IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
Archives
(PRELIMS & MAINS Focus)
Syllabus
- Prelims –Indian History/Important Personalities
Context: Prime Minister Narendra Modi paid his tributes to Bal Gangadhar Tilak and Chandra Shekhar Azad on their birth anniversaries on July 23.
Background:-
- Saluting Indian nationalist and freedom fighter Bal Gangadhar Tilak, Prime Minister Modi said in a tweet, Lokmanya Tilak shook the foundation of British rule by demanding complete Independence.
- While remembering revolutionary freedom fighter Chand Shekhar Azad fondly, the Prime Minister called him a gallant son of ‘Bharat Mata’ and a remarkable man.
About Bal Gangadhar Tilak:-
- Birth: July 23, 1856.
- Birthplace: Ratnagiri (now in Maharashtra state), India.
- Death: August 1, 1920, in Mumbai.
- He was a scholar, mathematician, philosopher, and ardent nationalist who helped lay the foundation for India’s independence by building his own defiance of British rule into a national movement.
- He was also known as Lokmanya Tilak.
- His famous declaration “Swaraj is my birthright, and I shall have it” served as an inspiration for future revolutionaries during India’s struggle for freedom.
- The British Government termed him the “Father of Indian Unrest”. (Sedition Law)
Important Institutions Started by Tilak:-
- Deccan Education Society (1884): He was the founder of the Deccan Education Society along with his associate Gopal Ganesh Agarkar and others.
- Fergusson College (1885): He was one of the founders of the Fergusson College in Pune.
The ideology of Tilak:-
- He vocalized his strong opposition to the moderate views of the Indian National Congress (INC) on self-rule.
- He maintained that simple constitutional agitation in itself was futile against the British.
- He wanted an armed revolt against the British.
- Following the partition of Bengal by Lord Curzon, Tilak wholeheartedly supported the Swadeshi (Indigenous) movement and the Boycott of British goods.
- Due to this fundamental difference in outlook, Tilak and his supporters came to be known as the extremist wing of INC.
- He was a great reformer and throughout his life, he advocated the cause of women’s education and women’s empowerment.
- Tilak proposed Grand celebrations on ‘Ganesh Chaturthi’ and ‘Shivaji Jayanti’.
- He envisioned these celebrations inciting a sense of unity and inspiring nationalist sentiment among Indians.
Political ventures of Tilak:-
- 1890: He joined the Indian National Congress (INC).
- Tilak protested against the oppressive nature of the British efforts and wrote provocative articles on it in his newspapers on the epidemic of the Plague in Pune and adjacent regions.
- His article inspired the Chapekar brothers and they carried out the assassination of Commissioner Rand and Lt. Ayerst on June 22,
- Because of this, Tilak was imprisoned for 18 months on Sedition charges for inciting murder.
- Indian Home Rule League (1914): He founded the Indian Home Rule League.
- Lucknow Pact (1916): he concluded the Lucknow Pact with Mohammed Ali Jinnah, which provided for Hindu-Muslim unity in the nationalist struggle.
Newspapers by Tilak:-
- Weeklies: Kesari (Marathi) and Mahratta (English)
Books by Tilak:-
- Gita Rhasya
- Arctic Home of the Vedas.
About Chandra Shekhar Azad:-
- Birth: 23rd July 1906.
- Birth Place: Alirajpur district of Madhya Pradesh. ( Chandra Shekhar Azad)
- Death: On February 27, 1931.
- He died at Azad Park in Allahabad on 27th February 1931.
- Chandrashekhar Azad was a great Indian freedom fighter.
- He was the mentor of Bhagat Singh.
- He is considered one of the greatest revolutionaries that India has produced.
Political ventures of Chandrashekhar Azad:-
- 1921: when Gandhiji launched the Non-Cooperation Movement, Chandra Shekhar, then a 15-year-old student, joined.
- He was arrested.
- On being presented before a magistrate, he gave his name as “Azad” (The Free), his father’s name as “Swatantrata” (Independence) and his residence as “Jail”.
- From that day, he came to be known as Chandra Shekhar Azad among the people.
- 1925: Involved in the Kakori train Robbery.
- 1926: he was involved in an attempt to blow up the Viceroy of India’s train.
- 1928: he was involved in the shooting of J. P. Saunders at Lahore to avenge the killing of Lala Lajpat Rai.
Organizations by Chandrashekhar Azad:-
- Hindustan Republican Association: After the suspension of the non-cooperation movement in 1922 by Gandhi, Azad joined Hindustan Republican Association (HRA).
MUST READ: Dayanand Saraswati
SOURCE: AIR
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) By which one of the following Acts was the Governor General of Bengal, designated as the Governor General of India? (2023)
- The Regulating Act
- The Pitt’s India Act
- The Charter Act of 1793
- The Charter Act of 1833
Q.2) Consider the following freedom fighters: (2022)
- Barindra Kumar Ghosh
- Jogesh Chandra Chatterjee
- Rash Behari Bose
Who of the above was/were actively associated with the Ghadar Party?
- 1 and 2
- 2 only
- 1 and 3
- 3 only
Syllabus
- Prelims –Economy
Context: An international symposium on sustainable livestock transformation was inaugurated at the National Dairy Development Board (NDDB).
About National Dairy Development Board (NDDB):-
- Establishment:
- Ministry: Ministry of Fisheries, Animal Husbandry and Dairying.
- HQ: Anand, Gujarat, India.
- Objective: to replace exploitation with empowerment, tradition with modernity, stagnation with growth, transforming dairying into an instrument for the development of India’s rural people.
- The NDDB is a statutory body set up by an act of Parliament and was founded by Dr Verghese Kurien.
Historical Background of NDDB:-
- It was initially constituted as a society under the Societies Act 1860.
- It was later merged with the former Indian Dairy Corporation, which was created and registered under the Companies Act 1956, by the NDDB Act 1987, which took effect on October 12, 1987.
Significance of NDDB:-
- Empowering Rural economy: The NDDB’s initiatives altered India’s rural economy by making dairying a viable and profitable business for millions of milk producers. ( Women and Cooperative Dairy Farming)
- Long-term livelihood: The NDDB reaches out to dairy farmers and provides them with alternative income-generating opportunities, allowing them to build long-term livelihoods.
- NDDB has been effective in combining dairy farmers’ traditional wisdom and experience with modern management strategies in order to capture the milk and milk products market while also assisting farmers.
- Operation Flood: Its most notable achievement is Operation Flood, which lasted 26 years and transformed India into the world’s greatest milk producer. (UPSC CSE: National Dairy Plan)
- The White Revolution is another name for this.
- Operation Flood: it is the world’s largest dairy development program, launched in the year 1970.
- It established a national milk grid that connected farmers across India to customers in over 700 towns and cities, decreasing seasonal and regional pricing differences and guaranteeing that producers receive a large portion of the profit by removing intermediaries.
MUST READ: Dairy Cooperatives
SOURCE: TIMES OF INDIA
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) Consider the following statements in relation to Janani Suraksha Yojana: (2023)
- It is a safe motherhood intervention of the State Health Departments.
- Its objective is to reduce maternal and neonatal mortality among poor pregnant women.
- It aims to promote institutional delivery among poor pregnant women.
- Its objective includes providing public health facilities to sick infants up to one year of age.
How many of the statements given above are correct?
- Only one
- Only two
- Only three
- All four
Q.2) With reference to organic farming in India, consider the following statements: (2018)
- ‘The National Programme for Organic Production’ (NPOP) is operated under the guidelines and ‘directions of the Union Ministry of Rural Development.
- ‘The Agricultural and Processed Food Product Export Development Authority ‘(APEDA) functions as the Secretariat for the implementation of NPOP.
- Sikkim has become India’s first fully organic State.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 and 2 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
Syllabus
- Prelims –Polity
Context: Recently, an adjournment motion was moved in the Lok Sabha, citing the need for urgent discussions on the ethnic violence in Manipur.
Background:-
- Opposition parties demanded a discussion on the alleged sexual assault of at least two women in Manipur, amid the ongoing ethnic violence in the state.
About the adjournment motion:-
- An adjournment motion is introduced in the Parliament to draw the attention of the House to a definite matter of urgent public importance.
- It needs the support of 50 members to be admitted.
