IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
Archives
(PRELIMS & MAINS Focus)
Syllabus
- Prelims – Current Affairs
- Mains – GS 2 (Regulatory Bodies)
Context: The sports administration in India was in the headlines frequently these past few weeks all for the wrong reasons.
- Both the All India Football Federation (AIFF) and the Indian Olympic Association (IOA) face potential ban/suspension if elections to the executive body are not done immediately.
- A seven-member delegation of the world football governing body FIFA and the Asian Football Confederation had come to the country last month for a meeting with the Committee of Administrators (CoA).
- The CoA was entrusted with the running of football by the Supreme Court after the executive committee of the AIFF was dissolved for violating the Central government’s sports code.
- Hockey India has also come under scrutiny by the International Hockey Federation (FIH) for the delay in conducting elections.
What is the Sports Code?
- The Sports Code, or National Sports Development Code of India to be precise, was introduced in 2011 by the Central government, which wanted good governance practices in the management of sports at the national level without interfering in the autonomy of the national sports bodies.
- It was widely accepted that such a sports code was needed as it was felt that most of the sports federations had become personal fiefdoms of certain individuals — many of them politicians — as they continued to remain in power for long periods.
- The National Spots Code laid down restrictions regarding age and tenure.
What happens when a sports body is found to be in violation of the Sports Code?
- The respective federations can be put under a CoA.
- That is what happened with the football and hockey associations.
- The Supreme Court had appointed a three-member CoA led by former Supreme Court judge A.R. Dave to run the AIFF, whose President Praful Patel had to resign.
- On similar lines, the Delhi High Court observed that the Sports Code was violated by Hockey India and a CoA was formed to run the game’s administration in India.
Previous instances
- In February, the Delhi High court appointed Gita Mittal as the chairperson of the CoA to run the Table Tennis Federation of India, which was suspended following an inquiry into the match-fixing allegations raised by one of India’s leading players.
- In 2017, the Supreme Court had appointed a CoA to implement the reforms in the administration of cricket in the country suggested by the Justice R.M. Lodha committee.
Source: The Hindu
Previous Year Question
Q.1) Which one of the following statements best describes the ‘Polar Code’? (2022)
- It is the international code of safety for ships operating in polar waters.
- It is the agreement of the countries around the North Pole regarding the demarcation of their territories in the polar region.
- It is a set of norms to be followed by the countries whose scientists undertake research studies In the North Pole and South Pole.
- It is a trade and security agreement of the member countries of the Arctic Council.
Syllabus
- Prelims – Geography
Virunga National Park
In News: Congo to Auction Land to Oil Companies
- The Democratic Republic of Congo, home to one of the largest old-growth rainforests on Earth, is auctioning off vast amounts of land in a push to become “the new destination for oil investments,” part of a global shift as the world retreats on fighting climate change in a scramble for fossil fuels.
- The oil and gas blocks, which will be auctioned, extend into Virunga National Park, the world’s most important gorilla sanctuary, as well as tropical peatlands that store vast amounts of carbon, keeping it out of the atmosphere and from contributing to global warming.

Peatlands in Equateur province in Congo
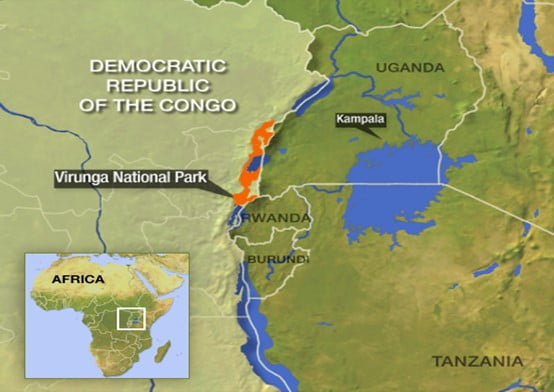
Source: Nytimes.com
Previous Year Question
Q.1) “If rainforests and tropical forests are the lungs of the Earth, then surely wetlands function as its kidneys.” Which one of the following functions of wetlands best reflects the above statement? (2022)
- The water cycle in wetlands involves surface runoff, subsoil percolation and evaporation.
