IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
Archives
(PRELIMS & MAINS Focus)
Syllabus
- Prelims –SPORTS
Context: Unnati Hooda won the women’s singles title at Abu Dhabi Masters 2023.
Background:-
- This is her second BWF Super 100 World Tour title.
- She became the youngest Indian to clinch a BWF title last year at 14 years of age.
About Abu Dhabi Masters 2023:-

IMAGE SOURCE: WorldAtlas
- Date: 17 – 22 OCTOBER, 2023.
- Venue: ADNEC Marina Hall, Abu Dhabi, UAE.
- Abu Dhabi Masters 2023 is the first-ever International badminton spectacle in the capital city.
- It will take place under the esteemed patronage of Shaikh Nahyan bin Mubarak Al Nahyan, the UAE Badminton Federation, in partnership with 316 Sports Services. (Grand Slam)
- This historic occasion promises to be a thrilling showcase of talent, skill, and sportsmanship, bringing together 200 professional players from around the world. (Sports Code)
MUST READ: Chess Olympiad
SOURCE: AIR
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) Consider the following statements in respect of the 44th Chess Olympiad, 2022: (2023)
- It was the first time that the Chess Olympiad was held in India.
- The official mascot was named Thambi’.
- The trophy for the winning team in the open section is the Vera Menchik Cup.
- The trophy for the winning team in the women’s section is the Hamilton-Russell Cup. ·
How many of the statements given above are correct?
- Only one
- Only two
- Only three
- All four
Q.2) Consider the following statements in respect of the 32nd Summer Olympics: (2021)
- The official motto for this Olympics is ‘A New World’.
- Sports climbing, Surfing, Skateboarding, Karate, and Baseball are included in this Olympics.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 and 2
Syllabus
- Prelims –SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Context: As per recent research, emerging drug resistance in eastern Africa is hindering the fight against malaria.
Key findings:-
- The treatment of malaria in eastern Africa is encountering a significant challenge as the parasites have started developing resistance to artemisinin, the core component used for treating the disease, according to a new study.
- Artemisinin-based combination therapy (ACT) has been a highly effective treatment for non-severe cases since the early 2000s.
- While the clinical effectiveness of ACT remains generally robust in the continent, the recent emergence of partial artemisinin resistance in the eastern African countries of Rwanda, Uganda and Eritrea has raised significant concerns.
- Most of the countries in Africa are not on track to achieving the goal of eliminating malaria in the continent by 2030, according to the African Union Malaria Progress Report 2022.
About Malaria:-
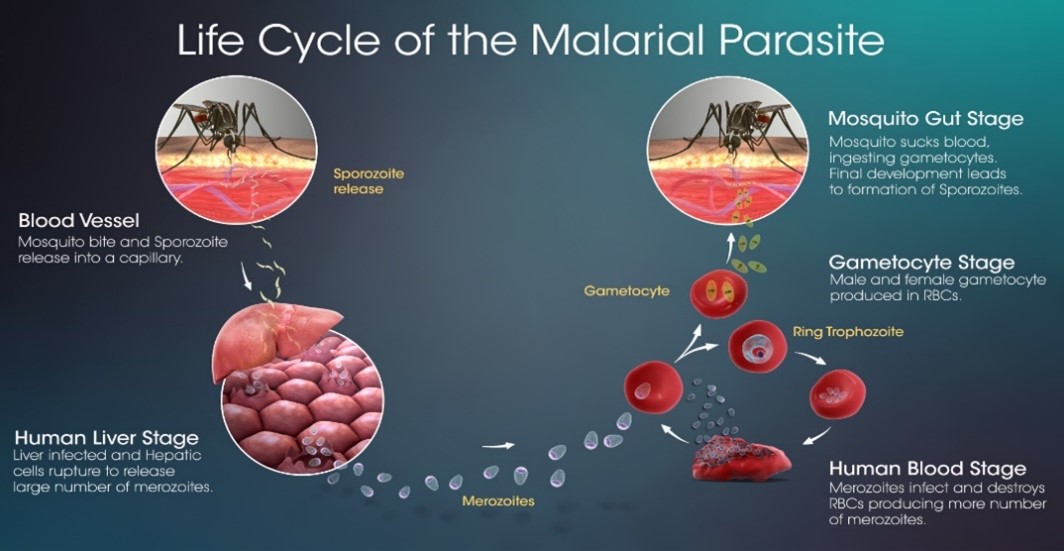
IMAGE SOURCE: A Happy Ending To Malaria Story? – Scientific Animations
- It is a life-threatening mosquito-borne blood disease.
- It is caused by Plasmodium parasites.
- It is predominantly found in the tropical and subtropical areas of Africa, South America as well and Asia.
- It is preventable as well as curable.
Symptoms:-
- Symptoms usually begin ten to fifteen days after being bitten by an infected mosquito.
- Symptoms include fever, tiredness, vomiting, and headaches.
- In severe cases, it can cause jaundice, seizures, coma, or death.
Transmission:-
- The parasites spread through the bites of infected female Anopheles mosquitoes.
- In the human body, parasites initially multiply in liver cells and then attack the Red Blood Cells (RBCs).
- There are 5 parasite species that cause Malaria in humans and 2 of these species (Plasmodium falciparum and Plasmodium vivax) pose the greatest threat.
Prevention:-
- Using mosquito nets when sleeping in places where malaria is present
- Using mosquito repellents (containing DEET, IR3535 or Icaridin) after dusk
- Using coils and vaporizers.
- Wearing protective clothing.
- Using window screens.
Treatment:-
- Artemisinin-based combination therapy medicines like artemether-lumefantrine are usually the most effective medicines.
- Chloroquine is recommended for the treatment of infection with the vivax parasite only in places where it is still sensitive to this medicine.
- Primaquine should be added to the main treatment to prevent relapses of infection with the P. vivax and P. ovale parasites.
- Most medicines used are in pill form.
- Some people may need to go to a health centre or hospital for injectable medicines. (Malaria Vaccine)
India’s status:-
- In India, malaria elimination efforts were initiated in 2015.
- These were intensified after the launch of the National Framework for Malaria Elimination (NFME) in 2016.
- It is an initiative under the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare.
- NFME is in line with WHO’s 2016-2030 Malaria Strategy. (World Malaria Report 2021)
- WHO’s 2016-2030 Malaria Strategy: guides the WHO Global Malaria Programme (GMP).
- Status on elimination: India continues to show a sustained decline in overall malaria but faces several challenges in its malaria elimination journey.
MUST READ: New hope for malaria vaccine
SOURCE: DOWN TO EARTH
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) Consider the following diseases (2014)
- Diphtheria
- Chickenpox
- Smallpox
Which of the above diseases has/have been eradicated in India?
- 1 and 2 only
- 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
- None
Q.2) Widespread resistance of the malarial parasites to drugs like chloroquine has prompted attempts to develop a malarial vaccine to combat malaria. Why is it difficult to develop an effective malaria vaccine? (2010)
- Malaria is caused by several species of Plasmodium
- Man does not develop immunity to malaria during natural infection
- Vaccines can be developed only against bacteria
- Man is only an intermediate host and not the definitive host
Syllabus
- Prelims –GOVERNMENT INITIATIVES
Context: The Centre recently, notified the Green Credit programme.
Background:-
- The Union Ministry of Environment, Forests and Climate Change on October 13, 2023, notified the ‘green credit’ programme.
About the Green credit programme:-
- Launched: 2023.
- Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman had launched “Green Credit Programme”(GCP) in Union Budget 2023-24.
- Ministry: Ministry of Environment, Forests and Climate Change.3234
- Objective: to create a market-based mechanism for undertaking environment-friendly activities such as afforestation programmes, and water conservation by providing additional incentives in the form of green credits.
