IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
Archives
(PRELIMS + MAINS FOCUS)
Creamy Layer in OBC Reservation
Part of: GS Prelims and GS – II – issues related to SCs and STs
In news Holding that annual earning cannot be the sole criteria for identifying creamy layer between backward class to deny reservation, the Supreme Court held that it has to be done on the basis of social economic and other relevant factors and not only economic criteria.
- SC quashed the 2016 notification issued by the Haryana government by which sections of backward classes earning above Rs.6,00,00 per annum were to be considered as a creamy layer, whereby the state wrongly sought to determine creamy layer solely on the basis of economic practice
- The court said that the decision of the state government was in violation of the principles laid down by the apex court in Indra Sawhney case
What was Indra Sawhney’s verdict related to creamy layer?
- In Indra Sawhney case the court had held that persons from backward classes who occupied posts in higher services like IAS, IPS and all India services had reached a higher level of social advancement and economic status and therefore were not entitled to be treated as backward.
- Such persons were to be treated as creamy layer without any further enquiry.
- Likewise people with sufficient income who are in a position to provide employment to others should also be taken to have reached a higher social status and therefore should be treated as outside the backward class.
- Similarly, persons from backward classes who had higher agricultural holdings or were receiving income from property beyond the prescribed limit do not deserve the benefit of reservation.
- The above mentioned categories were necessary to be excluded from backward classes.
News source: TH
India-Russia Defence trade worth $15bn in 3 years’
Part of: GS Prelims and GS – II – International Relations
In news In the last three years, since 2018, the defence trade between India and Russia was $15 billion because of some major defence deals.
- The S-400 air defence systems deal, for which deliveries are scheduled to begin by November 2021, was on schedule.
- One team of Indian Air Force (IAF) officials has been trained in Russia to operate the system while another team is undergoing training.
What is S-400?
- The S-400 is Russia’s most advanced long-range surface-to-air missile defence system.
- In 2018, India had signed a $5 billion deal with Russia to buy the S-400 air defence missile systems.
- The system is also known as the ‘Triumf’ interceptor-based missile system.
- It can simultaneously track numerous incoming objects — all kinds of aircraft, missiles and UAVs — in a radius of 400km and launch appropriate missiles to neutralise them.
- The U.S. imposed sanctions on Russia under its stringent Countering America’s Adversaries Through Sanctions Act (CAATSA) for manufacturing S-400.
- The law also provides for punitive action against countries purchasing defence hardware from Russia.
News Source: TH
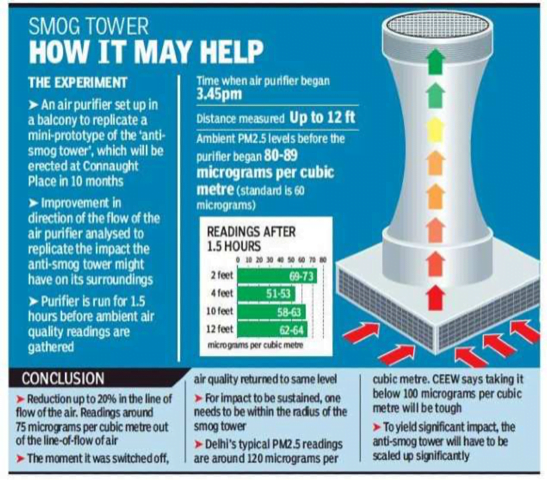
India’s First smog Tower in Delhi
Part of: GS Prelims and GS – III – Pollution
In news Chief Minister Arvind Kejriwal inaugurated a ‘smog tower’ in Connaught Place and said similar towers would be built across the city, if results of the current pilot project are satisfactory.
- In Jan 2020, the Supreme Court had ordered the Delhi government to build a ‘smog tower’ at Connaught Place by April, 2020, to control air pollution.
What is a Smog Tower?
- The smog tower is a 24 metre-high structure fitted with fans and air filters. This is to solve the problem of Air Pollution in Delhi.
- It will draw in polluted air from the top and release filtered air near the ground through fans fitted on the sides.
- The tower has 40 big fans and 5,000 filters to clean the air.
- These are electrostatic air filters that can filter out microparticles, including those that constitute smoke, household dust and pollen, according to the project description.
- A Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition (SCADA) system has been installed in the tower to collect data and monitor its functioning.
- This tower has been established as a pilot project
- The tower will take in air from a radius of 1 km. It has a capacity of cleaning 1,000 cubic metres of air per second. It is estimated that the area will see a rapid change in air quality due to this smog tower.
Do you know?
- There are different technologies used to clean the air. One uses HEPA filters, (used in indoor air purifiers), which filters PM 2.5 particles.
- Another uses electrostatic precipitators that attract PM 2.5 particles and collect them at the base of the tower.
- Both would work in closed spaces, but are ineffective in open spaces.
News Source: TH
Immune Cells in Sea Corals
Part of: GS Prelims and GS – II – issues related to SCs and STs
In news A new study has identified for the first time that specialised immune cells (phagocytic cells) exist in certain varieties of sea corals and anemones.
- It will help in better understanding how reef-building corals and other reef animals protect themselves from foreign invaders like bacteria and viruses found in and around coral reefs.
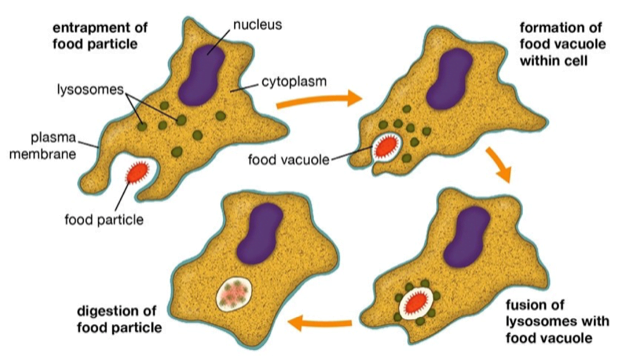
What is Phagocytosis?
- It is the process by which certain living cells called phagocytes ingest or engulf other cells or particles.
- The phagocyte may be a free-living one-celled organism, such as an amoeba, or one of the body cells, such as a white blood cell.
- In some forms of animal life, such as amoebas and sponges, phagocytosis is a means of feeding.
What are Sea anemones?
- They are sometimes called the ‘flowers of the sea’, sea anemones are actually beautiful animals, they are a close relative of coral and jellyfish, and are the marine, predatory animals of the order Actiniaria.
- They are found from the tidal zone of all oceans to depths of more than 10,000 metres.
What is Coral?
- Corals are made up of genetically identical organisms called polyps. These polyps have microscopic algae called zooxanthellae living within their tissues.
- The corals and algae have a mutualistic relationship.
- They are also called the “rainforests of the seas”.
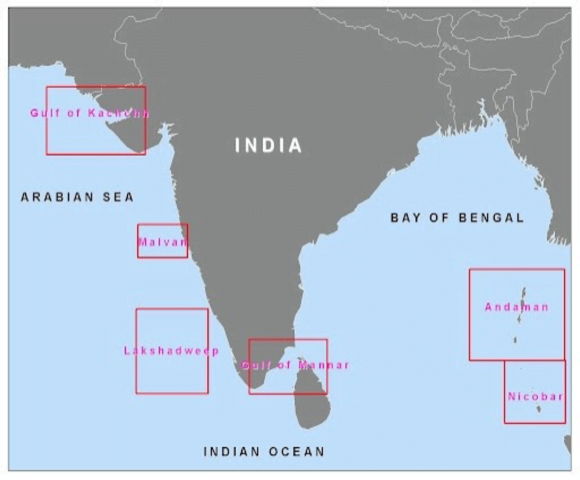
- Major locations of corals in India
- Coral reefs are present in the areas of Gulf of Kutch, Gulf of Mannar, Andaman & Nicobar, Lakshadweep Islands and Malvan.
News Source: DTE
Miscellaneous
Fatah-1
- Pakistan successfully test launched a indigenously developed guided multi-launch rocket system, Fatah-1.
- The weapon system has the capability of precision target engagement.
- The rocket was capable of delivering conventional warheads.
- This was the second flight of Fatah-1, after its first launch in January.
- The system can hit targets up to a range of 140 km.
News Source: TH
(News from PIB)
e-Shram portal – National Database on Unorganized Workers (NDUW)
Part of: GS Prelims and Mains GS-II- Governance
In News: Logo for e-Shram portal unveiled by Minister for Labor and Employment.
What is the e-Shram portal?
- e-Shram portal is a portal through which the government aims to register 38 crore unorganised workers, such as construction labourers, migrant workforce, street vendors and domestic workers, among others.
- The workers will be issued an e-Shram card containing a 12-digit unique number, which, going ahead, will help in including them in social security schemes.
Significance of e-Shram portal – National Database on Unorganized Workers (NDUW)
- Targeted identification of the unorganized workers was a much-needed step and the portal which will be the national database of our nation builders will help take welfare schemes to their doorstep, who are the builders of our Nation.
- Targeted delivery and last mile delivery, has been a major focus of the schemes of government of India and the National Database of Unorganised workers (E-Shram portal) is another key step towards that.
News Source: PIB
Nation’s first mRNA-based vaccine
Part of: GS Prelims
In news: Nation’s first mRNA-based vaccine developed by Gennova company is found to be safe and the Drugs Controller General of India DCG(I) has approved for its Phase II/III trial.
About Gennova’s mRNA-based COVID-19 vaccine development program
- Gennova’s mRNA-based COVID-19 vaccine development program was partly funded by the Department of Biotechnology (DBT), Govt. of India under Ind CEPI, way back in Jun 2020.
- Later on, the DBT further supported the program under the Mission COVID Suraksha- The Indian COVID-19 Vaccine Development Mission, implemented by BIRAC.
About Mission COVID Suraksha
- It is a mission to accelerate the development of approximately 5-6 vaccines for coronavirus.
- However, a total of 10 vaccine candidates have been supported by DBT till now.
- Under the mission complete focus on the preclinical and clinical development of the vaccine is to be taken care of, for quick release and to restrict any further spread of the Novel coronavirus in the country.
About DBT BIRAC
- Biotechnology Industry Research Assistance Council (BIRAC) is a not-for-profit Section 8, Schedule B, Public Sector Enterprise, set up by Department of Biotechnology (DBT), Government of India as an Interface Agency to strengthen and empower the emerging Biotech enterprise to undertake strategic research and innovation, addressing nationally relevant product development needs.
- BIRAC is an industry-academia interface and implements its mandate through a wide range of impact initiatives, be it providing access to risk capital through targeted funding, technology transfer, IP management and handholding schemes that help bring innovation excellence to the biotech firms and make them globally competitive.
About CEPI (Coalition for Epidemic Preparedness Innovations)
- CEPI is an innovative global partnership between public, private, philanthropic, and civil society organizations that are working together to accelerate the development of vaccines against emerging infectious diseases and enable equitable access to these vaccines for people during outbreaks.
- It is an alliance to finance and coordinate the development of new vaccines to prevent and contain infectious disease epidemics with the mission to accelerate the development of vaccines against emerging infectious diseases and enable equitable access to these vaccines for people during outbreaks.
News Source: PIB
Mission Sagar
Part of: GS Prelims
In news: Indian Navy’s Landing Ship Tank INS Airavat arrived at Tanjung Priok Port in Jakarta, Indonesia on 24 August 2021 to deliver 10 Liquid Medical Oxygen (LMO) containers, based on the requirement projected by the Government of Indonesia in its fight against covid 19
- On completion of disembarkation of the medical supplies and, as part of the ongoing Mission SAGAR, INS Airavat will continue onwards to deliver medical supplies to other friendly nations in the region hence strengthening the Act East Policy of India.
About mission SAGAR:
- Mission Sagar was a COVID-19 relief mission launched by the government of India in May 2020 as a part of its efforts to provide essential aid to the Indian Ocean countries.
- This was followed up by Mission Sagar II in November and Mission Sagar III in December 2020.
| MISSION SAGAR 1 | India sent INS Kesari in May 2020 with food items, medicines and medical assistance teams that made its way to the Indian Ocean nations of Mauritius, Seychelles, Madagascar, Comoros and La Reunion. |
| MISSION SAGAR 2 | In November 2020, INS Airavat was delivering food to Sudan, South Sudan, Djibouti and Eritrea. |
| MISSION SAGAR 3 | In December 2020, INS Kiltan made its way towards Cambodia and Vietnam carrying 15 tons of Humanitarian Assistance and Disaster Relief (HADR) for disaster relief following catastrophic floods in Vietnam and Cambodia. |
| MISSION SAGAR 4 | In March 2021, INS Jalashwa reached Port Anjouan, Comoros to deliver 1000 metric tonnes of rice to the island nation. This is the second time an Indian naval ship is arriving at Comoros. |
News Source: PIB
eSanjeevani initiative
Part of: GS Prelims
In news: Union Ministry of Health & Family Welfare’s National Telemedicine Service eSanjeevani has conducted more than 1 Crore (i.e. 10 million) tele-consultations across India.
- That eSanjeevani has been quickly adopted by patients, doctors and specialists across the country is evident from the fact that it has shown astounding growth of over 1000% in last 10 months.
- eSanjeevani is serving around 75,000 patients every day.
About eSanjeevani:
- Started in 2019, Sanjeevani is the first-ever online OPD (outpatient) consultation service offered by the government of India to citizens and is run by the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare.
- The scheme is also called the National Teleconsultation Service, it aims to provide healthcare services to patients in their homes.
- The eSanjeevani OPD portal and system has been developed by the Centre for Development of Advanced Computing (C-DAC) in Mohali and includes a structured and safe teleconsultation between a doctor and a patient through online mode (eSanjeevani OPD).
News Source: PIB
(Mains Focus)
GOVERNANCE/ SECURITY
- GS-3: Science & Technology; Security
- GS-2: Government policies and interventions for development in various sectors and issues arising out of their design and implementation
The ugly face of a crime-fighting move: Facial Recognition
In news Government has been exploring the potential of facial recognition technology.
About NAFRS
- To empower the Indian police with information technology, India approved implementation of the National Automated Facial Recognition System (NAFRS)
- It will function as a national-level search platform that will use facial recognition technology: to facilitate investigation of crime or for identifying a person of interest (e.g., a criminal) regardless of face mask, makeup, plastic surgery, beard or hair extension.
- The system compares the faceprint generated with a large existing database of faceprints (typically available to law enforcement agencies) through a database on driver’s licence or police mugshots).
Do You Know?
- FBI in US uses facial recognition technology for potential investigative leads; Police forces in England use facial recognition to tackle serious violence.
- China use facial recognition for racial profiling and mass surveillance — to track Uighur Muslims.
Criticism of NAFRS
- Violates Right to Privacy: As NAFRS will collect, process, and store sensitive private information: facial biometrics for long periods; if not permanently — it will impact the right to privacy.
- Not 100% accurate: Facial recognition does not return a definitive result — it ‘identifies’ or ‘verifies’ only in probabilities (e.g., a 70% likelihood. Though the accuracy of facial recognition has improved over the years due to modern machine-learning algorithms, the risk of error and bias still exists.
- Bias & Prejudice: Research suggests facial recognition software is based on pre-trained models. Therefore, if certain types of faces (such as female, children, ethnic minorities) are under-represented in training datasets, then this bias will negatively impact its performance.
- Fear of Profiling: With the element of error and bias, facial recognition can result in profiling of some overrepresented groups (such as Dalits and minorities) in the criminal justice system.
- Constitutionality Concerns: It is alleged that NAFRS fails the three tests of Puttaswamy Judgement: legitimacy (backed by law), proportionate to its need and least restrictive.
- Lacks Statutory Clarity: There is potential for abuse and misuse of NAFRS especially when there is absence of clear guidelines for its deployment and lack of Comprehensive Data Protection Bill.
- Chilling Effect on Civil Liberties: Unregulated use of facial recognition technology will dis-incentivise independent journalism or the right to assemble peaceably or any other form of civic society activism.
- Federal Challenges: Policing and law and order being State subjects, some Indian States have started the use of new technologies without fully appreciating the dangers involved.
Conclusion
Government must enact a strong and meaningful data protection law, in addition to statutory authorisation of NAFRS and guidelines for deployment to prevent its misuse and abuse.
Connecting the dots:
- Aadhar Public Data Ecosystem
- The Personal Data Protection Bill, 2019
GOVERNANCE/ SOCIETY
- GS-1: Indian Society & its challenges
- GS-2: Government policies and interventions for development in various sectors and issues arising out of their design and implementation.
Caste Census
Context: The caste system is India’s nemesis and has severely restricted the country’s ability to realise its immense potential.
- An Indian women’s hockey team player, who happened to be Dalit, had to face caste slurs, and her family had to confront upper-caste harassment after the team’s loss in the Tokyo Olympics.
Issues associated with Caste
- Regulates all aspects of Life: caste has been at the forefront of Indian’s social existence and regulates lives — from birth to death, customs, rituals, housing, professions, development planning, and even voting preferences
- Continues to influence Occupational Structure: Studies suggest that 90% of menial jobs are performed by the deprived castes, whereas this figure is reversed in white-collar jobs.
- Inequity in Gold Collar Jobs: The abysmal lack of caste diversity, especially at the decision-making levels in various sectors — the media, the judiciary, higher education, bureaucracy or the corporate sector — weakens these institutions and their performance.
Arguments for Caste Census
- A caste census, which will generate exhaustive data will allow policymakers to develop better policies, implementation strategies, and will also enable a more rational debate on sensitive issues.
- India needs to be bold and decisive in tackling caste questions through data and statistics in the way US does to tackle race issues, by collecting data around race, class, language, inter-race marriages, among other metrics.
- Our Constitution too favours conducting a caste census. Article 340 mandates the appointment of a commission to investigate the conditions of socially and educationally backward classes and make recommendations as to the steps that should be taken by governments.
- The Justice Rohini committee was appointed in 2017 to look into the sub-categorisation of the OBC communities; however, in the absence of data, there can be no data-bank or any proper sub-categorisation.
- All commissions have had to rely on data from the last caste census (1931). There has been substantive demographic changes since then and therefore, the data has to be updated.
- While census data has been captured for SC, ST, religions and linguistic profiles, there has been no profiling of all castes in India since 1931
Conclusion
If India has to emerge as a confident and strong nation, it must shed its hesitancy and ostrich-like escapism in conducting a caste-linked socio-economic census. This will kick-start a process that will eventually take the caste system away from an Indian.
Connecting the dots:
- Census 2021
- Delimitation Exercise
(TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE)
Model questions: (You can now post your answers in comment section)
Note:
- Correct answers of today’s questions will be provided in next day’s DNA section. Kindly refer to it and update your answers.
Q.1 Consider the following statement (s) related to the Coral Bleaching
- Bleaching causes corals to turn white or pale, because loss of pigment allows the limestone skeleton to become visible through transparent tissues.
- Zooxanthellae provide reef corals most of their carbon, limestone depositing ability, and colour.
Select the correct code:
- Only 1
- Only 2
- Both 1 & 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Q.2 Fatah-1, recently seen in news, is associated with Which of the following?
- Qatar’s maiden space mission to moon
- Pakistan’s indigenously developed guided multi-launch rocket system
- Taliban’s successful Mission to capture Afghanistan
- India’s evacuation Mission of its citizens from Afghanistan
Q.3 India’s First smog tower was recently inaugurated in which of the following state/UT?
- Delhi
- Haryana
- Punjab
- Jammu and Kashmir
ANSWERS FOR 24th August 2021 TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE (TYK)
| 1 | C |
| 2 | D |
| 3 | C |
Must Read
On Climate Change & arctic:
On criticism of Asset Monetisation:
On India-USA relations:











