IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
Archives
(PRELIMS + MAINS FOCUS)
Databank of migrant workers
Part of: GS Prelims and GS – II – Policies and interventions
In news For the first time in India, Tamil Nadu will soon create a digital databank of migrant workers employed in industries, particularly the Micro, Small & Medium Enterprises and hospitality sectors, across the State.
- The enumeration of workers, along with their profile, will help weed out illegal immigrants and anti-social elements
- It will also help in building a data portal on the industry-wise employment scenario.
- The real-time data management system could be of immense use in the event of an emergency as well.
News Source: TH
North Eastern Space Applications Centre
Part of: GS Prelims and GS – III – Sci and tech
In news NESAC (North Eastern Space Applications Centre) Society Meeting was recently held at NESAC, Shillong, Meghalaya.
- NESAC has released North Eastern Spatial Data Repository (NeSDR) with about 950 datasets.
- These datasets are related to infrastructure, land and water resources, disaster management support inputs.
- All the States are to take advantage of these data sets by signing MoUs with NESAC for specific activities such as detecting encroachments, and epidemic planning.
What are the focused areas of NESAC?
- Activities of NESAC are focused on the practical applications of space technology in agriculture, and allied fields like silk farming where it can help in early detection of diseases,
What are the achievements of NESAC?
- NESAC (North Eastern Space Applications Centre) has enabled the States to address issues and challenges of North Eastern region with the support of space technology.
- The organisation can also provide the required strategic inputs for the entire region for its overall development and strategic planning.
- NESAC has helped preserve forests by assessing forest fires and protecting endangered wildlife such as rhinos by studying the changing land cover.
- NESAC has used satellite communication for telemedicine, and tele-education
- NESAC has helped in weather prediction, and forecasting thunderstorms, lightning, and providing early flood warning.
Do you know?
- Union Home Minister is the President of the NESAC Society and the Chairman of the North Eastern Council (NEC).
News Source: PIB
NITI AAYOG -TRIFED join hands for successful implementation of Van Dhan Yojana
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-II – Policies and Interventions
In news Keeping in line with “Atmanirbhar Bharat” aligned to the slogan of “Be Vocal for Local Buy Tribal”, towards realizing the goal of “SabkaSaath, SabkaVikas”, TRIFED is collaborating with NITI Aayog to implement the Van Dhan Yojana in the districts that have been identified as aspirational districts by NITI Aayog.
The Pradhan Mantri Van Dhan Yojana (PMVDY)
- It was launched in 2018.
- The scheme is run by the Tribal Cooperative Marketing Development Federation of India (TRIFED).
- It is an initiative targeting livelihood generation for tribals by harnessing the wealth of forest i.e. Van Dhan.
- The programme aims to tap into traditional knowledge & skill sets of tribals by adding technology & IT to upgrade it at each stage.
- The initiative shall provide enhanced livelihood to about 45 lakhs tribal gatherers in one year.
- Tribal community owned Minor Forest Produce (MFP)-centric multi-purpose Van Dhan Vikas Kendras (the Kendra) are set up.
- Essential Features of the PMVDY:
-
- The State Nodal Department will have the flexibility to appoint any State Implementing Agency / District Implementing Unit for implementation of the PMVDY in the State and District levels.
- The Kendras would act as common facility centres for procurement cum value addition to locally available MFPs.
- A typical Van Dhan Vikas Kendra shall constitute of 15 tribal Van Dhan Self Help Groups (SHG)
Tribal Cooperative Marketing Development Federation of India (TRIFED)
- It came into existence in 1987.
- It is a national-level apex organization.
- The basic objective of the TRIFED is to provide good price of the ‘Minor Forest Produce (MFP) collected by the tribes of the country.
- It functions under Ministry of Tribal Affairs, Govt. of India.
- TRIFED has its Head Office at New Delhi.
- It has a network of 13 Regional Offices located at various places in the country.
News Source: PIB
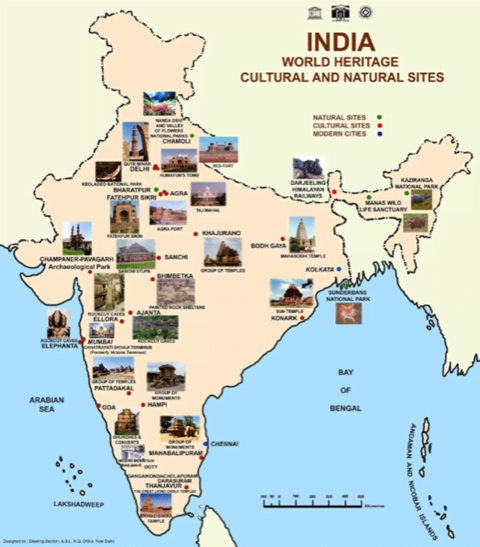
UNESCO declares Kakatiya Ramappa Temple a World Heritage site
Part of: GS Prelims and GS -I – Culture
In news UNESCO has recently declared Kakatiya Ramappa Temple a World Heritage site.
About Kakatiya Ramappa Temple
- The Ramappa Temple showcases the craftsmanship of Kakatiya dynasty.
- It also known as the Rudreshswara (Lord Siva) temple
- It lies in a valley in Palampet village of Venkatapur Mandal of Mulugu district, Telangana.
- The temple is a Sivalayam, where Lord Ramalingeswara is worshipped.
- Marco Polo, during his visit to the Kakatiya Empire, allegedly called the temple “the brightest star in the galaxy of temples”
- The hall in front of the sanctum has numerous carved pillars that have been positioned to create an effect that combines light and space wonderfully.
- The temple is named after the sculptor Ramappa, who built it, and is perhaps the only temple in South India to be named after a craftsman who built it.
- Columns of the temple are carved as mythical animals or female dancers or musicians, and are “the masterpieces of Kakatiya art, notable for their delicate carving, sensuous postures and elongated bodies and heads.”
About UNESCO World Heritage Site
- A World Heritage Site is a place that is listed by UNESCO for its special cultural or physical significance.
- The list of World Heritage Sites is maintained by the international ‘World Heritage Programme’, administered by the UNESCO World Heritage Committee.
- UNESCO seeks to encourage the identification, protection and preservation of cultural and natural heritage around the world considered to be of outstanding value to humanity.
- This is embodied in an international treaty called the Convention concerning the Protection of the World Cultural and Natural Heritage, adopted by UNESCO in 1972.
- India now has 39 world heritage sites
News Source: PIB
National Security Council (NSC)
Part of: GS Prelims and GS –III- Security
In news: Amid the Pegasus Controversy, it was reported that the Union Government’s expenditure on the National Security Council secretariat (NSCS) increased ten fold in 2017-18 to Rs 333 crores from Rs 33 cr. in 2016-17.
About
- NSC of India is a three-tiered organization that oversees political, economic, energy and security issues of strategic concern.
- It was formed in 1999, where all aspects of national security are deliberated upon.
- The National Security Advisor (NSA) presides over the NSC, and is also the primary advisor to the prime minister.
- NSC comprises the three tier structure-
- Strategic Policy Group (SPG)
- National Security Advisory Board (NSAB)
- National Security Council Secretariat.
- The SPG chaired by the Cabinet Secretary is the principal forum for inter-ministerial coordination and integration of the relevant inputs.
- The NSAB undertakes long-term analysis and provides perspectives on issues of national security.
- Functions: It operates within the executive office of the prime minister of India, liaising between the government’s executive branch and the intelligence services, advising leadership on intelligence and security issues.
- Members: The Ministers of Home Affairs, Defence, External Affairs and Finance
PLI Scheme For Specialty Steel
Part of: GS Prelims and GS –II- Governance; GS-III- Economy
In news: Recently, the Union Cabinet approved the Production-Linked Incentive (PLI) scheme (Central Sector Scheme) for manufacturing Speciality Steel (SS) with a budgetary outlay of Rs 6,322 crore over a period of five years from 2023-24.
About Speciality Steel
- It is value-added steel, which is made by processing normal finished steel.
- It is done by converting normal finished steel into high value-added steel by way of coating, plating and heat treatment.
