structure (RATS) based in Tashkent.
Miscellaneous
Coronavirus Variant found in India to be called ‘Delta’ in new WHO system
- The World Health Organisation (WHO) has recommended a set of names to label emerging coronavirus variants that are regarded as global concern.
- The Indian variant which was known as B.1.617.2 will be called ‘Delta’
- The existing scientific nomenclature system will also continue
- Four Variants of Concern (VOC) have been identified by the WHO: B.1.1.7, B.1.351, P2 and B.1.617.2.
- Their public labels will be: Alpha, Beta, Gamma and Delta respectively
(Mains Focus)
ECONOMY/ INTERNATIONAL
Topic:
- GS-3: Indian Economy and issues relating to planning, mobilization, of resources, growth, development and employment.
- GS-2: Effect of policies and politics of developed and developing countries on India’s interests
Oil Price Rise
Context: Crude oil prices have hit a two-year high with Brent crude rising above the $71 per barrel mark.
Why are crude oil prices rising?
- Economic recovery: Crude oil prices have been rising steadily since the beginning of 2021 when Brent Crude was trading at about $52 per barrel buoyed both by hopes of improving demand due to economic recoveries across geographies.
- Supply cuts by key oil-producing countries: The Organisation of Petroleum Exporting Countries extended supply cuts made in 2020 when crude oil prices had reached a low of under $19 per barrel through the first five months of 2021. Saudi Arabia notably made an additional voluntary production cut of 1 million barrels per day between February and April.
- No impact of Iran relief: A potential breakthrough in international efforts for a new Iran nuclear deal which would see international sanctions on Iranian oil removed would also not have a major impact on oil prices according to OPEC. Any increase in crude oil production from Iran would happen gradually and would not destabilise crude oil prices.
How are high crude oil prices impact India?
- Rising Fuel Prices: Rising crude oil prices have contributed to petrol and diesel prices rising to record high levels across the country. The price of petrol has been hiked by Rs 10.8 per litre since the beginning of the year while the price of diesel has been hiked by Rs 11.5 per litre in the same time period.
- Inflation: The prices of petrol & diesel are set to rise further unless there is a cut on levies on autofuels or a fall in crude oil prices. These rising prices will feed into transport costs of goods & services thus causing inflation.
- State and central taxes account for about 58 per cent of the pump price of petrol and 52 per cent of the pump price of diesel in the national capital.
Connecting the dots:
- 2020 Oil Market meltdown
- India’s GDP fall
- Strategic Oil Reserves in India
SCIENCE & TECH/ SCIENCE & TECH
Topic:
- GS-3: Science and Technology- developments and their applications and effects in everyday life.
- GS-3: Indian Economy and issues relating to planning, mobilization, of resources, growth, development and employment.
Low Earth Orbit (LEO) technology
Context: Following the successful launch of 36 satellites on May 28, OneWeb’s Low Earth Orbit (LEO) constellation reached 218 in-orbit satellites
- The company only has one more launch to complete before it obtains the capacity to enable its ‘Five to 50’ service of offering internet connectivity to all regions north of 50 degrees latitude.
What is OneWeb?
- OneWeb is a global communications company that aims to deliver broadband satellite Internet around the world through its fleet of LEO satellites.
- In 2010, the company declared bankruptcy but was able to resume operations following an inflow of investment from a consortium consisting of the UK Government, Hughes Communication, Sunil Mittal’s Bharti Global Limited, SoftBank and Eutelsat, a leading European satellite operator.
LEO technology
- LEO satellites have been orbiting the planet since the 1990s, providing companies and individuals with various communication services
- LEO satellites are positioned around 500km-2000km from earth, compared to stationary orbit satellites which are approximately 36,000km away.
- Latency, or the time needed for data to be sent and received, is contingent on proximity.
- As LEO satellites orbit closer to the earth, they are able to provide stronger signals and faster speeds than traditional fixed-satellite systems.
- Additionally, because signals travel faster through space than through fibre-optic cables, they also have the potential to rival if not exceed existing ground-based networks.
- However, LEO satellites travel at a speed of 27,000 kph and complete a full circuit of the planet in 90-120 minutes. As a result, individual satellites can only make direct contact with a land transmitter for a short period of time thus requiring massive LEO satellite fleets and consequently, a significant capital investment.
- Due to these costs, of the three mediums of Internet – fibre, spectrum and satellite – the latter is the most expensive.
- Therefore, LEO satellite broadband is only preferable in areas that cannot be reached by fibre and spectrum services. OneWeb’s target market will therefore be rural populations and military units operating away from urban areas.
Did You Know?
- Google launched its ‘Loon’ project in 2013, using high-altitude balloons to create an aerial wireless network. After testing the service in rural Kenya, Google’s parent company, Alphabet, abandoned the project in 2021.
- Taking a different track, Facebook attempted to beam internet down to earth using drones. However, after two failed test flights, it also abandoned the project in 2018.
- Over 70% of rural Indians do not have access to the Internet, a problem that is particularly worrisome given the increasing need for digital integration in the fields of education and banking in light of the pandemic.
Concerns of Leo Technology
- Complexity due to multiple players: OneWeb satellites are produced in the US, its rockets are made and launched in Russia and its launches are facilitated by a company based out of France. Due to multiple stakeholders involved, the regulatory framework will be complicated
- Regulation of Space activities: Also, there is confusion on who dictates activities in space. This is because, today, the balance of power has shifted from countries to companies.
- There are logistical challenges with launching thousands of satellites into space as well.
- Difficulties for astronomers: Satellites can sometimes be seen in the night skies which creates difficulties for astronomers as the satellites reflect sunlight to earth, leaving streaks across images.
- Frequency interruption: Satellites travelling at a lower orbit can also interrupt the frequency of those orbiting above them, an accusation that has been levelled against Starlink satellites already.
- Increased space junk & dangers of collision: Another worry is that there are already almost 1 million objects larger than 1cm in diameter in orbit, a byproduct of decades of space activities. Those objects, colloquially referred to as ‘space junk,’ have the potential to damage spacecrafts or collide with other satellites.
- High Cost: While companies like OneWeb and Starlink have marketed themselves to rural Indian consumers, given their price points it is unlikely that most rural Indians will be able to afford their services.
Connecting the dots:
- IN-SPACe: Growing Private Role
- SpaceX Crew Dragon: A new era in space exploration
- India needs reforms in Space sector
(TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE)
Model questions: (You can now post your answers in comment section)
Note:
- Correct answers of today’s questions will be provided in next day’s DNA section. Kindly refer to it and update your answers.
- Comments Up-voted by IASbaba are also the “correct answers”.
Q.1 Coronavirus Variant found in India will be called which of the following in new WHO system?
- Alpha
- Beta
- Gamma
- Delta
Q.2 Which of the following is not a member of Shanghai Cooperation Organization?
- China
- Tajikistan
- India
- Japan
Q.3 Consider the following statements regarding Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Act
- It is an initiative launched for both urban and rural areas
- It guarantees 200 days of wage employment.
Which of the above is or are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
ANSWERS FOR 2nd June 2021 TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE (TYK)
| 1 | A |
| 2 | C |
| 3 | C |
Must Read
On Global Minimum Alternate Tax:
On sedition:
About fiscal situation of India:
















