IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
Archives
(PRELIMS & MAINS Focus)
Syllabus
- Prelims – Science and Technology
Context: Chandrayaan III spacecraft was integrated with the GSLV Mark III launch vehicle recently. The launch is planned between 12-19th July 2023.
About Chandrayaan III:-

IMAGE SOURCE: indiandefensenews.in
- Chandrayaan-3 is the successor to the Chandrayaan-2 mission. (UPSC CSE:CHANDRAYAAN-2)
- Launch Vehicle Mark-III (LVM3).
- Launched from: Satish Dhawan Space Centre (SDSC), Sriharikota, Andhra Pradesh.
- It consists of an indigenous Lander module (LM), a Propulsion module (PM) and a Rover.
- Lander: a spacecraft that descends towards and comes to rest on, the surface of an astronomical body.
- Propulsion module: a box-like structure, mounted with a large solar panel on one side and a large cylinder on top.
- Rover: a small vehicle that can move over rough ground, often used on the surface of other planets, sometimes controlled from the earth.
- The Lander and the Rover have scientific payloads to carry out experiments on the lunar surface.
- There will not be any orbiters like Chandrayaan 2 in it. (UPSC CSE: CHANDRAYAAN-2)
Objectives of Chandrayaan-3 mission:-
- To demonstrate a Safe and Soft Landing on Lunar Surface
- To demonstrate Rover roving on the moon and
- To conduct in-situ scientific experiments.
Lander payloads:–
- Chandra’s Surface Thermophysical Experiment (ChaSTE): to measure the thermal conductivity and temperature
- Instrument for Lunar Seismic Activity (ILSA) for measuring the seismicity around the landing site
- Langmuir Probe (LP): to estimate the plasma density and its variations.
- A passive Laser Retroreflector Array from NASA is accommodated for lunar laser ranging studies.
Rover payloads:-
- Alpha Particle X-ray Spectrometer (APXS) and Laser Induced Breakdown Spectroscope (LIBS) for deriving the elemental composition near the landing site.
Propulsion Module Payload:-
- Spectro-polarimetry of Habitable Planet Earth (SHAPE): Future discoveries of smaller planets in reflected light would allow us to probe into a variety of Exo-planets which would qualify for habitability or for the presence of life.
GSLV-Mk III
- It is also known as the Launch Vehicle Mark 3 (LVM3).
- It is a three-stage vehicle with two solid motor strap-ons, a liquid propellant core stage and a cryogenic stage.
- It is the heaviest and the shortest among India’s operational launch vehicles.
- Weighs: 641 tonnes, which is equal to the weight of five fully loaded passenger planes.
- Capacity: GSLV can take 10,000-kg satellites to lower earth orbits.
MUST READ: Gaganyaan
SOURCE: AIR
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) Consider the following statements : (2023)
- Ballistic missiles are jet-propelled at subsonic speeds throughout their flights, while cruise missiles
are rocket-powered only in the initial phase of flight.
- Agni-V is a medium-range supersonic cruise missile, while BrahMos is a solid-fuelled intercontinental ballistic missile.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Q.2) Which one of the following countries has its own Satellite Navigation System? (2023)
- Australia
- Canada
- Israel
- Japan
Syllabus
- Prelims –International Relations
Context: The Directorate General of Civil Aviation (DGCA) of India has recently signed a memorandum of understanding with the European Union Aviation Safety Agency (EASA).
Background:-
- The MoU is for cooperation in Unmanned Aircraft Systems and Innovative Air Mobility.
- This MoU will facilitate collaboration on unmanned aircraft and innovative air mobility between the two civil aviation authorities.
About the Collaboration on Unmanned Aircraft Systems and Innovative Air Mobility:-
- This memorandum of understanding (MoU) will facilitate collaboration on unmanned aircraft and innovative air mobility between the two civil aviation
- Unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV): it is commonly known, as a drone. It is an aircraft without any human pilot, crew, or passengers on board.
- Innovative air mobility (IAM): The concept of innovative air mobility (IAM) accommodates commercial and non-commercial operations with novel aircraft designs that do not automatically fall under one of the known categories of aero planes or helicopters. They may have the capability to vertically takeoff and land, have specific (distributed) propulsion features, may be operated in unmanned configuration, etc.
- This collaboration would include cooperation between DGCA and EASA in the areas of development of certification standards and environmental standards and related requirements for the certification and use of unmanned aircraft systems and innovative air mobility operations which includes licensing of personnel, training, air traffic management and infrastructure, including Unmanned Aircraft System Traffic Management (UTM) standards and services.
- The MoU will also ensure regular information sharing between the two authorities on the technological developments and research in this area and their respective strategies for outreach to relevant stakeholders.
- Further, the MoU will result in collaboration in conducting conferences, workshops, and training programs by DGCA and EASA in this area.
About Directorate General of Civil Aviation (DGCA):-
IMAGE SOURCE: DGCA
- The Directorate General of Civil Aviation is the regulatory body in the field of Civil Aviation primarily dealing with safety issues. (UPSC CSE: DGCA)
- It is a statutory body of the Indian Central Government under the Aircraft (Amendment) Bill, 2020.
- Objectives: to regulate civil aviation in India.
- Ministry: Ministry for Civil Aviation.
- HQ: New Delhi.
- It has regional offices in various parts of India.
Functions of DGCA:-
- It investigates aviation accidents and incidents.
- It maintains all regulations related to aviation.
- It is responsible for the issuance of licenses.
- It is responsible for the regulation of air transport services to/from/within India.
- It is responsible for the enforcement of civil air regulations, air safety and airworthiness standards.
- It also coordinates all regulatory functions with International Civil Aviation Organization.
European Union Aviation Safety Agency (EASA)
- EASA is an Agency of the European Union (EU). (UPSC CSE: India-EU)
- EU: international organization comprising 27 European countries.
- It develops common safety and environmental rules at the European level.
- Objective: to promote the highest common standards of safety and environmental protection in civil aviation.
- Established: 4 July 2018.
- HQ: Cologne, Germany.
- It is headed by an Executive Director.
- The work of the Agency is overseen by a Management Board, which represents EU Member States and the European Commission.
- It is a body governed by European public law.
- It is distinct from the Community Institutions (Council, Parliament, Commission, etc.) and has its own legal personality.
- Exclusion: EASA’s remit does not encompass questions related to civil aviation security e.g. airport security measures, counter-terrorism.
MUST READ: Dornier aircraft
SOURCE: AIR
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) Consider the following actions: (2023)
- Detection of car crash/ collision which results in the deployment of airbags almost instantaneously.
- Detection of accidental free fall of a laptop towards the ground which results in the immediate turning off
- of the hard drive.
- Detection of the tilt of the smartphone which results in the rotation of display between portrait and landscape mode.
In how many of the above actions is the function of the accelerometer required?
- Only one
- Only two
- All three
- None
Q.2) Which one of the following is the context in which the term “qubit” is mentioned? (2022)
- Cloud Services
- Quantum Computing
- Visible Light Communication Technologies
- Wireless Communication Technologies
Syllabus
- Prelims –Environment and Ecology
Context: Recently, the forest staff in Similipal National Park, Odisha went on strike.
Background:-
- The Odisha government deployed armed police personnel at the Similipal Tiger Reserve (STR) recently to protect the 2,700 square kilometers reserve area that is home to unique melanistic tigers.
About Similipal National Park:-
IMAGE SOURCE: Wikimapia
- Location: it is located in the Mayurbhanj district of Odisha. (UPSC CSE: Similipal National Park)
- Nomenclature: Similipal derives its name from the abundance of ‘Simul’ (red silk cotton trees) that bloom here.