- Algae form the nutrient base upon which fish, crustaceans, molluscs, birds, reptiles and mammals thrive.
- 58 15 Wetlands play a vital role in maintaining sedimentation balance and soil stabilization.
- Aquatic plants absorb heavy metals and excess nutrients.
Syllabus
- Prelims – Geography
In News: All-party meeting in Rajasthan rejected Madhya Pradesh’s objections to canal project.
- Rajasthan government opposed centre’s objection to halt work on the proposed Eastern Rajasthan Canal Project (ERCP) until issues with Madhya Pradesh are resolved
- An all-party meeting on ERCP, reiterated the project’s significance for the State and offered to send a team of experts to the Centre for holding talks on its technical aspects.
- ERCP is an ambitious project that is set to benefit 13 districts with over 3.5 crore population through the interlinking of the Parvati, Kali Sindh and Chambal rivers.
What is the issue?
2005 agreement
- The Inter-State Water Control Board had decided in an agreement signed in 2005 that any of the two States could use water from its own catchment area as well as 10% of the water received from the catchment areas of the other for any project.
Rajasthan government’s stand
- Rajasthan claims to have prepared the DPR on ERCP in accordance with the Inter-State Water Control Board’s decision and in compliance with the 2010 guidelines of the Central Water Commission (CWC).
- Terming the objection to its project baseless, Rajasthan said MP had constructed the Mohanpura dam on the Newaj river, a tributary of Parbati river, and the Kundalia dam on Kali Sindh river, developing about 2.65-lakh hectare irrigation area in its territory.
- Madhya Pradesh obtained the no-objection certificate from Rajasthan after the construction of dams in 2017.
- The all-party meeting again raised the demand for the national project status for ERCP.
Madhya Pradesh’s Objection
- A significant aspect of Madhya Pradesh’s objection is related to the water dependability.
- According to the agreement between the two States, a project for water supply can be formulated only on 75% water dependability, whereas the detailed project report (DPR) of ERCP is based on 50% water dependability.
- This will result in the breach of agreement, according to the Madhya Pradesh.
River Chambal
- Chambal River is also known as Charmanwati or Charmawati
- The river flows much below its banks due to severe erosion because of poor rainfall and numerous deep ravines have been formed in the Chambal Valley, giving rise to badland topography.
| Origin | Janapav near Mhow (MP) in the Vindhaya mountain range |
| Length | 965 kms |
| Discharge | Yamuna, Pachnada near Bhareh in UP |
| States & Major Cities | Madhya Pradesh
Rajasthan: Kota Uttar Pradesh |
| Right Bank Tributaries | Parbati, Kali Sindh, Shipra |
| Left Bank Tributaries | Banas, Mej |
| Major Dams | Gandhi Sagar, Rana Pratap Sagar, Jawahar Sagar, Kota Barrage |
Kali Sindh
| Origin | Bagli, MP, enters Rajasthan at Binda Village |
| Length | 278 kms |
| Discharge | Chambal, Nonera village, Rajasthan |
| States & Major Cities | MP
Rajasthan: Jhalawar, Baran |
| Tributaries | Parwan, Niwaj and Ahu |
| Major Dams | Kalisindh Dam is a major dam across the river situated in Jhalawar district of Rajasthan |
Parbati River
- Parbati River is a river in Madhya Pradesh and Rajasthan, India that flows into the Chambal River.
- The river rises at a height of 610 m in the Vindhya range in Sehore district Madhya Pradesh and then enters in Rajasthan and flows from Baran District and Sawai Madhopur District of Rajasthan where it falls into Chambal River.
- It is one of the Chambal River’s three main tributaries, along with the Banas River and the Kali Sindh River.
- Ramgarh crater is located on its eastern bank.
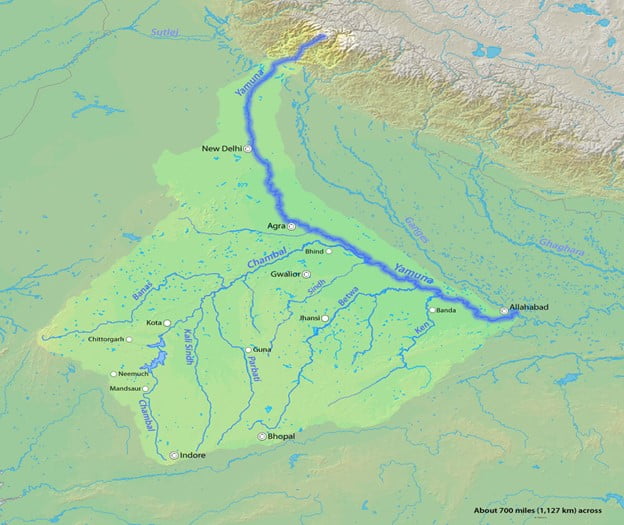
Source: The Hindu
Previous Year Question
Q.1) Consider the following pairs: (2022)
Reservoirs: States
- Ghataprabha: Telangana.
- Gandhi Sagar: Madhya Pradesh
- Indira Sagar: Andhra Pradesh
- Maithon: Chhattisgarh
How many pairs given above are not correctly matched?
- Only one pair
- Only two pairs
- Only three pairs
- All four pairs
Q.2) Consider the following rivers: (2021)
- Brahamani
- Nagalwali
- Subarnarekha
- Vamsadhara
Which of the above rise from the Eastern Ghats?
- 1 and 2
- 2 and 4
- 3 and 4
- 1 and 3
Syllabus
- Prelims – Science & Technology
- Mains – GS 3 (Science & Technology)
What is Fiberisation?
- The process of connecting radio towers with each other via optical fibre cables is called fiberisation.
- It helps provide full utilisation of network capacity, and carry large amounts of data once 5G services are rolled out.
- Aid in providing additional bandwidth and stronger backhaul support
- Fibre-based media, commonly called optical media, provides almost infinite bandwidth and coverage, low latency and high insulation from interference.
- With 5G, it will also be necessary to increase the density of mobile towers to provide better coverage to consumers and businesses. This calls for increased requirements for fibre deployment.
The Challenges
- Indian Prime Minister Narendra of India, in his 2020 Independence Day speech, laid out the vision to connect every village in the country with optical fiber cable (OFC) in 1,000 days.
- To reach the targeted level of fiberisation, India requires about ₹2.2 lakh crore of investment to help fiberise 70% towers.
- There is also a need to increase data capacity in the fiberised towers.
- These tower sites which are connected via fibre are called fibre point of presence (POP). Currently these fibre POPs at a tower site can handle data at one to five Gbps speed.
- One of the biggest issues in the way of fiberisation remains the Right of Way (RoW) rules. While all States/UTs are required to implement these rules, they are not in complete alignment and still require certain amendments to align.
Way Forward
- DoT’s GatiShakti Sanchar online portal can simplify RoW approvals and help deploy cables for 5G.
- Satellite communication also can facilitate 5G broadband connectivity to areas where it is not feasible to deploy terrestrial infrastructure like remote villages, islands or mountainous regions
Note:
- The right of way (RoW) rules provide for a framework to give approvals and settle disputes in a time-bound manner, as well as improve coordination between companies and government authoritie
Must Read: 5G Technology
Source: The Hindu
Previous Year Question
Q.1) Which one of the following is the context in which the term “qubit” is mentioned? (2022)
- Cloud Services
- Quantum Computing
- Visible Light Communication Technologies
- Wireless Communication Technologies
Syllabus
- Mains – GS 3 (Science and Technology)
In News: Principal Scientific Adviser stated that the government would soon come up with a new space policy that could initiate the rise of India’s private sector participation in space sector.
Why is development in the space sector important?
- Enhancing space technology would be beneficial to bolster connectivity and combat climate-related implications through a more secure and effective means.
- Satellites provide more accurate information on weather forecasts and assess (and record) long-term trends in the climate and habitability of a region.
- By monitoring the long-term impact of climate change at regional, territorial, and national scales, governments would be able to devise more pragmatic and combative plans of action for farmers and dependent industries.
- They can also serve as real-time monitoring and early-warning solutions against natural disasters such as earthquakes, tsunamis, floods, wildfires, mining etc. Real-time tracking can also serve multiple purposes in defence.
- As for connectivity, satellite communication can reach more remote areas where conventional networks would require a heavy complimenting infrastructure.
- As to reliability, the WEF had stated that satellite communication can help connect 49% of the world’s unconnected population.
- In this light, it must be noted that satellite communications, which are used to facilitate telecommunication services, are among the major categories for investment in the space technology sector.
- The space avenue is an integration of the aerospace, IT hardware and telecom sectors. It is thus argued that investment in this arena would foster positive carryover effects to other sectors as well.
Where does India stand in the global space market?
Market
- As per SpaceTech Analytics, India is the sixth-largest player in the industry internationally having 3.6% of the world’s space-tech companies.
- S. holds the leader’s spot housing 56.4% of all companies in the space-tech ecosystem. Other major players include U.K. (6.5%), Canada (5.3%), China (4.7%) and Germany (4.1%).
- The Indian Space Industry was valued at $7 billion in 2019 and aspires to grow to $50 billion by 2024.
- The country’s standout feature is its cost-effectiveness.
- India holds the distinction of being the first country to have reached the Mars’ orbit in its first attempt and at $75 million — way cheaper than Western standards.
Start-ups
- Most companies in the sector, globally, are involved in manufacture of spacecraft equipment and satellite communications.
- The Union Minister of State for Science and Technology had stated earlier this month that of the 60-odd start-ups that had registered with the ISRO, a majority of them were dealing in projects related to space debris management.
- As space becomes more congested with satellites, the technology would thus help in managing ‘space junk’.
Investment
- S. and Canada were the highest receivers of space-related investment in 2021.
- U.S. space budget was $41 billion in 2021, $23.3 billion of which was focused on NASA.
- India’s total budgetary allocation for FY2022-23 towards the Department of Space was ₹13,700 crore.
- Funding into the sector’s start-ups (in India) nearly tripled to $67.2 million on a year-over-year basis in 2021.
How is the private sector’s involvement regulated in India?
- In June 2020, the Union government announced reforms in the space sector enabling more private players to provide end-to-end services.
(IN-SPACe)
- An announcement for the establishment of the Indian National Space Promotion and Authorisation Centre (IN-SPACe) was made.
- It was mandated the task of promoting, authorising and licensing private players to carry out space activities.
- As an oversight and regulatory body, it is responsible for devising mechanisms to offer sharing of technology, expertise, and facilities free of cost to promote non-government private entities (NGPEs).
- IN-SPACe’s Monitoring and Promotion Directorate oversees NGPE’s activities as per prescribed regulations and reports back in case any corrective actions or resolutions are required.
- ISRO shares its expertise in matters pertaining to quality and reliability protocols, documentations and testing procedure through IN-SPACe’s ‘interface mechanism’.
NewSpace India Ltd (NSIL)
- Additionally, constituted in March 2019, NewSpace India Ltd (NSIL) is mandated to transfer the matured technologies developed by the ISRO to Indian industries.
With India having one of the best space programs in the world, the move to increase private sector participation in space will make India a bigger player in the global space economy.
Space sector can play a major catalytic role in the technological advancement and expansion of our Industrial base.
India is among a handful of countries with advanced capabilities in the space sector. With these reforms, the sector will receive new energy and dynamism, to help the country leapfrog to the next stages of space activities.
Must Read: Space Sustainability
Source: The Hindu
Syllabus
- Prelims – Polity
- Mains – GS 2 (Governance)
Context: A division bench of the Supreme Court of India in Satender Kumar Antil vs CBI laid down fresh guidelines on arrests in order to have strict compliance with the provisions of Section 41 and 41A of the Code of Criminal Procedure, 1973.
- These guidelines are in addition to the earlier ones which the apex court had already laid down in the case of Arnesh Kumar vs State of Bihar (2014).
- The Court in the present case has also emphasised upon separate legislation on the law relating to bail and has also issued specific directions in this regard.
How is a person arrested?
- Arrest in its simplest form is defined as, “when one is taken and restrained from his liberty”.
- The police has wide powers to arrest under the Code of Criminal Procedure, 1973.
- With regard to the Satender Kumar Antil case, the Court has issued specific directions and has also called for a compliance report.
- The Court said that the investigating agencies and their officers are duty-bound to comply with the mandate of Section 41 and 41A and the directions issued in the Arnesh Kumar case.
What are Sections 41 and 41A of the Code of Criminal Procedure?
- Section 41 of the Code provides for the circumstances in which arrest can be made by the police without a warrant and mandates for reasons to be recorded in writing for every arrest and non-arrest.
- Section 41A of the Code provides for the requirement of a notice to be sent by the investigating agencies before making an arrest in certain conditions prescribed by the Code. The Court stated that any dereliction on the part of the agencies has to be brought to the notice of the higher authorities by the court followed by appropriate action.
- The Bench further said that the courts will have to satisfy themselves on the compliance of Section 41 and 41A.
- Any non-compliance would entitle the accused for grant of bail.
What are the guidelines with respect to bail?
- The Court has made a specific observation in the form of an obiter that the Government of India may consider the introduction of a separate enactment, in the nature of a Bail Act, so as to streamline the grant of bails.
- As part of the new guidelines, it is clearly stated that there need not be any insistence on a bail application while considering the application under Sections 88, 170, 204 and 209 of the Code.
- The Court said that “there needs to be a strict compliance of the mandate laid down in the judgment of this court in Siddharth” ( Siddharth vs State of U.P., 2021).
- It is a clear direction of the Court that bail applications ought to be disposed of within a period of two weeks except if the provisions mandate otherwise
- The Court also said that “applications for anticipatory bail are expected to be disposed of within a period of six weeks with the exception of any intervening application”.
What steps need to be taken for compliance of these orders?
- The State and Central governments will have to comply with the directions issued by the Court from time to time with respect to the constitution of special courts.
- The High Court in consultation with the State governments will have to undertake an exercise on the need for special courts.
- The vacancies in the position of Presiding Officers of the special courts will have to be filled up expeditiously.
What about undertrial prisoners?
- The High Courts have been directed by the apex court to identify undertrial prisoners who cannot comply with bail conditions.
- After doing so, appropriate action will have to be taken in the light of Section 440 of the Code, facilitating their release.
- Under Section 440, the amount of bond shall not be excessive, and high courts and sessions courts may reduce the amount prescribed by the magistrate or a police officer.
- An exercise will have to be done similarly to comply with the mandate of Section 436A of the Code, under which a person imprisoned during investigation or trial shall be released on bail on completion of half of the jail term prescribed for that offence.
Must Read: Pressing need for Bail Law + Article 142
Source: The Hindu
Syllabus
- Mains – GS 3 (Environment)
Stats:
- Between 2018-19 and 2020-21, 222 elephants were killed by electrocution across the country, 45 by trains, 29 by poachers and 11 by poisoning.
- Among tigers, too, 29 were killed by poaching between 2019 and 2021, while 197 tiger deaths are under scrutiny.
- Among human casualties of conflict with animals, elephants killed 1,579 humans in three years.
- Odisha accounted for the highest number of these deaths at 322.
