IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
Archives
(PRELIMS + MAINS FOCUS)
No landless farmers in National Farmers Database
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-II – Policies and interventions and GS – III – Agriculture
In news
- The Central Government’s new National Farmers Database will only include land-owning farmers for now as it will be linked to digitised land records.
- A data policy is being prepared specifically for the agriculture sector in collaboration with the Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY).
- The Government can make use of the database for targeted service delivery with higher efficiency.
- It is the first step for the initiative that would serve as the core of the Agristack.
What is Agristack?
- AgriStack is a collection of technologies and digital databases that focuses on farmers and the agricultural sector.
- AgriStack will create a unified platform for farmers to provide them end to end services across the agriculture food value chain.
- It is in line with the Centre’s Digital India programme, aimed at providing a broader push to digitise data in India, from land titles to medical records.
- Each farmer will have a unique digital identification (farmers’ ID) that contains personal details,
- Each ID will be linked to the individual’s digital national ID Aadhaar.
- Benefits
- Problems such as inadequate access to credit and information, pest infestation, crop wastage, can be addressed by use of digital technology
- It will increase innovation and investment towards the agricultural sector
News Source: TH
Dholavira: India’s 40th World Heritage Site
Part of: GS Prelims and GS – I – Culture; Ancient History
In news India’s nomination of Dholavira, the Harappan City in the Rann of Kutch, Gujarat has been inscribed on UNESCO’s World Heritage list.
- This follows a few days after the Rudreswara Temple, (also known as the Ramappa Temple) in Telangana State becoming the 39th World Heritage Centre in India.
About Dholavira
- Dholavira is an exceptional example of a proto-historic Bronze Age urban settlement pertaining to the Harappan Civilization.
- It is one of the very few well preserved urban settlements in South Asia dating from the 3rd to mid-2nd millennium BCE.
- It is the 6th largest of more than 1,000 Harappan sites discovered so far.
- The property comprises two parts:
- A walled city and
- A cemetery to the west of the city.
- The walled city consists of a fortified Castle with attached fortified Bailey and Ceremonial Ground, and a fortified Middle Town and a Lower Town.
- A series of reservoirs are found to the east and south of the Citadel.
- Unlike other Harappan antecedent towns normally located near to rivers and perennial sources of water, the location of Dholavira in the island of Khadir was strategic to harness different mineral and raw material sources and to facilitate internal as well as external trade to the Magan (modern Oman peninsula) and Mesopotamian regions.
News Source: PIB
Marine Aids to Navigation Bill 2021
Part of: GS Prelims and GS – III – Infrastructure
In news Parliament has recently passed the Marine Aids to Navigation Bill 2021.
- It aims to replace over 90-year-old Lighthouse Act 1927, to incorporate the global best practices, technological developments and India’s International obligations in the field of Marine Aids to Navigation.
What is the Background?
- The administration and management of Lighthouse and Lightships in India is governed by Lighthouse Act 1927 for safe navigation.
- At the time of enactment of Lighthouse Act 1927, there were only 32 Lighthouses in the then British India spread across six regions viz. Aden, Karachi, Bombay, Madras, Calcutta and Rangoon.
- Post-Independence, 17 Lighthouses came under the administrative control of India, which have now increased manifold to meet the growing needs of the shipping industry.
- As the technology evolved, systems were put in place where with the help of Radar and other sensors, vessels were advised from shore about the position and thus Vessel Traffic Services (VTS) came into existence and found wide acceptability.
- These modern, technologically improved aids to marine navigation systems have changed their profile from a ‘passive’ service to that of ‘passive as well as interactive’ service.
- Lighthouses have also been globally identified as a major tourist attraction due to scenic location, typical architecture and heritage value.
- The need for enactment of a new Act is necessitated to provide an appropriate statutory framework which reflects the modern role of marine aids to navigation
What are the Benefits of the new Act?
- The new Act will facilitate harmonized and effective functioning of aids to marine navigation and Vessel Traffic Services along the Indian coastline.
- The benefits include:
- Improved Legal Framework for Matters related to Aids to Navigation & Vessel Traffic Services and covers the future developments in the field of Marine Navigation.
- Management of ‘Vessel Traffic Services’ for enhancing the safety and efficiency of shipping and to protect environment.
- Skill development through Training and Certification for the operators of ‘Aids to Navigation’ and ‘Vessel Traffic Services’ at par with International standards.
- Auditing and Accreditation of Institutes to cater to the need of Training and Certification at par with global standards.
- Marking of “Wreck” in general waters to identify sunken / stranded vessels for safe and efficient navigation.
- Development of Lighthouses for the purpose of education, culture and tourism, which would tap the tourism potential of coastal regions and contribute to their economy.
News Source: PIB
Gamma-ray burst
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-III – Space
In news A group of astronomers have detected a very short, powerful burst of high-energy radiation that lasted for about a second and had been racing toward Earth for nearly half the present age of the universe.
- The burst detected by NASA’s Fermi Gamma-ray Space Telescope on August 26, 2020, turned out to be one the shortest gamma-ray burst (GRB) caused by the death of a massive star.
- From India, The Inter-University Centre for Astronomy and Astrophysics, Pune (IUCAA), National Centre for Radio Astrophysics – Tata Institute of Fundamental Research, Pune (NCRA) and IIT Mumbai also participated in this work.
- The burst emitted 14 million times the energy released by the entire Milky Way galaxy over the same amount of time, making it one of the most energetic short-duration GRBs ever seen.
What are gamma-ray bursts (GRB)?
- GRBs are the most powerful events in the universe, detectable across billions of light-years.
- Astronomers classify them as long or short based on whether the event lasts for more or less than two seconds.
- They observe long bursts in association with the demise of massive stars, while short bursts have been linked to a different scenario.
- This recent identification of GRBs showed for the first time that a dying star can produce short bursts too.
- When a star much more massive than the Sun runs out of fuel, its core suddenly collapses and forms a black hole.
- As matter swirls toward the black hole, some of it escapes in the form of two powerful jets that rush outward at almost the speed of light in opposite directions.
- Astronomers only detect a GRB when one of these jets happens to point almost directly toward Earth.
Russia’s Nauka
Part of: GS Prelims and GS -III – Space
In news Russia is sending the module, Nauka, to the ISS
- Nauka was launched from the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan on July 21 using a Proton rocket.
- It is scheduled to be integrated with the ISS on July 29.
What is Nauka?
- Nauka, meaning “science” in Russian, is the biggest space laboratory Russia has launched to date.
- It will replace Pirs, a Russian module on the International Space Station (ISS) used as a docking port for spacecraft and as a door for cosmonauts to go out on spacewalks.
- Now, Nauka will serve as the Russia’s main research facility on the space station.
- Nauka is 42 feet long and weighs 20 tonnes.
- It is also bringing to the ISS another oxygen generator, a spare bed, another toilet, and a robotic cargo crane built by the European Space Agency (ESA).
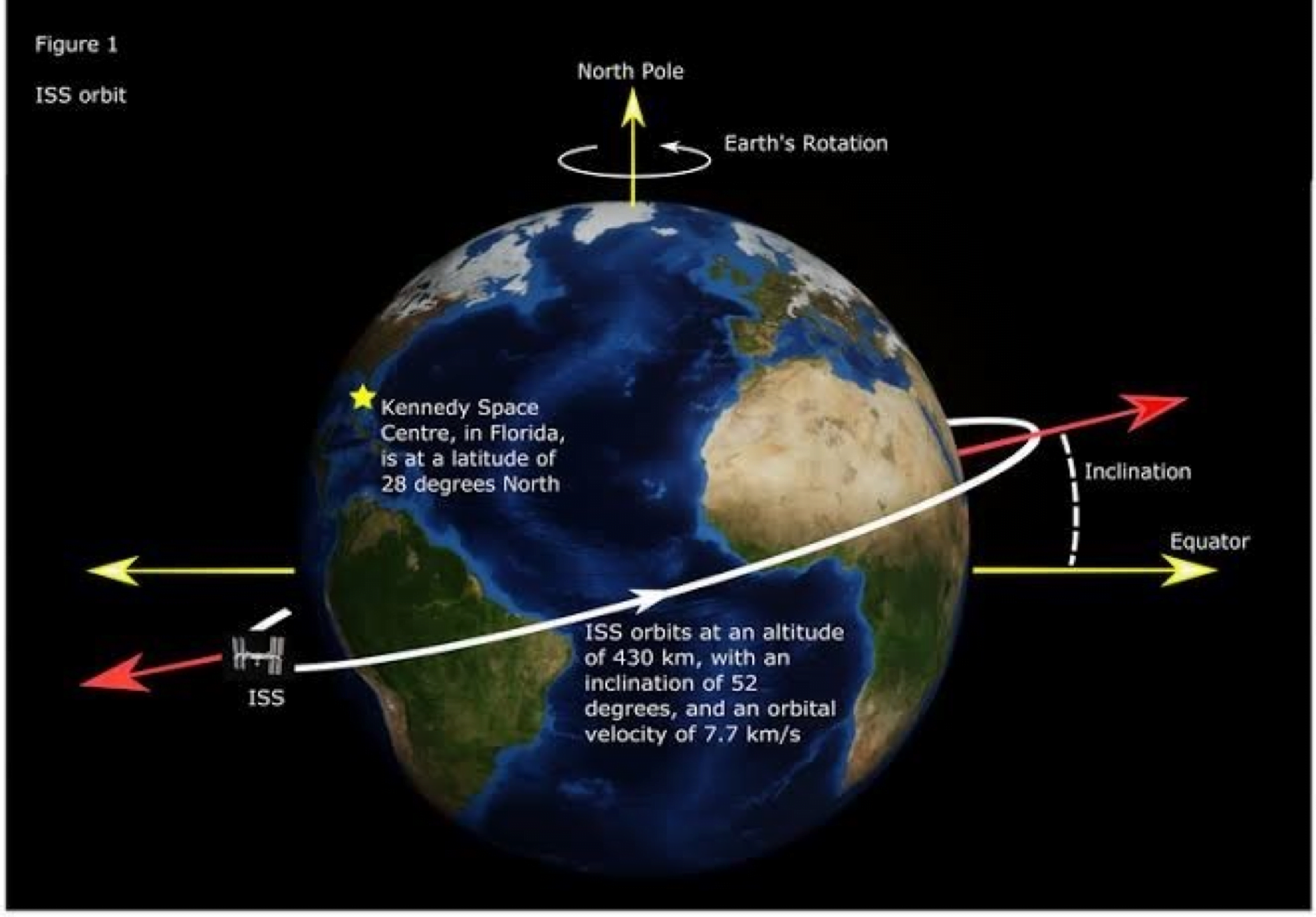
What is the International Space Station?
- A space station is essentially a large spacecraft that remains in low-earth orbit for extended periods of time.
- The ISS has been in space since 1998.
- It is a result of cooperation between the five participating space agencies that run it: NASA (United States), Roscosmos (Russia), JAXA (Japan), ESA (Europe), and CSA (Canada).
- The ISS circles the Earth in roughly 93 minutes, completing 15.5 orbits per day.
- The ISS serves as a microgravity and space environment research laboratory in which scientific experiments are conducted in astrobiology, astronomy, meteorology, physics, and other fields.
News Source: IE
Exercise Cutlass Express
Part of: GS Prelims and GS II – International relations
In news Recently, Indian Naval Ship Talwar participated in a multinational training exercise Cutlass Express 2021, being conducted along the East Coast of Africa.
About Exercise Cutlass Express
- The exercise is an annual maritime exercise conducted to promote national and regional maritime security in East Africa and the Western Indian Ocean.
- The 2021 edition of the exercise involves participation of 12 Eastern African countries, US, UK, India and various international organisations like International Maritime Organisation (IMO), United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime (UNODC), Interpol, European Union Naval Force (EUNAVFOR), Critical Maritime Routes Indian Ocean (CRIMARIO).
- The exercise is designed to assess and improve combined maritime law enforcement capacity, promote national and regional security and increase interoperability between the regional navies.
- India’s Information Fusion Centre – Indian Ocean Region (IFC-IOR) is also participating in the exercise.
- India’s participation is in accordance with India’s stated policy towards maritime cooperation in the Indian Ocean region and vision SAGAR (Security and Growth for All in the Region).
News Source: PIB
Garib Nawaz Employment Scheme
Part of: GS Prelims and GS II – Policies and interventions
In news Recently, the Union Minister for Minority Affairs replied in the Parliament that a total number of 371 training centers under Gharib Nawaz Employment Scheme were opened across the country.
About Gharib Nawaz Employment Scheme
- It was launched by the Ministry of Minority Affairs in 2017.
- Maulana Azad Education Foundation, an autonomous body under the aegis of Ministry of Minority Affairs, implements the Scheme.
- The main aim of this scheme is to provide short term job oriented skill development courses to minorities’ youth in order to enable them for skill based employment.
- This scheme is implemented as per common norms of the Ministry of Skill Development & Entrepreneurship (MSD&E) through the empanelled Program Implementation Agencies (PIAs).
- The PIA is mandated to place minimum 70% trainees out of total trained trainees.
- The monthly stipend for maximum of three months and post placement support for maximum of two months after getting employment are also being paid to the beneficiaries directly into their account.
What are the Other Schemes for Minority Communities?
- Usttad (Upgrading the Skills and Training in Traditional Arts/Crafts for Development)
- Garib Nawaz Kaushal Vikas Yojana
- Nai Manzil (for formal skilling of school dropouts)
- Nai Roshni (for leadership Development of Minority Women)
- Begum Hazrat Mahal Girls scholarships
USA to end its combat Mission in Iraq
Part of: GS Prelims and GS – II – International Relations
In news
- U.S. President Joe Biden and Iraqi Prime Minister Mustafa al-Kadhimi sealed an agreement recently formally ending the U.S. combat mission in Iraq by the end of 2021
- There are currently 2,500 U.S. troops in Iraq focusing on countering the remnants of ISIS.
- However, American forces will still operate in an advisory role.
- The U.S. role in Iraq will shift entirely to training and advising the Iraqi military to defend itself.
News Source: TH
(Mains Focus)
INTERNATIONAL/ SECURITY
Topic:
- GS-2: India and its neighborhood- relations.
- GS-2: Effect of policies and politics of developed and developing countries on India’s interests.
Needed, a more unified Asian voice for Afghanistan
In news: In the backdrop of US pull out of troops from Afghanistan, three recent meetings are turning the spotlight on the Central Asia’s role in dealing with the situation in Afghanistan
- Shanghai Cooperation Organisation (SCO) contact group on Afghanistan
- SCO Defence Ministers in Tajikistan,
- Central and South Asia conference on regional connectivity in Uzbekistan
Concerns for India in Central Asia
- The same powers that invaded Afghanistan post 9/11, and declared the Taliban leadership as UNSC-designated terrorists, are now advocating talks with the Taliban
- India’s original hesitation in opening talks with the Taliban has cut India out of the current reconciliation process.
- The end of any formal dialogue between India and Pakistan since 2016 and trade since 2019, have resulted in Pakistan blocking India’s over-land access to Afghanistan
- India’s alternative route through Chabahar, though operational, cannot be viable or cost-effective also long as U.S. sanctions on Iran are in place.
- India’s boycott of the Chinese Belt and Road Initiative (BRI) make another route to Afghanistan off-limits.
- U.S. has announced a new, surprise formation of a “Quad” on regional connectivity — U.S.-Uzbekistan-Afghanistan-Pakistan that does not include India
- All the above portends to India’s narrowing window of engagement in Central Asia.
What are the calculation of Central Asian neighbours?
- Necessity of Afghanistan for access to Ocean: First is that prosperity for these land-locked countries can only flow from access through Afghanistan to the closest ocean, i.e. the Indian Ocean.
- Need for Taliban’s Support: Second, all transit through Afghanistan depends on guarantees of safe passage from the Taliban, backed by the group’s mentors in Pakistan. Therefore, Central Asian countries have been at the forefront of mediation of talks with Taliban.
- Alignment with China: Third, all five Central Asian Countries are now a part of China’s BRI. Tying their connectivity initiatives with Beijing’s BRI will bring the double promise of investment and some modicum of control over Pakistan.
Given the above, New Delhi’s room for manoeuvre with the five Central Asian countries on Afghanistan appears limited.
Way Ahead for India
- Realizing Common Concerns: India and the Central Asian States share common concerns about an Afghanistan overrun by the Taliban and under Pakistan’s thumb: the worries of battles at their borders, safe havens for jihadist terror groups inside Afghanistan and the spill-over of radicalism into their own countries.
- Supporting Afghan Government: India to work with Central Asian states, and other neighbours to shore up finances for the Afghanistan government to ensure that the government structure does not collapse
- Fighting Terror: As part of the SCO’s Regional Anti-Terrorist Structure (RATS), India must also step up its engagement with the Central Asian countries on fighting terror.
- Supporting Afghan Defence Forces: India can support the Afghan National Defense and Security Forces (ANDSF) where it needs it most: in terms of air power.
- Engaging with Pakistan: India’s reluctant discussions with the Taliban leadership make little sense unless a less tactical and more strategic engagement with Pakistan is also envisaged.
Connecting the dots:
- March 2020: Donald Trump’s Doha Agreement
- March 2021: Joe Biden’s initial Peace Plan
- April 2021: Final Biden’s Plan of US Exit from Afghanistan
- June 2020: Rise of Taliban
- India must directly engage with Taliban 2.0
DISASTER MANAGEMENT/ ENVIRONMENT
Topic:
- GS-3: Disaster and disaster management.
- GS-2: Government policies and interventions for development in various sectors and issues arising out of their design and implementation.
Let’s make room for the river: Floods in Europe
Context: A month’s rain poured in just 24 hours in the worst-affected areas of Germany and Belgium. This caused multiple rivers to burst their banks and flood parts of the two countries as well as the Netherlands (managed well), Luxembourg and Switzerland.
- It is believed that these areas of Europe have not witnessed such heavy rainfall for more than a century.
- The floods & the subsequent efforts by authorities bore uncanny resemblance to what Kerala experienced in August 2018.
- These extreme & unpredictable events are attributed to Climate Change
How Climate Change is causing frequent floods?
- More CO2 the world emits into the atmosphere, the warmer will be the air temperature.
- Warmer air holds more moisture and results in excess rainfall, which leads to flooding.
- Additionally, increasing temperatures at the poles result in slower movement of storms in the mid-latitudes. As a result, storms linger longer at a specific place.
- The combination of a slow-moving storm and the presence of surplus moisture in the atmosphere results in intense rainfall in one location within a short period of time.
- In 2018, Kerala, for example, witnessed 414 mm of rain in just three days between August 15 and 17. Rainfall for the period of August 1 to 19, 2018, in Kerala was 164% more than normal.
- The advanced flood warning system of Germany did forecast heavy rains and the possibility of floods. But local authorities were unable to respond rapidly enough and communicate the warnings to the wider population.
- The rain and floods happened so fast that there was no time to evacuate all residents to safety and fully deploy the formidable rescue and relief infrastructure that they possessed.
What did the Netherlands do right in dealing with the floods?
- The Dutch have gone beyond their conventional dependence on dikes, dams, walls and gates to protect themselves from floods.
- Their current disaster resilience mantra is to live with water, build with nature and make room for the river.
- They champion creating adequate space for rivers to overflow by
- Protecting floodplains from human interference & human activities
- Deepening riverbeds
- Creating alternate channels for excess water.
- After two major floods in 1993 and 1995, the Dutch embarked on several projects to widen riverbanks and reshape the areas around rivers.
- Also, Superior organisation, better preparedness, advanced flood management system and centuries of experience has helped the Netherlands to manage floods better.
Way Ahead for India as well as other countries
- Learning from the Dutch model of “live with water, build with nature and make room for the river”
- Mapping Risk areas: Flood-prone areas should be identified, and projects initiated on an urgent basis to create room for rivers.
- Increasing Drainage capacity of rivers and canals by creating more room for the water to flow. This involves removing obstructions and encroachments from existing water channels, the proper maintenance of such channels and creating additional channels for water to flow.
- Storage of Excess Rainwater: Low-risk areas such as playgrounds, maidans, or agricultural fields should be earmarked to store excess rainwater.
- Drains must be built for diverting water into these storage units.
- This will relieve the stress on the existing drainage infrastructure.
- The stored water can later be discharged back into the drainage channel once the high water subsides.
- Strengthen Disaster Preparedness: In the short term, strengthened disaster readiness, planning and preparation will help us deal with sudden, intense rain and consequent floods
- While national and State disaster management authorities have grown in experience, competence and professionalism, there is need for a higher degree of coordination and preparation across all levels of government.
- Practice drills need to be conducted in flood-prone areas.
- Modifying Warning Messages: We need to test the effectiveness of flood warnings. The warnings should be in local languages and in simple terms.
- Rather than forecast the millimetres of rain expected, conveying specific information regarding the extent of damage to property and life would likely encourage affected communities to remain alert and respond quickly.
Conclusion
Nations must be conscious of their vulnerability to water and maintain a spirit of eternal vigilance to floods.
Connecting the dots:
(TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE)
Model questions: (You can now post your answers in comment section)
Note:
- Correct answers of today’s questions will be provided in next day’s DNA section. Kindly refer to it and update your answers.
Q.1 Consider the following statements about gamma-ray bursts (GRB)?
- GRBs are the most powerful events in the universe, detectable across billions of light-years.
- They can last up to 60 seconds
Select the correct statements
- 1 Only
- 2 Only
- Both 1 and 2 only
- Neither 1 nor 2
Q.2 Consider the following statements about Agristack?
- It is a part of MoU signed between Ministry of Agriculture and Microsoft.
- AgriStack is a collection of technologies and digital databases that focuses on farmers and the agricultural sector.
Select the correct statements
- 1 Only
- 2 Only
- Both 1 and 2 only
- Neither 1 nor 2
Q.3 Dholavira, the Harappan City was recently inscribed on UNESCO’s World Heritage list. Where is it located?
- Rann of Kutch
- Ahmednagar
- Indore
- Lucknow
ANSWERS FOR 27th July 2021 TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE (TYK)
| 1 | B |
| 2 | C |
| 3 | C |
Must Read
On Trafficking of human:
On North East & Internal Border Issues:












