IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
Archives
(PRELIMS & MAINS Focus)
Syllabus
- Prelims –Environment and Ecology
Context: Recently, the European Commission grants a GI tag for Himachal’s Kangra tea.
About Kangra tea:-
- In 1849, Dr Jameson, then superintendent of the Botanical Tea Gardens, pronounced the region ideal for tea cultivation.
- Being one of India’s smallest tea regions makes Kangra green and black tea all the more exclusive.
- While the black tea has a sweet lingering aftertaste, the green tea has a delicate woody aroma.
- It is hand-plucked and processed with traditional methods to bring out its full potential.
- It is exported to Kabul and Central Asia via Peshawar.
- Kangra tea is a registered Geographical Indication (GI).
- Tea Attributes: The first flush of Kangra tea is known for its quality, unique aroma and tinge of fruity flavour.
- A little milder than Darjeeling tea in terms of flavour.
- It has more body and liquor.
- Elevation: Teas are grown at elevations ranging from 900 to 1400 metres above sea level.
- Annual Rainfall: 270 to 350cm.
MUST READ: GI Tag for Mithila Makhana
SOURCE: BUSINESS LINE
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) With reference to the “Tea Board” in India, consider the following statements: (2022)
- The Tea Board is a statutory body.
- It is a regulatory body attached to the Ministry of Agriculture and Farmers Welfare.
- The Tea Board’s Head Office is situated in Bengaluru.
- The Board has overseas offices in Dubai and Moscow.
Which of the statements given above is correct?
- 1 and 3
- 2 and 4
- 3 and 4
- 1 and 4
Q.2) With reference to the ‘Changpa’ Community of India, consider the following statements: (2014)
- They live mainly in the state of Uttarakhand
- They rear the Pashmina goats that yield fine wool
- They are kept in the category of Scheduled Tribes
Which of the given statements is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
Syllabus
- Prelims – Governance
Context: Recently, Mahila Samman Savings Certificate (MSSC) 2023 has been notified.
About Mahila Samman Savings Certificate (MSSC) 2023:-

IMAGE SOURCE: Mahila Samman Saving Certificate Apply Post Office and Bank – Sarkari Yojana – TheHowPedia
- It is a one-time small savings scheme for women to commemorate celebrations of 75 years of Independence.
- It will be made available for a two-year period up to March 2025.
- It will be under the Ministry of Women and Child Development.
- The small saving certificate will have a fixed interest rate of 7.5% for two years.
- The deposit can be made in the name of a woman or a girl child.
- The maximum deposit amount has been kept at ₹2 lakhs and the scheme will have a partial withdrawal facility as well.
Eligibility:-
- Application for opening an account under the scheme can be made by a woman for herself or by the guardian on behalf of a minor girl.
Deposit limit:-
- Any number of MSSC accounts can be opened by a woman, or in the name of a minor girl by the guardian, subject to the maximum limit of Rs 2 lakh.
Interest Rate:-
- The Government has notified 7.5% interest on deposits in an MSSC account.
- The interest will be compounded on a quarterly basis and credited to the account.
Maturity and Payment:-
- The notification said that the deposit shall mature on completion of two years from the date of the deposit.
- The eligible balance may be paid to the account holder on an application in Form-2 submitted to the accounts office on maturity.
Partial Withdrawal:-
- An MSSC accountholder will be allowed to withdraw a maximum of up to 40% of the eligible balance once after the expiry of one year from the date of opening of the account but before the maturity of the account.
- The notification further said that in case of an account opened on behalf of a minor girl, the guardian may apply for the withdrawal for the benefit
MUST READ: SAMARTH initiative for women
SOURCE: FINANCIAL EXPRESS
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) Which of the following statements is/are correct regarding the Maternity Benefit Amendment Act, 2017? (2019)
- Pregnant women are entitled to three months of pre-delivery and three months of post-delivery paid leave.
- Enterprises with creches must allow the mother a minimum of six creche visits daily.
- Women with two children get reduced entitlements.
Select the correct answer using the code given below.
- 1 and 2 only
- 2 only
- 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
Q.2) With reference to the ‘stand up India scheme’, which of the following statement is/are correct? (2016)
- Its purpose is to promote entrepreneurship among SC/ST and women entrepreneurs.
- It provides for refinancing through SIDBI.
Select the correct answer using the code given below.
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Syllabus
- Prelims –International Relations
Context: Recently, President Joe Biden announced the opening of his second Summit for Democracy.
About Summit for Democracy 2023:-
- It is hosted by the U.S. Agency for International Development (USAID).