- It is part of the Similipal-Kuldiha-Hadgarh Elephant Reserve popularly known as Mayurbhanj Elephant Reserve.
- Mayurbhanj Elephant Reserve: it includes three protected areas i.e. Similipal Tiger Reserve, Hadagarh Wildlife Sanctuary and Kuldiha wildlife sanctuary.
- It is a national park and a Tiger Reserve.
- 1956: It was formally designated a tiger reserve. (UPSC CSE: Importance of Tiger Conservation)
- 1973: It was brought under Project Tiger.
- Government of India declared it as a biosphere reserve.
- 2009: It is a part of the UNESCO World Network of Biosphere Reserves.
- The tiger reserve is spread over 2750 sq. km and has some beautiful waterfalls like Joranda and Barehipani.
- The park is surrounded by high plateaus and hills, the highest peak being the twin peaks of Khairiburu and Meghashini.
- At least twelve rivers cut across the plain area, all of which drain into the Bay of Bengal.
- These include: Burhabalanga, Palpala Bandan, Salandi, Kahairi and Deo.
- Prominent tribes: Kolha, Santhala, Bhumija, Bhatudi, Gondas, Khadia, Mankadia and Sahara.
- Vegetation: it is a mix of deciduous with some semi-evergreen forests.
- Sal is the dominant tree species
- Fauna: it is famous for gaurs (Indian bison), causing as well as an orchidarium.
- The STR is the only tiger habitat in the world with melanistic tigers, which have broad black stripes running across their bodies and thicker than those seen on normal tigers.
- Tribes: Two tribes, the Erenga Kharias and the Mankirdias, inhabit the reserve’s forests and practice traditional agricultural activities.
SOURCE: DOWN TO EARTH
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) Consider the following statements : (2023)
- In India, the Biodiversity Management Committees are key to the realization of the objectives of the Nagoya Protocol.
- The Biodiversity Management Committees have important functions in determining access and benefit sharing, including the power to levy collection fees on the access of biological resources within its jurisdiction.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Q.2) Consider the following statements: (2023)
Once the Central Government notifies an area as a ‘Community Reserve’
- the Chief Wildlife Warden of the State becomes the governing authority of such forest
- hunting is not allowed in such area
- people in such areas are allowed to collect non-timber forest produce
- people of such areas are allowed traditional agricultural practices
How many of the above statements are correct?
- Only one
- Only two
- Only three
- All four
Syllabus
- Prelims –Science and Technology
Context: Recently, the James Webb Space Telescope detected a carbon molecule in the Orion Nebula.
Background:-
- The James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) has detected the CH3+ molecule, which is also known as methyl cation, in space for the first time.
Orion Nebula
IMAGE SOURCE: NASA
- It lies in the constellation Orion.
- Discovery: it was discovered in 1610 by the French scholar Nicolas-Claude Fabri de Peiresc and independently in 1618 by the Swiss astronomer Johann Cysat.
- The Orion nebula lies about 1,350 light-years from Earth.
- Nebula: any of the various tenuous clouds of gas and dust that occur in interstellar space.
- They are often star-forming regions.
- It contains hundreds of very hot (O-type) young stars clustered about a nexus of four massive stars known as the Trapezium.
- Radiation from these stars makes the nebula to glow.
- It was the first nebula to be photographed (1880), by Henry Draper of the United States.
About James Webb Space Telescope:-
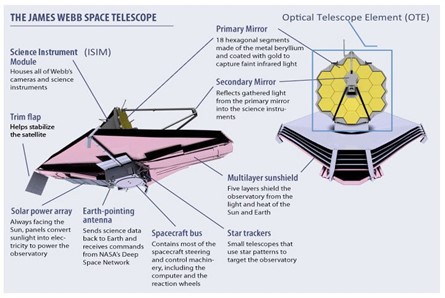
IMAGE SOURCE: jpl.nasa.gov
- It is an infrared observatory orbiting the Sun. (UPSC CSE: International Space Station (ISS))
- Launched: 2021.
- Type: Orbiter.
- Launched by: National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA).
- Launch Vehicle: Ariane 5 rocket, provided by the European Space Agency (ESA).
- Launch site: French Guiana.
- Objective: to find the first galaxies that formed in the early universe and to see stars forming planetary systems.
- It is NASA’s largest and most powerful space science telescope.
Functions of the telescope:-
- It will study every phase in the history of our universe, ranging from the first luminous glows after the big bang, to the formation of solar systems capable of supporting life on planets like Earth, to the evolution of our own solar system.
- It will build on the Hubble Space Telescope’s (UPSC CSE: ISRO’s hybrid propulsion system)
- NASA’s Hubble Space Telescope: it is the first astronomical observatory placed into orbit around Earth with the ability to record images in wavelengths of light spanning from ultraviolet to near infrared.
- It will look deeper into the cosmos and thus further back in time than is possible with Hubble.
- It will attempt to detect the light from the very first population of stars in the Universe to switch on more than 13.5 billion years ago.
MUST READ: IN-SPACe
SOURCE: THE INDIAN EXPRESS
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) Which one of the following statements best reflects the idea behind the “Fractional Orbital Bombardment System” often talked about in media? (2022)
- A hypersonic missile is launched into space to counter the asteroid approaching the Earth and explode it in space.
- A spacecraft lands on another planet after making several orbital motions.
- A missile is put into a stable orbit around the Earth and deorbits over a target on the Earth.
- A spacecraft moves along a comet with the same surface speed.
Q.2) If a major solar storm (solar flare) reaches the Earth, which of the following are the possible effects on the Earth? (2022)
- GPS and navigation systems could fail.
- Tsunamis could occur in equatorial regions.
- Power grids could be damaged.
- Intense auroras could occur over much of the Earth.
- Forest fires could take place over much of the planet.
- Orbits of the satellites could be disturbed.
- Shortwave radio communication of the aircraft flying over polar regions could be interrupted.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
- 1, 2, 4 and 5 only
- 2, 3, 5, 6 and 7 only
- 1, 3, 4, 6 and 7 only
- 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 and 7
Syllabus
- Prelims –Governance
Context: Recently, the Prime Minister, Shri Narendra Modi congratulated new homeowners in Bengaluru’s first project under Special Window for Funding Stalled Affordable and Middle-Income Housing Projects (SWAMIH) Fund.
Background:-
- The SWAMIH Fund has helped more than 3000 families in owning their dream homes.
About SWAMIH Fund:-
- Launched: 2019.
- It is a social impact fund specifically formed for completing stressed and stalled residential projects. (UPSC CSE: Pradhan Mantri Awas Yojana-Urban (PMAY-U))
- Sponsored by: Ministry of Finance, Government of India.
- Managed by: SBICAP Ventures Ltd., a State Bank Group company.
- Objective:-to provide priority debt financing for the completion of stalled housing projects falling under the affordable and middle-income housing categories. (UPSC CSE: Urban Housing)
- Implementation of the scheme: The fund was set up as a Category-II AIF (Alternate Investment Fund) debt fund registered with SEBI.
- AIFs: they are defined under the Securities and Exchange Board of India (Alternative Investment Funds) Regulations, 2012.
- AIFs created/funded under the Special Window would solicit investment into the fund from the Government and other private investors including cash-rich financial institutions, sovereign wealth funds, public and private banks, domestic pension and provident funds, global pension funds and other institutional investors.
Eligibility criteria for funding:-
- Real estate projects must be registered under the Real Estate (Regulation and Development) Act (RERA) 2016.
- Project must be classified as a non-performing asset (NPA) or be under insolvency proceedings.
- The project should have been declared as a “stalled” or “delayed” project by a competent authority.
- The fund is available only for projects that fall under the affordable and mid-income housing categories.
