IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
Archives
(PRELIMS & MAINS Focus)
Syllabus
- Prelims –Science and Technology
Context: Prime Minister Narendra Modi recently launched 91 new 100-watt capacity FM transmitters.
About Frequency Modulation (FM):-
- It is the encoding of information in a carrier wave by varying the instantaneous frequency of the wave.
- In analogue FM (radio broadcasting), the instantaneous frequency deviation has a functional relation to the modulating signal amplitude.
- frequency deviation – the difference between the frequency of the carrier and its centre frequency.
- Digital data can be encoded and transmitted with a type of FM known as frequency-shift keying (FSK), in which the instantaneous frequency of the carrier is shifted among a set of frequencies.
FM transmitters:-
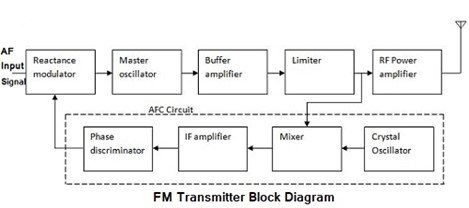
IMAGE SOURCE: FM Transmitter Block Diagram with Explanation (electronicsandcommunications.com)
- It is a low-power FM radio transmitter that broadcasts a signal from a portable audio device (such as an MP3 player) to a standard FM radio.
- Most of these transmitters plug into the device’s headphone jack and then broadcast the signal over an FM broadcast band frequeny so that it can be picked up by any nearby radio.
- This allows portable audio devices to make use of the louder or better sound quality of a home audio system or car stereo without requiring a wired connection.
- Being low-powered, most transmitters typically have a short range of 100-300 feet (30–91 metres), depending on the quality of the receiver, obstructions and elevation.
FM vs AM:-
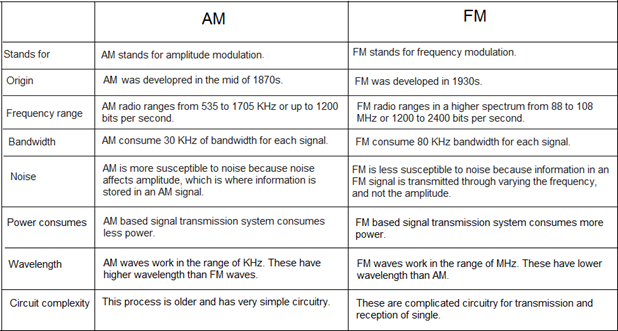
IMAGE SOURCE: Research – VANXFILMS OFFICIAL WEBSITE (weebly.com)
- Radio signals are broadcast using AM (or Amplitude Modulation) and FM (or Frequency Modulation).
- Electromagnetic waves are used to transfer data in both cases
- The amplitude of the signal or carrier delivered is modulated (changing) depending on the information being sent, but the frequency remains fixed.
About AIR:-
- It is the national public radio broadcaster of India.
- It is a division of Prasar Bharati.
- It was established in 1936.
- Headquarters: New Delhi
Mission
- Uphold the unity of the country and the democratic values enshrined in the constitution.
- Present a fair and balanced flow of information on national, regional, local and international interests, including contrasting views. (UPSC PRELIMS: Asia-Pacific Broadcasting Union)
- Promote the interest and concerns of the entire nation. (UPSC PRELIMS: News Broadcasting & Digital Standards Authority)
- Serve the rural, illiterate and underprivileged population, keeping in mind the special needs and interests of the young, social and cultural minorities, the tribal population and those residing in border regions, backward or remote areas.
- Promote social justice and combat exploitation, inequality and such evils as untouchability and narrow parochial loyalties.
- Promote national integration.
- National programmes are broadcast from Delhi for relay by the Capital, Regional and Local Radio Stations.
- The Regional Stations in different States form the middle tier of broadcasting.
- They originate programmes in regional languages and dialects.
- Local radio stations serve small communities, showcase local culture and broadcast area-specific programmes for the benefit of the community.
- The first FM Channel was launched on an experimental basis in 1977 in Chennai.
- At present AIR have 497 FM transmitters across the country.
MUST READ: Broadcasting Infrastructure and Network Development (BIND) scheme
SOURCE: ET NOW
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) Which one of the following is the context in which the term “qubit” is mentioned? (2022)
- Cloud Services
- Quantum Computing
- Visible Light Communication Technologies
- Wireless Communication Technologies
Q.2) With reference to Web 3.0, consider the following statements: (2022)
- Web 3.0 technology enables people to control their own data.
- In the Web 3.0 world, there can be blockchain-based social networks.
- Web 3.0 is operated by users collectively rather than by a corporation
Which of the following given above is correct?
- 1 and 2 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
Syllabus
- Prelims –Environment and Ecology
Context: Recently, the latest technology has been used to study Soniferous fishes on the coast of Goa.
About Soniferous fishes:-
IMAGE SOURCE: PPT – Nonvertebrate Chordates, Fishes, and Amphibians PowerPoint Presentation – ID:3223997 (slideserve.com)
- These fishes are known to make sounds associated with specific behaviours including disturbance, competition for food, territory defence, and courtship or spawning.
- They produce sound mainly by using modified muscles attached to their swim bladders(drumming) or rubbing body parts together.
- Sound production in fish is vital to an array of behaviours including territorial defence.
- There are over 700 known soniferous species worldwide.(UPSC CSE: Conservation of species)
- Passive acoustics is a technique that enables scientists to listen to and record underwater sounds of aquatic and marine fishes and invertebrates.
- Using this technique, scientists can gain useful information about the temporal and spatial distribution patterns of soniferous fishes and the locations of spawning and feeding grounds. (UPSC Mains: Government’s Initiatives for a Robust Fishery Sector )
MUST READ: Puffer Fish
SOURCE: DOWN TO EARTH
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) Which of the following is not a bird? (2022)
- Golden Mahseer
- Indian Nightjar
- Spoonbill
- White Ibis
Q.2) Certain species of which one of the following organisms are well known as cultivators of
fungi? (2022)
- Ant
- Cockroach
- Crab
- Spider
Syllabus
- Prelims –Economy
Context: Recent reports show that the combined Index of Eight Core Industries (ICI) increased by 3.6 per cent (provisional) in March 2023 as compared to the Index of March 2022.
About the Index of Eight Core Industries (ICI):-

IMAGE SOURCE: Index of Eight Core Industries (Base: 2011-12=100) March 2019 (indiangovtscheme.com)
- ICI measures combined and individual performance of the production of eight core industries.
- These include Coal, Crude Oil, Natural Gas, Refinery Products, Fertilizers, Steel, Cement and Electricity.
- These Eight Core Industries comprise 40.27 per cent of the weight of items included in the Index of Industrial Production (IIP). (UPSC PRELIMS: Index of Industrial Production (IIP)
- Details of annual and monthly indices and growth rates are provided in Annex I & II respectively.
- It is compiled and released by the Office of Economic Adviser (OEA), Department for Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade (DPIIT), Ministry of Commerce and Industry.
- It provides an advance indication of the production performance of industries of a ‘core’ nature prior to the IIP (UPSC PRELIMS: IIP growth slowed to 0.4% in December)
MUST READ: Purchasing Manager’s Index
SOURCE: PIB
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) Which of the following brings out the ‘Consumer Price Index Number for Industrial Workers’?(2017)
- The Reserve Bank of India
- The Department of Economic Affairs
- The Labour Bureau
- The Department of Personnel and Training
Q.2) In the ‘Index of Eight Core Industries’, which one of the following is given the highest weight? (2015)
- Coal production
- Electricity generation
- Fertilizer production
- Steel production
Syllabus
- Prelims –Environment and Ecology
Context: As per recent announcements, India will start participating in the International Civil Aviation Organisation’s (ICAO) Carbon Offsetting and Reduction Scheme for International Aviation (CORSIA)
Long-Term Aspirational Goals (LTAG) from 2027.
About International Civil Aviation Organisation (ICAO):-
- The International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO) is a specialized funding agency of the United Nations.
- It changes the principles and techniques of international air navigation.
- It fosters the planning and development of international air transport to ensure safe and orderly growth.
- Its headquarters is located in the Quartier International of Montreal, Quebec, Canada.
- It has 193 Member States.
- India is one of ICAO’s founder members, having attended the Chicago Convention in 1944. (UPSC CSE: Directorate General of Civil Aviation (DGCA))
- The ICAO Council adopts standards and recommended practices concerning air navigation, its infrastructure, flight inspection, prevention of unlawful interference, and facilitation of border-crossing procedures for international civil aviation. (UPSC CSE: Issue – Civil Aviation)
- The Air Navigation Commission (ANC) is the technical body within ICAO.
- ICAO defines the protocols for air accident investigation that are followed by transport safety authorities in countries signatory to the Chicago Convention on International Civil Aviation.
- Convention on International Civil Aviation also known as the Chicago Convention, established the International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO), a specialized agency of the UN charged with coordinating international air travel.
- The Convention establishes rules of airspace, aircraft registration and safety, security, and sustainability, and details the rights of the signatories in relation to air travel. The Convention also contains provisions pertaining to taxation.
- It came into effect in 1947.
About CORSIA:-
- It is the first global market-based measure for any sector.
- It represents a cooperative approach that moves away from a “patchwork” of national or regional regulatory initiatives.
- It offers a harmonized way to reduce emissions from international aviation, minimizing market distortion, while respecting the special circumstances and respective capabilities of ICAO Member States.
- CORSIA complements the other elements of the basket of measures by offsetting the number of CO2 emissions that cannot be reduced through the use of technological improvements, operational improvements, and sustainable aviation fuels with emissions units from the carbon market.
- CORSIA is implemented in three phases: a pilot phase (2021-2023), a first phase (2024-2026), and a second phase (2027-2035).
- For the first two phases (2021-2026), participation is voluntary.
- From 2027 onwards, participation will be determined based on 2018 RTK data.
About Long-Term Aspirational Goals (LTAG):-
- The 41st ICAO Assembly adopted a long-term global aspirational goal (LTAG).
- The international aviation of net-zero carbon emissions by 2050 in support of the UNFCCC Paris Agreement’s temperature goal.
- This is a historic agreement that reinforces the leadership of ICAO on issues relating to international aviation and climate change.
- The adopted Resolution A41-21 is available here.
- The LTAG does not attribute specific obligations or commitments in the form of emissions reduction goals to individual States.
- Instead, it recognizes that each State’s special circumstances and respective capabilities (e.g., the level of development, maturity of aviation markets, sustainable growth of its international aviation, just transition, and national priorities of air transport development) will inform the ability of each State to contribute to the LTAG within its own national timeframe.
- Each State will contribute to achieving the goal in a socially, economically and environmentally sustainable manner and in accordance with its national circumstances.
MUST READ: 5G Rollout and Aviation Challenge
SOURCE: ECONOMIC TIMES
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) Consider the following: (2022)
- Carbon monoxide
- Nitrogen oxide
- Ozone
- Sulphur dioxide
Excess of which of the above in the environment is/are the cause(s) of acid rain?
- 1, 2 and 3
- 2 and 4 only
- 4 only
- 1, 3 and 4
Q.2) The “Common Carbon Metric” supported by UNEP, has been developed for (2022)
- Assessing the carbon footprint of building operations around the world
- Enabling commercial farming entities around the world to enter carbon emission trading
- Enabling governments to assess the overall carbon footprint caused by their countries
- Assessing the overall carbon footprint caused by the use of fossil fuels by the world in a unit of time
Syllabus
- Prelims –Science and Technology
Context: Recently, the Department of Science and Technology, released the National Manufacturing Innovation Survey (NMIS) 2021-22.
About National Manufacturing Innovation Survey (NMIS):-
- NMIS 2021-22 is a joint study by the Department of Science and Technology (DST) and the United Nations Industrial Development Organization (UNIDO).
- Objective: to evaluate the innovation performance of manufacturing firms in India.
- This study is a follow-up of DST’s first National Innovation Survey held in 2011.
- The survey offered an empirical understanding of current innovation activities of the manufacturing economy in India as well as ways to navigate organisational rigidity to facilitate market demand for innovations. (UPSC CSE: National Science, Technology and Innovation Policy (STIP 2020) )
Key Highlights of the NMIS 2021-22 Survey:-
- The NMIS survey shows that innovation is not yet common in manufacturing but has proved to be profitable for firms. (UPSC MAINS: Global Competitiveness of Indian Manufacturing)
- The NMIS 2021-22 survey had two specific components: the firm-level survey and the sectorial systems of innovation (SSI) survey.
- The Firm-level survey: captured data related to types of innovations and innovative measures taken by firms.
- This includes the process of innovation, access to finance, resources, and information for innovation, besides also recording the factors impacting the innovation activities in a firm.
- One in four firms was found to have successfully implemented an innovation in the observation period, and over 80% of these firms benefitted significantly in expanding markets and production and reducing costs.
- The Sectorial System of Innovation survey: mapped the manufacturing innovation system and its enabling role in achieving innovations in firms.
- The SSI study measured the interactions between stakeholders of the innovation ecosystem, relative barriers to innovation, as well as the convergence or divergence of current policy instruments in select five key manufacturing sectors important to the Indian economy – textiles; food & beverage; automotive; pharma; and ICT.
- The Firm-level survey: captured data related to types of innovations and innovative measures taken by firms.
- The findings from the firm-level survey are captured in the ‘Assessment of Firm-Level Innovation in Indian Manufacturing’.
- Separately, five reports from the study of the sectorial systems of innovation within five manufacturing sectors, namely, Automotive, Pharmaceutical, Textile, Food & Beverages, and Information & Communication Technologies (ICT), have been developed.
MUST READ: India Semiconductor Mission
SOURCE: PIB
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) Consider the following: (2022)
- Aarogya Setu
- COWIN
- DigiLocker
- DIKSHA
Which of the above are built on top of open-source digital platforms?
- 1 and 2 only
- 2, 3 and 4 only
- 1, 3 and 4 only
- 1, 2, 3 and 4
Q.2) In India, the term “Public Key Infrastructure” is used in the context of (2020)
- Digital security infrastructure
- Food security infrastructure
- Health care and education infrastructure
- Telecommunication and transportation infrastructure
Syllabus
- Prelims –Science and Technology
Context: Recently studies probe the role of psychedelics in treating depression.
About Psychedelics:-

IMAGE SOURCE: Psychedelics: Everything you need to know about these powerful plant medicines – Artem Zen
- Psychedelics are a group of drugs that alter perception, mood, and thought processing while a person is still clearly conscious.
- Usually, the person’s insight also remains unimpaired.
- Psychedelics are non-addictive and non-toxic.
- Compared to illicit drugs, psychedelics cause much less harm to the end user.
- The two most commonly used psychedelics are d-lysergic acid diethylamide (LSD) and psilocybin.
- Less common ones include mescaline, found in the North American peyote cactus ( Lophophora williamsii), and N, N-dimethyltryptamine, the principal component of the South American ceremonial sacrament ayahuasca.
- In India, the Narcotic Drugs and Psychotropic Substances Act 1985 (UPSC CSE: NDPSA,1985), prohibits the use of psychedelic substances.
- Ketamine: a dissociative anaesthetic with psychedelic properties, is used under strict medical supervision, for anaesthesia and to treat treatment-resistant depression. (UPSC MAINS: Fighting Drug Menace)
MUST READ: Potency drugs not under NDPS Act: SC
SOURCE: THE HINDU
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) Bisphenol A (BPA), a cause of concern, is a structural/key component in the manufacture of which of the following kinds of plastics? (2021)
- Low-density polyethene
- Polycarbonate
- Polyethene terephthalate
- Polyvinyl Chloride
Q.2) “Triclosan” considered harmful when exposed to high levels for a long time, is most likely present in which of the following? (2021)
- Food preservatives
- Fruit ripening substances
- reused plastic containers
- Toiletries
Syllabus
- Prelims –Economy
Context: Recent reports show that Patent filing in India registered a decade-high growth of 14%.
About Patent filing in India:-
- A patent is a form of preservation of intellectual property.
- It is an exclusive right granted for an invention, which is a product or a process that provides, a new way of doing something, or offers a new technical solution to a problem.
- To get a patent, technical information about the invention must be disclosed to the public in a patent application. (UPSC MAINS: IPR Regime of India)
Patentability Criteria for an Invention:-
- It should be novel.
- Must involve an inventive step (technical advancement)
- Capable of industrial application
Term of Patent:-
- The term of every patent in India is twenty years from the date of filing the patent application, irrespective of whether it is filed with provisional or complete specifications.
Patents Act, 1970:-
- This principal law for the patenting system in India came into force in the year 1972.
- It replaced the Indian Patents and Designs Act 1911.
- The Act was amended by the Patents (Amendment) Act, 2005, wherein product patent was extended to all fields of technology including food, drugs, chemicals and microorganisms.
- After the amendment, the provisions relating to Exclusive Marketing Rights (EMRs) have been repealed, and a provision for enabling the grant of compulsory license has been introduced.
- The provisions relating to pre-grant and post-grant opposition have also been introduced.
Patents (Amendment) Rules, 2021:-
- Patent Fees for Educational Institutions Reduced(UPSC CSE: Understanding Patents (Amendment) Rules, 2021)
- Benefits related to an 80% reduced fee for patent filing & prosecution have been extended to all educational institutions.
Extension of Expedited Examination System:
- The fastest granted patent is the one which was granted 41 days after the filing of such a request.
- This facility of the Expedited Examination system was initially provided for patent applications filed by Startups.
- It has been now extended to 8 more categories of Patent Applicants:
- SME (Small and Medium Enterprises), Female applicants, Government Departments, Institutions established by a Central, Provincial or State Act, Government Company, an Institution wholly or substantially financed by the Government and applicants under Patents Prosecution Highway.
- The Patent Prosecution Highway (PPH) is a set of initiatives for providing accelerated patent prosecution procedures by sharing information between some patent offices.
MUST READ: U.S. Supports India’s vaccine patent waiver proposal
SOURCE: THE TIMES OF INDIA
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) In the context of vaccines manufactured to prevent the COVID-19 pandemic, consider the following statements: (2022)
- The Serum Institute of India produced a COVID-19 vaccine named Covishield using an mRNA platform.
- Sputnik V vaccine is manufactured using a vector-based platform.
- COVAXIN is an inactivated pathogen-based vaccine.
Which of the statements given above is correct?
- 1 and 2 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
Q.2) With reference to recent developments regarding ‘Recombinant vector Vaccines’, consider the following statements: (2021)
- Genetic engineering is applied in the development of these vaccines.
- Bacteria and viruses are used as vectors.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Syllabus
- Mains – GS 2 (Polity and Governance)
Context: Recently the Supreme Court has given a reminder to Governors that the Constitution expects that a decision to return a Bill to the State Assembly for reconsideration should be made “as soon as possible”.
About the office of Governor:
- Article 153 of the Constitution provides the provision that there shall be a Governor for each State.
- This Article also provides that it is not necessary for every State to have a different Governor and thus a person can be appointed as the Governor of more than one State.
- Article 154: The Governor’s position in the State is identical to the position of the President of India and just like the President, the Governor is the Executive Head of the State.
- This authority is conferred on him under Article 154 of the Constitution which provides that the Executive power of the State is vested in the Governor.
The Constitutional power of the Governor related to State Bills:
- Article 200 of the Indian Constitution deals with the Governor’s powers in relation to assenting to legislation enacted by the State legislature and other functions of the Governor such as reserving the bill for consideration by the President.
- Article 201 relates to “Bills Reserved for Consideration”: Governors have absolute veto power, suspense veto power (except on money bills), but no pocket veto power.
- Absolute Veto: This refers to the Governor’s power to refuse to sign a bill passed by the Assembly.
- Suspensive Veto: A suspensive veto is used by the Governor when he returns a bill to the State Assembly for reconsideration.
- If the Assembly resends the bill to the Governor, with or without alteration, he must approve it without using any of his veto powers.
- The Governor may not use his suspensive veto in connection to the Money Bill
- Pocket Veto: Power of the President, in pocket veto, the bill is held pending indefinitely. He neither rejects nor sends the measure back for review.
Sending for reconsideration:
- The Governor can send the bill back to the House for reconsideration but if the bill is sent back by the House without any change, the Governor has to give his assent to that bill.
- He cannot send the bill back to the State Legislature if it is a Money Bill.
Reserving the bill for the president’s consideration:
- The Governor also has the right to reserve some bills for the consideration of the President.
- when a governor reserves bill for the president’s consideration, he is no longer involved in the bill’s enactment.
- Even if the President refers it to the Assembly for reconsideration, the Bill will still be brought before the President and not the Governor following the reconsideration.
Withhold assent:
- The Governor also has power to withhold assent to a Bill
Pending bill in the legislature:
- If any Bill is pending in the House(s), the governor can send a message to such House(s) for reminding them about the same.
Supreme Court’s Observation:
- While referring to the first proviso to Article 200 of the Constitution, the SC mandated that Governors should not delay over Bills sent to them for assent after they had been passed by Legislative Assemblies.
- They should be returned “as soon as possible” and not sit over them.
- The expression “as soon as possible” in this article has significant constitutional intent and that constitutional authorities should keep this in mind.
Recent Instances of Gubernatorial Procrastination:
- Chhattisgarh chief recently questioned the governor over the delayed assent to the state’s amended reservation bill that was passed in the Chhattisgarh assembly last year which is since waiting for the governor’s assent.
- Tamil Nadu Assembly passed a resolution urging the President of India, among other things, to fix a timeline for assent to be given to Bills passed by the Assembly.
- For instance, in the TN Governor forwarded the Bill for exemption from the National Eligibility cum Entrance Test (NEET) to the President after considerable delay.
Legal Arguments against Delaying Assent:
States’ Constitutional Obligation:
- The Governor’s inaction on bills passed by the Assembly creates a situation where the state government is unable to function in accordance with the Constitution.
- If the Governor continues to fail to act in accordance with the Constitution, the State government has a constitutional obligation to invoke Article 355 and notify the President, requesting that appropriate instructions be issued to the Governor to ensure that the process of government is conducted in accordance with the Constitution.
Role of Apex Court:
- The framers of the Constitution would never have imagined that Governors would sit on Bills indefinitely without exercising any of the options given in Article 200.
- This is a new development that needs new solutions within the framework of the Constitution.
- So, it falls to the Supreme Court to fix a reasonable time frame for Governors to take a decision on a Bill passed by the Assembly in the larger interest of federalism in the country.
Way Forward:
In order to establish cordial relations between the Governor and the state legislature, the recommendations of Sarkaria Commission, Punchi Commission and Justice V.Chelliah Commission must be implemented.
Supreme Court in the Nabam Rebia judgement (2016) ruled that the exercise of Governor’s discretion Article 163 is limited and his choice of action should not be arbitrary or fanciful. It must be a choice dictated by reason, actuated by good faith and tempered by caution – the same should be implemented in letter and spirit.
Source: The Hindu
Previous Questions
Q.1) Consider the following statements: (2018)
- No criminal proceedings shall be instituted against the Governor of a State in any court during his term of office.
- The emoluments and allowances of the Governor of a State shall not be diminished during his term of office.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Q.2) Which of the following are the discretionary powers given to the Governor of a State? (2014)
- Sending a report to the President of India for imposing the President’s rule
- Appointing the Ministers
- Reserving certain bills passed by the State Legislature for consideration of the President of India
- Making the rules to conduct the business of the State Government
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
- 1 and 2 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 2, 3 and 4 only
- 1, 2, 3 and 4
Practice MCQs
Q.1) The drugs ‘d-lysergic acid diethylamide (LSD) and psilocybin’ often mentioned in the news are related to
- Psychedelic substances
- Cancer treatment
- Technical textiles
- Pesticides used in Agriculture
Q.2) The National Manufacturing Innovation Survey (NMIS) 2021-22 recently released by
- Ministry of Commerce and Industry
- Ministry of MSME
- Ministry of Science and Technology
- NITI Aayog
Q.3) With reference to Radio services in India, consider the following statements:
- All India Radio is the national public radio broadcaster of India.
- Amplitude Modulation (AM) Radio is more susceptible to noise when compared to the Frequency Modulation (FM) Radio.
- FM Radio signal transmission system consumes more power when compared to AM Radio signal transmission system.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
- 1 and 2 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 1 2 and 3
Comment the answers to the above questions in the comment section below!!
ANSWERS FOR ’ 1st May 2023 – Daily Practice MCQs’ will be updated along with tomorrow’s Daily Current Affairs.st
ANSWERS FOR 29th April – Daily Practice MCQs
Q.1) – c
Q.2) – c
Q.3) – b