- Objectives: to renew democracy at home and confront autocracies abroad.
- The Summit comprises a series of events and a Year of Action (YoA) led by the US Government to support democratic renewal around the world.
- The Summit for Democracy as a process is an extraordinary opportunity to galvanize attention and mobilize international action.
- This is the second Summit for Democracy, the U.S. Agency for International Development (USAID).
- It unveils new efforts to advance democracy abroad like:
- Presidential Initiative for Democratic Renewal (PIDR)
- USAID is contributing eight new initiatives, many of which are focused on policy reforms, to the PIDR.
- The PIDR comprises five lines of effort in response to significant challenges to democracy in the 21st Century.
- This includes the Partnerships for Democratic Development (PDD), which provides multi-year support to countries that demonstrate sustained democratic progress.
- The USAID has announced the first wave of nine PDD partner countries: Armenia, Dominican Republic, Ecuador, Malawi, Nepal, North Macedonia, Paraguay, Timor-Leste, and Zambia.
MUST READ: 2022 Resilient Democracies Statement
SOURCE: TIMES OF INDIA
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) Consider the following pairs: (2020)
International agreement/ set-up Subject
- Alma-Ata Declaration – Healthcare of the people
- Hague Convention – Biological and Chemical Weapons
- Talanoa Dialogue – Global Climate Change
- Under2 Coalition – Child Rights
Which of the pairs given above is/are correctly matched?
- 1 and 2 only
- 4 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 2,3 and 4 only
Q.2) ‘Beijing Declaration and Platform for Action’ often seen in the news, is (2015)
- a strategy to tackle regional terrorism, an outcome of a meeting of the Shanghai Cooperation Organization.
- a plan of action for sustainable economic growth in the Asia-Pacific Region, an outcome of deliberations of the Asia-Pacific Economic Forum
- an agenda for women’s empowerment, an outcome of a World Conference convened by the United Nations
- a strategy to combat wildlife trafficking, a declaration of the East Asia Summit
Syllabus
- Prelims – Geography
Context: Recent reports suggest that the closure of the Indira Gandhi Canal for repairs may impact Rajasthan’s drinking water, and irrigation needs.
About Indira Gandhi Canal:-
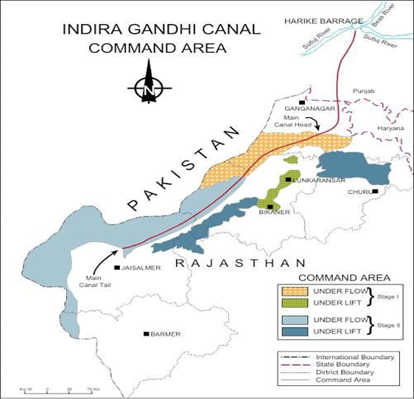
IMAGE SOURCE: https://nwa.mah.nic.in/sdmc/irrigation/04_projects.htm
- Indira Gandhi canal is the longest in India
- It was constructed from 1952 to 2010.
- It was originally known as the Rajasthan canal.
- It was renamed in 1984 as a tribute and honour after the assassination of Indira Gandhi.
- The origin of this canal is from the Harike barrage, Harike situated in Punjab.
- It is built on Sutlej and Beas rivers.
- Its length is connected with Rajasthan and Punjab Indira Gandhi canal was constructed to develop agricultural activities in the desperation of Rajasthan.
- Objective: The Indian government has decided to build a canal on the Sutlej and Beas so that farmers can get water to harvest different kinds of crops for food.
- This is the largest canal in Rajasthan.
- It starts from Haryana in Punjab and to Lohgarh district in Rajasthan.
- The canal water flows through seven districts of Rajasthan that include Churu, Jaisalmer, Jodhpur, Barmer, Bikaner and Sri Ganganagar.
- There are two stages to the construction process:-
- STAGE – I
- The command area lies in Ganganagar, Hanumangarh, and the northern part of the Bikaner districts.
- STAGE – II
- The command area spans the districts of Bikaner, Jaisalmer, Barmer, Jodhpur, Nagaur, and Churu.
- STAGE – I
MUST READ: Eastern Rajasthan Canal Project (ERCP)
SOURCE: THE HINDU
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) With reference to the Indus River system, of the following four rivers, three of them pour into one of which joins the Indus direct. Among the following, which one is a such river that joins the Indus direct? (2021)
- Chenab
- Jhelum
- Ravi
- Sutlej
Q.2) With reference to river Teesta, consider the following statements: (2017)
- The source of river Teesta is the same as that of Brahmaputra but it flows through Sikkim.
- River Rangeet originates in Sikkim and is a tributary of river Teesta.
- River Teesta flows into the Bay of Bengal on the border of India and Bangladesh.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 and 3 only
- 2 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
Syllabus
- Prelims –Polity (Important Organizations)
Context: Prime Minister Narendra Modi to inaugurate the Diamond Jubilee Celebrations of the Central Bureau of Investigation (CBI).
About the Central Bureau of Investigation (CBI):-
Background:-
- It was established as the Special Police Establishment in 194.
- Objective: to investigate cases of corruption in procurement during the Second World War.
- Later, the Santhanam Committee on Prevention of Corruption recommended the establishment of the CBI.
- As a result, it was set up in 1963 by a resolution of the Union Home Ministry.
- The Special Police Establishment (which looked into vigilance cases) setup in 1941 was also merged with the CBI
- Later, it was transferred to the Ministry of Personnel and now it enjoys the status of an attached office.
- The CBI is not a statutory body.
- It derives its powers from the Delhi Special Police Establishment Act, of 1946.
- The CBI is the main investigating agency of the Central Government.
- The CBI investigates the crime of corruption, economic offences and serious and organized crime other than terrorism.
- The CBI is headed by a Director who is assisted by a special/additional director.
- The Director of CBI has been provided security of two-year tenure by the CVC Act, 2003.
- As per the CVC Act of 2003, the Central Government shall appoint the Director of CBI on the recommendation of a three-member committee consisting of the
- Prime Minister as Chairperson,
- Leader of Opposition in the Lok Sabha
- Chief Justice of India or Judge of the Supreme Court nominated by him.
- If there is no recognized leader of the opposition in the Lok Sabha, then the leader of the single largest opposition party in the Lok Sabha would be a member of that committee.
- The CBI Academy is located in Ghaziabad, UP and started functioning in 1996.
- It also has three regional training centres at Kolkata, Mumbai & Chennai.
- The superintendence of CBI related to the investigation of offences under the Prevention of Corruption Act, 1988 lies with the Central Vigilance Commission (CVC).
- Other matters with the Department of Personnel & Training (DOPT) in the Ministry of Personnel, Pension & Grievances of the Government of India
Functions:-
- Investigating cases of corruption, bribery and misconduct of Union govt employees
- Investigating cases relating to infringement of fiscal and economic laws
- Investigating serious crimes, having national and international ramifications, committed by organised gangs of professional criminals.
- Coordinating activities of the anticorruption agencies and various state police forces
- Taking up, on the request of a state government, any case of public importance for investigation.
- The Central Government can authorize CBI to investigate such a crime in a State but only with the consent of the concerned State Government.
- It takes up investigation of conventional crimes like murder, kidnapping, rape etc., on reference from the state governments or when directed by the Supreme Court/High Courts.
- Maintaining crime statistics and disseminating criminal information.
- The CBI acts as the “National Central Bureau” of Interpol in India.
MUST READ: CBI and ED
SOURCE: AIR
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) With reference to the ‘Banks Board Bureau (BBB)’, which of the following statements are correct? (2022)
- The Governor of RBI is the Chairman of BBB.
- BBB recommends the selection of heads for Public Sector Banks.
- BBB helps Public Sector Banks develop strategies and capital-raising plans.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
- 1 and 2 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
Q.2) Consider the following statements: (2022)
- In India, credit rating agencies are regulated by the Reserve Bank of India.
- The rating agency popularly known as ICRA is a public limited company.
- Brickwork Ratings is an Indian credit rating agency.
Which of the statements given above is correct?
- 1 and 2 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
Syllabus
- Prelims –Polity
Context: Recently, a ‘hue and cry’ notice was issued against Amritpal Singh.
About Hue and cry notice:-
- It is issued by the Police.
- It is issued when it requires the help of the public in cases such as:
- locating missing persons
- identifying unclaimed bodies
- looking out for a suspect
- It traces its origin to 1285.
- England’s King Edward I signed the “Statute of Winchester” to deal with security and peacekeeping on a local level by revamping the existing police system.
- The ‘hue and cry’ rule simply means that if a suspect or a criminal is found running down the street in front of some bystanders, each of them needs to yell out to help the police identify and catch them.
MUST READ: Guidelines on arrests and bail orders
SOURCE: THE INDIAN EXPRESS
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) With reference to India, consider the following statements: (2021)
- When a prisoner makes out a sufficient case, parole cannot be denied to a such prisoner because it becomes a matter of his/her right.
