IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
Archives
(PRELIMS & MAINS Focus)
Syllabus
- Prelims –Important Awards
Context: President Droupadi Murmu approved 76 Gallantry awards on the eve of Independence Day.
Background:-
- These include four Kirti Chakra, all posthumous, 11 Shaurya Chakras, including five posthumous, two Bar to Sena Medals (Gallantry), 52 Sena Medals (Gallantry), three Nao Sena Medals (Gallantry) and four Vayu Sena Medals (Gallantry).
About Gallantry Awards:-
- These gallantry awards are announced twice a year.
- The first on the occasion of Republic Day and then on the occasion of Independence Day.
- Order of precedence: Param Vir Chakra, the Ashoka Chakra, the Mahavir Chakra, the Kirti Chakra, the Vir Chakra, and the Shaurya Chakra.
- All the gallantry awards may be awarded posthumously.
Historical Background:-
- Post-independence, the first three gallantry awards namely Param Vir Chakra, Maha Vir Chakra, and Vir Chakra.
- They were instituted by the Government of India on 26th January 1950.
- Thereafter, other three gallantry awardse. Ashoka Chakra Class-I, Ashoka Chakra Class-II, and Ashoka Chakra Class-III were instituted by the Government of India on 4th January 1952.
- These awards were renamed Ashoka Chakra, Kirti Chakra, and Shaurya Chakra respectively in January 1967.
MUST READ: Padma awards
SOURCE: AIR
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) Consider the following statements in respect of the 44th Chess Olympiad, 2022: (2023)
- It was the first time that Chess Olympiad was held in India.
- The official mascot was named Thambi’.
- The trophy for the winning team in the open section is the Vera Menchik Cup.
- The trophy for the winning team in the women’s section is the Hamilton-Russell Cup.
How many of the statements given above are correct?
- Only one
- Only two
- Only three
- All four
Syllabus
- Prelims – Important Personalities
Context: The founder of ‘Sulabh International’ Bindeshwar Pathak passed away. He was awarded the Padma Bhushan in 1991.
About Sulabh International:-
- Founded: 1970.
- Founded by: Dr Bindeshwar Pathak.
- HQ: New Delhi.
- Objectives: to achieve equitable sanitation and hygiene for all.
- It has been at the forefront of the Government of India’s flagship Swachh Bharat Abhiyan (Clean India Campaign) with a focus on ending open defecation.
- It stresses adopting a gender-inclusive approach in its intervention programmes.
- It has been awarded the Gandhi Peace Prize for 2016.
- ‘SULABH MUSEUM OF TOILETS’, was rated by Time magazine as One of the 10 unique museums in the world.
Areas of Functioning:-
- Equitable sanitation (Preventive Measures for Manual Scavenging)
- Rural sanitation
- Urban Sanitation
- Water for all
- Community toilets in slums (Stop Manual Scavenging)
- Fecal sludge Management
- Awareness and advocacy
- Ensuring the Dignity of Manual Scavengers
MUST READ: Manual Scavenging in India
SOURCE: AIR
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) Consider the following statements regarding mercury pollution: (2023)
- Gold mining activity is a source of mercury pollution in the world.
- Coal-based thermal power plants cause mercury pollution.
- There is no known ·safe level of exposure to mercury.
How many of the above statements are correct?
- Only one
- Only two
- All three
- None
Q.2) In India, what is the role of the Coal Controller’s Organization (CCO)? (2022)
- CCO is the major source of coal Statistics in the Government of India.
- It monitors the progress of the development of Captive Coal/ Lignite blocks.
- It hears any objection to the Government’s notification relating to the acquisition of coal-bearing areas.
- It ensures that coal mining companies deliver the coal to end users in the prescribed time.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
- 1, 2 and 3
- 3 and 4 only
- 1 and 2 only
- 1, 2 and 4
Syllabus
- Prelims –Art and Culture
Context: On the occasion of 77th Independence Day, President Droupadi Murmu on August 15 hosted ‘At Home’ reception at Rashtrapati Bhavan in Delhi.
About Rashtrapati Bhavan:-
- Location: on Rajpath, New Delhi, India.
- It is situated on Raisina Hill.
- Designed by: Sir Edwin Lutyens and Herbert Baker.
- Built in 1929.
- The Rashtrapati Bhavan (‘Presidential Palace’) is the official residence of the President of India.
- This presidential residence took seventeen years to build and was finished in 1929.
- The presidential office, guest rooms, and staff rooms are among the more than 300 rooms.
- It employs 750 people, including 245 working in the President’s Secretariat.
- The King George V’s silver chair, can be found at the Gift Museum of Rashtrapati Bhavan, where he sat at the Delhi Durbar in 1911.
- The Ashoka Hall of Rashtrapati Bhavan is used for ceremonial functions such as the swearing-in of Ministers.
- Rashtrapati Bhavan Museum
- It is a world-class museum inside the Bhavan with a high-tech story-telling format.
- It is a contextual narrative woven around original exhibits.
- Rashtrapati Bhavan Mughal Garden
- The designs for the Mughal Gardens were created by Sir Edwin Lutyens as early as 1917.
MUST READ: C.Rajagopalachari (1878-1972)
SOURCE: AIR
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) The Prime Minister recently inaugurated the new Circuit House near Somnath Temple Veraval. Which of the following statements are correct regarding Somnath Temple? (2022)
- Somnath Temple is one of the Jyotirlinga shrines.
- A description of Somnath Temple was given by Al-Biruni.
- Pran Pratishtha of Somnath Temple (installation of the present-day temple) was done by President S. Radhakrishnan.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
- 1 and 2 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 1,2 and 3
Q.2) Which one of the following statements is correct? (2021)
- Ajanta Caves lie in the gorge of the Waghora River.
- Sanchi Stupa lies in the gorge of the Chambal River.
- Pandu – lena cave shrines lie in the gorge of the Narmada River.
- Amaravati Stupa lies in the gorge of the Godavari River.
Syllabus
- Prelims – Environment and Ecology/Geography
Context: National Green Tribunal (NGT) has asked the Odisha government to stop ‘illegal’ construction in and around Tampara Lake.
Background:-
- The National Green Tribunal, Eastern Zone, has directed the Odisha government not to go ahead with ‘illegal’ construction in and around Tampara Lake, a designated Ramasar site and one of the largest picturesque freshwater lakes of the State. ( NGT)
About Tampara Lake:-
- Location: Ganjam district, Odisha.
- Formed: 1766.
- Formation: It was formed due to explosives used during a battle.
- The depression on the ground gradually filled with rainwater from the catchment flow.
- It was called “Tamp” by the British and subsequently termed “Tampra” by the locals
- it is connected to the Rushikulya River.
- It is among the most prominent freshwater lakes in Odisha.
- The wetland is an important habitat for vulnerable species such as Cyprinus carpio, common pochard (Aythya ferina), and river tern (Sterna aurantia).
- It was given Ramsar site status in 2021.
MUST READ: COP14 of Ramsar Convention on Wetlands
SOURCE: THE HINDU
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) Consider the following statements: (2019)
- Under Ramsar Convention, it is mandatory on the part of the Government of India to protect and conserve all the wetlands in the territory of India.
- The Wetlands (Conservation and Management) Rules, 2010 were framed by the Government of India based on the recommendations of the Ramsar Convention.
- The Wetlands (Conservation and Management) Rules, 2010 also encompass the drainage area or catchment regions of the wetlands as determined by the authority.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 and 2 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
Syllabus
- Prelims –Geography/Disaster Management
Context: Recently, an Earthquake jolted Dhaka, and nearby areas in Bangladesh.
Background:-
- An earthquake measuring around 5.4 on the Richter scale jolted Dhaka and some other areas in Bangladesh this evening.
About Earthquake:-
- An earthquake is the shaking or trembling of the earth’s surface.
- It is caused by the seismic waves or earthquake waves that are generated due to a sudden movement (sudden release of energy) in the earth’s crust (shallow-focus earthquakes) or upper mantle (some shallow-focus and all intermediate and deep-focus earthquakes).
- A seismograph, or seismometer, is an instrument used to detect and record earthquakes.
- Hypocentre/Focus: The point where the energy is released.
- Epicentre: The point on the surface directly above the focus.
- Isoseismic line: A line connecting all points on the surface where the intensity is the same.
Causes of Earthquakes:-
- Fault Zones
- Plate tectonics
- Volcanic activity
- Human-Induced Earthquakes
Types of Earthquakes:-
Tectonic Earthquakes
- The most common ones are tectonic earthquakes.
- The Earth is made of four basic layers (generally three): a solid crust, a hot, nearly solid mantle, a liquid outer core and a solid inner core.
- Tectonic plates (Lithospheric plates) are constantly shifting as they drift around on the viscous, or slowly flowing, mantle layer below.
- When tectonic plates move, it also causes movements at the (Anatolian Plate)
- Thus, the slipping of land along the faultline along convergent, divergent and transform boundaries cause earthquakes.
Volcanic Earthquake
- Earthquakes produced by stress changes in solid rock due to the injection or withdrawal of magma (molten rock) are called volcano earthquakes. (Volcano)
Human Induced Earthquakes
- In areas of intense mining activity, sometimes the roofs of underground mines collapse causing minor tremors. These are called collapse earthquakes.
- Ground shaking may also occur due to the explosion of chemical or nuclear devices. Such tremors are called explosion earthquakes.
MUST READ: Urban Flooding
SOURCE: AIR
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) Consider the following pairs: (2022)
The region often mentioned in the news: Country
- Anatolia Turkey
- Amhara Ethiopia
- Cabo Delgado Spain
- Catalonia Italy
How many pairs given above are correctly matched?
- Only one pair
- Only two pairs
- Only three pairs
- All four pairs
Q.2) consider the following statements: (2020)
- Jet streams occur in the Northern Hemisphere only.
- Only some cyclones develop an eye.
- The temperature inside the eye of a cyclone is nearly 10°C lesser than that of the surroundings.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 2 only
- 1 and 3 only
Syllabus
- Prelims –Economy
Context: The Centre has decided to release 50 Lakh Metric Tonnes of wheat and 25 LMT of rice through E-auctions under the Open Market Sale Scheme (Domestic) or OMSS (D) scheme.
About Open Market Sale Scheme scheme (OMSS):-
- Launched: 1965.
- Ministry: Ministry of Agriculture.
- Implementing Agency: Food Corporation of India (FCI).
- Objectives: to enhance the supply of food grains (ensuring food security) during the lean season and thereby moderate the open market prices (controlling inflation), especially in the deficit regions.
Salient Features of OMSS:-
- The purpose of OMSS is to dispose of surplus stocks of wheat and rice held by FCI and to regulate the prices of wheat in the open market.
- Under the OMSS, the FCI from time to time sells surplus food grains from the central pool, especially wheat and rice in the open market to traders, bulk consumers, retail chains, etc., at predetermined prices.
- The FCI does this through e-auctions where open market bidders can buy specified quantities.
- FCI conducts weekly auctions for the OMSS for wheat on the platform of the National Commodity and Derivatives Exchange Limited (NCDEX).
- NCDEX: a commodity exchange platform in India that provides a platform for trading in various agricultural and other commodities.
- States are also allowed to procure food grains through the OMSS without participating in the auctions, for their needs.
Revision of OMSS:-
- The Centre decided to restrict the quantity that a single bidder can purchase from 3,000 metric tonnes (MT) to 10-100 MT.
- This was done to accommodate more small and marginal buyers, curb retail prices as allowing smaller bids should ideally break monopolies of bulk buyers, allowing more competitive bids by small buyers
Steps Taken by States:-
- States are considering alternative methods of obtaining wheat and rice.
- For example, TN is trying to purchase rice from government agencies other than FCI.
MUST READ: Agriculture Infrastructure Fund (AIF)
SOURCE: AIR
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) Consider the following statements: (2023)
- The Government of India provides Minimum Support Price for niger( Guizotia aoyssinica) seeds.
