IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
Archives
(PRELIMS & MAINS Focus)
Syllabus
- Prelims – Science & Technology
In News: With fears of a nuclear disaster at Ukraine’s Zaporizhzhia power plant growing, the European Union has decided to pre-emptively supply 5.5 million anti-radiation pills to be distributed among residents in the vicinity.
What is a radiation emergency?
- These are unplanned or accidental events that create radio-nuclear hazard to humans and the environment.
- Such situations involve radiation exposure from a radioactive source and require prompt intervention to mitigate the threat.
- Dealing with such an emergency also involves the use of anti-radiation tablets.
What are anti-radiation pills?
- Potassium iodide (KI) tablets, or anti-radiation pills, are known to provide some protection in cases of radiation exposure.
- They contain non-radioactive iodine and can help block absorption, and subsequent concentration, of radioactive iodine in the thyroid gland.

How do these pills work?
- After a radiation leak, radioactive iodine floats through the air and then contaminates food, water and soil.
- While radioactive iodine deposited during external exposure can be removed using warm water and soap, according to the World Health Organisation, the bigger risk is inhaling it.
- Internal exposure, or irradiation, occurs when radioactive iodine enters the body and accumulates in the thyroid gland.
- The thyroid gland, which uses iodine to produce hormones to regulate the body’s metabolism, has no way of telling radioactive from non-radioactive iodine.
- Potassium iodide (KI) tablets rely on this to achieve ‘thyroid blocking’.
- KI pills taken a few hours before or soon after radiation exposure ensure that non-radioactive iodine in the medicine is absorbed quickly to make the thyroid “full”.
- Because KI contains so much non-radioactive iodine, the thyroid becomes full and cannot absorb any more iodine – either stable or radioactive – for the next 24 hours.
- But KI pills are preventive only and cannot reverse any damage done by radiation to the thyroid gland.
- Once thyroid gland absorbs radioactive iodine, those exposed are at a high risk of developing thyroid cancer.
Is the method fool-proof?
- Anti-radiation pills do not provide 100% protection.
- The effectiveness of KI also depends on how much radioactive iodine gets into the body and how quickly it is absorbed in the body
- Also, the pills are not meant for everybody. They are recommended for people under 40 years of age.
- While it can protect the thyroid against radioactive iodine, it cannot protect other organs against radiation contamination.
Source: Indian Express
Previous Year Question
Q.1) The function of heavy water in a nuclear reactor is to (2011)
- Slow down the speed of neutrons
- Increase the speed of neutrons
- Cool down the reactor
- Stop the nuclear reaction
Syllabus
- Prelims – Science & Technology – Defence
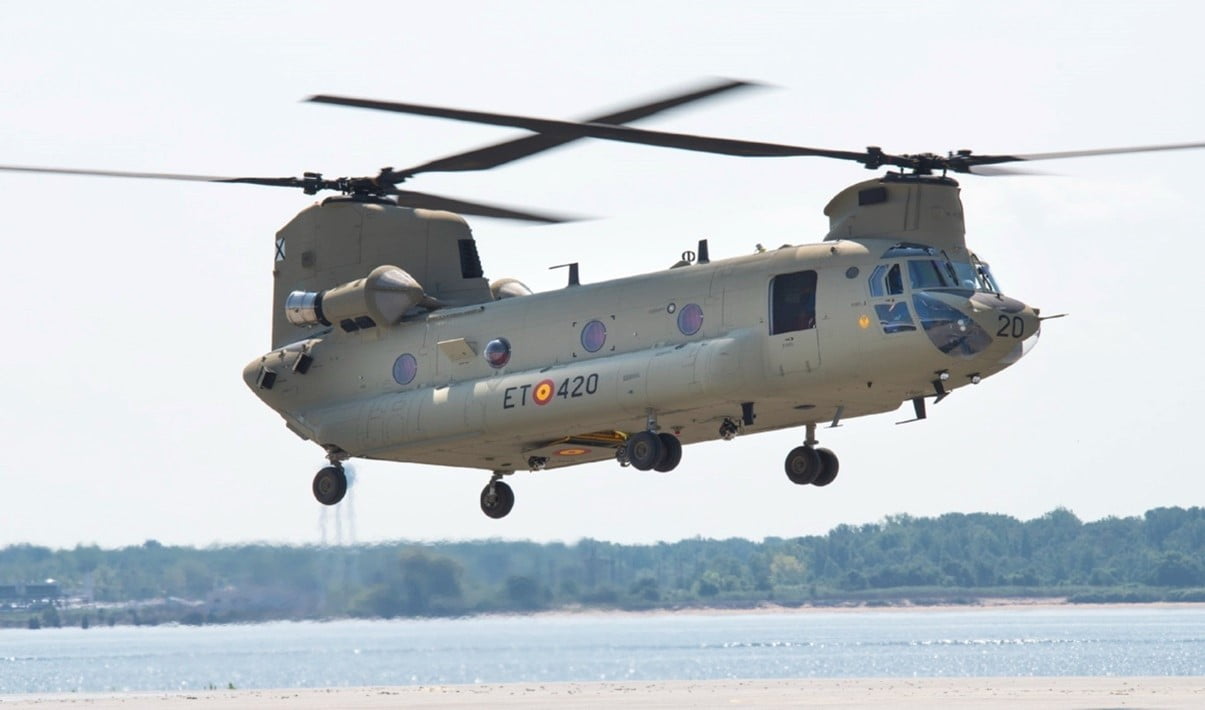
In News: The US Army has grounded its fleet of CH-47 Chinook helicopters after finding the helicopter to be at risk of engine fires. The Indian Air Force (IAF) also operates a fleet of Chinook Helicopters.
Why has the US Army grounded Chinooks?
- The US Army operates around 400 Chinook helicopters which are medium-lift, multi-role helicopters manufactured by Boeing who perform a variety of tasks in support of Army operations.
- As per the news, the Chinook fleet has been grounded by the US Army as it is suspected that some engine fires broke out on an unspecified number of helicopters.
About Chinnok
- India had signed a 3-billion-dollar deal with the US in 2015 for the purchase of 15 Chinook heavy lift and 22 AH-64E Apache attack helicopters.

Features:
- The Chinook is a multi-role, vertical-lift platform, which is used for transporting troops, artillery, equipment and fuel.
- It is also used for humanitarian and disaster relief operations and in missions such as transportation of relief supplies and mass evacuation of refugees.
- Chinooks have a unique twin engine, tandem rotor design which has become one of the most visibly recognised symbols of the American armed forces.
- The helicopter, which can carry around 10 tonnes of load, significantly enhanced IAF’s air lift capabilities.
Source: Indian Express
Previous Year Question
Q.1) With reference to the Agni-IV Missile, which of the following statement(s) is/are correct? (2014)
- It is a surface-to-surface missile.
- It is fuelled by liquid propellant only.
- It can deliver a one-tonne nuclear warhead about 7500 km away.
Select the correct answer using the codes given below.
- 1 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
Syllabus
- Prelims: Current Affairs ( Economy)
In news: Growth in the output of eight core infrastructure sectors decelerated sharply for a second straight month to hit a six-month low of 4.5 per cent in July from a year ago, as a conducive base effect waned considerably.
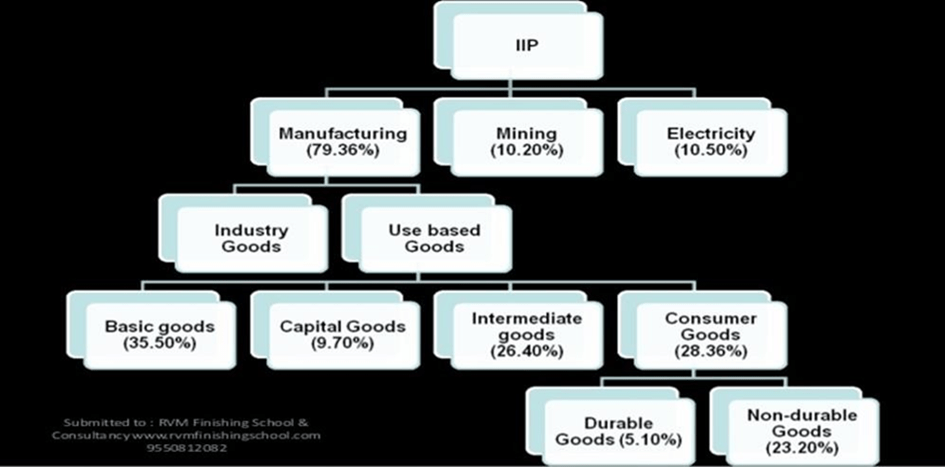
This may weigh down the growth of the index of industrial production (IIP) in July from 6.7 percent in June, given that the core industries make up for 40.30 per cent of the IIP. What is the Index of Industrial Production?
- IIP is a composite indicator measuring changes in the volume of production of a basket of industrial products over a period, with respect to a chosen base period.
- It is compiled and published monthly by the National Statistical Office (NSO), Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation.
- It is a composite indicator that measures the growth rate of industry groups classified under:
- Broad sectors, namely, Mining, Manufacturing, and Electricity.
- Use-based sectors, namely Basic Goods, Capital Goods, and Intermediate Goods.
- Base Year for IIP is 2011-2012.
Significance of IIP:
- It is used by government agencies including the Ministry of Finance, the Reserve Bank of India, etc, for policy-making purposes.
- IP is the only measure on the physical volume of production.
- It forms a crucial input for compilation of Gross Value Added (GVA) of the manufacturing sector in the Gross Domestic Product (GDP) on a quarterly basis.
- IIP remains extremely relevant for the calculation of the quarterly and advance GDP estimates.
- It is also used extensively by financial intermediaries, policy analysts and private companies for various analytical purposes.
About Eight Core Sectors:
- These comprise 40.30% of the weight of items included in the Index of Industrial Production (IIP).
- The eight core sector industries in decreasing order of their weightage: Refinery Products> Electricity> Steel> Coal> Crude Oil> Natural Gas> Cement> Fertilizers.
Source: Indianexpress
Previous year question
Q.1) In the ‘Index of Eight Core Industries’, which one of the following is given the highest weight? (2015)
- Coal production
- Electricity generation
- Fertilizer production
- Steel production
Syllabus
- Prelims – Geography (Map Based)
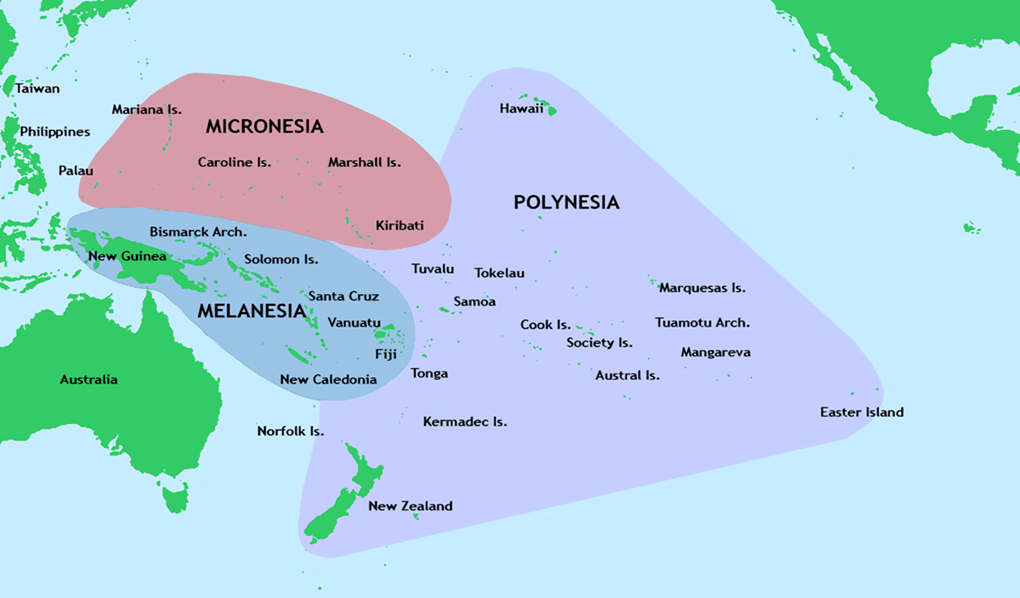
In news: Recently, the Solomon Islands has temporarily halted all naval visits.
Key details of the Issue:
- The country’s move to refuse access to its ports is a departure from the norm and raises concerns about China’s growing influence in the country and the region at
- Earlier this year, the Solomon Islands established a security agreement with China, saying it needed China’s assistance with its domestic security situation.
- The announcement had rattled the US, Australia, and others in the Indo-Pacific region.
- The concerns were that the agreement could potentially lead to a Chinese military base on the island nation, and the power-projection capabilities the People’s Liberation Army (PLA) would gain as a
Must Read: Solomon Islands and China Security Pact
Source: Indian Express
Syllabus
- Prelims – Current Affairs
- Mains – GS 2 (Governance)
In News: While granting bail to a man arrested for possessing bhang and 400 g of ganja, Karnataka High Court recently observed that nowhere in the Narcotic Drugs and Psychotropic Substances (NDPS) Act is bhang referred to as a prohibited drink or prohibited drug.
- The Bench relied on two earlier judgments, Madhukar vs the State of Maharashtra, 2002 and Arjun Singh vs State of Haryana, 2004, where the courts had ruled that bhang is not ganja, and is therefore not covered under the NDPS Act.
What is bhang?
- Bhang is the edible preparation made from the leaves of the cannabis plant, often incorporated into drinks such as thandai and lassi, along with various foods.
- Bhang has been consumed in the Indian subcontinent for centuries, and is frequently consumed during the festivals of Holi and Mahashivratri.

Bhang and the law
- Enacted in 1985, the NDPS Act is the main legislation that deals with drugs and their trafficking.
- Various provisions of the Act punish production, manufacture, sale, possession, consumption, purchase, transport, and use of banned drugs, except for medical and scientific purposes.
The NDPS Act defines cannabis (hemp) as a narcotic drug based on the parts of the plant that come under its purview. The Act lists these parts as:
- Charas: The separated resin, whether crude or purified, obtained from the cannabis plant and also includes concentrated preparation and resin known as hashish oil or liquid hashish.
- Ganja: The flowering or fruiting tops of the cannabis plant.
- Any mixture, with or without any neutral material, of any of the above forms of cannabis or any drink prepared therefrom.
- The Act, in its definition, excludes seeds and leaves “when not accompanied by the tops”.
- Bhang, which is made with the leaves of the plant, is not mentioned in the NDPS Act.
Narcotic Drugs and Psychotropic Substances Act, 1985
- The NDPS Act prohibits a person from the production/manufacturing/cultivation, possession, sale, purchasing, transport, storage, and/or consumption of any narcotic drug or psychotropic substance.
- Initially enacted in 1985, the Act was amended three times in 1988, 2001 and 2014.
- According to the Act, narcotic drugs include coca leaf, cannabis (hemp), opium, and poppy straw; and psychotropic substances include any natural or synthetic material or any salt or preparation protected by the Psychotropic Substances Convention of 1971.
- All the offences under the NDPS Act are non-bailable.
- Under the Act, property acquired by a person from drug-related offences, who has been convicted under the Act can be seized, frozen and forfeited by the government.
- Also, no relief can be sought by the drug convicts by termination, remission, and commutation of sentences passed.
- The bail provision under NDPS requires the court to have “reasonable grounds” to believe that the accused is not guilty and that he is unlikely to commit another offence while on bail.
Penalty
- The penalties under this Act are severe considering the consequences of drug abuse and its trafficking.
- The offences under the Act attract jail terms ranging from one year to 20 years and fine depending on the crime.
- Under the Act, abetment, criminal conspiracy and even attempts to commit an offence attract the same punishment as the offence itself.
- Preparation to commit an offence attracts half the penalty.
- Repeat offences attract one and a half times the penalty and in some cases, the death penalty.
Narcotics Control Bureau
- NCB is the nodal drug law enforcement and intelligence agency of India responsible for fighting drug trafficking and the abuse of illegal substance.
- It functions under Union Ministry of Home Affairs (MHA).
- It is headquartered in New Delhi.
- It was established in March 1986 to enable full implementation of Narcotic Drugs and Psychotropic Substances Act, 1985 and fight its violation through Prevention of Illicit Trafficking in Narcotic Drugs and Psychotropic Substances Act, 1988.
- Its mandate is to fight drug trafficking on an all-India level.
Source: Indian Express
Baba’s Explainer – Aadhaar-Voter ID linkage
Syllabus
- GS-2: Functions and responsibilities of various Constitutional Bodies.
- GS-2: Government policies and interventions for development in various sectors and issues arising out of their design and implementation
Context: Reports have surfaced online of instances where block level officers have asked individuals to link their Aadhaar with their Voter IDs, failing which their Voter IDs could be cancelled. This comes in the aftermath of the Election Commission’s (EC) campaign to promote the linkage of Voter ID and Aadhaar that began on August 1.
- In the first ten days since its launch, the campaign saw almost 2.5 crore Aadhaar holders voluntarily submitting their details to the EC.
Read Complete Details on Aadhaar-Voter ID linkage
Daily Practice MCQs
Q.1) With reference to ‘The National Policy on Narcotic Drugs and Psychotropic Substances’, which of the following statements is/are correct?
- It is based on the Directive Principles, contained in Article 49 of the Indian Constitution.
- India is a signatory to the United Nations Convention against Illicit Traffic in Narcotic Drugs and Psychotropic Substances, 1988.
- Narcotics Control Bureau is the nodal drug law enforcement and intelligence agency of India responsible for fighting drug trafficking and the abuse of illegal substance.
Select the correct answer using the codes given below.
- 1 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 3 only
- 2 and 3 only
Q.2) Consider the following pairs:
Places in news and its location
- Solomon Islands – North Pacific Ocean
- Zaporizhzhia Nuclear power plant – Ukraine
- Ambarnaya River – Japan
- Mount Nyiragongo – Philippines
How many pair/pairs given above are correctly matched?
- One pair only
- Two pairs only
- Three pairs only
- All four pairs
Q.3) In the ‘Index of Eight Core Industries’, which one of the following is given the highest weight?
- Refinery Products
- Natural Gas
- Crude Oil
- Steel
Comment the answers to the above questions in the comment section below!!
ANSWERS FOR ’1st September 2022 – Daily Practice MCQs’ will be updated along with tomorrow’s Daily Current Affairs.
ANSWERS FOR 31st August 2022 – Daily Practice MCQs
Q.1) – d
Q.2) – b
Q.3) – a