- Apart from the automobile sector and specialised capital goods, they can be used in various strategic applications such as defence, space, power etc.
- SS are categorized in various types such as, coated/plated steel products, high strength/wear resistant steel, speciality rails, alloy steel products and steel wires, electrical steel etc.
About PLI Scheme
- It is a scheme that aims to give companies incentives on incremental sales from products manufactured in domestic units.
- The scheme invites foreign companies to set up units in India, however, it also aims to encourage local companies to set up or expand existing manufacturing units and also to generate more employment
- It aims to cut down the country’s reliance on imports from other countries.
- It was launched in April 2020, for the Large Scale Electronics Manufacturing sector, but later towards the end of 2020 was introduced for 10 other sectors.
- It gave incentives of 4-6% to electronic companies, manufacturing electronic components like mobile phones, transistors, diodes, etc.
- This scheme was introduced in line with India’s Atmanirbhar Bharat campaign.
- The government aims to make India an integral part of the global supply chain and enhance exports
- And Rs. 1.97 lakh crores have been allocated for this scheme from Financial Year 2022
(Mains Focus)
GOVERNANCE/ SECURITY
Topic:
- GS-2: Government policies and interventions for development in various sectors and issues arising out of their design and implementation
Surveillance Laws in India
Context: A global collaborative investigative project has discovered Israeli spyware Pegasus was used to target thousands of people across the world. In India, at least 300 people are believed to have been targeted.
The government says that, contrary to what the Pegasus report alleges, existing laws in India make it impossible for authorities to put politicians, journalists and activists under illegal surveillance.
What do Indian laws outline?
Communication surveillance in India takes place primarily under two laws
- Telegraph Act deals with interception of calls
- IT Act was enacted to deal with surveillance of all electronic communication,
- Telegraph Act
Section 5(2) of The Indian Telegraph Act, 1885, states that the government can intercept a “message or class of messages” on certain situatinos
- Certain situations — the interests of the sovereignty and integrity of India, the security of the state, friendly relations with foreign states or public order, or for preventing incitement to the commission of an offence.
- These are the same restrictions imposed on free speech under Article 19(2) of the Constitution.
- Significantly, even these restrictions can be imposed only when there is a condition precedent — the occurrence of any public emergency, or in the interest of public safety.
The operational process and procedures for Interception
- The procedures appear in Rule 419A of the Indian Telegraph Rules, 1951.
- Rule 419A was added to the Telegraph Rules in 2007 after the verdict in the People’s Union for Civil Liberties (PUCL) vs Union of India case in 1996, in which the Supreme Court said telephonic conversations are covered by the right to privacy, which can be breached only if there are established procedures.
- Under Rule 419A, surveillance needs the sanction of the Home Secretary at the Central or State level, but in “unavoidable circumstance” can be cleared by a Joint Secretary or officers above, if they have the Home Secretary’s authorisation.
- In the K.S. Puttaswamy vs Union of India verdict of 2017, the Supreme Court further reiterated the need for oversight of surveillance, stating that it should be legally valid and serve a legitimate aim of the government.
- The court also said the means adopted should be proportional to the need for surveillance, and there should be procedures to check any abuse of surveillance.
- Information Technology Act, 2000
-
- Section 69 of the IT Act, 2000 deals with electronic surveillance.
- It facilitates government “interception or monitoring or decryption of any information through any computer resource” if it is in the interest of the “sovereignty or integrity of India, defence of India, security of the State, friendly relations with foreign States or public order” or for preventing or investigating any cognizable offence.
- The procedure for electronic surveillance as authorised by Section 69 is detailed in the 2009 rules which are broader in its scope.
- Section 69 the IT Act adds another aspect that makes it broader — interception, monitoring and decryption of digital information “for the investigation of an offence”.
- Significantly, it dispenses with the condition precedent set under the Telegraph Act that requires “the occurrence of public emergency of the interest of public safety” which widens the ambit of powers under the law.
Conclusion
So, for a Pegasus-like spyware to be used lawfully, the government would have to invoke both the IT Act and the Telegraph Act.
Connecting the dots:
INTERNATIONAL/ SECURITY
Topic:
- GS-2: India and its neighborhood- relations.
China’s President visits Tibet
In news China’s President Xi Jinping became the first Chinese leader in many years to visit Tibet as well as its southeastern border region with India.
Important places that he visited
- He landed at the airport in Nyingchi, located near the border with India’s Arunachal Pradesh.
- He visited Nyang river bridge to inspect the Yarlung Zangbo river/Brahmaputra river
- He also visited Nyingchi’s railway station to inspect the newly built Sichuan-Tibet railway.
- He visited the Potala Palace — the traditional home of the Dalai Lamas — and Drepung monastery.
Do you know?
- The Lhasa-Nyingchi rail is one among several major infrastructure projects recently completed in Tibet’s southern and southeastern counties near the Arunachal border.
- Last month, China completed construction of a strategically significant highway through the Grand Canyon of the Yarlung Zangbo river, the “second significant passageway” to Medog county that borders Arunachal.
Tibet and China: Background
- Tibet at various points of time in History has remained autonomous & also under the reign of Chinese rule.
- Tibet had traditionally served as a buffer zone between India and China.
- In the wake of independence from British Colonial rule, China sent in thousands of troops to enforce its claim on the region in 1950.
- With Indian support, Tibetan delegates signed 17 point agreement in May 1951 recognizing PRC sovereignty but guaranteeing that the existing political and social system of Tibet would continue (autonomy & non-interference in internal affairs)
- But the agreement was never honoured by China. Also, China was accused of suppressing cultural and religious freedom in Tibet, which forced Tibetans to rise up against the Chinese authority.
- Besides, the agreement has been rejected by the Dalai Lama ( Politico-Spiritual head of Tibetan Buddhists), who said the Communist Party had both forced it on Tibet and subsequently violated its commitments, leading him to eventually flee to India in exile in 1959.
- Chinese government denies the accusations and says Tibet has developed considerably under its rule.
- In a nutshell, Tibetans wants autonomy while Chinese want complete authority over it.
What is the background of India’s Tibet Policy?
- For centuries, Tibet was India’s actual neighbour, as most of India’s boundaries is with the Tibetan Autonomous Region, and not the rest of China.
- In 1914, Tibetan representatives, along with the Chinese signed the Simla convention that delineated boundaries.
- After China’s full accession of Tibet in 1950, China rejected the convention and the McMahon line.
- In 1954, India signed an agreement with China, agreeing to recognize Tibet as “Tibet region of China”.
- In 1959, following the Tibetan uprising, the Dalai Lama and many of his followers fled to India.
- Former Prime Minister Jawahar Lal Nehru gave him and Tibetan refugees shelter, and helped in setting up the Tibetan government in exile.
- This led to suspicion among Chinese that India is trying to meddle in its internal affairs by giving refuge to Dalai Lama. This still remain an area of distrust between India and China.
- The official Indian policy is that the Dalai Lama is a spiritual leader of Tibet, and the Tibetan community in India, with more than a lakh exiles, is not allowed to undertake any political activity.
Connecting the dots:
- India-China relations, a year after Galwan
- India-China Border flare-up
- Galwan Valley Clashes in 2020
(TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE)
Model questions: (You can now post your answers in comment section)
Note:
- Correct answers of today’s questions will be provided in next day’s DNA section. Kindly refer to it and update your answers.
Q.1 Which of the following is not a UNESCO’s world heritage site of India?
- SunTemple
- Ramappa temple
- Taj Mahal
- Red Fort
Q.2 Consider the following statements about TRIFED:
- It functions under Ministry of Tribal Affairs.
- TRIFED has its Head Office at New Delhi.
Select the correct statements
- 1 Only
- 2 Only
- Both 1 and 2 only
- Neither 1 nor 2
Q.3 Where is Drepung monastery located?
- Ladakh
- Sikkim
- Tibet
- Bhutan
ANSWERS FOR 24th July 2021 TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE (TYK)
| 1 | A |
| 2 | A |
| 3 | C |
Must Read
On India’s Food Security:
On Fake News:
On China & World order:













