IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
Archives
(PRELIMS & MAINS Focus)
Syllabus
- Prelims – Art and Culture
Context: The first festival celebrated the linguistic and cultural ties between the Barak Valley region of Assam and the Sylhet segment of Bangladesh recently.
- The festival coincides with the 75th year of India’s independence and the 50th anniversary of the liberation of Bangladesh from Pakistan.
About Sylhet-Silchar festival:

- Organised by the India Foundation and has been supported by the Union Ministry of Culture and the Assam government in association with the Bangladesh India Friendship Society and India-Bangladesh Chamber of Commerce and Industry.
- The festival underlines the commonalities between India and Bangladesh, specifically the Sylheti variant of the Bengali language and the Sylheti culture.
Significance:
- The aim of the festival is to revisit the common values and shared heritage of the twin cities and their people separated by international borders.
- The festival will showcase tribal culture, cuisine, literature, arts, and crafts.
- The festival will also bring together eminent people from public and social life, industrialists, artists, scholars, and practitioners from both sides to discuss and deliberate on issues of mutual growth and opportunity.
- In addition, the Festival will also provide a platform to explore multi-disciplinary trade opportunities in sectors such as healthcare, tourism, education, and digital infrastructure.
Source: Indian Express
Previous Year Question
Q.1) Consider the following pairs:
Tradition State
- Chapchar Kut festival Mizoram
- Khongjom Parba ballad Manipur
- Thang-Ta dance Sikkim
Which of the pairs given above is/are correct? (2016)
- 1 only
- 1 and 2
- 3 only
- 2 and 3
Syllabus
- Prelims – Art and Culture
Context: Beleaguered tanpura makers get some support from the Indian Council for Cultural Relations. Traditional makers of classical Indian string instruments worry about the extinction of their art, with little interest among the younger generation, and most of their clientele now based abroad.
About Tanpura/Tambura:

- The tanpura, also referred to as tambura and tanpuri, is a long-necked plucked string musical instrument, originating in India.
- It does not play melody, but rather supports and sustains the melody of another instrument or singer.
- A tanpura is not played in rhythm with the soloist or percussionist.
- Hindustani musicians favour the term tanpura whereas Carnatic musicians say tambura.
- Tanpuras are designed in two different styles:
- Miraj style: This is the favourite form of tanpura for Hindustani performers.
- Tanjore style: This is a south Indian style of tambura, used widely by Carnatic performers.
About Indian Council for Cultural Relations:
- The Indian Council for Cultural Relations (ICCR), is an autonomous organisation of the Government of India.
- It is involved in India’s global cultural relations, through cultural exchange with other countries and their people.
- It was founded in 1950 by Maulana Abul Kalam Azad, the first Education Minister of independent India.
- Headquarter: New Delhi.
- The council also operates missions internationally, with established cultural centres in various countries.
- In addition to organising cultural festivals in India and overseas, the ICCR financially supports a number of cultural institutions across India, and sponsors individual performers in dance, music, photography, theatre, and the visual arts.
- It also administers the Jawaharlal Nehru Award for International Understanding, established in 1965, whose last award was in 2009.
Source: The Hindu
Syllabus
- Prelims – Governance and Environment
Context: According to the Sambhavna Trust, the leakage of 27 tonnes of deadly methyl isocyanate (MIC) gas from the pesticide plant owned by Union Carbide Corporation in Bhopal 38 years ago is still wreaking havoc on the city. The latest is the spike in incidences of fungal infection among survivors.
About Bhopal Gas Tragedy:

- In the early hours of December 3, 1984, methylisocyanate (MIC) gas leaked from a plant operated by Union Carbide India Limited (UCIL) at Bhopal (Madhya Pradesh).
- The gas drifted over the densely populated neighbourhoods around the plant, killing thousands of people immediately and creating a panic as tens of thousands of others attempted to flee Bhopal.
- The final death toll was estimated to be between 15,000 and 20,000.
- Some half a million survivors suffered respiratory problems, eye irritation or blindness, muscular dystrophy and other maladies resulting from exposure to the toxic gas.
- The study found out that babies born to women exposed to gas were significantly more likely to have “congenital malformations” than those born to women unexposed to gas.
- Congenital malformations can be defined as structural or functional anomalies that occur during intrauterine (within the uterus) life and can be identified prenatally, at birth, or sometimes may only be detected later in infancy.
Government’s response to Bhopal Gas tragedy:
- The government passed the Bhopal Gas Leak Act in March 1985, which allowed it to act as the legal representative for victims.
- The Supreme Court of India also laid down guidelines for the money — the family of the dead were to be given Rs 100,000-300,000.
- In addition, fully or partially disabled were to get Rs 50,000-500,000 and those with a temporary injury, Rs 25,000-100,000.
- In June 2010, seven former employees of Union Carbide, who were all Indian nationals, were convicted of causing death by negligence and sentenced to two years of imprisonment. However, they were later released on bail.
Fungal Infections:
- Ringworm disease, caused by a fungus called tinea, is on the rise.
- Red itchy patches occur in the groin, on the head or in different places of the body. The rash spreads if left untreated.
- Yeast infection candida albicans is also being reported to the Sambhavna Clinic by female survivors.
About Methyl Isocyanate (MIC):
- Methyl isocyanate is a colourless highly flammable liquid that evaporates quickly when exposed to the air. It has a sharp, strong odour.
- It is used in the production of pesticides, polyurethane foam, and plastics.
- The chemical is highly reactive to heat. When exposed to water, the compounds in MIC react with each other causing a heat reaction.
- Immediate health effects include ulcers, photophobia, respiratory issues, anorexia, persistent abdominal pain, genetic issue, neuroses, impaired audio and visual memory, impaired reasoning ability, and a lot more.
- Long-term health effects include chronic conjunctivitis, decreased lung function, increased pregnancy loss, increased infant mortality, increased chromosomal abnormalities, impaired associate learning and more.
Source: DownToEarth
Previous Year Question
Q.1) Magnetite particles, suspected to cause neurodegenerative problems are generated as environmental pollutants from which of the following? (2021)
- Brakes of motor vehicles
- Engines of motor vehicles
- Microwave stoves within homes
- Power plants
- Telephone lines
Select the correct answer using the code given below
- 1, 2, 3 and 5only
- 1, 2 and 4 only
- 3, 4 and 5 only
- 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5
Syllabus
- Prelims –Economy
In news: The National Financial Reporting Authority (NFRA) has started inspections of five audit firms.
- The Conference on “Financial Reporting & Governance Framework – Building Trust” was organised by the Confederation of Indian Industry(CII)
- There is a need to revisit the existing short-term and vague ‘Going Concern’ accounting concept and replace it with long-term viability or Resilience Statements by the Management and Board.
About NFRA:
- It is the country’s sole independent audit regulator.
- It was constituted in 2018 by the Government of India
- It was established under the Companies Act, 2013.
- It comes under Ministry of Corporate Affairs.
Aim:
- To continuously improve the quality of all corporate financial reporting in India.
Composition:
- Chairperson is a Chartered Accountant and a person of eminence having expertise in accountancy, auditing, finance or law (appointed by the Central Government) and a maximum of 15 members.
Functions and Duties:
- Recommend accounting and auditing policies and standards to be adopted by companies for approval by the Central Government;
- Monitor and enforce compliance with accounting standards and auditing standards;
- Oversee the quality of service of the professions associated with ensuring compliance with such standards and suggest measures for improvement in the quality of service
Powers:
- The NFRA has the same powers as the Civil Court.
- Debarring the member/firm from practice as a member of ICAI between 6 months to 10 years as may be decided.
- To investigate the matters of professional or other misconduct.
Scope:
- Companies listed in India
- Unlisted Companies whose:
- Net worth ≥ Rs. 500 crore; or
- Paid up Capital ≥ Rs. 500 crore; or
- Annual turnover ≥ Rs. 1000 crore (As on 31st March of the preceding financial year); OR
- Companies whose securities are listed outside India
Source: The Hindu Business Line
Syllabus
- Prelims – Current Affairs
In news: India to assume chairmanship of Wassenaar arrangement on 1 Jan 2023
- India has also assumed the presidency of the UNSC.
Wassenaar arrangement:
- Established in 1996
- It is a voluntary multilateral export control regime.
- Member states exchange information on various issues like transfer of conventional arms and dual-use goods and technologies.
- India became a member of the Arrangement in 2017.
Aim:
- To promote “greater responsibility” and transparency among its members in exports of weapons and dual-use goods.
- Controlling the movement of technology, material or components to countries or entities which undermine international security and stability.
- To prevent “destabilizing accumulations”
Procedure:
- Wassenaar members lack veto authority over other member’s proposed exports.
- Its predecessor was the Cold War-era Coordinating Committee for Multilateral Export Controls (COCOM), which was created to restrict exports to the former Soviet Union and Eastern bloc.
- The plenary comprising all 42 countries of the group, is the primary decision-making body and is chaired on a rotation basis annually.
- The decisions of the plenary are taken by consensus.
Significance:
- India would be able to prevent arms diversion to terrorists or to sovereign nations supporting terrorism.
- India could play a significant role in democratising access to technologies and processes that can serve as crucial building blocks for the newly emerging defence and space manufacturing sectors in India.
- India is slowly emerging as a low-cost producer of several items in the WA’s control lists.
- Establishing the credibility of the country as a responsible stakeholder in the global non-proliferation architecture.
Source: NewsOnAir
Previous Year Questions
Q.1) What is/are the consequence/consequences of a country becoming the member of the ‘Nuclear Suppliers Group’? (2018)
- It will have access to the latest and most efficient nuclear technologies.
- It automatically becomes a member of “The Treaty on the Non-Proliferation of Nuclear Weapons (NPT)”.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Syllabus
- Prelims – Current Affairs
In News: Government has revised the scheme for facilitating Start-Ups Intellectual Property Protection (SIPP) to upgrade the professional charges of the facilitators.
- The facilitation fees increased by at least 100 percent.
About the scheme:
- The scheme was launched in 2016
- The revised scheme is applicable from 02 December 2022.
- The Scheme is implemented by the Controller General of Patents, Designs, and Trade Mark CGPDTM (under DPITT – MoCI).
Aim:
- to protect and promote Intellectual Property Rights (IPR) of Startups.
- to encourage innovation and creativity
- to promote awareness and acquire of IPRs among the Start-Ups.
- To assist in protecting and commercializing IPRs by providing access to high-quality IP services and resources.
Eligibility:
- Companies must be recognized as Start-Up by DPIIT under Start Up India Initiative.
- Period of existence should not exceed 10 years.
- Annual turnover Rs. 100 crore for any financial year since inception.
- Entity should be working towards development of a product, process, or service.
Findings:
- Patent applications filed by Start-Ups have increased from 179 in 2016-17 to 1500 in 2021-22.
- Trade Mark applications filed by Start-Ups have increased from four in 2016-17 to eight thousand 649 in 2021-22.
Source: NewsOnAir
Syllabus
- Prelims – Environment
In News: Supreme Court exempted Maharashtra’s Tungareshwar Wildlife Sanctuary (TWS) from creation of a one-kilometre eco-sensitive zone (ESZ) around all Protected Areas in India.
- The bench is hearing applications filed in the TN Godavarman Thirumalpad case that has sought exemption from the order.
- We are all for the protection of the environment. But at the same time, we cannot halt development,” Justice Gavai said.
About TWS:

- It was declared a wildlife sanctuary in 2003.
- It is in the suburbs of Mumbai.
- Tungareshwar is a mountain plateau situated between Virar and Vasai.
- Spread over 85 sq.km, it forms a corridor between Sanjay Gandhi National Park (also known as Borivali National Park) and Tansa Wildlife Sanctuary.
- There are three different types of forests – Dry Deciduous, Moist Deciduous and Semi Evergreen.
- It is a popular picnic destination.
- The region is rich in biodiversity: Oriental dwarf kingfisher (a migrant bird known as the Jewel of the forest), the Leopard, Wild Boar, Barking Deer, Langur, Bonnet and Rhesus Macaque, and Black-naped Hare, as well as a multitude of birds, including the Crested Serpent-eagle, Jungle Owlet, White-eyed Buzzard, Oriental Honey-buzzard, Emerald Dove and Heart-spotted Woodpecker can be found here.
Source Down to Earth
Previous Year Question
Q.1) Which one of the following protected areas is well-known for the conservation of a sub-species of the Indian swamp deer (Barasingha) that thrives well on hard ground and is exclusively graminivorous? (2020)
- Kanha National Park
- Manas National Park
- Mudumalai Wildlife Sanctuary
- Tal Chhaper Wildlife Sanctuary
Q.2) Which of the following are the most likely places to find the musk deer in its natural habitat? (2020)
- Askot Wildlife Sanctuary
- Gangotri National Park
- Kishanpur Wildlife Sanctuary
- Manas National Park
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
- 1 and 2 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 3 and 4 only
- 1 and 4 only
Syllabus
- Mains – GS 2 (Governance)
Context: The global supply chain dynamics was severely disrupted in the last two years of the pandemic couples with the geopolitical shocks of the Ukrainian crisis. Thus, there is an urgent need to make global supply chains more resilient to endure another ‘black swan’ event like the Covid-19 pandemic.
About Supply Chains:
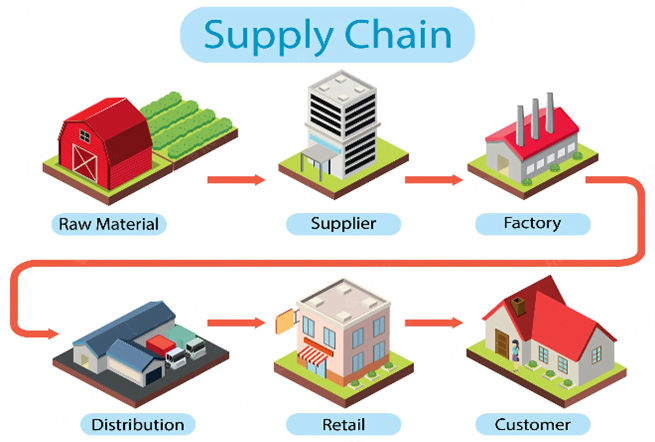
- A supply chain transforms raw materials and components into a finished product that’s delivered to a customer.
- It is made up of a complex network of organizations and activities, such as raw materials suppliers, manufacturers, distributors, retailers and the customer.
- Examples of supply chain activities can include designing, farming, manufacturing, packaging, or transporting.
Significance of Global Supply Chain management:
- Higher Efficiency: Supply chain management uses various strategies to optimize the overall operations by improving the flow of products, materials, and information. It enhances the efficiency of businesses by accurately analyzing the demand and sales forecasting.
- Therefore, investing in SCM leads to the timely delivery of finished goods or services to the customers.
- Reduced Overall Operational Cost and risk assessment: Organizations are investing in effective supply chain management as it can minimize the expenditure by analyzing the real-time data to decrease the purchasing and production costs.
- Therefore, realizing the importance of supply chain management can allow the organization to keep a watchful eye on the operations to control costs and allocate resources.
- The supply chain tends to deploy predictive analysis which offers end-to-end visibility which detects the issue and mitigates the risk.
- Enhance Customer Experience: Supply chain management is important to effectively manage and execute the tasks to help businesses enhance customer experience.
- Prioritizing the customer’s wants is foremost essential as it is useful in customer retention and even establishes the strong reputation of the company.
- Manage Supply and Demand: Getting deep insights into the overall supply chain ecosystem enables organizations to predict demands better and adequately.
- Crafting innovative strategies has now become necessary for businesses to respond to the changing market trends.
- In the contemporary world, an overview of everything across your supply chains enables businesses to be agile and highly responsive.
- Embrace Technologies: New-age technological trends have the ability to enhance the functionality of supply chain management.
- Managing the overall operations using automation tools can be extremely beneficial to scaling your business. Undoubtedly, implementing the new-age technology can optimize the processes and provide your businesses with a competitive advantage.
- Technology plays a vital role to strengthen the overall functionality of supply chain management which allows businesses to scale.
- Business Agility: Supply chain management enables businesses to be more resilient and adaptive to opportunities.
- Supply chain agility tends to meet actual and unexpected demand changes as it implements new-age technologies like Internet of Things, Big Data, Artificial Intelligence in Logistics and so on.
- Therefore, understanding the importance of supply chain management can enable stronger cash flow and shipping optimization enabled with the right technology.
Need for diversification of supply chains across countries and companies:
- Inflation in food and medicine has sparked unrest and tensions the world over.
- Ideas over identifying affordable, resilient, and sustainable supply chains started being discussed in regional forums such as the QUAD, G10, and even multilateral forums such as UNCTAD as soon as the pandemic began to recede.
- The resilience of supply chains was stressed during the pandemic as they were on the verge of collapse.
- Although, though there is a softening of prices and a relative redundancy in the logistics component of the supply chain today, there is still a worry among the shipping lines for sustaining operations and resilience in the logistics domain in the long term.
- Resilience is necessary for the logistics sector to supplement the global supply, especially when the world is just coming out of the pandemic’s impact.
- Now, there is a need to think about various strategies to bring about resilience in GSC, GVC, and the logistics continuum.
Government of India’s Initiatives to boost strong GSC:
- The National Logistics Policy (NLP): Known as the Comprehensive Logistics Action Plan, the National Logistics Policy is an agenda to transform India’s logistics landscape by 2024.
- The policy comes at a time when the country is already witnessing major changes in infrastructure planning such as-
- PM Gatishakti National Master Plan (NMP): By adopting a ‘whole of the government approach’ more than 1,400 connectivity projects have been planned which include 2,00,000 km of National Highways, more than 65 ports, three National Waterways, over 100 airports, and helipads and increasing the capacity of the rail network in the next few years.
- The National Logistics Policy adopts a similar approach and the proposals include efficiency drivers such as digitisation for enhancing human resource development.
- The policy dedicates specific chapters to creating an efficient EXIM Logistics landscape.
- The NMP-NLP complementarity will provide a greater boost to the ongoing initiatives of the government.
- For instance, the government’s One District, One Product (ODOP) and District as Export Hubs (DEH) schemes have been a significant effort towards building regional value chains across districts and their primary focus has been on identifying, branding, and promoting products from each district for exporters through district-level management and production.
- While the PM GatiShakti NMP can provide the infrastructure for these districts, the NLP can help the exporters from the district in developing their regional supply chains.
- The introduction of new age technologies such as AI, Blockchain, Machine Learning, along with creation of a pool of skilled and knowledgeable workforce through the policy will enhance resilience.
- PM GatiShakti and the National Logistics Policy together have the potential to not only bring resilience to the global supply chain dynamics that India can be connected to but also make the supply chain more standardised, predictable, and cost-efficient.
- The combination will enable synergies between human resource and technology and increase the efficiency of logistics.
- Such a complementarity between the two will also de-risk global investments in setting up manufacturing bases within the country thus helping India leverage the China+ 1 strategy.
Way Forward:
The GSC will aid India’s manufacturing competitiveness and increase its global trade share. In this pursuit, there is a need to build infrastructure that boosts India’s export competitiveness. While India appears to be an appealing option for potential investors as both a market and a manufacturing base, it needs to accelerate progress in terms of ease of doing business and skill development.
As India takes over the presidency of G20, opportunities open up for India to lead by example in bringing about the desired resilience through transformative policy interventions and state-of-the-art technology.
Source: The Hindu
Syllabus
- Mains – GS 2 (Governance)
Context: In its Migration and Development Brief, the World Bank has said India’s remittance will grow 12 per cent from 7.5 per cent last year, resulting in $100 billion flow as compared to $89.4 billion in 2021.
- It attributed the feat to the large share of Indian migrants earning relatively high salaries in the United States, United Kingdom and East Asia.
About Remittance:
- The sum of worker’s remittances, compensation of employees, and migrants’ transfers as recorded in the IMF Balance of Payments. Workers remittances are current transfers by migrants who are considered residents in the source.
- Remittances are a vital source of household income for low- and middle-income countries.
Key findings of the report: South Asia
- Led by strong performances in India and Nepal, the WB has predicted that this year will grow 3.5 percent to reach $163 billion in 2022.
- While India has gained 12 percent and Nepal 4 percent, other countries have reported an aggregate decline of 10 percent.
- The report also says that despite global challenges in 2022, remittances to low- and middle-income countries will grow by 5% to $626 billion.
- This is, however, a slowdown from the 6.7 percent gain of 2021, reflecting the impact of an amalgam of external global shocks (inflation, slowing demand) in destination and source countries alike, as well as domestic factors.
Global remittance:
- The growth of remittance flows into South Asia in 2023 is expected to slow to 0.7 percent.
- The year will stand as a test for the resilience of remittances from white-collar South Asian migrants in high-income countries.
- Remittance flows in India, specifically, are predicted to decrease due to inflation and an economic slowdown in the United States.
- Decline in economic growth in the GCC coupled with a fall in oil prices will further pull remittance flows down to all South Asian countries, the report states.
Reason for this rise:
- The large share of Indian migrants earning relatively high salaries in the United States, United Kingdom and East Asia.
- There’s been a gradual shift in destinations for Indian migrants.
- Migrants moved from largely low-skipped, informal employment in the Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC) countries to a dominant share of high-skilled jobs in high-income countries such as the United States, the United Kingdom, and East Asia (Singapore, Japan, Australia, New Zealand).
- A structural shift in qualifications helped them move into the highest-income-earner-category, especially in services.
- Higher education mapped onto high income levels with direct implications for remittance flows.
- During the Covid-19 pandemic, Indian migrants in high-income countries benefited from work-from-home and large fiscal stimulus packages.
- As the pandemic eased, the wage hikes and “record-high employment conditions” helped migrants send money home despite high global inflation.
- Despite Indian migrants in the Gulf Cooperation Council returning to India during the pandemic, price support policies kept inflation at bay and demand for labour increased with higher oil prices, which in turn increased remittances for Indian labourers.
- Depreciation of the Indian rupee to the US dollar — it fell 10 percent between January and September 2022 — proved to be advantageous for Indian migrants and increased remittance flows.
- In last two years, vaccinations and the resumption of travel helped migrants resume work, increasing remittance to the country.
Significance of rise in remittances:
- Money sent home by migrants is one of the largest financial inflows to developing countries.
- Workers’ remittances are a significant part of international capital flows, especially with regard to labour-exporting countries.
- Remittances are a more stable and reliable form of foreign earnings in many developing countries in comparison to FDI or international aid.
- It helps in alleviating the Balance-Of-Payments (BOP) and the debt crisis of such countries.
- Remittances are a stabilising factor for national currencies of developing countries.
- Remittances are helping to meet families’ increased need for livelihood support.
- As COVID-19 still devastates families around the world, remittances continue to provide a critical lifeline for the poor and vulnerable.
Way Forward:
- The World Bank is assisting member states in monitoring the flow of remittances through various channels, the costs and convenience of sending money, and regulations to protect financial integrity that affect remittance flows.
- Growing significance of remittances as a source of external financing for low- and middle-income countries, there is a need for better collection of data on remittances, in terms of frequency, and timely reporting.
- Supportive policy responses, together with national social protection systems, should continue to be inclusive of all communities, including migrants.
According to the RBI surveys, the share of remittances meant to finance family maintenance varied between 49 – 61% of total remittances. Thus, the benefit provided by migrant workers in the form of remittances help manage India’s balance of payments to a considerable extent.
Source: Indian Express
Syllabus
- Mains –GS 3 Science and Technology, GS 2 international relations
In News: In 2022, Quad signed a New Memorandum of Cooperation on 5G Supplier Diversification and Open RAN, and reaffirmed their desire to “collaborate on the deployment of open and secure telecommunications technologies in the region.”
Context:

- The advent of 5G provides the Quadrilateral Security Dialogue—or the Quad of the United States (US), Japan, Australia and India—a unique opportunity to demonstrate how democracies can engage in effective technology collaboration
- Maintaining momentum requires close coordination of resources and policies.
- No one country can build resilient, open, and secure telecommunications networks on its own, particularly as countries deploy 5G and think ahead to 6G.
What is Quad:
- Known as the ‘Quadrilateral Security Dialogue’ (QSD)
- The Quad is an informal strategic forum comprising four nations, namely — USA, India, Australia and Japan.
- One of the primary objectives of the Quad is to work for a free, open, prosperous and inclusive Indo-Pacific region.
- The group met for the first time in 2007
Status of 5G rollout:
- Recognising the risks that companies like Huawei, which is connected to the Chinese Communist Party, pose to telecommunications networks, each member country of the Quad has taken steps to ensure secure and resilient access to 5G.
- India is deploying its first 5G services in select cities in October 2022 and is unlikely to include Huawei in its networks, given the Galwan Valley clash.
- Australia banned Huawei from its 5G rollout in 2018
- Japan has accelerated its efforts to create ‘Open Radio Access Networks (Open RAN)’, which promote vendor diversification and competition for better solution
Significance:
- To promote secure 5G rollout in the Indo-Pacific.
- To serve as a model for other democracies in other parts of the globe
- To “build trust, integrity, and resilience” into technology ecosystems by having suppliers, vendors, and distributors ensure strong safety and security-by-design processes
- To ensure a fair and open marketplace.
- Quad member countries must work together in four key areas:
- standard-setting
- security
- talent development
- vendor diversity
Standard Setting:
- Global standards enable interoperability and facilitate trade.
- Allow international standard-setting costs to qualify as expenditures under R&D tax credits.
- Providing guidance on how to engage in standard-setting with sanctioned companies
- Coordinate and harmonise their respective policies on how industry can participate in standard-setting alongside sanctioned entities.
Security:
- 5G networks are critical infrastructure and vulnerable to risks posed by untrustworthy vendors on 5G networks.
- Firstly, Virtualised (software-based) networks will be the norm in the next 10 years.
- Secondly, early attention to security issues for emerging telecommunications technologies will help ensure that there is sufficient focus on security in the runup to 5G rollouts.
- Focus on a unified zero-trust strategy for 5G networks, with special emphasis on Open RAN deployments.
- Partner with the EU to develop an Open RAN risk assessment and security framework
Talent development:
- Quad Fellowship will support 100 students per year to pursue STEM-related graduate degrees in the United States.
- Australia has raised its permanent immigration cap by 35,000 for the current fiscal year.
- As jobs disperse across the country and remote work accelerated by the pandemic becomes permanent, it is time to seize talent in overlooked areas and communities.
- Recruitment in rural areas to address significant tech worker shortages that may stymie a growing start-up ecosystem.
Vendor Diversity:
- With current 5G infrastructure, software, hardware, and antennae are all supplied by one company.
- Only three companies control 80% of world’s supply of wireless network-based stations: Huawei, Nokia, and Ericsson
- Due to risks of national security and opportunity for diversification, Quad countries can embrace Open RAN in following ways:
- Create a subject matter expert (SME) grant program
- Skill development
- Business growth
- Coordinate vendor diversification efforts
- Provide R&D incentives
- Develop a recruitment framework for telecommunications
- Incentivise 5G deployment in underserved areas
- Enhance public-private partnerships.
Way forward:
- By working together, Quad countries can leverage their individual strengths to improve standard-setting engagement processes, bolster security, and create more opportunities for talent development and vendor diversification.
- Their alignment on Open RAN makes them key to operationalising discussions that other democratic nations are still hesitant to have.
- Quad countries will provide a secure, resilient, and open 5G network model to the Indo-Pacific.
Source: Orfonline
Baba’s Explainer – UPI and NPCI Regulation
Syllabus
- GS-3: Indian Economy and issues relating to planning, mobilization, of resources, growth, development and employment.
- GS-3: Science & Technology
Context: The National Payments Corporation of India (NPCI) has extended by two years the deadline to comply with its 30 per cent cap on the market share of platforms operating on the Unified Payments Interface (UPI).
The UPI transaction value touched a new high of Rs 12.11 lakh crore in October 2022, clearing reflecting the India is witnessing retail payment revolution.
India’s payment revolution comes from
- A clear vision – shifting the system from low volume, high value, and high cost to high volume, low value, low cost
- A clear strategy -regulated and unregulated private players innovating on top of public infrastructure (UPI)
- Trade-offs balanced by design -regulation vs innovation, privacy vs personalisation, and ease-of-use vs fraud prevention
Read Complete Details on UPI and NPCI Regulation
Practice MCQs
Q.1) With reference to “National Financial Reporting Authority”, consider the following statements:
- It was formed in 2008 under the National Financial Reporting Authority Act.
- It is the sole audit regulator for listed and unlisted companies in India.
- It comes under Ministry of Commerce and Industry.
Which of the statements given below is/are correct?
- 1 and 2 only
- 2 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 3 only
Q.2) Recently in news, the “Wassenaar arrangement” is related to which of the following:
- To prohibit development, production, and transfer of biological weapons.
- To prevent the spread of nuclear weapons and its technologies.
- To establish accountability and compensation for loss and destruction.
- To facilitate exchange of information on transfer of conventional weapons.
Q.3) Consider the following statements regarding Indian Council for Cultural Relations (ICCR):
- It was founded in 1950 by Maulana Abul Kalam Azad.
- It is headquartered in Hyderabad.
- In addition to organising cultural festivals in India and overseas, the ICCR financially supports a number of cultural institutions across India, and sponsors individual performers.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 and 2 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 1 2 and 3
Comment the answers to the above questions in the comment section below!!
ANSWERS FOR ’ 5th December 2022 – Daily Practice MCQs’ will be updated along with tomorrow’s Daily Current Affairs.st
ANSWERS FOR 3rd December – Daily Practice MCQs
Q.1) – d
Q.2) – b
Q.3) – a











