IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
Archives
(PRELIMS & MAINS Focus)
Syllabus
- Prelims –Science and Technology
Context: Mission on Advanced and High-Impact Research (MAHIR) was launched recently to leverage Emerging Technologies in Power Sector.
About the Mission of Advanced and High-Impact Research (MAHIR):-
- It aims to facilitate indigenous research, development and demonstration of the latest and emerging technologies in the power sector.
- Timeline: It is planned for an initial period of five years from 2023-24 to 2027-28.
- Ministry: Ministry of Power and the Ministry of New and Renewable Energy
Objectives of MAHIR:-
- To identify emerging technologies in the power sector that have the potential for future relevance globally.
- To serve as a platform for collective brainstorming.
- To Support pilot projects for indigenous technologies.
- Leverage foreign alliances to accelerate research and development efforts.
- To create a vibrant and innovative ecosystem in the power sector.
Funding and Collaboration:-
- MAHIR is funded through pooling of resources from the Ministry of Power, Ministry of New and Renewable Energy, and Central Public Sector Enterprises under these ministries.
- Additional funding will be from the budgetary resources of the Government of India.
- The mission encourages funding by inviting proposals from companies and organizations worldwide.
Structure of MAHIR:-
- MAHIR operates through a two-tier structure comprising a Technical Scoping Committee and an Apex Committee.
- Led by the Chairperson of the Central Electricity Authority.
Areas Identified for Research:-
- Alternatives to Lithium-Ion storage batteries
- Modifying electric cookers/pans to suit Indian cooking methods
- Carbon capture (UPSC CSE: Decarbonisation of India’s Power Sector)
- Geothermal energy
- Solid-state refrigeration.
- Nanotechnology for EV battery
- Indigenous CRGO technology
Central Electricity Authority (CEA)
- It is a statutory organization constituted under Section 3 (1) of the repealed Electricity (Supply) Act, of 1948.
- It is now under Section 70 of the Electricity Act, 2003.
- As per Section 70 (3) of the Electricity Act, 2003, the authority shall consist of not more than 14 members, including its chairperson.
- Not more than eight shall be full-time members to be appointed by the Central Government.
Functions of Central Electricity Authority:-
- It advises the government on matters relating to the National Electricity Plan (NEP).
- It formulates short-term and perspective plans for the development of electricity systems.
- It is the designated authority for cross border trade of electricity.
- It also prescribes the standards on matters such as the construction of electrical plants, electric lines and connectivity to the grid etc.
- It is also responsible for the concurrence of hydropower development schemes of central, state and private sectors.
National Electricity Plan (NEP)
- The latest draft of the National Electricity Plan (NEP), which covers the period 2022-27.
- The NEP guides the development of the power sector in India.
- The Central Electricity Authority (CEA) formulates it every five years under the Electricity Act, 2003.
- The new NEP recognizes the need for additional coal-based capacity, ranging from 17 GW to nearly 28 GW, till 2031-32, over and above the 25 GW of coal-based capacity that is currently under construction.
- The draft Plan also highlights the need for significant investments in battery storage, with an estimated requirement of between 51 GW to 84 GW by 2031-32.
- It projects an increase in the Plant Load Factor (PLF) of coal-fired power plants from 55% up to 2026-27 to 62 % in 2031-32.
- It also emphasizes the challenges posed by the increasing reliance on renewables, which will require careful management and planning in the years ahead.
MUST READ: Energy Security
SOURCE: PIB
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) Which of the following are the reasons/factors for exposure to benzene pollution? (2020)
- Automobile exhaust
- Tobacco smoke
- Woodburning
- Using varnished wooden furniture
- Using products made of polyurethane
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
- 1, 2 and 3 only
- 2 and 4 only
- 1, 3 and 4 only
- 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5
Q.2) Recently, India’s first ‘National Investment and Manufacturing Zone’ was proposed to be set up in (2016)
- Andhra Pradesh
- Gujarat
- Maharashtra
- Uttar Pradesh
Syllabus
- Prelims –Science and Technology
Context: India recently conducted a successful flight test of the Agni Prime ballistic missile.
About Agni Prime:-

IMAGE SOURCE: autojournalism.com
- Agni Prime is the advanced version of the ‘Agni-1’ missile. (UPSC CSE: New generation ballistic missile ‘Agni P’)
- It is a short-range ballistic missile.
- Range: 1000 km to 1500 km
- It is a two-stage
- It is the latest and sixth variant of the Agni series missiles.
- It is under Integrated Guided Missile Development Program (IGMDP)
- Agni Prime has multiple independently targetable re-entry vehicles.
- It is capable of delivering a number of warheads at separate locations.
- It can carry warheads up to 1.5 tonnes.
- It has a dual redundant navigation and guidance system.
- The Agni-P missile would further strengthen India’s credible deterrence capabilities.
Integrated Guided Missile Development Program (IGMDP)
- It was conceived by Dr A.P.J. Abdul Kalam to enable India to attain self-sufficiency in the field of missile technology.
- 5 missiles developed under this program are:-
- Prithvi: Short-range surface-to-surface ballistic missile.
- Agni: Ballistic missiles with different ranges.
- Trishul: Short-range low-level surface-to-air missile.
- Nag: 3rd generation anti-tank missile.
- Akash: Medium-range surface-to-air missile.
Other Agni Class of Missiles
- Agni I: Range of 700-800 km.
- Agni II: Range more than 2000 km.
- Agni III: Range of more than 2,500 Km
- Agni IV: Range is more than 3,500 km and can fire from a road-mobile launcher.
- Agni-V: The longest of the Agni series, an Inter-Continental Ballistic Missile (ICBM) with a range of over 5,000 km.
MUST READ: Ballistic Missile Defence (BMD) Interceptor
SOURCE: NEWSONAIR
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) With reference to Agni-IV Missile, which of the following statements is/are correct? (2014)
- It is a surface-to-surface missile.
- It is fuelled by liquid propellant only.
- It can deliver one-tonne nuclear warheads about 7500 km away.
Select the correct answer using the code given below
- 1 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
Q.2) Which one of the following statements best reflects the idea behind the “Fractional Orbital Bombardment System” often talked about in media? (2022)
- A hypersonic missile is launched into space to counter the asteroid approaching the Earth and explode it in space.
- A spacecraft lands on another planet after making several orbital motions.
- A missile is put into a stable orbit around the Earth and deorbits over a target on the Earth.
- A spacecraft moves along a comet with the same surface.
Syllabus
- Prelims –International Relations
Context: The 20th edition of the Shangri-La Dialogue, concluded in Singapore recently.
About Shangri-La Dialogue:-
IMAGE SOURCE: scholars-stage.org
- The Shangri-La Dialogue (SLD) is an inter-governmental security forum.
- Originally known as the Asia Security Summit was initiated in 2002 in response to the evident need for a forum where Asia-Pacific defence ministers could engage in dialogue aimed at building confidence and fostering practical cooperation.
- It is a Track 1inter-governmental security forum.
- It is held every year in Singapore since 2002.
- Organised by: International Institute for Strategic Studies (IISS).
- IISS is a London-based independent think tank.
- Defence ministers, permanent heads of ministries and military chiefs of 28 Asia-Pacific states attend it.
- The ministers debate the region’s most pressing security challenges engage in important bilateral talks and come up with fresh approaches together.
- The forum gets its name from the Shangri-La Hotel in Singapore where it has been held since 2002.
- It is Asia’s largest annual security forum. ( UPSC CSE: Indo-Pacific Relations )
- The 2023 event took place in
- Australia’s Prime Minister Anthony Albanese delivered the Keynote Address at the Shangri-La Dialogue 2023. (UPSC CSE: Prime Minister’s Key Note Address at Shangri La Dialogue)
Different levels of Diplomacy:
- Track 1 Diplomacy: Official discussions typically involving high-level political and military leaders.
- Track 2 Diplomacy: Unofficial dialogue and problem-solving activitiesInvolving influential academic, religious, and NGO leaders and other civil society actors who can interact more freely than high-ranking officials can.
- Track 3 Diplomacy: People-to-people diplomacy undertaken by individuals and private groups.
MUST READ: Raisina Dialogue
SOURCE: THE INDIAN EXPRESS
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) Consider the following countries: (2018)
- Australia
- Canada
- China
- India
- Japan
- USA
Which of the above are among the ‘free-trade partners’ of ASEAN?
- 1, 2, 4 and 5
- 3, 4, 5 and 6
- 1, 3, 4 and 5
- 2, 3, 4 and 6
Q.2) “Rule of Law Index” is released by which of the following? (2018)
- Amnesty International
- International Court of Justice
- The Office of UN Commissioner for Human Rights
- World Justice Project
Syllabus
- Prelims –Governance
Context: Kerala has secured the first position in the recently released national food safety index.
About the national food safety index:-
- The first State Food Safety Index was published in 2018-19.
- It was announced on the first-ever World Food Safety Day on 7th June 2019.
- World Food Safety Day: The World Health Organization (WHO) and the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO) jointly facilitate the observance of World Food Safety Day. (UPSC CSE: WHO)
- Objective of Food safety index: creating a competitive and positive change in the food safety ecosystem in the country.
- Developed by: FSSAI (Food Safety and Standards Authority of India) (UPSC CSE: FSSAI)
- The Parameters include Human Resources and Institutional Data, Compliance, Food Testing – Infrastructure and Surveillance, Training & Capacity Building and Consumer Empowerment. (UPSC CSE: Food Security)
- The food safety index, at the national level, is determined based on enforcement activities.
- These include food safety checks, sample collection, sample examination prosecution cases, number of NABL-recognised food safety labs in the State etc.
Food Safety and Standards Authority of India (FSSAI)
- It is an autonomous statutory body established under the Food Safety and Standards Act, 2006 (FSS Act).
- Ministry: Ministry of Health & Family Welfare
- Headquarters: Delhi
- FSSAI is responsible for protecting and promoting public health through the regulation and supervision of food safety.
- Composition: The FSSAI comprises of a Chairperson and twenty-two members. One-third of the members are to be
- The Central Government appoints the Chairperson of FSSAI.
Functions:-
- Framing of regulations to lay down the standards and guidelines of food safety.
- Granting FSSAI food safety license and certification for food businesses.
- Laying down procedures and guidelines for laboratories in food businesses.
- To provide suggestions to the government in framing the policies.
- To collect data regarding contaminants in food products, identification of emerging risks and introduction of the rapid alert system.
- Promote general awareness about food safety and food standards.
MUST READ: FSSAI releases draft notification on a star rating for packaged food
SOURCE: THE HINDU
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) With reference to organic farming in India, consider the following statements: (2018)
- ‘The National ‘Programme for Organic Production’ (NPOP) is operated under the guidelines and ‘directions of the Union Ministry of Rural Development.
- ‘The Agricultural and Processed Food Product Export Development Authority ‘(APEDA) functions as the Secretariat for the implementation of NPOP.
- Sikkim has become India’s first fully organic State.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 and 2 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
Q.2) Which of the following are the objectives of the ‘National Nutrition Mission’? (2018)
- To create awareness relating to malnutrition among pregnant women and lactating mothers.
- To reduce the incidence of anaemia among young children, adolescent girls and women.
- To promote the consumption of millets, coarse cereals and unpolished rice.
- To promote the consumption of poultry eggs.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
- 1 and 2 only
- 1, 2 and 3 only
- 1, 2 and 4 only
- 3 and 4 only
Syllabus
- Prelims –Important Institutions
Context: Recently, Financial Services Institution Bureau (FSIB) selected new chiefs for General Insurance Corporation of India and National Insurance Company Limited.
About Financial Services Institution Bureau (FSIB):-
- It was established by passing a resolution by the Cabinet Appointments Committee (ACC) to establish it in place of the Banks Board Bureau (BBB).
Composition:-
- FSIB would be headed by a chairman, a central government nominee.
- The board would comprise the Secretaries of the DFS, the chairman of IRDAI, and a deputy governor of the RBI.
- Additionally, it will have three part-time members who are experts in banking and three more from the insurance sector.
Functions:-
- The FSIB selects the chiefs of public sector banks and insurance companies. (UPSC CSE: Financial Services Institutions Bureau (FSIB))
- It has the mandate to issue guidelines and select general managers and directors of state-run non-life insurers, general insurers and Financial Institutions.
- It works under the Department of Financial Service, Ministry of Finance.
- It also monitors and assesses the performance of public sector banks, government-owned financial institutions and insurance companies.
- It is the single entity for making recommendations for appointments of WTD (Whole-time Director) and NEC (Non-executive Chairman) in Public Sector Banks, India Private Limited companies and Financial Institutions.
General Insurance Corporation of India (GIC)
- GIC is an Indian nationalised reinsurance company.
- It was set up by the General Insurance Business (Nationalisation) Act, of 1972.
- It was enacted to nationalise all private companies undertaking general insurance business in India.
- Four subsidiary companies of GIC are:-
- National Insurance.
- New India Assurance.
- Oriental Insurance.
- United India Insurance.
- The General Insurance Business (Nationalisation) Act, 1972 was subsequently amended in 2002 to transfer the control of these four subsidiary companies from GIC to the central government.
- Since 2000, GIC exclusively undertakes the reinsurance business.
National Insurance Company Limited (NIC)
- It is India’s oldest l Insurance Company.
- It was s
- tarted in Kolkata, West Bengal in 1906.
- 66 years later, after the passing of the General Insurance Business Nationalisation Act in 1972, it was merged along with 21 foreign and 11 Indian companies to form National Insurance Company Limited.
- It became one of the four subsidiaries of the General Insurance Corporation of India.
- It is fully owned by Govt. of India.
- 2002: National insurance was delinked from GIC and formed as an independent insurance company.
- Products of National Insurance:
- Personal Line of Insurance
- Motor Vehicle Insurance.
- Rural Insurance
- Industrial & Commercial Insurance.
MUST READ: Leadership Development programme
SOURCE: THE INDIAN EXPRESS
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) With reference to the ‘Banks Board Bureau (BBB)’, which of the following statements are correct? (2022)
- The Governor of RBI is the Chairman of BBB.
- BBB recommends the selection of heads for Public Sector Banks.
- BBB helps Public Sector Banks develop strategies and capital-raising plans.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
- 1 and 2 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
Q.2) Consider the following statements: (2021)
- The Governor of the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) is appointed by the Central Government.
- Certain provisions in the Constitution of India give the Central Government the right to issue directions to the RBI in the public interest.
- The Governor of the RBI draws his power from the RBI Act.
Which of the above statements is correct?
- 1 and 2 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
Syllabus
- Prelims –Geography
Context: Kilauea, one of the most active volcanoes in the world, began erupting recently.
About Kilauea:-
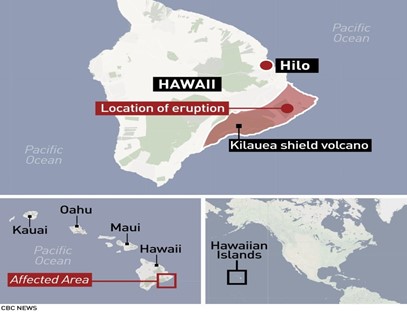
IMAGE SOURCE: CBC.ca
- Kilauea volcano is located in Hawaii Volcanoes National Park on the south-eastern part of the island of Hawaii, U.S.A.
- It is one of the world’s most active volcanoes.
- It has erupted 34 times since 1952.From 1983 to 2018, it erupted almost continuously.
- It is an active shield volcano.
- Shield volcanoes: these are formed where a volcano produces low viscosity, runny lava, spreading far from the source and forming a volcano with gentle slopes.
Features of Kilauea volcano:-
- It has an elongated dome-shaped structure.
- It has a
- Caldera: a depression formed after a volcano releases the bulk of its magma in an explosive eruption.
- It has a lava lake.
- Lava lake: a lake produced by the build-up of water over the caldera.
- Its slopes merge with that of the adjacent volcano, Mauna Loa.(UPSC CSE: Mt. Mauna Loa)
Volcanoes in India:-
- Barren Island: Andaman Islands (India’s only active volcano)
- Narcondam: Andaman Islands
- Baratang: Andaman Islands
- Deccan Traps: Maharashtra
- Dhinodhar Hills: Gujarat
- Dhosi Hill: Haryana
MUST READ: Volcanic Eruption at Mount Semeru
SOURCE: THE HINDU
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) Consider the following pairs: (2022)
The region often mentioned in the news: Country
- Anatolia Turkey
- Amhara Ethiopia
- Cabo Delgado Spain
- Catalonia Italy
How many pairs given above are correctly matched?
- Only one pair
- Only two pairs
- Only three pairs
- All four pairs
Q.2) Consider the following statements: (2018)
- The Barren Island volcano is an active volcano located in the Indian Territory.
- Barren Island lies about 140 km east of Great Nicobar.
- The last time the Barren Island volcano erupted was in 1991 and it has remained inactive since then.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 and 3
- 3 only
- 1 and 3
Syllabus
- Prelims –Geography
Context: Recently, a cyclonic storm Biparjoy formed over the east-central Arabian Sea.
About Biparjoy:-
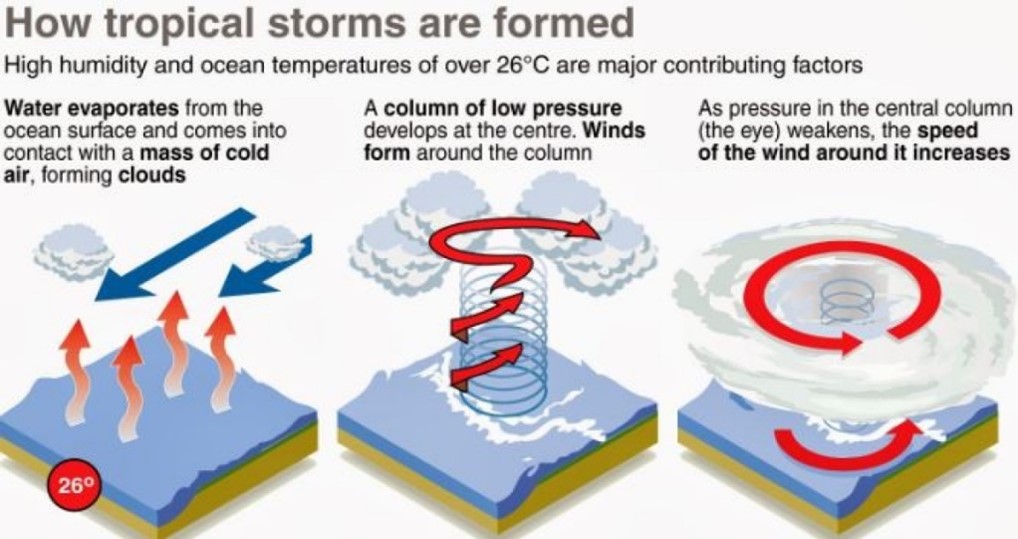
IMAGE SOURCE: Swarajya
- Biparjoy was a deep depression formed over the southeast Arabian Sea, which intensified into a cyclonic storm.
- The name ‘Biparjoy’ was given by It means ‘calamity’ or ‘disaster’.
- In 2000, a group of nations called WMO/ESCAP (World Meteorological Organisation/United Nations Economic and Social Commission for Asia and the Pacific), which comprised Bangladesh, India, the Maldives, Myanmar, Oman, Pakistan, Sri Lanka and Thailand, decided to start naming cyclones in the region.
- The WMO/ESCAP expanded to include five more countries in 2018 — Iran, Qatar, Saudi Arabia, United Arab Emirates and Yemen.
- After each country send their suggestions, the WMO/ESCAP Panel on Tropical Cyclones (PTC) finalises the list of names of Cyclones.
- The list of 169 cyclone names released by IMD in April 2020 were provided by these countries — 13 suggestions from each of the 13 countries.
Guidelines to adopt names of cyclones?
- The proposed name should be neutral to (a) politics and political figures (b) religious believes, (c) cultures etc.
- Name should be chosen in such a way that it does not hurt the sentiments of any group of population over the globe.
- It should not be very rude and cruel in nature
- It should be short, easy to pronounce.
- The maximum length of the name will be eight letters.
- The proposed name should be provided with its pronunciation and voice over.
- The names of tropical cyclones over the north Indian Ocean will not be repeated. Once used, it will cease to be used again.
World Meteorological Organisation (WMO)
- It is a specialized agency of the United Nations.
- It is dedicated to meteorology (weather), climatology (climate), operational hydrology (water) and other related geophysical sciences such as oceanography and atmospheric chemistry.
- International Meteorological Organization (IMO), founded in 1873 was its predecessor organization.
- Membership: it has 192 Member States and Territories.India is a member of WMO.
- HQ: Geneva, Switzerland
- Reports:-
- Greenhouse Gas Bulletin.
- Status of the World Climate.
MUST READ: More Cyclones in the Arabian Sea
SOURCE: DOWN TO EARTH
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) With reference to the ‘Indian Ocean Dipole (IOD)’ sometimes mentioned in the news while forecasting the Indian monsoon, which of the following statements is/are correct? (2017)
- IOD phenomenon is characterised by a difference in sea surface temperature between the tropical
- Western Indian Ocean and the tropical Eastern Pacific Ocean.
An IOD phenomenon can influence El Nino’s impact on the monsoon.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Q.2) Which of the following is geographically closest to Great Nicobar? (2017)
- Sumatra
- Borneo
- Java
- Sri Lanka
Transition to a low-carbon City
Syllabus
- Mains – GS 3 (Environment)
Context: It has been observed that Cities are critical actors in the energy transition.
About Energy-system transitions:
- An energy-system transition could reduce urban carbon dioxide emissions by around 74%.
- With rapid advancements in clean energy and related technologies and nosediving prices, we have also crossed the economic and technological barriers to implementing low-carbon solutions.
- The transition must be implemented on both the demand and the supply sides.
- Mitigation options on the supply side include phasing out fossil fuels and increasing the share of renewables in the energy mix, and using carbon capture and storage (CCS) technologies.
- On the demand side, using the ‘avoid, shift, improve’ framework would entail reducing the demand for materials and energy, and substituting the demand for fossil fuels with renewables.
- Additionally, in order to address residual emissions in the energy sector, we must implement carbon-dioxide removal (CDR) technologies.
Role of Cities in energy-system transitions:
- In 2020, cities dumped a whopping 29 trillion tonnes of carbon dioxide into the atmosphere.
- This carbon dioxide along with other greenhouse gases poses a serious health hazard.
- It also manifests as extreme weather events, leading to the loss of lives, livelihoods, assets, and social well-being.
- Therefore, given the significant impact that cities have on the environment, low-carbon cities are crucial to mitigate the effects of climate change.
- An energy-system transition could reduce urban carbon dioxide emissions by around 74%.
Implications of rising CO2 and Need for low-carbon cities/net-zero cities:
- This may lead to extreme weather events, can lead to the loss of lives and livelihoods, property and resources, and overall social wellbeing.
- By 2050, seven billion people will be living in cities, and that will accentuate the concerns regarding worsening climate, sustainability.
- Global warming may have adverse impact on health like damage in lung tissue, heightened complications for asthma patients due to increase the ozone concentration.
- It may affect food security and can lead to the resource conflicts.
- This transition to low carbon cities will help to mitigate the effects of climate change.
Challenges of Energy Transition:
- Groups of people or communities of developing economies depends on fossil fuels and has limited access to renewable energy options.
- Hence, they could be affected disproportionately.
- For example Nigeria, Angola, and Venezuela.
- In developed countries, it may lead to inequity due to high-energy costs and associated poverty/low incomes.
- There is an inherent issue of energy justice and social equity, which has severe implications for -economic well-being of people, livelihoods and economic development.
- Concerns related to Justice concerns are land evictions for large-scale renewable energy projects, the marginalisation of few communities, increased gender gaps etc.,
- There need to be a focus on energy-transition policies that are socially and environmentally fair.
- As a city’s requirement is different, spatial form, land-use pattern, level of development etc. to be given a special focus.
Government interventions:
- System of Air Quality and Weather Forecasting and Research (SAFAR) Portal
- Air Quality Index: AQI has been developed for eight pollutants viz. PM2.5, PM10, Ammonia, Lead, nitrogen oxides, sulphur dioxide, ozone, and carbon monoxide.
- Graded Response Action Plan (for Delhi)
- For Reducing Vehicular Pollution:
- BS-VI Vehicles,
- Push for Electric Vehicles (EVs),
- Odd-Even Policy as an emergency measure (for Delhi)
- New Commission for Air Quality Management
- Subsidy to farmers for buying Turbo Happy Seeder (THS) Machine for reducing stubble burning.
- National Air Quality Monitoring Programme (NAMP):
- Under NAMP, four air pollutants viz. SO2, NO2, PM10, and PM2.5 have been identified for regular monitoring at all locations.
Way Forward:
Transitioning cities to low-carbon energy systems requires efforts that consider factors such as urbanization, national contexts, and institutional capacities. Hence, it is important to engage multiple stakeholders in energy governance and decision-making processes.
Source: The Hindu
Syllabus
- Mains – GS 3 (Science and Technology)
Context: India-Russia defence Joint Venture BrahMos Aerospace has embarked on a glorious milestone as it completed 25 years.
About BrahMos:
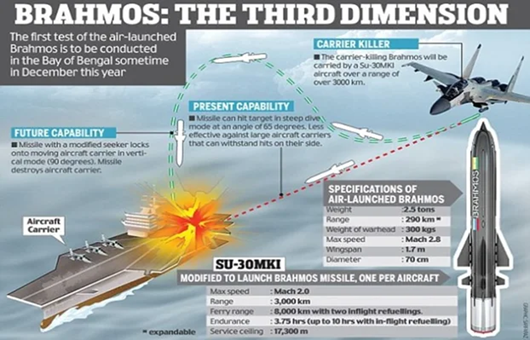
- The BrahMos is a medium-range ramjet supersonic cruise missile that can be launched from submarine, ships, aircraft or land.
- It is a joint venture between the Russian Federation’s NPO Mashinostroyeniya (NPOM), a subsidiary of the state-owned JSC Tactical Missiles Corporation and India’s Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO), who together have formed BrahMos Aerospace.
- In the joint venture, Indian side holds a share of 50.5% and the Russian side 49.5%.
- It is based on the Russian P-800 Oniks cruise missile and other similar sea-skimming Russian cruise missile technology.
- The name BrahMos is a portmanteau formed from the names of two rivers, the Brahmaputra of India and the Moskva of Russia.
- With a carrying capacity of 250-300 kgs, the BrahMos missile is capable of carrying a regular warhead as well as a nuclear warhead.
Features:
- Stages: BrahMos is a two-stage missile with a solid propellant booster engine.
- Its first stage brings the missile to supersonic speed and then is separated.
- The liquid ramjet or the second stage then takes the missile closer to three times the speed of sound in the cruise phase.
- Capability: the missile is capable of being launched from land, sea, sub-sea, air against surface and sea-based targets, and has been long inducted by the Indian armed forces.
- The ship-based version was inducted in the Navy in 2005, the land-based version in the Army in 2007, and the air-launched version was inducted in the Air Force in 2020.
- Range: The range of the BrahMos was originally limited to 290 km as per obligations of the Missile Technology Control Regime (MTCR) of which Russia was a signatory.
- Following India’s entry into the club in June 2016, plans were announced to extend the range initially to 450 km and subsequently to 600 km.
- Speed: The BrahMos missile has a speed of 2.8 Mach, which is nearly three times the speed of sound
- Indigenised: The missiles now contain a high level of indigenised content and several systems have been indigenised to maximise the participation of Indian industry in the development of the ordnance.
- The ‘fire and forget’ type missile can achieve a cruising altitude of 15 km and a terminal altitude as low as 10 m to hit the target.
- Cruise missiles such as BrahMos, called “standoff range weapons”, are fired from a range far enough to allow the attacker to evade defensive counter-fire.
- These are in the arsenal of most major militaries in the world.
Significance:
- The Brahmos JV has helped India develop its military-industrial complex.
- The deal between the Philippines and BrahMos is a milestone in India’s efforts to become one of the largest defence exporters in the world.
- In addition, it also shows the growing capabilities of India’s public and private defence sectors.
- It helps the country achieve strategic autonomy in the defence sector, which is important to safeguard the country’s national interests.
- Additional BrahMos exports could to some extent help in fulfilling Prime Minister vision of ‘Making in India, Making for the world’, achieving the defence hardware export target of US$ 5 billion by 2025.
- BrahMos missile provides India strategic airpower in the face of 2 inimical neighbours.
Challenges and competitors:
- One of the most prominent cruise missiles in the world is the Tomahawk, developed by the US.
- Notably, it is subsonic and flies around 0.8 Mach.
- It has a range of about 1,600 km, much more than the BrahMos, but its speed makes it relatively slow and somewhat easier to intercept.
- The French Apache series of missiles is also a prominent cruise missile, with a top speed of 1 Mach.
- This has been inducted by UAE, Greece, Saudi Arabia, the UK and Italy, besides France.
- The Chinese inducted the YJ-1814 into the PLA in 2014.
- It has a range of 220–540 km and cruises at subsonic speed before accelerating to supersonic speed in the terminal stage.
- The Russian P-800 Oniks is a supersonic cruise missile with specifications somewhat similar to BrahMos and flies at a top speed of 2.2 Mach.
- The BrahMos missile is not significantly different from the P-800 Oniks, it costs twice as much.
- This can be attributed perhaps to a more developed military industrial base in Russia, which results in a lower cost of production.
- Possible defence deals are highly competitive, with major players extensively marketing their products.
Way Forward:
BrahMos has very few competitors in the international market and The 2022 Philippines deal should spur additional exports of the supersonic cruise missile. India needs to develop marketing and promotion networks akin more actively to established players in the global market to promote defence sales.
Source: Financial Express
Practice MCQs
Q1) Consider the following statements with reference to the Shangri-La Dialogue (SLD):
- It is held in Singapore.
- It is organised by International Institute for Strategic Studies.
- Australia’s Prime Minister Anthony Albanese delivered the Keynote Address in 2023.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
Q2) With reference to Agni Prime, which of the following statements is/are incorrect?
- It is a supersonic missile.
- It is developed in collaboration with Russia.
Select the incorrect answer using the code given below:
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Q3) With reference to Tropical Cyclones, which of the following statements is/are correct?
- Tropical cyclones are called Willy-willies in Western Australia.
- Greenhouse Gas Bulletin is published by UNEP.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Comment the answers to the above questions in the comment section below!!
ANSWERS FOR ’ 9th June 2023 – Daily Practice MCQs’ will be updated along with tomorrow’s Daily Current Affairs.st
ANSWERS FOR 8th June – Daily Practice MCQs
Q.1) – a
Q.2) – b
Q.3) – d