- State Governments have their own Prisoners Release on Parole Rules.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Q.2) With reference to India, consider the following statements: (2021)
- Judicial custody means an accused is in the custody of the concerned magistrate and such an accused is locked up in a police station, not in jail.
- During judicial custody, the police officer in charge of the case is not allowed to interrogate the suspect without the approval of the court.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Syllabus
- Prelims –Science and Technology
Context: Recently, ISRO successfully carried out the Reusable Launch Vehicle Autonomous Landing Mission.
About Reusable Launch Vehicle Autonomous Landing Mission (RLV LEX):-
- RLV-LEX involves taking an unmanned, winged prototype to an altitude of about 2.3 km to 2.4 km on a helicopter and releasing it to land.
- It must travel the distance autonomously, gain velocity, maintain control and come in like any typical aircraft, touching down with the rear wheels first.
- The first in the series of experimental flights is the hypersonic flight experiment (HEX).
- It was followed by the landing experiment (LEX), return flight experiment (REX) and scramjet propulsion experiment (SPEX).
- A reusable launch system is a launch system that allows for the reuse of some or all of the component stages.
- The vehicle returns to earth intact after a mission.
Benefits of RLV:-
- Cheaper access to space is what makes an RLV attractive
Challenges of RLV:-
- Reusable stages weigh more than equivalent expendable stages.
- After the launcher lands, it may need to be refurbished to prepare it for its next flight.
- This process may be lengthy and expensive.
MUST READ: Next Generation Launch Vehicle (NGLV)
SOURCE: AIR
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) With reference to the Indian Regional Navigation Satellite System (IRNSS), consider the following statements(2018)
- IRNSS has three satellites in geostationary and four satellites in geosynchronous orbits.
- IRNSS covers the entire India and about 5500 sq. km beyond its borders
- India will have its own satellite navigation system with full global coverage by the middle of 2019.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 1 and 2 only
- 2 and 3 only
- None
Q.2) With reference to India’s satellite launch vehicles, consider the following statements: (2016)
- PSLVs launch satellites useful for Earth resources monitoring whereas GSLVs are designed mainly to launch communication satellites.
- Satellites launched by PSLV appear to remain permanently fixed in the same position in the sky, as viewed from a particular location on Earth.
- GSLV Mk III is a four-stage launch vehicle with the first and third stages using solid rocket motors, and the second and fourth stages using liquid rocket engines.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct.?
- 1 only
- 2 and 3
- 1 and 2
- 3 only
Syllabus
- Mains – GS 2 (International Relations) and GS 3 (Economy)
Context: Recently, the Union Minister of Commerce and Industry, Consumer Affairs, Food and Public Distribution and Textiles has launched the Foreign Trade Policy 2023.
The Key Approach to the Foreign Trade Policy is based on 4 pillars:
- Incentive to Remission,
- Export promotion through collaboration – Exporters, States, Districts, Indian Missions,
- Ease of doing business, reduction in transaction cost and e-initiatives and
- Emerging Areas – E-Commerce Developing Districts as Export Hubs and streamlining SCOMET policy.
Key Features of Foreign Trade Policy 2023
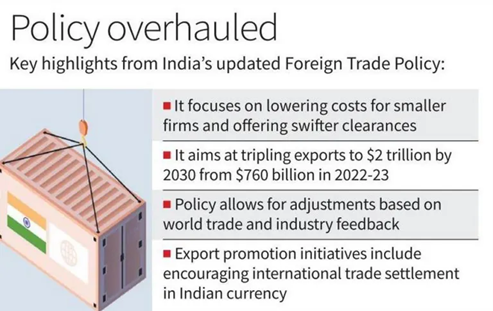
Source: The Hindu
- The new policy will have no sunset date (ending date) and will be tweaked based on the emerging world trade scenario and industry feedback. While the policy will be open-ended, the schemes sanctioned under it will be time bound.
- There are no major new schemes, barring a one-time amnesty under the existing Advance Authorisation and Export Promotion Capital Goods (EPCG) schemes, that allow imports of capital goods subject to specified export obligations.
- The Policy had opened up a new area of potential exports called “merchanting trade”.
- Merchanting trade refers to shipment of goods from one foreign country to another foreign country without touching Indian ports, involving an Indian intermediary. This will also enable exports of restricted goods
- Four towns in Uttar Pradesh — Faridabad, Moradabad, Mirzapur and Varanasi — were announced as centres of export excellence for their performance in the apparel, handicrafts, handmade carpets and handlooms, respectively.
- The policy also plans to launch a special advance authorisation scheme for the clothing and apparel sector so that they can react to market demands and fashion trends faster.
- It is also looking to lower qualification thresholds for star ratings which recognise exporters based on export performance.
- The importance of simplifying the SCOMET( Special Chemicals, Organisms, Materials, Equipment, and Technologies) Licensing Procedure which aims at streamlining the export of dual-use items.
- Special one-time Amnesty Program for Export Obligations Default.
- The dairy industry will be excused from maintaining average export obligations under the new foreign trade strategy, and a particular advance authorization procedure has been extended to textiles and clothing.
Challenges:
- Low credit access: Indian exporters have very low access to trade finance and export credit. This is especially true for Micro, Small, and Medium Enterprises (MSMEs), even though they account for close to half of India’s total exports.
- The financial support Indian exporters receive is far less than in other countries.
- Export credit agencies doled out $7.6 billion in funds in India while the figure for China stood at $39.1 billion.
- Inadequate Infrastructure: Infrastructure is India’s weakest link. In data firm Statista’s ranking of 100 countries based on the quality of their infrastructure in 2019, India’s score was 68.1.
- To put this in perspective, top-ranked Singapore scored 95.4 while bottom-ranked Bolivia was 10-odd points behind India, at 57.1. .
- Bureaucracy: The export process in India is more time-consuming than in many other countries due to a high documentation requirement.
- Indian exporters must prepare a large set of documents for each stage of the shipping process.
- It is also important to plan ahead because certification authorities at Indian ports are not available round the clock or on all days of the week.
- Pendencies: There is long list of pending cases of redemption with respect to Advance Authorization scheme due to pre-import conditions.
- This needs to be sorted out immediately by withdrawing the pre-import condition retrospectively.
Govt Initiatives for Improving Exports:
- Remission of Duties or Taxes on Export Product (RoDTEP): It is a fully automated route for Input Tax Credit (ITC) in the GST (Goods and Service Tax) to help increase exports in India.
- ITC is provided to set off tax paid on the purchase of raw materials, consumables, goods or services that were used in the manufacturing of goods or services.
- This helps in avoiding double taxation and the cascading effect of taxes.
- Merchandise Exports from India Scheme: MEIS was introduced in the Foreign Trade Policy (FTP) 2015-20, under MEIS, the government provides duty benefits depending on product and country.
- Rewards under the scheme are payable as percentage of realised free-on-board value (of 2%, 3% and 5%) and MEIS duty credit scrip can be transferred or used for payment of a number of duties including the basic customs duty.
- Rebate of State and Central Taxes and Levies: The scheme was offered for embedded state and central duties and taxes that are not refunded through Goods and Services Tax (GST).
- It was available only for garments.
- It was introduced by the Ministry of Textiles.
- Common Digital Platform for Certificate of Origin has been launched to facilitate trade and increase Free Trade Agreement (FTA) utilisation by exporters.
Source: The Hindu
Syllabus
- Mains – GS 1 (History)
Context: Recently, Kerala Chief Minister and Tamil Nadu Chief Minister jointly inaugurated the centenary year celebrations of the anti-caste struggle Vaikom Satyagraha.
About Vaikom Satyagraha
- Vaikom Satyagraha was a historic non-violent movement against untouchability and caste discrimination in the country.
- The Satyagraha took place between March 30, 1924 and November 23, 1925 and also marked the start of temple entry movements across India.
- The movement was spearheaded by Congress leader T.K. Madhavan, as an opposition against social injustice.
- Apart from Madhavan, K.P. Kesava Menon (then secretary of Kerala Congress) and Congress leader and educationist K. Kelappan are considered the pioneers of the Vaikom Satyagraha movement.
- Vaikom is situated on the western side of Kottayam district in the Indian state of Kerala.
- It shares its border with Vembanad Lake.
- Its importance in Indian history is due to the Vaikom Satyagraha against untouchability, in which Mahatma Gandhi and Periyar Ramasamy
- The Satyagraha aimed at securing freedom of movement for all sections of society through the public roads leading to the Sri Mahadevar Temple at Vaikom.
Situation Prior to Vaikom Satyagraha
- The Kingdom of Travancore had rigid and oppressive caste system.
- The people belonging to the oppressed classes, especially the Ezhavas, had no right to walk on the four roads surrounding the Vaikom Mahadeva temple.
- The injustice meted out to the depressed classes was brought to the notice as a resolution at the Kakinada meet of All India Congress Committee.
- The Congress Untouchability Committee formed by the Kerala Pradesh Congress Committee in January 1924, decided to take up this issue.
- K Kelappan (Kerala Gandhi), T K Madhavan, Velayudha Menon, K Neelakantan Namboothiri and TR Krishnaswami Iyer were members of the committee.
- The committee decided to launch a ‘Kerala Paryatanam’ to urge temple entry and also advocate the opening of all public roads for everyone regardless of caste or creed.
Role of Periyar:
- Periyar accepted the request of leaders such as Neelakandan Nampoothiri and George Joseph and led the protest making the protest successful.
- Vi. Kalyanasundaram (Thiru.Vi.Ka.) conferred the title Vaikom Veerar (Hero of Vaikom) on Periyar.
- Tamil Nadu played a pivotal role in Vaikom Satyagraha, which symbolised a struggle by the untouchables.
- Emperumal Naidu and Sivathanu Pillai were prominent leaders in Nagercoil, Tamil Nadu.
Reach of the movement
- The movement was backed by Gandhiji, ChatampiSwamikal, and Sree Narayana Guru.
- Prominent Leaders in Kerala such as Madhavan, K.P. Kesava Menon and George Joseph launched the movement.
- Periyar and KovaiAyyamuthu from Tamil Nadu worked in tandem with leaders in Kerala despite facing repressive action.
- The campaign gained popularity throughout India, and supporters arrived from around the country.
- Punjab’s Akalis helped by establishing kitchens to feed the Satyagrahis.
- Even Muslim and Christian authorities backed the initiative.
Impacts of the Vaikom Satyagraha
- Vaikom Satyagraha was a testing ground for the Gandhian Principles of Satyagraha.
- In 1925, Gandhiji wrote to H. Pitt, then Police Commissioner of Travancore to resolve the ongoing matter.
- Thus, Pitt intervened and a settlement was signed between the Government and Gandhiji.
- In 1925, the Government agreed to nullify the prohibitory orders passed in February 1924, and Gandhiji gave his consent to withdraw the Satyagraha.
- It was announced by the government that roads (pathways) on three sides of the Shiv shrine or Mahadev temple of Vaikom (north, south, and west) would be open for all public but the road on the eastern side i.e the roads leading to that eastern approach would be reserved for Savarnas only.
- Many historians believed the Vaikom Satyagraha had not given the desired outcome, while considered the settlement was humiliating as compared to the enigma of the revolutionary cause.
- However, this movement laid the foundation which ultimately laid the fruit to end orthodox colonialism.
- The Vaikom Satyagraha proclaimed its significance almost a decade later when in November 1936, the historic Temple Entry Proclamation was passed, which lifted the age-old orthodox ban on the entry of marginalized depressed castes into the temples of Travancore.
- It was also a great opportunity for the Indian National Congress Party to Grow in Kerala.
- It became the first struggle for human rights in India.
- The Vaikom Satyagraha had a significant impact on Indian society and politics.
- It led to the formation of the Sree Narayana Dharma Paripalana Yogam (SNDP), a social reform organization that worked for the upliftment of the lower castes in Kerala.
Way Forward:
The Vaikom Satyagraha was a pivotal moment in the Indian independence movement that brought attention to the injustices of the caste system and the need for social reform. The protest helped pave the way for a more inclusive and equitable society and demonstrated the power of nonviolent resistance in achieving social change. The movement has been documented in history as one of the most non-violent struggles against caste oppression and discrimination.
Source: The Hindu
Practice MCQs
Q.1) With reference to India, consider the following statements regarding Hue and cry notice:
- It is issued by the District Magistrate
- It is issued when it requires the help of the public in cases such as locating missing persons, identifying unclaimed bodies and looking out for a suspect
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Q.2) Consider the following statements regarding the Mahila Samman Savings Certificate (MSSC):
- It is a one-time small savings scheme for women to commemorate celebrations of 75 years of Independence.
- It will be under the Ministry of Finance.
- The small saving certificate will have a fixed interest rate of 7.5% for two years.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
- 1 and 2 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 1 2 and 3
Q.3) Consider the following:
- K. Madhavan,
- P. Kesava Menon
- George Joseph
Who among the above personalities associated with Vaikom Satyagraha?
- 1 and 2 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 1 2 and 3
Comment the answers to the above questions in the comment section below!!
ANSWERS FOR ’ 3rd April 2023 – Daily Practice MCQs’ will be updated along with tomorrow’s Daily Current Affairs.