MUST READ: Social Stock Exchange
SOURCE: PIB
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) Consider the following statements: (2020)
- Aadhaar metadata cannot be stored for more than three months.
- State cannot enter into any contract with private corporations for sharing of Aadhaar data.
- Aadhaar is mandatory for obtaining insurance products.
- Aadhaar is mandatory for getting benefits funded out of the Consolidated Fund of India.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 and 4 only
- 2 and 4 only
- 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3 only
Q.2) Atal Innovation Mission is set up under the (2019)
- Department of Science and Technology
- Ministry of Labour and Employment
- NITI Aayog
- Ministry of Skill Development and Entrepreneurship
Syllabus
- Prelims –Governance
Context: The Union Minister for Women and Child Development Smriti Irani recently launched a scheme for shelter, and aid to pregnant minor rape victims under the Nirbhaya Fund.
Background:-
- The proposal for “critical care and support for accessing justice to rape/gang rape survivors and minor girls who get pregnant” has been approved by the WCD Ministry.
- It has been approved with an outlay of Rs. 74.10 crore and will be applicable across the country in a week’s time.
- The scheme aims to provide shelter, food, daily needs, safe transportation for attending court hearings and legal aid to minor girls who have been abandoned by their family due to forced pregnancy, either due to rape or gang rape, or due to any other reason, and have no other means to support themselves.
- The administrative structure has been additionally leveraged with Mission Vatsalya, in collaboration with state governments and childcare institutions, to actualise this support to minor victims on the ground.
About Nirbhaya Fund:-
- Historical Background:-
- The fund was created by the Ministry of Finance in 2013 with a corpus of Rs 1000 crore.
- The Government of India established the Nirbhaya Fund in response to the Nirbhaya Case in 2013.
- Objective: It is aimed specifically at projects for improving women’s safety and security. (UPSC CSE: Protection of Women from Sexual Harassment (POSH) Act)
- Managed by: Ministry of Women and Child Development (MWCD).
- Administered by: Department of Economic Affairs of the finance ministry.
- It is a non-lapsable corpus fund.
- Major projects under the fund: Central Victim Compensation Fund (CVCF), One Stop Centers (OSCs), Universalization of Women Helpline (WHL), Mahila Police Volunteer (MPV), etc.
Mission Vatsalya Scheme
- Launched in 2021. (UPSC CSE: Mission Vatsalya Scheme)
- Ministry: Ministry of Women and Child Development (MWCD).
- Objective: to strengthen the juvenile justice care and protection system with the motto to ‘leave no child behind’.
- The scheme provides a roadmap to achieve development and child protection priorities aligned with the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs).
- It lays emphasis on child rights, advocacy and awareness.
- Framework: The Juvenile Justice (Care and Protection of Children) Act 2015 [JJ Act] provisions and the Protection of Children from Sexual Offences Act 2012 [POCSO Act] form the basic framework for the implementation of the Mission.
- Implementation and Funding: The Scheme is implemented as a Centrally Sponsored Scheme in partnership with State Governments and UT Administrations to support them in universalizing access and improving the quality of services across the country.
MUST READ: Mission Shakti
SOURCE: THE INDIAN EXPRESS
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) Which of the following statements is/are correct regarding the Maternity Benefit Amendment Act, 2017? (2019)
- Pregnant women are entitled to three months of pre-delivery and three months of post-delivery paid leave.
- Enterprises with creches must allow the mother a minimum of six creche visits daily.
- Women with two children get reduced entitlements.
Select the correct answer using the code given below.
- 1 and 2 only
- 2 only
- 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
Q.2) Which of the following is/are the aim/aims of the “Digital India” Plan of the Government of India? (2018)
- Formation of India’s own Internet companies like China did.
- Establish a policy framework to encourage overseas multinational corporations that collect Big Data to build their large data centres within our national geographical boundaries.
- Connect many of our villages to the Internet and bring Wi-Fi to many of our schools, public places and major tourist centres.
Select the correct answer using the code given below :
- 1 and 2 only
- 3 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
American Freedom Struggle
Syllabus
- Mains – GS 1 (World History)
Context: Recently, America celebrated their hard won victory from the oppressive tax system of the British Empire and their freedom from the British Empire.
About the American War of Independence:
- The American Revolution was an ideological and political revolution that occurred in British America between 1765 and 1783.
- In the American Revolutionary War, which lasted from 1775 to 1783, the colonies secured their independence from the British Crown and established the United States as the first sovereign nation-state founded on Enlightenment principles of constitutionalism and liberal democracy.
- The American struggle for independence was very different from nationalist uprisings in other colonies of the British in the East.
- In America it was the British settlers who entered into a bitter scuffle with British government authorities.
- In colonies like India or the West Indies on the other hand, the natives rose unanimously against the tyranny of the rulers from the West.
Circumstances leading up to the American War of Independence:
- Seven Years War: End of the Seven Years War in 1763 and the transfer of Canada from France to England removed the fear of French attack from the minds of the Americans.
- They could now fully focus on countering the British adversities.
- Granville Measures: British PM Granville passed a series of Acts which affected the interests of the American colonies such as The Sugar Act of 1764, The Stamp Act of 1765, The Quartering Act etc.
- These measures were severely opposed by the colonists.
- They raised the slogan “No Taxation without Representation” thus insisting for the American representation in the English Parliament.
- Townshend Laws: British minister Townshend imposed new taxes on glass, paper, tea, paints, etc in 1767.
- The Americans protested these measures and boycotted British goods.
- The protest led to the killing of five Americans by British soldiers which came to be known as the Boston Massacre.
- Boston Tea Party: In 1773, a new Tea Act was passed imposing a tax on import of tea which was protested by Americans.
- A group of Americans dressed as Red Indians climbed on the ships and threw away the tea bundles into the sea at the Boston harbour.
- This event was known as the Boston Tea Party.
- Philadelphia Congress: In 1774 and 1775 representatives of American colonies met twice at Philadelphia.
- They appealed to the British King to remove restrictions on industries and trade and not to impose any taxes without their consent which was rejected by the British monarch.
- As a last attempt, an Olive Branch Petition was sent to the British King George III, who rejected it. Thus American colonists decided to unite in their fight against the British.
- Declaration of Independence: A pamphlet named “Common Sense” began to be circulated in the colonies which attacked the idea of hereditary monarchy and advocated democratic government.
- The pamphlet inculcated the fighting spirit among the Americans. Ultimately On 4th July 1776, the American Declaration of Independence was adopted by the Continental Congress.
- The declaration included the ideals of human freedom in it and laid emphasis on the unalienable rights of men namely, “Life, Liberty and Pursuit of Happiness”.
The Mahatma Gandhi Link:
- In his call to Indians to resist British domination, Mahatma Gandhi often referred to and drew inspiration from the American revolution.
- In March 1930, when Gandhi had embarked upon the famous Dandi march to protest against the draconian salt tax imposed by the British authorities, his movement had resonances with the historic Boston Tea Party.
The significance of the American Revolution:
- The revolution led to the establishment of a republic based on the first written constitution in the world.
- This was a marked contrast to the other states were Monarchies were still in power. This inspired people across the world to struggle for democratic and republican forms of government.
- It established a federal state with powers divided between the federal government and states.
- This provided a nice template for power-sharing in diverse countries that needed complex polities.
- Besides, there was a separation of powers between various organs of the state.
- Certain inalienable rights were given to the people – this limited the government against the authority of people and reduced government interference in their lives.
- Democracy was established, but it was far from perfect. Sections like Negroes and women were denied voting rights. But the journey to democracy had begun.
- It led to many uprisings in Europe, with the French revolution being the biggest. Many generals who participated in the war was instrumental in the French revolution.
- Thinkers like Thomas Paine also participated in the revolution. This led to a spread of modern ideas in Europe.
Way Forward:
- The American revolution had a profound impact on the history of the modern world. It provided a template through which modern ideas could defeat oppressive regimes.
- The subsequent success of the USA in world arena is a testimony to how powerful is the idea of liberal democracy and emancipation of the populace. This model was successfully emulated by many countries (especially in Europe) post World War II.
- India also has learned a lot from the American experience and adopted many of these democratic principles, adding to our own democratic socialist principles.
Source: Indian Express
Syllabus
- Mains – GS 3 (Economy)
Context: It has been observed that States’ fiscal health improved after Covid-19 pandemic stress.
About Fiscal Condition of Various States:
- Stress tests show that the fiscal conditions of the most indebted State governments are expected to deteriorate further, with their debt-GSDP ratio likely to remain above 35 per cent in 2026-27.
- Based on the debt-GSDP ratio in 2020-21, Punjab, Rajasthan, Kerala, West Bengal, Bihar, Andhra Pradesh, Jharkhand, Madhya Pradesh, Uttar Pradesh and Haryana turn out to be the states with the highest debt burden.
- These 10 States account for around half of the total expenditure by all State governments in India. Other vulnerability indicators also capture these 10 States in their cross hairs.
- Their GFD-GSDP ratios were equal to or more than 3 per cent in 2021-22, besides deficits in their revenue accounts (except Uttar Pradesh and Jharkhand).
- Moreover, the Interest Payment to Revenue Receipts (IP-RR) ratio, a measure of debt servicing burden on States’ revenues, in 8 of these States was more than 10 per cent.
- Among the 10 States, Andhra Pradesh, Bihar, Rajasthan and Punjab exceeded both debt and fiscal deficit targets for 2020-21 set by the 15th Finance Commission (FC-XV).
- Kerala, Jharkhand and West Bengal exceeded the debt target, while Madhya Pradesh overshot the fiscal deficit target. Haryana and Uttar Pradesh were exceptions as they met both criteria.
- Rajasthan, Kerala and West Bengal are projected to surpass the FC-XV targets for debt and fiscal deficit in 2022-23 (Budget Estimate/BE).
Basic terminologies:
- Revenue expenditure refers to the expenditure that neither creates an asset nor reduces the liability of the government. They are regular and recurring; Short-term; Example-Payment of salaries, maintenance of roads, street lights, etc.
- Capital expenditure refers to the expenditure that either creates an asset or reduces the liability of the government. They are irregular and non-recurring; Long-term; Example- Construction of metros, dams etc., repayment of loans to IMF etc., purchase of machinery, etc.
- Monetary policy is concerned with the management of interest rates and the total supply of money in circulation. It is generally carried out by the RBI.
- Fiscal policy estimates taxation and government spending. It should ideally be in line with the monetary policy, but since it is created by lawmakers, people’s interest often takes precedence over growth.
- Fiscal Responsibility and Budget Management (FRBM) Act was enacted in 2003. The objective of the Act is
- to ensure inter-generational equity in fiscal management;
- long-run macroeconomic stability;
- better coordination between fiscal and monetary policy and
- transparency in the fiscal operations of the Government.
Fiscal Challenges Faced by Indian States:
Revenue Related Challenges:
- The impact of the Covid-19 pandemic on the economic activity and tax collection.
- The uncertainty and volatility of GST revenue and compensation.
- The dependence on tax devolution from the Union and its formula-based allocation.
- The erosion of fiscal autonomy due to the subsumption of various taxes under GST.
- The limited scope for raising non-tax revenues such as user charges, fees, etc.
- The compliance and administrative issues in collecting own taxes such as property tax, stamp duty, etc.
- Out of 17 major States, 13 States have revenue deficits, and seven States have revenue deficits as the main driver of their fiscal deficits.
- These States are Andhra Pradesh, Haryana, Kerala, Punjab, Rajasthan, Tamil Nadu, and West Bengal.
Expenditure Related Challenges:
- The rising demand for public health and education services due to the pandemic and demographic factors.
- The need to invest in infrastructure and urban development to support growth and employment.
- The fiscal implications of various welfare schemes and subsidies for the poor and vulnerable sections.
- The burden of pension and salary liabilities for the public sector employees.
- The contingent liabilities arising from guarantees, loans, etc. given to public sector enterprises and other entities.
- The sustainability and servicing of the debt stock accumulated over the years.
Framework of Revenue Deficit Consolidation:
- Data from the last 20 years suggests that revenue deficit had almost disappeared from State Budgets before COVID-19.
- States, in aggregate, were generating revenue surpluses almost all the years during this period.
- However, the re-emergence of revenue deficit in recent years should take the focus back on the management of revenue deficit by creating an incentive compatible framework.
Benefits of Reducing Revenue Deficits for Indian States?
- Improving the fiscal health and sustainability of State finances and reducing their debt burden.
- Enhancing the quality of expenditure and increasing the share of capital expenditure in total expenditure.
- Boosting public investment in infrastructure and human capital, which can foster economic growth and development.
- Strengthening the credibility and confidence of investors and creditors in State finances.
- Ensuring macroeconomic stability and coordination with the Union Government.
Measures to Manage Revenue Deficit Effectively
Interest Free Loans
- Interest-free loans to the States by the Union Government may be linked to a reduction in revenue deficit.
- This will help eliminate the possibility of a substitution of States’ own capital spending and also prevent the diversion of borrowed resources to finance revenue expenditure.
- Defined Time Path: For revenue deficit reduction with a credible fiscal adjustment plan would help restore fiscal balance and improve quality of expenditure.
Incentive Grants
- A forward-looking performance incentive grants could also be considered for a reduction of revenue deficit.
- In this context, different approaches provided by earlier Finance Commissions can be considered to decide the framework of the incentive structure.
Way Forward:
There has to be a differentiated approach for different States. The policy, for example, for Gujarat cannot be the same as for West Bengal because the starting conditions are different and their political economy is different. So different states cannot shrink their debt-to-GSDP ratio at the same speed.
There is a need for some kind of fiscal council or interstate mechanism that can ensure that FRBM limits on spending are strictly adhered to, along with ensuring the quality of expenditure of the States.
Source: The Hindu
Practice MCQs
Q1) Consider the following statements
Statement-I:
James Webb Space Telescope is launched by the European Space Agency.
Statement-II:
James Webb Space Telescope was launched in Ariane 5 rocket.
Which one of the following is correct in respect of the above statements?
- Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and Statement-11 is the correct explanation for Statement-I
- Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and Statement-II is not the correct explanation for Statement-I
- Statement-I is correct but Statement II is incorrect
- Statement-I is incorrect but Statement II is correct
Q2) Consider the following pairs:
- Mission Vatsalya Scheme: Ministry of Women and Child Development.
- SWAMIH Fund: Ministry of Finance.
- Nirbhaya Fund: Ministry of Agriculture.
How many of the above pairs are correctly matched?
- Only one
- Only two
- Only three
- None
Q3) Consider the following statements
Statement-I:
Directorate General of Civil Aviation (DGCA) headquarters is in Kolkata.
Statement-II:
DGCA is a statutory body.
Which one of the following is correct in respect of the above statements?
- Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and Statement-11 is the correct explanation for Statement-I
- Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and Statement-II is not the correct explanation for Statement-I
- Statement-I is correct but Statement-II is incorrect
- Statement-I is incorrect but Statement II is correct
Comment the answers to the above questions in the comment section below!!
ANSWERS FOR ’ 6th July 2023 – Daily Practice MCQs’ will be updated along with tomorrow’s Daily Current Affairs.st
ANSWERS FOR 5th July – Daily Practice MCQs
Q.1) – c
Q.2) – b
Q.3) -b