- Around 222 elephant deaths is caused by electrocution
- Tigers killed 125 humans in reserves between 2019 and 2021. Maharashtra accounted for nearly half these deaths, at 61
Assessments of human-wildlife conflicts indicate that the main causes of human wildlife conflict include habitat loss, growth of population of wild animals, changing cropping patterns that attract wild animals to farmlands, movement of wild animals from forests area to human dominated landscapes for food and fodder, movement of human beings to forests for illegal collection of forest produce, habitat degradation due to growth of invasive alien species, etc.
Must Read: Man-Animal Conflict
Source: Indian Express
Syllabus
- Mains – Governance
In News: At least 26 states of India have less number of Indian Administrative Services (IAS) officials than sanctioned strength. This is the situation when India is the first country in the world where a unique model, called ‘National Standards for Civil Services Training Institutions’ (NSCST), has recently been launched for the training of civil servants.
- The number of IAS officials currently stands at 5,317 against the sanctioned strength of 6,789.
- According to data, among the sanctioned strength of 6,789, 4,712 are to be recruited through UPSC while the remaining via state civil services.
- Although the Union government claims to have started recruiting 180 IAS officers directly annually since 2012 following the recommendation of the Baswan Committee, the shortages still persist.
The Effect: The gap between sanctioned and available strength is hampering policy-making and implementation of national welfare schemes in the states.
Must Read: Link 1
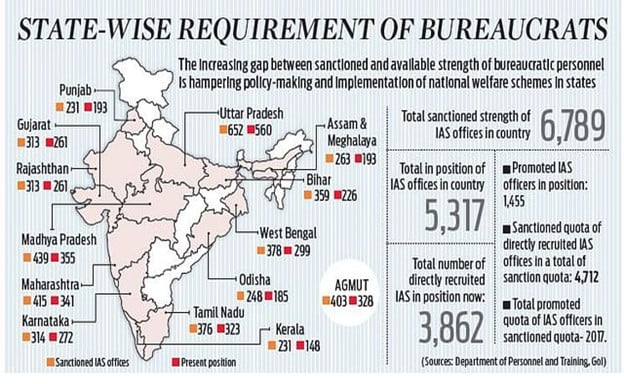
Source: Newindian Express
Baba’s Explainer – Privatisation in Space Sector
Syllabus
- GS-3: Science and Technology- developments and their applications and effects in everyday life.
- GS-2: Government policies and interventions for development in various sectors
- GS-3: Indian Economy and issues relating to planning, mobilization, of resources
Context: In 2022, the space sector is witnessing what the information technology sector experienced in the 1990s. As a result, government would soon come up with a new space policy that could initiate the rise of India’s own “SpaceX-like ventures”.
- The proposed move would increase private sector participation in the industry.
Read Complete Details on Privatisation in Space Sector
Daily Practice MCQs
Q.1) Consider the following statements about National Sports Development Code of India
- It was introduced in 2011 by the Government of India with an aim of bringing good governance practices in the management of sports at the national level.
- The sports code does not interfere with the autonomy of the national sports bodies.
Choose the correct statements:
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Q.2) Consider the following statements
- River Chambal originates in the Aravalli hills of Rajasthan
- River Parbati and Kali Sindh are left bank tributaries of River Chambal
- Gandhi Sagar and Kota Barrage on the River Barrage
Choose the incorrect statements:
- 1, 2 and 3
- 1 and 2
- 2 and 3
- 1 only
Q.3) Consider the following statements about fiberisation
- It is the process of connecting radio towers with each other via optical fibre cables.
- It aids in providing additional bandwidth and stronger backhaul support.
Choose the incorrect statements:
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Comment the answers to the above questions in the comment section below!!
ANSWERS FOR ’26th JULY 2022 – Daily Practice MCQs’ will be updated along with tomorrow’s Daily Current Affairs.
ANSWERS FOR 25th JULY 2022 – Daily Practice MCQs
Q.1) – c
Q.2) – b
Q.3) – d











