IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
Archives
(PRELIMS & MAINS Focus)
Syllabus
- Prelims –SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Context: Recent studies have found out that India has the 2nd-highest number of diabetes diagnostic centres globally.
Background:-
- In 2021, nearly seven million people died globally as a result of diabetes, while $970 billion was the world’s quantified healthcare expenditure that year, according to a new report titled Diabetes Global Industry Overview 2023.
- Currently, 537 million adults globally are living with diabetes, with three in four of them living in low- and middle-income countries.
- After the US, the highest numbers of medical centres for diabetes are located in India (58), Canada (51), the UK (42), Japan (29), and Australia (24).
About Diabetes:-
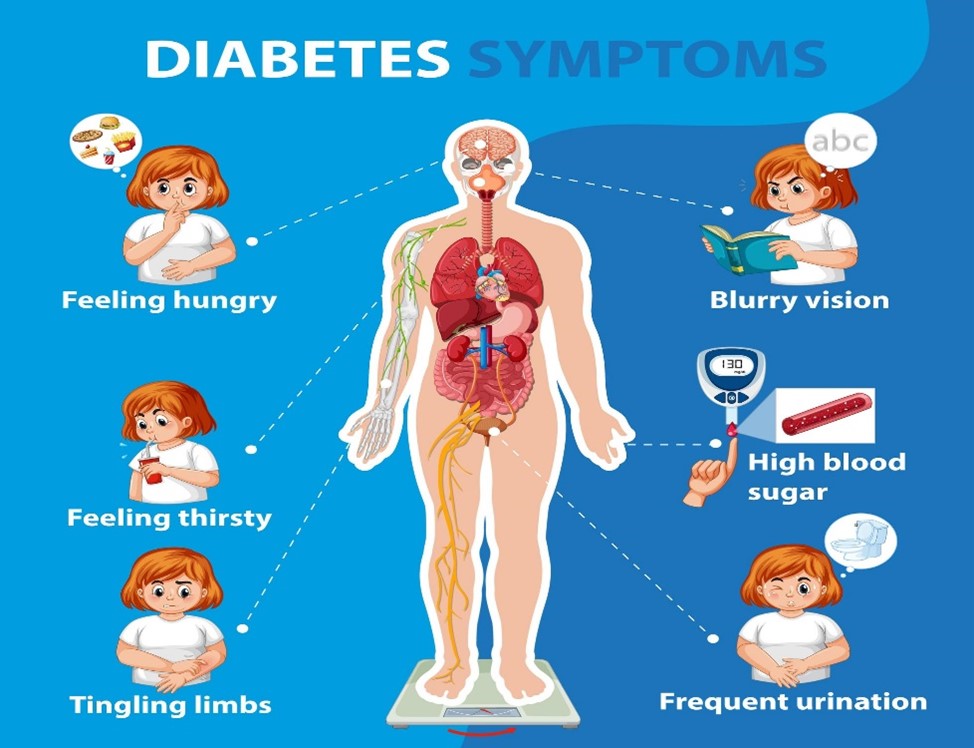
IMAGE SOURCE: vecteezy.com
- Diabetes mellitus refers to a group of diseases that affect how the body uses blood sugar (glucose).
- Glucose is an important source of energy for the cells that make up the muscles and tissues.
- It is a condition that happens when the blood sugar (glucose) is too high.
- It develops when your pancreas doesn’t make enough insulin or any at all, or when the body isn’t responding to the effects of insulin properly.
- Diabetes affects people of all ages.
Types of diabetes:-
- There are several types of diabetes. The most common forms include:-
- Type 2 diabetes: With this type, the body doesn’t make enough insulin, and/or the body’s cells don’t respond normally to the insulin (insulin resistance).
- This is the most common type of diabetes.
- Prediabetes: The blood glucose levels are higher than normal but not high enough to be officially diagnosed with Type 2 diabetes.
- Type 1 diabetes: This type is an autoimmune disease in which your immune system attacks and destroys insulin-producing cells in your pancreas for unknown reasons.
- Gestational diabetes: This type develops in some people during pregnancy.
