IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
Archives
(PRELIMS & MAINS Focus)
Syllabus
- Prelims –Sports
Context: The Indian men’s visually impaired team won silver medal after defeat against Pakistan in the final of the men’s T20 cricket event at the International Blind Sports Federation (IBSA) World Games 2023.
About International Blind Sports Federation (IBSA) World Games 2023:-
- Convened on: 18th – 27th August 2023.
- Venue: Birmingham, Great Britain.
- It is the world’s biggest gathering of athletes with visual impairments.
- Events: Powerlifting, judo, goalball, football, chess, tenpin bowling, shooting, and showdown, as well as cricket, archery, and tennis, form the programme.
- The men’s and women’s IBSA Blind Football World Championships and the partially sighted World Championships will take place as part of the event.
- The World Games are normally conducted every four years.
- It has three Paralympic and eight non-Paralympic sports.
- Last IBSA World Games: Seoul, South Korea, in 2015.
About IBSA:-
- Founded: 1981.
- HQ: Bonn, GERMANY.
- IBSA’s first congress was held at the UNESCO headquarters in Paris, France.
- It was attended by 30 countries.
- IBSA is the world’s leading organization for the development of sports for people with visual impairments.
- It has more than 100 members in every region of the world.
- It is involved with sports that are on the Paralympic programme such as athletics, swimming, and shooting.
- IBSA is a member of the International Paralympic Committee with full voting rights.
MUST READ: Chess Olympiad
SOURCE: AIR
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) Consider the following statements in respect of the 44th Chess Olympiad, 2022: (2023)
- It was the first time that Chess Olympiad was held in India.
- The official mascot was named Thambi’.
- The trophy for the winning team in the open section is the Vera Menchik Cup.
- The trophy for the winning team in the women’s section is the Hamilton-Russell Cup. ·
How many of the statements given above are correct?
- Only one
- Only two
- Only three
- All four
Q.2) Consider the following statements in respect of the 32nd Summer Olympics: (2021)
- The official motto for this Olympics is ‘A New World’.
- Sports climbing, Surfing, Skateboarding, Karate, and Baseball are included in this Olympics.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 and 2
Syllabus
- Prelims –Environment and Ecology
Context: The State of India’s Birds report 2023 was released recently.
Key Highlights of the report:-
- 39% of species show clear declines over the past decades.
- 178 species classified as of High Conservation Priority, and require immediate attention.
- Raptors, migratory shorebirds, and ducks have experienced the most significant declines.
- Long-distance migratory birds, such as those from Eurasia and the Arctic, have suffered significant declines.
- Several species like the Indian Peafowl, Rock Pigeon, Asian Koel, and House Crow are thriving and increasing in both abundance and distribution.
- 150% increase in the abundance of peafowl across the country over the past decades.
- Birds with diets focused on vertebrates and carrion have seen notable declines due to harmful pollutants present in these food resources.
- The report emphasizes the decline of species endemic to the Western Ghats and Sri Lanka biodiversity hotspots. (Global Biodiversity Framework)
About the State of India’s Birds Report 2023:-
- Developed by: State of India’s Birds Partnership.
- State of India’s Birds Partnership: a group of 13 government and non-government organizations.
- Objective: to assess the conservation status of the majority of species that regularly occur in the country.
- This year, the report assessed the “status of 942 bird species.
- The earlier assessment carried out in 2020 had listed 15 species of conservation priority.
Threats to Bird Species:-
- The report mentions threats like forest degradation, urbanization, and energy infrastructure.
- Birds are highly impacted by environmental pollutants, climate change’s impacts on migratory species, avian diseases, and illegal hunting and trade. (Bird flu)
MUST READ: American foulbrood (AFB) disease
SOURCE: THE HINDU
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) The H1N1 virus is sometimes mentioned in the news with reference to which one of the following diseases? (2015)
- AIDS
- Bird flu
- Dengue
- Swine flu
Q.2) Which of the following is not a bird? (2022)
- Golden Mahseer
- Indian Nightjar
- Spoonbill
- White Ibis
Syllabus
- Prelims –Polity
Context: Recently, the Supreme Court observed that abrogated Article 35A in Jammu and Kashmir had negative affect on the fundamental rights of the people especially those who were not from Jammu and Kashmir.