- Niger is cultivated as a Kharif crop.
- Some tribal people in India use niger seed oil for cooking.
How many of the above statements are correct?
- Only one
- Only two
- All three
- None
Q.2) Which one of the following countries has been suffering from decades of civil strife and food shortages and was in the news in the recent past for its very severe famine? (2023)
- Angola
- Costa Rica
- Ecuador
- Somalia
Cloudbursts
Syllabus
- Mains – GS 1 (Geography)
Context: Recently, cloudbursts have been reported from several places in India.
About cloudbursts:
- A cloudburst is a localized but intense rainfall activity.
- According to the India Meteorological Department (IMD) a cloudburst features very heavy rainfall over a localized area at a very high rate of the order of 10 cm per hour featuring strong winds and lightning over a geographical region of approximately 20 to 30 Sq. Kms.
- By this definition, 5 cm of rainfall in a half-hour period over the same area would also be categorized as a cloudburst.
Occurrence:
- The relative humidity and cloud cover is at the maximum level with low temperature and slow winds because of which a high amount of clouds may get condensed at a very rapid rate and result in a cloudburst.
- As temperatures increase, the atmosphere can hold more and more moisture and this moisture comes down as a short very intense rainfall for a short duration probably half an hour or one hour resulting in flash floods in the mountainous areas and urban floods in the cities.
Cloudburst are different from Rainfall:
- Rain is condensed water falling from a cloud while cloudburst is a sudden heavy rainstorm.
- Rain over 100mm per hour is categorised as a cloudburst.
- The cloudburst is a natural phenomenon, but occurs quite unexpectedly, very abruptly, and rather drenching.
Impact of Climate Change:
- Several studies have shown that climate change will increase the frequency and intensity of cloudbursts in many cities across the globe.
- In May 2021, the World Meteorological Organization noted that there is about a 40% chance of the annual average global temperature temporarily reaching 1.5°C above the pre-industrial level in at least one of the next five years.
- It added that there is a 90% likelihood of at least one year between 2021 and 2025 becoming the warmest on record and dislodge 2016 from the top rank.
Impacts of Cloudburst:
- Flooding: A cloudburst can have a devastating impact triggering flash floods. These floods can cause uprooting of trees and movement of boulders and other debris.
- Damage to infrastructure: Cloudbursts can also damage houses, roads, loss of bridges because of the sheer force in which the downpour occurs.
- Landslides: Sudden heavy rain caused by cloudbursts in hilly and mountainous areas can trigger landslides.
- Another effect of cloudbursts is the damage they can cause to trees, plants, and crops, loss of arable land, livestock.
Cloudburst prone areas in India:
- Cloudbursts in India occur mostly over the rugged terrains of the Himalayas, the Western Ghats, and northeastern hill States of India.
- The heavy spells of rain on the fragile steep slopes trigger landslides, debris flows, and flash floods, causing large-scale destruction and loss of people and property.
- On July 8, 2022, flash floods occurred in the Lidder Valley en route to Amarnath Temple in Jammu and Kashmir, taking the lives of several pilgrims.
- Strong monsoon wind surges along the coast can also result in cloudbursts, as in the case of Mumbai (2005) and Chennai (2015).
- Coastal cities are particularly vulnerable to cloudbursts since the flash floods make the conventional storm water and flood management policies in these cities dysfunctional.
Measures to prevent and reduce the devastating impacts of cloudbursts:
- Regulation of construction activities along riverbanks with special consideration to water level during heavy rainfall.
- Strengthening of embankments, barrages and dams to constrain and regulate water flow.
- Localized planning taking into consideration the ecologically fragile nature of the region and involving the local communities.
- Regulate infrastructure projects and preserve the sanctity of eco-sensitive zones.
- Better forecasting by IMD and incorporation of advanced technology to monitor and predict extreme weather events can enable early warning, evacuation and preparedness
- Adoption of ecofriendly policies and eco-sensitive tourism for development of the region.
- Incorporation of disaster management and prevention into the developmental planning process.
- It is seen that more cloudbursts are happening in Himalayan region because the decadal temperature rise in the Himalayan region is higher than the global rate of rising temperatures.
Is it possible to forecast cloudburst?
- The India Meteorological Department forecasts rainfall events well in advance, but it does not predict the quantum of rainfall — in fact, no meteorological agency does.
- The forecasts are for a relatively large geographical area, usually a region, a state, a meteorological sub-division, or at best a district. As they zoom in over smaller areas, the forecasts get more and more uncertain.
- Therefore, specific cloudburst events cannot be forecast.
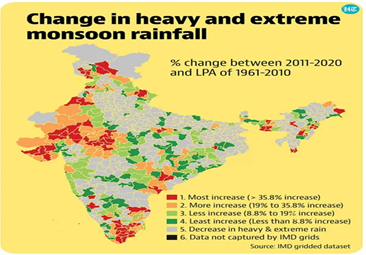
Way Forward:
Climate change is projected to increase the frequency and intensity of cloudbursts worldwide. A 1-degree Celsius rise in temperature may correspond to a 7-10% increase in moisture and rainfall. As the moisture holding capacity of air increases, it results in prolonged dry periods intermittent with short spells of extreme rains and thus, deeper cumulonimbus clouds form, and the chances of cloudbursts increase.
Thus, urgent action and policies are needed to protect lives and property from extreme events that will amplify as the global temperature change doubles.
Source: Indian Express
Syllabus
- Mains – GS 2 (Polity and Governance)
Context: The Chief Election Commissioner and other Election Commissioners (Appointment, Conditions of Service and Term of Office) Bill, 2023, was recently introduced in Rajya Sabha.
Key Features of the Bill
- Election Commission: As per Article 324 of the Constitution, the Election Commission consists of the Chief Election Commissioner (CEC) and such number of other Election Commissioners (ECs), as the President may decide.
- The CEC and other ECs are appointed by the President. The Bill specifies the same composition of the Election Commission.
- It adds that the CEC and other ECs will be appointed by the President on the recommendation of a Selection Committee.
- Selection Committee: The Selection Committee will consist of: (i) the Prime Minister as Chairperson, (ii) the Leader of the Opposition in Lok Sabha as member, and (iii) a Union Cabinet Minister nominated by the Prime Minister as member.
- If the Leader of Opposition in Lok Sabha has not been recognised, the leader of the single largest opposition party in Lok Sabha will assume the role.
- Search Committee: A Search Committee will prepare a panel of five persons for the consideration of the Selection Committee.
- The Search Committee will be headed by the Cabinet Secretary. It will have two other members, not below the rank of Secretary to the central government, having knowledge and experience in matters related to elections.
- The Selection Committee may also consider candidates who have not been included in the panel prepared by the Search Committee.
- Qualification of CEC and ECs: Persons who are holding or have held posts equivalent to the rank of Secretary to the central government will be eligible to be appointed as CEC and ECs.
- Such persons must have expertise in managing and conducting elections.
- Salary and allowances: The 1991 Act provides that the salary of the ECs will be equal to that of a Supreme Court judge.
- The Bill provides that salary, allowance, and service conditions of the CEC and other ECs will be the same as that of the Cabinet Secretary.
- Term of office: The 1991 Act mandates that the CEC and other ECs will hold office for a term of six years or until they reach the age of 65 years, whichever is earlier.
- If an EC is appointed as the CEC, his total term cannot exceed six years. The Bill retains the same tenure.
- Further, under the Bill, the CEC and other ECs will not be eligible for re-appointment.
- Conduct of business: All business of the Election Commission is to be conducted unanimously. In case of difference of opinion between the CEC and the other ECs on any matter, it shall be decided through majority.
- Removal and resignation: Under Article 324 of the Constitution, the CEC can only be removed from his office in a manner similar to that of a Supreme Court judge.
- This is done through an order of the President, based on a motion passed by both Houses of Parliament in the same session.
- The motion for removal must be adopted with: (i) majority support of total membership of each House, and (ii) at least two-thirds support from members present and voting. An EC can only be removed from office on the recommendation of the CEC.
- The Bill retains this removal procedure.
- Further, the 1991 Act provides that the CEC and other ECs may submit their resignation to the President.
- The Bill has the same provision.
Significance of the bill:
- The Election Commission, led by a CEC and two other commissioners, is much too critical a body for the functioning of India’s democracy and integrity of elections to leave exposed to charges of external influence.
- A Supreme Court judgement stated that the Prime Minister, Leader of Opposition in the Lok Sabha and Chief Justice of India (CJI) would decide the EC’s leadership—until the Centre came up with a law.
Concerns about the bill:
Balance of Power:
- The Prime Minister and a Cabinet Minister (nominated by the Prime Minister) forming part of the three-member committee, the Leader of Opposition is left with a minority vote even before the process begins.
- This raises questions about the balance of power within the committee and whether the selection process truly ensures independence or remains skewed in favour of the Executive.
Impact on Electoral Governance:
- The proposed changes may have implications for the autonomy and functioning of the ECI.
- The independence of the Election Commission is crucial for ensuring impartiality and integrity in the conduct of elections.
- Any perceived influence of the Executive in the selection process might raise concerns about the EC’s ability to carry out its responsibilities without bias.
Alignment with Framers’ Intentions:
- The SC, in its previous ruling, emphasized that the framers of the Constitution intended for an independent body to oversee elections.
- Critics of the proposed Bill raise questions about whether the new composition of the Selection Committee aligns with the framers’ objective of creating an impartial and independent body responsible for elections.
Way Forward:
The independent V-Dem Institute in Sweden, which compares democracies worldwide, has downgraded India to an “electoral autocracy”, citing the loss in autonomy of the ECI. The need for a selection process that embodies insulation from executive preponderance makes sense. A non-partisan and independent ECI is a sine qua non for the robustness of electoral democracy.
Source: The Hindu
Must Read: UPSC CSE 2024
Practice MCQs
Q1) Consider the following pairs:
| Ramsar sites | Location |
| 1.Tampara Lake | Jharkhand |
| 2.Deepor Beel | Assam |
| 3.Hirakud Reservoir | Rajasthan |
How many of the above pairs are correctly matched?
- Only one
- Only two
- All three
- None
Q2) Consider the following statements
Statement-I:
Order of precedence of gallantry Awards is Param Vir Chakra, the Mahavir Chakra, the Kirti Chakra, the Ashoka Chakra, the Vir Chakra, and the Shaurya Chakra.
Statement-II:
All the gallantry awards may be awarded posthumously.
Which one of the following is correct in respect of the above statements?
- Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and Statement-II is the correct explanation for Statement-I
- Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and Statement-II is not the correct explanation for Statement-I
- Statement-I is correct but Statement II is incorrect
- Statement-I is incorrect but Statement II is correct
Q3) Consider the following statements
Statement-I:
A line connecting all points on the surface where the intensity is the same is called an Isoseismic line.
Statement-II:
The point where the energy is released is called the epicentre.
Which one of the following is correct in respect of the above statements?
- Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and Statement-II is the correct explanation for Statement-I
- Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and Statement-II is not the correct explanation for Statement-I
- Statement-I is correct but Statement II is incorrect
- Statement-I is incorrect but Statement II is correct
Mains Practice Questions
Q.1) What is a cloudburst? What is the mechanism behind the occurrence of the cloudbursts? Discuss the measures to prevent and reduce the devastating impacts of cloudbursts. (250 words)
Q.2) Discuss the role, powers, and responsibilities of the Chief Election Commissioner (CEC) in ensuring free and fair elections in India. Examine the significance of the autonomy of the Election Commission of India (ECI) and its impact on the democratic process, with reference to recent electoral reforms and challenges faced by the commission. (250 words)
Comment the answers to the above questions in the comment section below!!
ANSWERS FOR ’ 16th August 2023 – Daily Practice MCQs’ will be updated along with tomorrow’s Daily Current Affairs.st
ANSWERS FOR 14th August – Daily Practice MCQs
Q.1) – c
Q.2) – a
Q.3) – d