Symptoms:-
- feeling very thirsty
- needing to urinate more often than usual
- blurred vision
- feeling tired
- losing weight unintentionally
Management and Treatment:-
- Blood sugar monitoring.
- Oral diabetes medications.
- Insulin injections.
- Diet management.
- Exercise.
Prevention:-
- Keeping a healthy body weight.
- Staying physically active with at least 30 minutes of moderate exercise each day.
- Eating a healthy diet and avoiding sugar and saturated fat.
- Avoiding smoke tobacco.
- Avoiding stress. (Mental Health)
Government initiatives:-
- India’s National non-communicable disease (NCD) Target aims to prevent the rise in obesity and diabetes prevalence. (Disease Surveillance System)
- National Programme for Prevention and Control of Cancers, Diabetes, Cardiovascular Diseases and Stroke (NPCDCS) in 2010, was launched to provide support for diagnosis and cost-effective treatment at various levels of health care.
MUST READ: Non communicable and communicable diseases
SOURCE: DOWN TO EARTH
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) Consider the following statements in respect of probiotics: (2022)
- Probiotics are made of both bacteria and yeast.
- The organisms in probiotics are found in foods we ingest but they do not naturally occur in our gut.
- Probiotics help in the digestion of milk sugars.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- 1 and 3
- 2 and 3
Q.2) Which one of the following statements best describes the role of B cells and T cells in the human body? (2022)
- They protect the environmental allergens. body
- They alleviate the body’s pain and inflammation.
- They act as immunosuppressants in the body.
- They protect the body from the diseases caused by pathogens.
Syllabus
- Prelims –POLITY-GOVERNANCE
Context: Prime Minister Narendra Modi recently, announced the setting up of a National Turmeric Board for Telangana.
About National Turmeric Board:-
- Location: Telangana.
- Set up: 2023.
- Objective: to harness the potential of our turmeric farmers and give them the support they rightly deserve.
- The National Turmeric Board will focus on value addition to the supply chain.
- The board will extend help to all turmeric farmers on all aspects of Turmeric crops.
- It would serve various purposes, including enhancing value addition in the turmeric supply chain.
- It will help in addressing infrastructure-related needs for farmers.
- It will help the Telangana farmers in having a value chain right from production to export and research in addition to infrastructure.
- It will boost the country’s position as a key player in the global turmeric market.
Significance:-
- These infrastructure and developmental projects will increase employment opportunities.
- It improves the lives of people.
Turmeric:-
- Turmeric is a flowering plant. (Lakadong Turmeric)
- It is used as a condiment, dye, drug, and cosmetic in addition to its use in religious ceremonies.
- Its color comes mainly from curcumin, a bright yellow phenolic compound.
- It requires temperatures between 20 and 30 °C (68 and 86 °F).
Significance of Turmeric for India:-
- India holds a prominent position as a major producer, consumer, and exporter.
- Currently, India contributes to approximately 80 percent of the world’s turmeric production, yielding nearly 1.1 million tonnes of spice annually.
- The top five turmeric-producing states of India in 2020-21 are Telangana, Maharashtra, Karnataka, Tamil Nadu and Andhra Pradesh.
- Awareness of the health benefits of turmeric had grown during the COVID-19 pandemic, leading to increased demand for the spice globally.
- Turmeric exports have been on the rise, with shipments totaling around 1.5 lakh tonnes, particularly since the onset of the pandemic.
Health Benefits of Turmeric:-
- Depression
- Type 2 Diabetes
- Viral Infections
- Premenstrual Syndrome
- High Cholesterol
MUST READ: Soil-less agriculture
SOURCE: AIR
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) If a particular area is brought under the Fifth Schedule of the Constitution of India, which one of the following statements best reflects the consequence of it? (2022)
- This would prevent the transfer of land from tribal people to non-tribal people.
- This would create a local self-governing body in that area.
- This would convert that area into a Union Territory.
- The State having such areas would be declared a Special Category State.
Q.2) Consider the following statements about Particularly Vulnerable Tribal Groups (PVTGs) in India: (2019)
- PVTGs reside in 18 States and one Union Territory.
- A stagnant or declining population is one of the criteria for determining PVTG status.
- There are 95 PVTGs officially notified in the country so far.
- Irular and Konda Reddi tribes are included in the list of PVTGs.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
- 1, 2 and 3
- 2, 3 and 4
- 1, 2 and 4
- 1, 3 and 4
Syllabus
- Prelims –POLITY
Context: The Law Commission in its recent report on the Protection of Children from Sexual Offences (POCSO) Act suggested the government keep the consent age 18.
Background:-
- Headed by former Karnataka High Court Chief Justice Ritu Raj Awasthi, the Commission, in its Report No. 283 on ‘Age of Consent under the Protection of Children from Sexual Offences Act, 2012’ submitted to Union Law Minister Arjun Ram Meghwal, has accordingly called for certain amendments to the Act “to remedy the situation in cases wherein there is tacit approval in fact though not consent in law on part of the child aged between I6 to l8 years”.
- Stating that “it is not advisable to tinker with” the existing age of consent — 18 years — under the Protection of Children from Sexual Offences (POCSO) Act to exempt adolescent sexual acts from the purview of the criminal law, the Law Commission of India has instead favoured introducing “guided judicial discretion in the matter of sentencing” in cases involving those in the 16-18 age group.
- It says “This will ensure that the law is balanced, thus safeguarding the best interests of the child”.
About the Protection of Children from Sexual Offences (POCSO) Act:-
- Enacted: 2012. (National Commission for Protection of Child Rights)
- Ministry: Ministry of Women and Child Development.
- Objectives: to address offenses of sexual exploitation and sexual abuse of children, which were either not specifically defined or adequately penalized.
Historic Background:-
- It was enacted as a consequence of India’s ratification of the UN Convention on the Rights of the Child in 1992.
- The POCSO Act was enacted in 2012 to provide a robust legal framework for the protection of children from offences of sexual assault, sexual harassment, and pornography while safeguarding the interests of children at every stage of the judicial process.
- In 2019, the Act was amended to strengthen the penalties for specified offenses in order to deter abusers and promote a dignified upbringing.
Salient Features:-
- The Act defines a child as “any person” under the age of 18. ( Mandatory Minimum Sentencing)
- The Act recognizes that both girls and boys can be victims of sexual abuse.
- Any person in charge of an institution (excluding children) who fails to report the commission of a sexual offense involving a subordinate faces punishment.
- A victim may report an offense at any time, even years after the abuse has occurred.
- The Act forbids the disclosure of the victim’s identity in any form of media unless authorized by the special courts established by the Act.
- The new rules include the provision of mandatory police verification of staff in schools and care homes, procedures to report sexual abuse material (pornography), and imparting age-appropriate child rights education among others.
- For a crackdown on child pornography, any person who has received any pornographic material involving a child or any information regarding such pornographic material shall report the contents to the Special Juvenile Police Unit (SJPU) or police, or the cybercrime portal.
- Under the rules, the State Governments have been asked to formulate a child protection policy based on the principle of zero-tolerance to violence against children, which shall be adopted by all institutions, organizations, or any other agency working with or coming in contact with children.
- The Central Government and every State Government shall provide periodic training.
- The Centre and State Governments have been asked to prepare age-appropriate educational material and curriculum for children, informing them about various aspects of personal safety.
- According to rules, orientation programme and intensive courses may also be organized for police personnel and forensic experts.
- Any institution housing children or coming in regular contact with children, including schools, crèches, sports academies, or any other facility for children must ensure a police verification and background check on a periodic basis of every staff.
Challenges:-
- Low Representation of Women in the Police Force.
- Lapses in the Investigation.
- No Conditions to Prove Recent Intercourse.
MUST READ: Sexual intent is key to POCSO Act: SC
SOURCE: THE INDIAN EXPRESS
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) With reference to India, consider the following statements (2021)
- Judicial custody means an accused is in the custody of the concerned magistrate and such accused is locked up in a police station, not in jail.
- During judicial custody, the police officer in charge of the case is not allowed to interrogate the suspect without the approval of the court.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Q.2) Consider the following statements: (2021)
- 21st February is declared to be International Mother Language Day by UNICEF.
- The demand that Bangla has to be one of the national languages was raised in the Constituent Assembly of Pakistan.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Syllabus
- Prelims –GOVERNANCE
Context: A recent report discussed the effects of India’s improved ranking in the Global Terrorism Index.
Background:-
- India’s Global Terrorism Index (GTI) score of 7.43 and crime index score of 44.7 indicated a decline in terror and crime incidents since 2016 which can be attributed to strengthened security measures.
- The report by Ficci Cascade highlighted the need to curb illicit trade, which threatens national security and has negative impacts on manufacturing, government revenue, public health, and consumer trust.
About Global Terrorism Index:-
- Published by: Institute for Economics and Peace (IEP).
- Publication timing: annually.
- The Institute for Economics and Peace (IEP), a global think tank.
- HQ: Sydney, Australia.
- The index is based primarily on the Global Terrorism Database (GTD) collated by the National Consortium for the Study of Terrorism and Responses to Terrorism (START) at the University of Maryland, besides other sources.
- The index provides a comprehensive summary of the key global trends and patterns in terrorism since 2000.
- GTI scores are directly used in the Global Peace Index, the Global Slavery Report.
- It is also indirectly used in reports of the World Economic Forum’s Travel and Tourism Competitiveness and Global Competitiveness Indices and compilation of the Safe Cities Index by the Economist Intelligence Unit.
Key Highlights of the report:-
- Attacks have become more deadly with the lethality rising by 26%.
- Islamic State (IS) and its affiliates remained the world’s deadliest terrorist group in 2022 for the eighth consecutive year, with attacks in 21 countries.
- Ideological terrorism continues to be the most prominent and deadliest form of terrorism in the West.
- The Sahel is the most impacted region, representing 43% of global terrorism deaths.
- Pakistan recorded the second-largest surge in terror-related deaths worldwide in 2022, with the toll increasing significantly to 643.
- South Asia remains the region with the worst average GTI score.
- India ranks 13th on The Global Terrorism Index (GTI).
MUST READ: Terrorism & and its financing
SOURCE: TIMES OF INDIA
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) With reference to the “G20 Common Framework”, consider the following statements (2022)
- It is an initiative endorsed by the G20 together with the Paris Club.
- It is an initiative to support Income Countries with unsustainable debt.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Q.2) Consider the following statements: (2019)
- The United Nations Convention against Corruption (UNCAC) has a ‘Protocol against the Smuggling of Migrants by Land, Sea and Air’.
- The UNCAC is the ever-first legally binding global anti-corruption instrument.
- A highlight of the United Nations Convention against Transnational Organized Crime (UNTOC) is the inclusion of a specific chapter aimed at returning assets to their rightful owners from whom they had been taken illicitly.
- The United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime (UNODC) is mandated by its member states to assist in the implementation of both UNCAC and UNTOC.
Which of the statements given above is correct?
- 1 and 3 only
- 2, 3 and 4 only
- 2 and 4 only
- 1, 2, 3 and 4
Syllabus
- Prelims –POLITY
Context: Gandhi Jayanti will be celebrated on 2nd October 2023.
Background:
- This year (2023) will be the 154th birth anniversary.
About Gandhi Jayanti :-
- October 2 is observed as Gandhi Jayanti to commemorate the birth anniversary of Mahatma Gandhi.
- He is also known as the ‘Father of the Nation’.
- He was born on October 2, 1869.
- He was born in Porbandar, Gujarat.
- As a mark of respect to the leader, the day is observed as a national holiday.
- It is celebrated with various events with prayer services and cultural events in educational institutions, and even government institutions.
- On the day, political leaders pay homage to Raj Ghat, the samadhi of Mahatma Gandhi in New Delhi.
- His favorite songs, ‘Raghupati Raghava’ and ‘Vaishnav Jan To Tene Kahiye’, are also sung on the occasion in various events as a tribute to the leader.
- In his honour, the United Nations declared this day as the ‘International Day of Non-Violence’ on June 15, 2007.
- Gandhi implemented the nonviolent Civil Disobedience Movement against the African officials.
Important events in Mahatama Gandhi’s life:-
- Gandhi completed his graduation from London and went to South Africa to practice law where he saw miserable treatment being meted out to many Indian peasants in South Africa.
- 1915-1918: As he returned to India in 1915 and saw the state of affairs under the British Government with Indian peasants imposed with excessive taxes, he began protesting it.
- 1921: Gandhi became the leader of the Indian National Congress.
- 1922: Soon, he led multiple campaigns for attaining ‘Swaraj’ or self-rule for Indian workers through non-violence or Ahimsa.
- 1930: He led the 400-km long Dandi Salt March to put an end to the salt tax.
- 1942: Later, with the Quit India Movement against British rule in 1942, and persistent efforts led to India becoming a sovereign nation with Lord Mountbatten’s declaration of Partition.
- 1948: He was assassinated on January 30, 1948.
MUST READ: Gandhi as Political thinker and a Social reformer
SOURCE: DOWN TO EARTH
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) Consider the following freedom fighters: (2022)
- Barindra Kumar Ghosh
- Jogesh Chandra Chatterjee
- Rash Behari Bose
Who of the above was/were actively associated with the Ghadar Party?
- 1 and 2
- 2 only
- 1 and 3
- 3 only
Q.2) Who among the following is associated with ‘Songs from Prison’, a translation of ancient Indian religious lyrics in English? (2022)
- Bal Gangadhar Tilak
- Jawaharlal Nehru
- Mohandas Karamchand Gandhi
- Sarojini Naidu
Syllabus
- Prelims –IMPORTANT PERSONALITIES
Context: Bhagat Singh’s 116th birth anniversary was celebrated in Lahore, Pakistan recently.
About Bhagat Singh:-
- Birth: September 27, 1907.
- Birth Place: in Lyallpur, Western Punjab (now in Pakistan).
- Death: 23rd March 1931. (Shaheed Diwas)
- It is also known as Martyrs’ Day or Sarvodaya Day.
- It was on this day that Bhagat Singh, Sukhdev, and Rajguru were executed by the British government in 1931.
- Bhagat Singh was a revolutionary hero of the Indian independence movement.
- He attended Dayanand Anglo Vedic High School, which was operated by Arya Samaj.
- He quit education at the age of thirteen and got admitted to the National College in Lahore, where he studied European revolutionary movements.
- He worked as a writer and editor in Amritsar for Punjabi– and Urdu-language newspapers espousing Marxist theories.
Nationalist activities:-
- He is credited with popularizing the catchphrase “Inquilab zindabad” (“Long live the revolution”)
- Hindustan Socialist Republican Association (HSRA): it was founded in 1928 by Chandrashekhar Azad, Bhagat Singh, and others.
- John Saunders’ assassination: In 1928, Bhagat Singh and Rajguru shot dead a British police officer, John Saunders, in Lahore, mistaking Saunders, for the British senior police superintendent, James Scott.
- They held Scott responsible for the death of Lala Lajpat Rai in a lathi charge of Simon Commission.
- 1929: Bhagat Singh and Batukeshwar Dutt threw bombs at the Central Legislative Assembly in Delhi ‘to make the deaf hear’.
- Trial: In the Lahore conspiracy case, Bhagat Singh along with, Rajguru and Sukhdev were sentenced to death. Bhagat Singh was under one-year imprisonment.
- He was in the Lahore jail when he was hanged in March 1931.
- Widespread coverage in Indian-owned newspapers about his courage and spirit—turned him into a household name in India and after his execution into a martyr of Indian Freedom Struggle.
- Philosophy: He was an avid reader of the teachings of Mikhail Bakunin and also read Karl Marx, Vladimir Lenin, and Leon Trotsky.
- Books: Why I am an Atheist, Letter to My Father, Jail Notebook.