Background:-
- The Supreme Court observed this while hearing the matter of the abrogation of Article 370 and the restructuring of J& K into two Union territories.
- The Constitution bench was headed by Chief Justice of India Dhananjaya Y Chandrachud.
About Article 35A:-
- Article 35A was part of Article 370, which granted special status to Jammu and Kashmir until it was scrapped in 2019.
- Article 370: It allowed the state its own constitution, a separate flag, and independence over all matters except foreign affairs, defense, and communications.
- Article 35-A deals with empowering the Jammu and Kashmir Constitution to define “permanent residents” of the state.
- It also empowers the Jammu and Kashmir Legislature to confer on permanent residents or state subjects special rights and privileges.
- These include rights and privileges in public sector jobs, acquisition of property in the state, scholarships, and other public aid and welfare.
- It disallows people from outside the state from:-
- Buying or owning immovable property there
- Settling permanently
- Availing themselves of state-sponsored scholarship schemes.
- Only the Jammu-Kashmir assembly can change the definition of Permanent Residents through a law ratified by a two-thirds majority.
Historical Background:-
- The law came into place during the Dogra times when Maharaja Hari Singh passed it in 1927.
- It was enacted to prevent the influx of Punjabis into the state.
- Later, in 1954, an amended version of the law was added through the Constitution (Application to Jammu and Kashmir) Order, 1954 issued by the President of India (Rajendra Prasad) on aid and advice of Jawaharlal Nehru’s cabinet.
- It replaced the 1952 Delhi Agreement between Nehru and the then Prime Minister of J&K Sheikh Abdullah, which extended Indian citizenship to the ‘State subjects’ of J&K.
- Under the Jammu and Kashmir Constitution, which was adopted on November 17, 1956, a permanent resident is one who has been living in the State as of May 14, 1954, or who has been a resident of the state for 10 years, and has “lawfully acquired immovable property in the state”.
Controversy regarding Article 35A:-
- Article 35 A is believed to be incorporated unconstitutionally, dodging Article 368 which emancipates only the Parliament to amend the constitution.
- Article 368: deals with the powers of Parliament to amend the Constitution and its procedure.
- It is considered against the “very spirit of oneness of India” as it created a “class within a class of Indian citizens” by treating non-permanent residents of J&K as ‘second class’ citizens.
- Restricting citizens from other States from getting employment or buying property within J&K is a violation of fundamental rights under Articles 14, 19, and 21 of the Indian Constitution. (Article 19)
- There is also probable discrimination on the basis of gender – since it denies property rights to children of women who marry those from outside the state.
Current Status:-
- On 5th of August 2019, the President of India promulgated the Constitution (Application to Jammu and Kashmir) Order, 2019.
- The order effectively revoked the special status accorded to Jammu and Kashmir under the provision of Article 370.
- It “superseded the Constitution (Application to Jammu and Kashmir) Order, 1954” under which Article 35A was added to the Indian Constitution. (Jammu and Kashmir Reorganisation (Adaptation of State Laws) Order, 2020)
MUST READ: Passport as a fundamental right under Article 21
SOURCE: HINDUSTAN TIMES
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) Consider the following organizations/bodies in India: (2023)
- The National Commission for Backward Classes
- The National Human Rights Commission
- The National Law Commission
- The National Consumer Disputes Redressal Commission
How many of the above are constitutional bodies?
- Only one
- Only two
- Only three
- All four
Q.2) Which of the following is/are the exclusive power(s) of Lok Sabha? (2022)
- To ratify the declaration of Emergency
- To pass a motion of no-confidence against the Council of Ministers
- To impeach the President of India
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
- 1 and 2
- 2 only
- 1 and 3
- 3 only
Syllabus
- Prelims – Environment and Ecology
Context: The 10th plenary of the Intergovernmental Science-Policy Platform on Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services (IPBES) was held recently.
About the 10th plenary of IPBES:-
- Dates: 28 August – 2 September 2023.
- Location: Bonn, Germany.
- Agenda: the scientific assessment report on “Invasive Alien Species and their Control”.( Invasive Species)
- The focus of IPBES 10 will be the thematic assessment of invasive alien species and their control, whose preparation was approved at IPBES 8.