- It is done after obtaining the Speaker’s consent. (UPSC CSE: Adjournment sine die)
- It is introduced only in the Lok Sabha.
- The Rajya Sabha Rule Book does not provide for an adjournment motion.
- It is regarded as an extraordinary device as it interrupts the normal business of the House.
- Notice of an adjournment motion is required to be given before 10 am on the day on which the motion is proposed.
- If the adjournment motion is accepted, the House adjourns after voting. (Delegated Legislation)
- The adoption of an adjournment motion is seen as a censure of the government.
- However, there is no compulsion on the government to resign.
Restrictions for moving an adjournment motion:-
- It must raise a matter which is definite, factual, urgent and of public importance.
- It must not cover more than one matter.
- It must be restricted to a specific matter of recent occurrence.
- It must not raise a question of privilege.
- It must not revive discussion on a matter that has been discussed in the same session.
- It must not deal with any matter that is under adjudication of court.
- It must not raise any question that can be raised on a distinct motion.
- The discussion on this motion should last for not less than two hours and thirty minutes.
MUST READ: Privilege Motion
SOURCE: THE INDIAN EXPRESS
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) Consider the following statements in respect of the election to the President of India: (2023)
- The members nominated to either House of the Parliament or the Legislative Assemblies of States are also eligible to be included in the Electoral College.
- Higher the number of elective Assembly seats, the higher the value of the vote of each MLA of that State.
- The value of the vote of each MLA of Madhya Pradesh is greater than that of Kerala.
- The value of the vote of each MLA of Puducherry is higher than that of Arunachal Pradesh because the ratio of total population to total number of elective seats in Puducherry is greater as compared to Arunachal Pradesh.
How many of the above statements are correct?
- Only one
- Only two
- Only three
- All four
Q.2) Consider the following statements: (2022)
- A bill amending the Constitution requires a prior recommendation of the President of India.
- When a Constitution Amendment Bill is presented to the President of India, it is obligatory for the President of India to give his/her assent.
- A Constitution Amendment Bill must be passed by both the Lok Sabha and Rajya Sabha by a special majority and there is no provision for joint sitting.
Which of the statements given above is correct?
- 1 and 2 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
Syllabus
- Prelims – Polity
Context: Recently, the National Commission for Protection of Child Rights (NCPCR) has written to the Manipur DGP, seeking FIR against three persons.
Background:-
- An FIR has been filed against Communist Party of India (Marxist) leader Politburo member Subhashini Ali, Tarun Bharatiya of Meghalaya, and Kamaludeen M from Tamil Nadu for posting photographs of a minor that they alleged was involved in the incident on May 4 in which two women were paraded naked.
About the National Commission for Protection of Child Rights (NCPCR):-

IMAGE SOURCE: twitter.com
- Establishment: 2007.
- HQ: New Delhi.
- Ministry: Ministry of Women and Child Development. ( NCPCR)
- It is a statutory body established under the Commission for Protection of Child Rights Act, 2005.
- Mandate: to ensure that all laws, policies, programs and administrative systems conform to the vision of the rights of the child as enunciated in the Constitution of India as well as the United Nations Convention on the Rights of the Child.
- Definition of a child as per NCPCR: A child is defined as a person falling in the age group of 0 to 18 years.
Functions of NCPCR:-
- Examine and review the safeguards provided by or under any law for the protection of child rights and recommend measures for their effective implementation.
- Inquire into violation of child rights and recommend initiation of proceedings.
- Examine all factors that inhibit the enjoyment of rights of children affected by terrorism, natural disasters, domestic violence, HIV/AIDS, trafficking, prostitution etc. and recommend appropriate remedial measures. (Sexual intent is key to POCSO Act: SC)
- Look into the matters relating to the children in need of special care and protection.
- Study treaties and other international instruments.
- Undertake a periodical review of existing policies, programmes and other activities on child rights.
- Spread child rights literacy among various sections of society.
- Promote awareness of the safeguards available for the protection of these rights through publications, the media, seminars and other available means.
- Inspect or cause to be inspected any juveniles custodial home, or any other place of residence or institution meant for children, under the control of the Central Government or any State Government or any other authority.
- Analyze existing law, policy and practice.
- Present to the Central Government annually and at such other intervals as the Commission may deem fit, reports upon the working of those safeguards.
- Undertake formal investigation where concern has been expressed either by the children themselves or by a concerned person on their behalf.
- Compile and analyze data on children. (UPSC CSE: Portal ‘Bal Swaraj)
- Promote the incorporation of child rights into the school curriculum, training of teachers or personnel dealing with children.
Powers of NCPCR:-
- The Commission, while inquiring into any matter under Section 13(1)(j) of CPCR Act, 2005 has all the powers of a civil court trying a suit under the Code of Civil Procedure, 1908 and, in particular, in respect of the following matters, namely:-
- summoning and enforcing the attendance of any person and examining him on oath.
- discovery and production of any document.
- receiving evidence on affidavits.
- requisitioning any public record or copy thereof from any court or office.
- issuing commissions for the examination of witnesses or documents.
- The Commission also has the power to forward any case to a Magistrate having jurisdiction to try the same
- The Magistrate to whom any such case is forwarded shall proceed to hear the complaint against the accused as if the case has been forwarded to him under section 346 of the Code of Criminal Procedure, 1973 (2 of 1974).
MUST READ: Child Marriage in India
SOURCE: THE INDIAN EXPRESS
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) Consider the following organizations/ bodies in India: (2023)
- The National Commission for Backward Classes
- The National Human Rights Commission
- The National Law Commission
- The National Consumer Disputes Redressal Commission
How many of the above are constitutional bodies?
- Only one
- Only two
- Only three
- All four
Q.2) With reference to ‘Scheduled Areas’ in India, consider the following statements: (2023)
- Within a State, the notification of an area as a Scheduled Area takes place through an Order of the President.
- The largest administrative unit forming the Scheduled Area is the District and the lowest is the cluster of villages in the Block.
- The Chief Ministers Of the concerned States are required to submit annual reports to the Union Home Ministry on the administration of Scheduled Areas in the States.
How many of the above statements are correct?
- Only one
- Only two
- All three
- None
Syllabus
- Prelims –Environment and Ecology
Context: The Goa bench of the Bombay High Court has directed the Goa government to notify the Mhadei Wildlife Sanctuary as a tiger reserve.
About Mhadei Wildlife Sanctuary:-
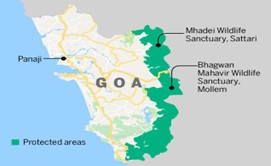
IMAGE SOURCE: The Times of India
- Location: in the northeast of Goa, in the taluka of Sattari.
- Its official declaration as a wildlife preserve came in 1999.
- The Mhadei River, known downstream as the Mandovi River, the lifeline of the state of Goa, originates in Karnataka, passes through the Mhadei Wildlife Sanctuary and meets the Arabian Sea at Panaji in Goa.
- The whole sanctuary acts as a catchment for the river.
- Prominent Waterfalls: Vazra Sakla Falls and the Virdi Falls.
- The cliff face near the Vazra Falls is notable for being the nesting grounds of the critically endangered Long-billed vultures. (Wildlife Protection)
- It has been declared an International Bird Area because of the presence of the Nilgiri wood pigeon, Malabar parakeet, Malabar grey hornbill, Grey-headed Bulbul, Rufous babbler, White-bellied blue-flycatcher and Crimson-backed sunbird.
- The three highest peaks in Goa are situated in the hill ranges of the sanctuary. They are Sonsogod (1027 mts), Talavche Sada (812 mts) and Vageri (725 mts).
- Flora:-
- The area of the sanctuary is thickly forested with moist deciduous vegetation and some evergreen species
- The sanctuary is particularly well known for its sacred groves that protect rare and indigenous trees.
- Fauna:-
- Commonly seen animals: Indian gaur, Barking deer, Sambar deer, Asian palm civet, small Indian civet, Wild boar, Indian hare, Ruddy mongoose, Black-faced langur and Bonnet macaque.
- Rarely seen: Black Panther, Sloth bear, Leopard, Tiger, Dhole, Jungle cat, Mouse deer, Giant squirrel, Flying squirrel, Indian pangolin and the Slender loris.
MUST READ: Anamalai Tiger Reserve
SOURCE: THE INDIAN EXPRESS
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) Consider the following statements (2023)
Statement-I:
The soil in tropical rainforests is rich in nutrients.
Statement-II:
The high temperature and moisture of tropical rainforests cause dead organic matter in the soil to decompose quickly.
Which one of the following is correct in respect of the above statements?
- Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and Statement-II is the correct explanation for Statement-I
- Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and Statement-II is not the correct explanation for Statement-I
- Statement-I is correct but Statement II is incorrect
- Statement-I is incorrect but Statement II is correct
Q.2) With reference to India’s Desert National Park, which of the following statements is correct? (2020)
- It is spread over two districts.
- There is no human habitation inside the Park.
- It is one of the natural habitats of the Great Indian Bustard.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
- 1 and 2 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
A big step in reducing the risk of disasters
Syllabus
- Mains – GS 3 (Disaster Management)
Context: The world needs to do more to prevent the risk of losses from all disasters, whether they are weather-related, earthquakes, or biological ones like COVID-19.
About a Disaster:
- A disaster refers to a significant disturbance in the normal functioning of a community, leading to human, material, economic, and environmental damages that surpass the community’s capacity to manage.
- It results from the combination of hazards, conditions of vulnerability and insufficient capacity or measures to reduce the potential negative consequences of risk.
Classification of Disasters
On the Basis of Source
- Natural Disasters: They are caused by natural phenomena (meteorological, geological or even biological origin).
- Examples of natural disasters are cyclones, tsunamis, earthquakes and volcanic eruptions, which are exclusively of natural origin.
- Landslides, floods, drought, fires are socio-natural disasters since their causes are both natural and manmade.
- Anthropogenic Disasters: They occur due to human intervention or negligence.
- These are associated with industries or energy generation facilities and include explosions, leakage of toxic waste, pollution, dam failure, wars or civil strife etc.
On the Basis of Duration
- Rapid Onset Disasters: They are characterised by the sudden and acute intensity of the impact during a short period.
- Earthquakes, cyclones, floods, tsunamis would fall under the category of rapid onset disasters.
- Slow Onset Disasters: Also termed as ‘Creeping Emergencies’, can be predicted much further in advance and unfold over months or even years.
- Climate change (global warming), desertification, soil degradation, and droughts, would fall under the category of slow onset disasters.
Disasters around the world
- Disasters around the world are claiming more and more lives. The consequences of climate change are already on our doorstep.
- Recently, three continents were gripped by heat waves.
- Massive forest fires have ravaged parts of Greece and Canada.
- Two weeks ago, the river Yamuna breached the highest flood level, recorded 45 years ago, and inundated parts of Delhi.
Sendai Framework 2015-2030
- The Sendai Framework works hand in hand with the other 2030 Agenda agreements, including the Paris Agreement on Climate Change, The Addis Ababa Action Agenda on Financing for Development, the New Urban Agenda, and ultimately the SDG
- It was endorsed by the UN General Assembly following the 2015 Third UN World Conference on Disaster Risk Reduction (WCDRR).
- It advocates for the substantial reduction of disaster risk and losses in lives, livelihoods, and health and in the economic, physical, social, cultural, and environmental assets of persons, businesses, communities, and countries.
- State has the primary role to reduce disaster risk but that responsibility should be shared with other stakeholders including local government, the private sector, and other stakeholders.
Challenges to Disaster Risk Reduction Mechanism
- The lack of competent financial risk management and insurance has provided a fertile breeding ground for these risks to proliferate and intensify.
- There is also a scarcity of investment in a development-oriented approach that unites all parties into a transparent framework of action at the national level.
- Significant difficulty in collecting and analysing data on hazards and exposures.
- The lack of technical and institutional capacity for risk assessment and modelling.
- Achieving comprehensive coverage of disaster risks.
Impacts of Disaster:
- Loss of Economy and Infrastructure: Disaster results in huge economic loss due to destruction of property, human settlements etc.
- Loss of Biodiversity: Disaster can change the natural environment, loss of habitat to many plants and animals and cause ecological stress that can result in biodiversity loss.
- Scarcity of basic necessities: Post- disasters, food, water and other natural resources become scarce resulting in food and water scarcity.
- Increase in Inequality: The disaster results in displacement of people and displaced populations often face several challenges in new settlements, in this process, they become poorer.
- Psychological Impact: Disaster increases the level of vulnerability and affects psychologically too.
Disaster Management in India
Initiatives by India
Coalition for Disaster Resilient Infrastructure (CDRI):
- Coalition for Disaster Resilient Infrastructure (CDRI) was first proposed by India during the 2016 Asian Ministerial Conference on Disaster Risk Reduction held in New Delhi.
- India is taking the lead and offering the expertise of Disaster Resilient Infrastructure (DRI) to its friendly countries.
Humanitarian Aid and Disaster Relief (HADR) operations:
- Indian defence forces, under the aegis of Headquarters Integrated Defence Staff (HQ IDS) have been carrying out HADR operations within the country as well as outside the country to deepen coordination with its neighbours and friendly countries with a focus on sharing expertise and building capabilities.
India’s initiative at G20 – Disaster Risk Reduction Working Group:
- India has established the first G20 Disaster Risk Reduction Working Group.
- Countries that make up the G20 hold around 85% of the global GDP and about two-thirds of the world population.
- As human vulnerability to disasters is strongly linked to economic decisions, the G20 is in a unique position to chart a new path of disaster risk-informed decision-making.
Way Forward:
- Early Warning System: There is a need to work on receiving early warnings as much as possible, which helps in mitigating the disasters.
- High Budget Allocation: High allocation of budget and resources are necessary to take mitigating actions and after-effect actions.
- Resilient Infrastructure: It should be focused on to prevent extreme situations.
- Transparency: Transparency mechanisms should include transparency boards, clearly mentioning the cost, quality and quantity of relief items, social audits and citizens’ reports.
- Awareness and Knowledge: Awareness is the best practice that can prevent and reduce the impact of disasters. Traditional and modern knowledge both should be spread and implied to mitigate the impacts of disasters.
- Example: The tribal communities in India adopt low-cost traditional technologies that help them mitigate the impact of natural disasters like drought.
Source: The Hindu
Syllabus
- Mains – GS 3 (Economy)
Context: Recently the Rajasthan government passed the Rajasthan Platform Based Gig Workers (Registration and Welfare) Bill, 2023.
Highlights of the bill:
- Registration of a gig worker: The Bill states any person has the right to be registered the minute they join an app-based platform, regardless of the duration of work or how many providers they work for.
The Bill applies to:
- “Aggregators” (digital intermediaries connecting buyers and sellers) and “Primary employers” (individual or organisations engaging platform-based workers).
- Welfare Board: The Bill proposes a Welfare Board comprising State officials, five representatives each from gig workers and aggregators, and two others from civil society.
- The Board will set up a welfare fund, register platform-based gig workers, aggregators and primary employers, facilitate guarantee of social security to platform-based gig workers and to provide for matters connected therewith or incidental thereto.
- The Board will maintain a database of companies and workers and each worker will receive a unique ID, which “shall be valid in perpetuity.
- Social Security and Welfare Fund: According to the Bill, the Board will create a “Social Security and Welfare Fund”.
- The fund will comprise of contributions made by individual workers, State government aids, other sources and a ‘welfare cess’ — a cut from each transaction — which the aggregator is required to pay.
- Grievance redressal: Gig workers “have an opportunity to be heard for any grievances” with “entitlements, payments and benefits provided under the Act.”
- As per the bill, a worker can file a petition physically before an officer or online through the web portal.
- The employer can object to the order within 90 days before an ‘Appellate Authority’.
Gig Economy in India:
- The gig economy is about individual workers carrying out tasks for clients through the intermediation of a platform attributing those tasks and taking care of the transfer of payment on a task-by-task basis.
- In 2020, 7.7 million workers were engaged in the gig economy.
- The gig workforce is expected to expand to 23.5 million workers by 2029-30.
- At present about 47% of the gig, work is in medium skilled jobs, about 22% in high skilled and about 31% in low skilled jobs.
- Trend shows the concentration of workers in medium skills is gradually declining and that of the low skilled and high skilled is increasing.
Gig workers:

- NITI Aayog defines ‘gig workers’ as those engaged in work outside of the traditional employer-employee arrangement.
- NITI Aayog’s report titled ‘India’s Booming Gig and Platform Economy’ defines a gig worker as “someone who engages in income-earning activities outside of a traditional employer-employee relationship, as well as in the informal sector”.
- Additionally, it defines those working with platforms such as Ola, Uber, Dunzo, Swiggy, Zomato and Urban Company as platform workers.
Challenges faced by gig workers:
- Hurdle in growth of full time employee: While not all employers are inclined to hire contracted employees, the gig economy trend can make it harder for full-time employees to develop in their careers since temporary employees are often cheaper to hire and more flexible in their availability.
- Work-life balance: For some workers, the flexibility of working gigs can actually disrupt the work-life balance, sleep patterns, and activities of daily life
- Can replace Full time employees: The number of full-time employees required by the company can be reduced as freelance workers take over the work.
- No job security: In effect, workers in a gig economy are more like entrepreneurs than traditional workers. While this may mean greater freedom of choice for the individual worker, it also means that the security of a steady job with regular pay and benefits.
- No regular job benefits: Many employers save money by avoiding paying benefits such as health coverage and paid vacation time.
- Because there is no formal employment relationship with the platform company, there are usually no employee benefits in short-term contracts, which are less guaranteed than full-time and part-time jobs, and are difficult to write on resumes.
Steps Taken by Government of India for Gig Workers:
- Code of Social Security, 2020: The Government has formulated the Code on Social Security, 2020 that envisages framing of suitable social security schemes for gig workers and platform workers on matters relating to life and disability cover, accident insurance, health and maternity benefits, old age protection, etc. However, these provisions under the Code have not come into force.
- e-Shram Portal: The Government has also launched e-Shram portal in 2021 for registration and creation of a Comprehensive National Database of Unorganized Workers including gig workers and platform workers.
- It allows a person to register himself or herself on the portal on a self-declaration basis, which is spread across around 400 occupations.
Way Forward:
Gig Economy has the potential to create jobs for India’s large workforce, especially the low-skilled workers. The Government must take appropriate steps to support the expansion of gig economy and platforms. At the same time, the interests of the gig workers must be protected to provide them with just work conditions as well as social security benefits. Achieving the balance will need some effort from all stakeholders.
Source: Indian Express
Practice MCQs
Q1) Consider the following pairs:
| Institution | Ministry |
| 1.National Dairy Development Board | Ministry of Fisheries, Animal Husbandry and Dairying |
| 2.University Grants Commission | Ministry of Women and Child Development |
| 3.National Commission for Protection of Child Rights | Ministry of Education |
How many of the above pairs are correctly matched?
- Only one
- Only two
- All three
- None
Q2) Consider the following statements
Statement-I:
Mhadei Wildlife Sanctuary is located in Cochin.
Statement-II:
Vazra Sakla Falls and Virdi Falls are located in this sanctuary.
Which one of the following is correct in respect of the above statements?
- Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and Statement-II is the correct explanation for Statement-I
- Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and Statement-II is not the correct explanation for Statement-I
- Statement-I is correct but Statement II is incorrect
- Statement-I is incorrect but Statement II is correct
Q3) Consider the following statements
Statement-I:
An adjournment motion needs the support of 50 members to be admitted.
Statement-II:
It is introduced only in the Lok Sabha.
Which one of the following is correct in respect of the above statements?
- Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and Statement-II is the correct explanation for Statement-I
- Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and Statement-II is not the correct explanation for Statement-I
- Statement-I is correct but Statement II is incorrect
- Statement-I is incorrect but Statement II is correct
Mains Practice Questions
Q.1) What can be done to prevent the risk of losses from all disasters, whether they are weather-related or biological? Highlight India’s initiative at G20 for the Disaster Risk Reduction. (250 words)
Q.2) Discuss the role of ‘Gig Economy’ in the process of empowerment of women in India. (250 words)
Comment the answers to the above questions in the comment section below!!
ANSWERS FOR ’ 26th July 2023 – Daily Practice MCQs’ will be updated along with tomorrow’s Daily Current Affairs.st
ANSWERS FOR 25th July – Daily Practice MCQs
Q.1) – c
Q.2) – d
Q.3) -b