- It is a first-of-a-kind market-based instrument designed to incentivize individuals, industries and local bodies for their voluntary environmental actions across diverse sectors.
- It will be launched at the national level to incentivize voluntary environmental actions of various stakeholders.
- It will encourage private sector industries by taking actions which are able to converge with activities relevant to generating or buying Green Credits.
- Green Credit: it is an incentive that individuals, farmer-producer organizations (FPOs), industries, and rural and urban local bodies, among other stakeholders, will be able to earn for environment-positive actions.
Governance Structure of GCP:-
GCP Administrator
- The Indian Council of Forestry Research and Education (ICFRE) will be the administrator of GCP.
- ICFRE: it is an autonomous organization or governmental agency under the MoEFCC.
- Its aim is to generate, advance and disseminate scientific knowledge and technologies for ecological security, improved productivity, livelihood enhancement and sustainable use of forest resources through forestry research and education.
- It will manage, monitor and operate the entire programme.
Steering committee
- It will be set up to approve procedures for institutionalizing the GCP, rules and regulations
- It will recommend it to the central government for issuance of a Green Credit Certificate. (Green Bonds)
- It will also determine the type and amount of fees and charges for the purpose of meeting the cost and expense towards implementation of GCP.
Working of GCP:-
- The GCP administrator will collect the environmental compensation and deposit it in a separate dedicated account.
- This fund shall be utilized for activities related to the implementation of GCP.
- For instance, an individual who undertakes tree plantation in an area, can earn green credits, which he can sell at the trading platform after validation by the steering committee.
Benefits of GCP:-
- It allows forests to be traded as a commodity.
- It allows the Forest Department to outsource one of its responsibilities of reforesting to non-government agencies.
- It will encourage plantation by individuals outside the traditional forest area.
- It will help in meeting international commitments such as sustainable development goals and nationally determined contributions.
MUST READ: Green Urban Oases Programme
SOURCE: DOWN TO EARTH
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) Which one of the following has been constituted under the Environment (Protection) Act, 1986? (2022)
- Central Water Commission
- Central Ground Water Board
- Central Ground Water Authority
- National Water Development Agency
Q.2) With reference to organic farming in India, consider the following statements: (2018)
- The National ‘Programme for Organic Production’ (NPOP) is operated under the guidelines and ‘directions of the Union Ministry of Rural Development.
- The Agricultural and Processed Food Product Export Development Authority ‘(APEDA) functions as the Secretariat for the implementation of NPOP.
- Sikkim has become India’s first fully organic State.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 and 2 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
Syllabus
- Prelims –DEFENSE
Context: Indian Army will begin phase-out of Cheetah, Chetak helicopters from 2027.
Background:-
- The Army will start phasing out the first lot of the vintage Cheetah and Chetak helicopters from 2027 onwards on completion of their Total Technical Life (TTL) while it looks to induct the indigenous Light Utility Helicopters (LUH) in numbers to replace them.
- The Army is expected to receive six LUH between December 2024 and June 2025.
About Chetak helicopters:-
- Year of Manufacture: 1962.
- Manufactured by: Hindustan Aeronautics Limited (HAL).
- Maximum speed: Over 210 km/hrs.
- The Helicopter Division started manufacturing helicopters in 1962, by entering an agreement with France for the production of Aloutte III helicopters (Chetak).
- The first Chetak in ‘Fly Away’ condition was delivered in 1965.
- The Chetak helicopter is the oldest helicopter of the Indian Air Force inducted by Hindustan Aeronautics Ltd (HAL) in 1965.
- It is a two-ton class helicopter.
- It is a single-engine helicopter that can carry seven people, including two pilots.
- The helicopter is versatile, multi-role, multi-purpose, and spacious.
- The Chetak is operated by each of the three services and also the Coast Guard, however, it has been the military’s workhorse for decades.
- The helicopter is suitable for commuting, cargo/material transport, casualty evacuation, Search and rescue (SAR), Aerial Survey and patrolling, Emergency Medical Services, Off-shore operations, and Underslung operations.
- The Chetak helicopter is powered by a single Turbomeca Artoustte III B turboshaft engine.
Cheetah helicopter:-
- Operated by: both the Indian Air Force and the Army Aviation Corps.
- Hindustan Aeronautics Limited signed a licence agreement for the Lama with Aérospatiale in 1970 and christened the India-made aircraft “Cheetah”.
- The first Cheetah manufactured from raw materials was delivered in 1976-77.
- It is a licence-built version of the French Aérospatiale SA 315B Lama.
- It is known for its capability to operate in hot tropical weather as well as high altitude conditions. (MH-60R helicopters)
- The SA315B Lama was first flown in 1969, over 50 years ago.
- Over the years, it has developed a reputation for being unsafe, with the armed forces attempting to find upgrades for these rotorcraft.
- It has been used for transporting men and material, search and rescue, and reconnaissance.
- Cheetahs have especially been crucial for operations in Siachen, the world’s highest battleground at over 6,000 m.
MUST READ: Asia’s largest helicopter manufacturing facility
SOURCE: THE HINDU
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) With reference to Home Guards, consider the following statements: (2023)
- Home Guards are raised under the Home Guards Act and Rules of the Central Government.
- The role of the Home Guards is to serve as an auxiliary force to the police in the maintenance of internal security.
- To prevent infiltration on the international border/ coastal areas, the Border Wing Home Guards Battalions have been raised in some states.
How many of the above statements are correct?
- Only one
- Only two
- All three
- None
Q.2) Which one of the following statements best reflects the idea behind the “Fractional Orbital Bombardment System” often talked about in media? (2022)
- A hypersonic missile is launched into space to counter the asteroid approaching the Earth and explode it in space.
- A spacecraft lands on another planet after making several orbital motions.
- A missile is put into a stable orbit around the Earth and deorbits over a target on the Earth.
- A spacecraft moves along a comet with the same surface. speed and places a probe on it.
Syllabus
- Prelims –GEOGRAPHY
Context: Recent studies show evidence of the leaking of Earth’s core.
Background:-
- Record concentrations of a helium isotope found inside 62-million-year-old Arctic rocks could be the most compelling evidence to date of a slow leak in our planet’s core.
- Building on the results of a previous analysis of ancient lava flows, a team of geochemists from Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution and the California Institute of Technology are now more certain than ever that helium trapped in the core as our planet was forming is making its way to the surface.
About Earth’s core:-
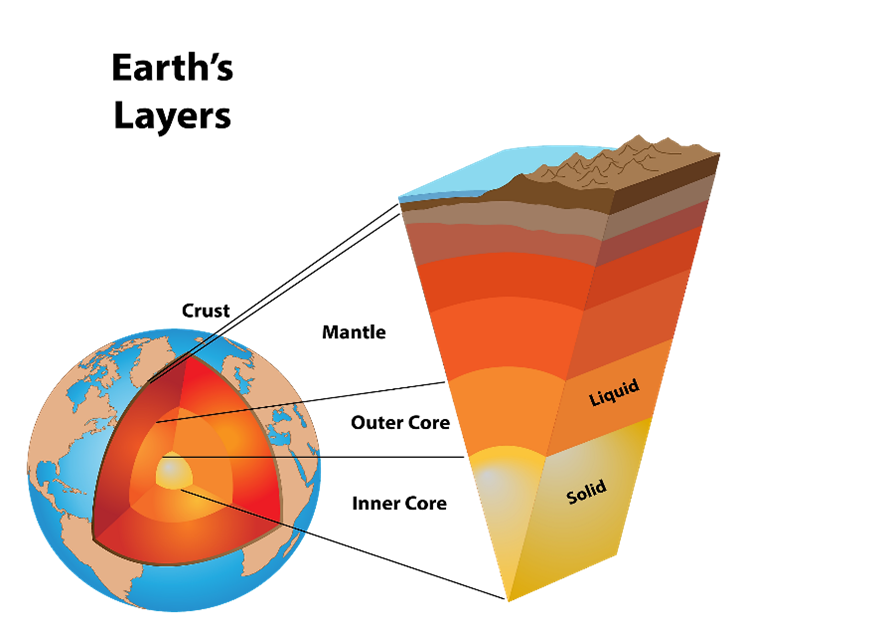
IMAGE SOURCE: WorldAtlas
- The Earth can be divided into one of two ways: mechanically or chemically.
- Mechanically ( or through the study of liquid states )– it can be divided into the lithosphere, asthenosphere, mesospheric mantle, outer core, and inner core.
- Chemically (or by composition), which is the more popular of the two, it can be divided into the crust, the mantle (subdivided into the upper and lower mantle), and the core (subdivided into the outer core, and inner core.)
The Crust
- The Crust is the cold, fragile, and rock-based outer layer.
- There are two types of crust, each with unique physical and chemical characteristics: (i) continental crust; and (ii) oceanic crust.
- Basalt lava flows are produced when magma under the seafloor erupts, forming the oceanic crust.
- The oceanic crust is 5 km thinner than the continental crust (about 30 km).
- Silica (Si) and Aluminum (Al) are the two main components of the crust.
Mantle
- The mantle is the layer beneath the crust.
- The Mohorovich Discontinuity is the separation between the crust and mantle.
- The mantle has a thickness of around 2900 km.
- Approximately 84% of the earth’s volume and 67% of its mass are made up of the mantle.
- It is primarily composed of silicon and magnesium.
- The entire crust and the topmost solid portion of the mantle comprise the
- An extremely vicious, weakly elastic, ductile, deforming zone of the upper mantle, the asthenosphere (between 80 and 200 km), is located just beneath the lithosphere.
Core
- It is the layer that surrounds the earth’s core that is the
- Guttenberg’s Discontinuity divides the mantle from the core.
- It is also called NIFE since it contains nickel (Ni) and iron (Fe).
- Nearly 15% of the earth’s volume and 32.5 per cent of its mass are made up of the core.
- The density of the earth’s core fluctuates around 5 and 14.5 g/cm3.
- The inner core and the outer core are the sub-layers that make up the Core.
- The inner core is solid, but the outer core is liquid (or semi-liquid).
MUST READ: Supermoon
SOURCE: SCIENCE ALERT
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) In the northern hemisphere, the longest day of the year normally occurs on the: (2022)
- The first half of the month of June
- The second half of the month of June
- The first half of the month of July
- The second half of the month of July
Q.2) On 21st June, the Sun (2019)
- does not set below the horizon at the Arctic Circle
- does not set below the horizon at the Antarctic Circle
- shines vertically overhead at noon on the Equator
- shines vertically overhead at the Tropic of Capricorn
VIENNA CONVECTION ON DIPLOMATS
Syllabus
- GS-II
The “Vienna Convention on Diplomats,” is an international treaty that was adopted by 61 countries on April 18, 1961. This convention is a fundamental document in international law and governs the conduct of diplomatic relations between independent states. It was drafted during the United Nations Conference on Diplomatic Intercourse and Immunities, held in Vienna, Austria. It is considered a cornerstone of modern diplomatic law and practice.
KEY PROVISIONS
Diplomatic Immunity (Articles 29 to 36)
- Diplomats and their families are granted immunity from the jurisdiction of the host country’s legal system for their official actions.
- Extends to criminal and civil matters and ensures that diplomats cannot be prosecuted or sued in the host country’s courts.
Inviolability of Diplomatic Premises (Articles 22 to 27)
- Diplomatic premises, such as embassies and consulates, are considered inviolable.
- They cannot be entered or searched by the host country’s authorities without the permission of the sending state.
Non-Interference (Article 41)
- Diplomatic agents are expected not to interfere in the internal affairs of the host country.
- This principle promotes peaceful coexistence and respectful relations between states.
Protection of Diplomatic Missions (Articles 22 to 27)
- Host country is responsible for ensuring the security and protection of diplomatic missions and their staff.
- Includes safeguarding the physical premises and preventing any intrusion or damage.
Termination of Diplomatic Relations (Articles 45 to 50)
- Outlines procedures for the termination of diplomatic relations between states.
- Includes orderly withdrawal of diplomatic personnel and the closure of diplomatic missions.
Article 11.1
- It deals with the size of international missions within other countries.
- In the absence of a specific agreement as to the size of the mission, the receiving State may require that the size of a mission be kept within limits considered to be reasonable and normal.
NEED OF VIENNA CONVECTION
- Establishing a Standardized Framework: The convention provides a universally accepted and standardized framework for diplomatic relations between states. This common set of rules and principles helps to avoid misunderstandings and conflicts related to diplomatic conduct.
- Promoting Diplomatic Relations: By establishing a clear legal framework for diplomatic relations, the convention encourages states to engage in diplomatic relationships. This, in turn, contributes to open channels of communication and peaceful means of dispute resolution.
- Protection of Diplomats: It ensures that diplomats can perform their duties without fear of harassment, arrest, or harm. This protection is essential for diplomats to represent their countries effectively and safely.
- Promoting Diplomatic Immunity: It allows diplomats to carry out their responsibilities without being subject to the jurisdiction of the host country’s legal system, which could lead to politically motivated arrests or interference in their work.
- Respect for the Principle of Non-Interference: The Vienna Convention reinforces the principle of non-interference in the internal affairs of the host country. This principle is essential for maintaining peaceful relations and respecting the sovereignty of states.
- Preventing Diplomatic Crises: Clear rules and guidelines help prevent diplomatic incidents that could lead to crises. The convention stipulates how diplomatic missions and agents should conduct themselves, minimizing the potential for misunderstandings and conflicts.
Conclusion:
The Vienna Convention on Diplomatic Relations has been widely adopted by countries around the world and is considered a cornerstone of diplomatic law and practice. It establishes a framework that helps maintain peaceful relations among nations and ensures the functioning of diplomatic missions in a manner that respects the sovereignty and dignity of both sending and receiving states. Violations of the convention can have significant diplomatic and legal consequences.
Practice MCQs
Q1) Consider the following pairs:
| Institutions | Headquarters |
| 1.CBI | Kolkata |
| 2.NIA | New Delhi |
| 3.SEBI | Mumbai |
How many of the above pairs are correctly matched?
- Only one
- Only two
- All three
- None
Q2) Consider the following statements
Statement-I :
Abu Dhabi Masters 2023 has a cash prize of $120,000.
Statement-II :
It is the first-ever International badminton spectacle in the capital city.
Which one of the following is correct in respect of the above statements?
- Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and Statement-II is the correct explanation for Statement-I
- Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and Statement-II is not the correct explanation for Statement-I
- Statement-I is correct but Statement II is incorrect
- Statement-I is incorrect but Statement II is correct
Q3) With reference to the Chetak Helicopters, consider the following statements:
- It is a two-ton class helicopter.
- It is a double-engine helicopter that can carry seven people.
- The helicopter was inducted by Hindustan Aeronautics Ltd (HAL) in 1960.
How many of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 1, 2 and 3 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 2 only
Mains Question:
Q.1) Comment on the need and importance of international convention on diplomatic relations.
Comment the answers to the above questions in the comment section below!!
ANSWERS FOR ’ 23rd October 2023 – Daily Practice MCQs’ will be updated along with tomorrow’s Daily Current Affairs.st
ANSWERS FOR 21st October – Daily Practice MCQs
Q.1) – b
Q.2) – c
Q.3) – c