- IPBES10 is the first meeting of this global body since the adoption of the Kunming-Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework (GBF).
About Intergovernmental Science-Policy Platform on Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services (IPBES):-
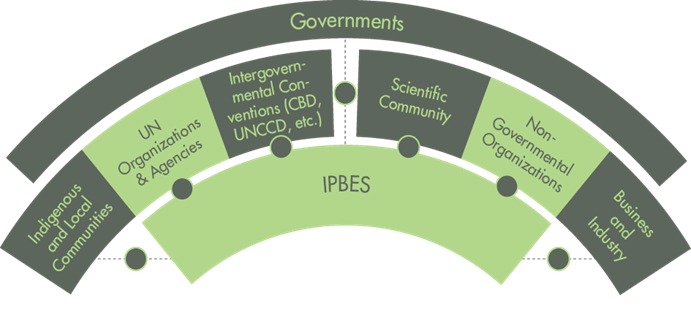
IMAGE SOURCE: IPEB
- Established: 2012.
- HQ: Bonn, Germany.
- IPBES Member States: 143.
- It is an independent intergovernmental body.
- It provides evidence-based and policy-relevant information on biodiversity and ecosystem services. ( Biodiversity conservation)
- Observer states and stakeholders also participate in Plenary sessions.
- IPBES assesses the state of biodiversity and the ecosystem services it provides to society, in response to requests from decision-makers.
- It is not a United Nations body. (UN Biodiversity Summit)
- The United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) provides secretariat services to IPBES. (UNEP’s Emission Gap Report 2022)
IPBES structure:-
- Plenary:
- The governing body of IPBES.
- It is made up of the representatives of IPBES member States.
- It usually meets once per year.
- Observers: Any State not yet a member of IPBES.
- Bureau: Comprising the IPBES Chair, four Vice-Chairs, and five additional officers who oversee the administrative functions of IPBES.
- Multidisciplinary Expert Panel (MEP): Five expert participants from each of the five UN regions, overseeing all IPBES scientific and technical functions.
- Stakeholders: All contributors to and end-users of the IPBES outputs.
- Expert Groups & Taskforces: Selected scientists and knowledge holders carrying out the IPBES assessments and other deliverables.
- Secretariat: Ensures the efficient functioning of IPBES through support to the Plenary, Bureau, and MEP, as well as implementing the Platform’s work and administrative functions.
Functions of IPEBS:-
- Assessments: On specific themes (e.g. “Pollinators, Pollination and Food Production”); methodological issues (e.g. “Scenarios and Modelling); and at both the regional and global levels (e.g. “Global Assessment of Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services”).
- Policy Support: Identifying policy-relevant tools and methodologies, facilitating their use, and catalyzing their further development.
- Building Capacity & Knowledge: Identifying and meeting the priority capacity, knowledge, and data needs of our member States, experts, and stakeholders.
- Communications & Outreach: Ensuring the widest reach and impact of our work.
MUST READ: Expansion of the Invasive Plants
SOURCE: DOWN TO EARTH
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) ‘Invasive Species Specialist group’ (that develops Global Invasive Species Database) belongs to which one of the following organizations? (2023)
- The International Union for Conservation of Nature
- The United Nations Environment Programme
- The United Nations World Commission for Environment and Development
- The World Wide Fund for Nature
Q.2) Consider the following statements: (2023)
Statement-I:
Carbon markets are likely to be one of the most widespread tools in the fight against climate change.
Statement-II:
Carbon markets transfer resources from the private sector to the State.
Which one of the following is correct in respect of the above statements?
- Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and Statement-II is the correct explanation for Statement-I
- Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and Statement-II is not the correct explanation for Statement-I
- Statement-I is correct but Statement II is incorrect
- Statement-I is incorrect but Statement II is correct
Syllabus
- Prelims –Art and Culture
Context: Artists recently performed Seethakali folk art outside Kerala for the first time.
About Seethakali folk art:-
- It is a centuries-old folk art form.
- Origin: Perinad in Kollam district, Kerala.
- This art form was first performed some 150 years back by the people of Vedar and Pulayar communities.
- It is based on certain episodes taken from the Indian epic Ramayana.
- Mythic characters such as Rama, Seetha, Ravana, and Hanuman come alive in Seethakali performances that portray the tale of Seetha’s journey, from the time she accompanied Rama to the woods to her ascent to the heavens.
- In the early times, Seethakali was performed as part of the harvest festival Onam.
- The props and instruments used during performances are all made of natural materials like bamboo and palm leaves.
- The costumes and the make-up are loud and eye-catching.
- The characters of Rama and Laxmana appear in green since the colour is used to represent gods and goddesses in Kathakali.
MUST READ: Mohiniyattam
SOURCE: THE HINDU
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) With reference to Manipuri Sankirtana, consider the following statements: (2017)
- It is a song and dance performance
- Cymbals are the only musical instruments used in the performance
- It is performed to narrate the life and deeds of Lord Krishna
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1, 2 and 3
- 1 and 3 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1 only
Q.2) With reference to the famous Sattriya dance, consider the following statements: (2014)
- Sattriya is a combination of music, dance and drama
- It is a centuries-old living tradition of Vaishnavites of Assam
- It is based on classical Ragas and Talas of devotional songs composed by Tulsidas, Kabir and Mirabai
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 1 and 2 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
Syllabus
- Prelims –Art and Culture
Context: Recently, it was announced that a 28-ft. Nataraja bronze sculpture, from Tamil Nadu would grace the G20 summit venue in New Delhi.
Background:-
- The statue, weighing 19 tonnes, and made of eight metals: gold, silver, lead, copper, tin, mercury, iron, and zinc (Ashtadhatu).
About Nataraja:-
- It is the representation of the Hindu god Shiva during his form as the cosmic dance.
- It is represented in metal or stone in many Shaivite temples, particularly in South India.
- It is an important piece of Chola sculpture.
Features of the Nataraja:-
- The upper right hand holds the drum: it signifies the sound of creation.
- All creations spring from the great sound of the damru.
- The upper left hand holds the eternal fire: it represents the destruction. Destruction is the precursor and inevitable counterpart of creation.
- The lower right hand is raised in the gesture of Abhay Mudra signifying benediction and reassuring the devotee to not be afraid.
- The lower left hand points towards the upraised foot and indicates the path of salvation.
- Shiva is dancing on the figure of a small dwarf.
- The dwarf symbolizes ignorance and the ego of an individual.
- The matted and flowing locks of Shiva represent the flow of the river Ganges.
- In ornamentation, one ear of Shiva has a male earring while the other has a female.
- This represents the fusion of male and female and is often referred to as
- A snake is wrapped around the arm of Shiva.
- The snake symbolizes the kundalini power, which resides in the human spine in the dormant stage.
MUST READ: Shore temple
SOURCE: THE HINDU
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) Which one of the following statements about Sangam literature in ancient South India is correct? (2022)
- Sangam poems are devoid of any reference to material culture.
- The social classification of Varna was known to Sangam poets.
- Sangam poems have no reference to warrior ethics.
- Sangam literature refers to magical forces as irrational.
Q.2) The Prime Minister recently inaugurated the new Circuit House near Somnath Temple Veraval. Which of the following statements are correct regarding Somnath Temple? (2022)
- Somnath Temple is one of the Jyotirlinga shrines.
- A description of Somnath Temple was given by Al-Biruni.
- Pran Pratishtha of Somnath Temple (installation of the present-day temple) was done by President S. Radhakrishnan.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
- 1 and 2 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 1,2 and 3
Syllabus
- Prelims – Defense
Context: As per recent reports, thirty-four countries including India will participate in the joint military exercise, BRIGHT STAR-23.
About BRIGHT STAR-23:-
- Date: 31 August to 14 October 2023.
- Venue: Mohammed Naguib Military Base,
- Indian Army contingent comprising 137 personnel will participate in a military exercise.
- It is a multinational tri-services joint military exercise.
- It will be led by US CENTCOM and the Egyptian Army.
- This year 34 countries will participate in the Exercise.
- It will be the largest-ever joint military exercise in West Asia and North Africa region.
- This is the first time that the Indian Armed Force with 549 personnel participated in the exercise.
- During the exercise participating countries will share the best practices to combat emerging unconventional threats and enhance regional partnerships.
- Significance: The exercise will provide a unique opportunity for the Indian Army to share best practices and experiences with other armies aimed at enhancing defense cooperation.
MUST READ: Exercise Varuna
SOURCE: AIR
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) With reference to Home Guards, consider the following statements: (2023)
- Home Guards are raised under the Home Guards Act and Rules of the Central Government.
- The role of the Home Guards is to serve as an auxiliary force to the police in the maintenance of internal security.
- To prevent infiltration on the international border/ coastal areas, the Border Wing Home Guards Battalions have been raised in some states.
How many of the above statements are correct?
- Only one
- Only two
- All three
- None
Q.2) Recently, India signed a deal known as ‘Action Plan for Prioritization and Implementation of Cooperation Areas in the Nuclear Field’ with which of the following countries? (2019)
- Japan
- Russia
- The United Kingdom
- The United States of America
India needs comprehensive sexuality education
Syllabus
- Mains – GS 1 (Society) and GS 2 (Governance)
Context: According to the National Crime Records Bureau (NCRB), 51,863 cases were reported under the Protection of Children from Sexual Offences Act in 2021; of them, 33,348 or 64% were of sexual assault.
- In this context, understanding sexual consent is important not only to learn about violation and abuse, but also to maintain healthy relationships.
About sexual consent:
- It is a mutual agreement between individuals to engage in any form of intimate activity.
- It is essential for maintaining healthy relationships and understanding boundaries.
- Consent can be given, asked for, and withdrawn at any point.
- Many teenagers and young adults in India may not fully understand this concept.
- According to the United Nations, comprehensive sexuality education is a curriculum-based process of teaching and learning about the cognitive, emotional, physical and social aspects of sexuality.
- There is a need for clear language and education in regional languages to discuss and teach about consent and its significance.
Significance of sexual education:
- Rights of Individual and sexuality: According to the World Health Organization (WHO), with comprehensive sexuality education, young people will be better informed of their rights and sexuality, and will be more likely to engage in sexual activity later.
- Sexual consent: Understanding sexual consent is important not only to learn about violation and abuse, but also to maintain healthy relationships.
- Lead to early awareness: The UN global guidance recommends starting comprehensive sexuality education from the age of five along with formal education.
- This means that young children will be taught about their bodies, emotions, the basic principles of consent, and how to deal with violence, bullying or abuse.
- Reducing the intimate partner violence: The ramifications of a comprehensive sexuality education are far-reaching, especially in the matter of intimate partner violence.
- Sexual habits and health: Studies have shown that sexually aware students are most likely to say no to unprotected sex.
- Through sex education, teenagers can be taught the positive and negative sides of sex. They can learn about sexually transmitted disease, teenage unintended pregnancy, and emotional effects of sex.
- Educating women on sex: When women are educated and aware of sexual wellness, they make better reproductive decisions.
- This means lesser teenage pregnancies, child mortality, or sexually transmitted infections.
- The Kerala High Court was informed that awareness about the Protection of Children from Sexual Offences (POCSO) Act would be included in the curriculum from 2024-25.
- This reflects an effort to integrate relevant legal and awareness components into the education system.
Challenges associated with sexual education in India:
- Data vs reality: The research has found that more than 90% of students think sex education in school curriculum is important. 60% also stated that they had exposure to sex education in school.
- However, only 45% said that they had received appropriate sex education.
- Lack of interest by the State governments: Several State governments and certain sections of society in India have adopted an ostrich-like approach to comprehensive sexuality education.
- The governments that it sexualises children, they have either watered down the existing programmes or withdrawn them on the grounds that they violate “Indian values”.
- Patriarchal in the society: Traditional values are often shaped by patriarchal and hierarchical social structures.
- Mass media often propagates such values and it negatively affects young adults of all genders.
- Lack of teacher’s education: Teachers reported that they lacked the knowledge to talk about diverse topics with the existing programmes along with sexual education.
- Lack of sexual awareness to women and young girls: The victims of poor sexual awareness are primarily women.
- It is women who suffer most because of social taboo, menstrual issues, or unwarranted pregnancies.
- Women also have lower awareness and knowledge around contraception, sex, pregnancy, and reproductive health.
Suggestive measures:
- United Nations (UN) recommends comprehensive sexuality education, which is a curriculum-based process of teaching and learning about the cognitive, emotional, physical and social aspects of sexuality.
- Role of state govts: In India, the responsibility of sexuality education is vested with the State governments.
- Each State has the freedom to develop creative curriculums within the framework suggested by the UNFPA.
- Role of Teachers: NCRB data show that it is necessary for schools to impart comprehensive sexuality education not only to children, but also to parents and caregivers.
- Skill training for teachers: According to the UNESCO 2021 Global Status Report on ‘the journey towards comprehensive sexuality education’, capacity-building of teachers is critical as the curriculum requires non-intuitive participatory pedagogies.
- Educating the parents: The sex education advice for parents is that they educate themselves first.
- They should also let go of their inhibitions and reservations.
- Regional languages to discuss the concept of sexual consent: While the concept of sexual consent is evolving through criminal jurisprudence, the term itself may have been borrowed from English or other Western languages.
- With the non-English language speaking population becoming substantial, an explicit creation of vocabulary in regional languages to discuss the concept of sexual consent and its nuances is urgently required.
A case study from Jharkhand demonstrates the successful mainstreaming of a school-based program, Udaan, which began as an Adolescent Reproductive and Sexual Health initiative and was later integrated into the education department.
Source: The Hindu
Syllabus
- Mains – GS 2 (Governance) and GS 3 (Economy)
Context: Recently, Pradhan Mantri Jan Dhan Yojana (PMJDY)- a revolutionary financial inclusion programme completed nine years of successful implementation.
About Pradhan Mantri Jan Dhan Yojana (PMJDY):
- Launched in 2014, the Pradhan Mantri Jan Dhan Yojana (PMJDY) is a scheme run by the Ministry of Finance of the Government of India.
- This scheme assists underprivileged and needy sections of our society with simple access to financial services such as remittance, credit, insurance, pension, savings, and deposit accounts.
Basic tenets of the scheme:
- Banking the unbanked: Opening of basic savings bank deposit (BSBD) account with minimal paperwork, relaxed KYC, e-KYC, account opening in camp mode, zero balance and zero charges.
- Securing the unsecured: Issuance of Indigenous Debit cards for cash withdrawals & payments at merchant locations, with free accident insurance coverage of Rs. 2 lakhs
- Funding the unfunded: Other financial products like micro-insurance, overdraft for consumption, micro-pension & micro-credit.
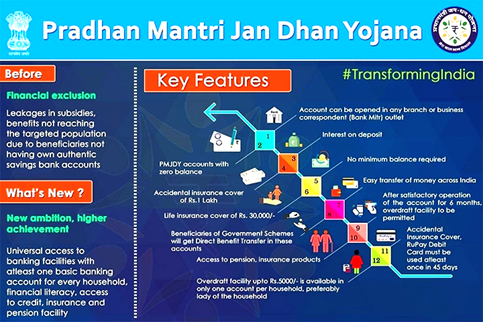
Features of the scheme:
- Basic savings bank accounts with overdraft facility of Rs. 10,000/- to every eligible adult.
- Creation of Credit Guarantee Fund.
- After 28.8.2018, free accidental insurance cover on RuPay cards increased from Rs. 1 lakh to Rs. 2 lakhs.
- OD limit doubled from Rs 5,000/- to Rs 10,000/-; OD upto Rs 2,000/- (without conditions) with Increase in upper age limit for OD from 60 to 65 years.
Significance of PMJDY:
- Catalyst for economic initiatives: PMJDY has acted as a catalyst for various people-centric economic initiatives, including direct benefit transfers, COVID-19 financial assistance, PM-KISAN (an income support scheme for farmers), and increased wages under MGNREGA (a rural employment guarantee program).
- The existence of a bank account, which PMJDY has facilitated, serves as the foundational step for these initiatives to reach beneficiaries efficiently and directly.
- Significant role played during lockdown: The agility and responsiveness of PMJDY were evident during the COVID-19 pandemic and the subsequent nationwide lockdown.
- Within just 10 days of the lockdown, over 20 crore women PMJDY accounts received financial assistance of Rs. 500 per month for three months through the Direct Benefit Transfer (DBT) mechanism.
- This rapid disbursement of funds showcased the program’s ability to provide swift financial support to vulnerable sections of society during crises.
- Widespread adoption: PMJDY has achieved remarkable success in terms of adoption.
- One out of every two accounts opened between March 2014 and March 2020 was a PMJDY account, underscoring the program’s popularity and effectiveness.
- Efficiency and transparency of DBTs: PMJDY has played a significant role in ensuring the efficiency and transparency of Direct Benefit Transfers (DBTs).
- DBTs via PMJDY accounts have been successful in delivering financial security to beneficiaries while preventing leakages and ensuring that funds reach their intended recipients.
- Transformation of financial landscape: One of the most noteworthy impacts of PMJDY is its role in bringing the unbanked population into the formal banking system.
Source: AIR
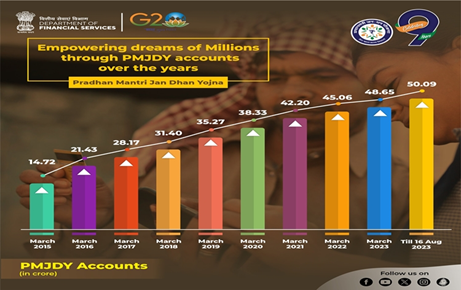
Concerns associated with PMJDY:
- Lack of banking connectivity: Bank account penetration is growing but in rural areas physical connectivity to the banking system remains limited, and mobile money providers have not yet solved this last mile problem.
- Financial Literacy: Enhancing financial literacy is a long-term endeavour.
- Providing easily understandable financial education, workshops, and guidance can help individuals better understand banking services, manage their money, and make informed decisions.
- Data privacy and security: As digital transactions increase, the risk of data breaches and privacy concerns also rises.
- Implementing robust cybersecurity measures, educating users about safe digital practices, and stringent data protection regulations are vital to address this challenge.
- Sustainability of BC Model: Business Correspondents play a crucial role in bridging the gap between formal financial institutions and rural communities.
- Ensuring their sustainability involves fair compensation, training, and monitoring mechanisms to maintain quality service delivery.
Way forward:
The PMJDY has made multifaceted achievements in the past nine years, from extending banking access to rural and urban populations to empowering women and enabling welfare distribution, underscore its transformative impact. PMJDY can play a pivotal role in shaping a more inclusive and robust financial landscape in India. The key lies in the continuous adaptation and evolution of the initiative to meet the changing needs of the population it aims to serve.
Source: AIR
Practice MCQs
Q1) Consider the following pairs:
| Birds | IUCN Status |
| 1.Himalayan Quail | Vulnerable |
| 2.Siberian Crane | Endangered |
| 3.Pink-headed Duck | Least Concern |
How many of the above pairs are correctly matched?
- Only one
- Only two
- All three
- None
Q2) Consider the following statements
Statement-I:
United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) provides secretariat services to IPBES.
Statement-II:
IPBES is a United Nations body.
Which one of the following is correct in respect of the above statements?
- Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and Statement-II is the correct explanation for Statement-I
- Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and Statement-II is not the correct explanation for Statement-I
- Statement-I is correct but Statement II is incorrect
- Statement-I is incorrect but Statement II is correct
Q3) Consider the following statements
Statement-I:
The Constitution (Application to Jammu and Kashmir) Order, 2019 effectively revoked the special status accorded to Jammu and Kashmir under the provision of Article 370.
Statement-II:
Article 370 allowed the state its constitution.
Which one of the following is correct in respect of the above statements?
- Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and Statement-II is the correct explanation for Statement-I
- Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and Statement-II is not the correct explanation for Statement-I
- Statement-I is correct but Statement II is incorrect
- Statement-I is incorrect but Statement II is correct
Mains Practice Questions
Q.1) Discuss the significance of Comprehensive Sexuality Education (CSE) and its challenges in India. (250 words)
Q.2) Pradhan Mantri Jan Dhan Yojana (PMJDY) is necessary for bringing unbanked to the institutional finance fold. Do you agree with this for financial inclusion of the poorer section of the Indian society? Give arguments to justify your opinion. (250 words)
Comment the answers to the above questions in the comment section below!!
ANSWERS FOR ’ 30th August 2023 – Daily Practice MCQs’ will be updated along with tomorrow’s Daily Current Affairs.st
ANSWERS FOR 29th August – Daily Practice MCQs
Q.1) – b
Q.2) – c
Q.3) – a