MUST READ: Maulana Abul Kalam Azad
SOURCE: THE HINDU
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) With reference to Madanapalle of Andhra Pradesh, which one of the following statements is correct? (2022)
- Pingali Venkayya designed the tricolour Indian National Flag here.
- Pattabhi Sitaramaiah led the Quit India Movement of the Andhra region from here.
- Rabindranath Tagore translated the National Anthem from Bengali to English here.
- Madame Blavatsky and Colonel Olcott set up the headquarters of the Theosophical Society first here.
Q.2) The Ghadr (Ghadar) was a: (2014)
- revolutionary association of Indians with headquarters at San Francisco
- nationalist organization operating from Singapore
- militant organization with headquarters at Berlin
- communist movement for India’s freedom with headquarters at Tashkent
Regulating Generative Artificial Intelligence
Syllabus
- Mains – GS 3 (Science and Technology) and GS 4 (Ethics)
Context: The Governments across the world are grappling with the regulation of Artificial Intelligence.
- In less than a year, chatbots like ChatGPT, Bard, Claude, and Pi have shown what gen AI-powered applications can do. These tools have also revealed their vulnerabilities, which has pushed policymakers and scientists to think deeply about these new systems.
About Generative Artificial Intelligence:
- Generative AI is a type of AI system that can create new content or data that resembles human-made content, such as text, images, music, code, etc.
- It works by using neural networks to learn from large amounts of data and then generate outputs based on the patterns and rules it has learned.
Various significant reasons to regulate AI:
- Lack of transparency: Many AI algorithms operate as black boxes, making it difficult to understand how they reach their decisions.
- This lack of transparency raises concerns about accountability and the potential for unfair or biased outcomes.
- Discrimination and bias outcomes: AI systems can inherit biases from the data they are trained on, leading to discriminatory outcomes.
- For example, facial recognition algorithms have been shown to have higher error rates for women and people with darker skin tones.
- Privacy and data protection: AI systems often rely on vast amounts of personal data, raising concerns about privacy and data protection.
- Improper handling of data can result in unauthorized access, misuse, or breaches of sensitive information.
- Security risks: AI systems can be vulnerable to cybersecurity threats and attacks.
- Adversarial attacks can manipulate AI models to produce incorrect or malicious results, posing risks in critical domains such as autonomous vehicles or healthcare.
- Ethical considerations: AI raises ethical questions related to the impact on jobs, social inequality, and the concentration of power.
- For example, automated decision-making in hiring processes may perpetuate existing biases and result in unfair outcomes.
- Lack of regulation and standards: The rapid advancement of AI has outpaced the development of comprehensive regulatory frameworks and industry standards.
- This creates a regulatory gap and potential risks associated with unchecked AI development and deployment.
Advantages of Generative AI:
- Creative assistance: Generative AI tools can assist and inspire creative professionals in their work.
- Professionals such as artists, designers, and writers can use generative AI to generate ideas, explore new possibilities, and overcome creative blocks.
- Real data augmentation: Generative AI can generate synthetic data that closely resembles real data.
- This is particularly useful in machine learning applications where a large amount of labelled data is required.
- Creation of multiple content: Generative AI enables the automated creation of various types of content, such as text, images, videos, music, and more.
- This can significantly speed up the content generation process for industries like advertising, entertainment, and marketing.
- Healthcare: By generating new medical images and simulations, improving the accuracy and efficiency of medical diagnoses and treatments.
- Personalization: Generative AI can be used to create personalized experiences for users.
- By analysing user preferences and behaviour, generative AI systems can generate tailored recommendations, product suggestions, and customized content, enhancing customer satisfaction and engagement.
- Problem Solving: Generative AI can be applied to problem-solving tasks, such as generating new drug compounds, optimizing supply chain logistics, or creating efficient designs.
- By exploring vast solution spaces, generative AI algorithms can propose novel solutions and accelerate the discovery process.
- Simulation and training: Industries like autonomous vehicles or robotics, generative AI can create virtual environments to train algorithms and test systems without the need for physical resources or risking safety.
Concerns associated with regulating AI:
- Rapid technological advancement: Recent advancements in AI posing challenges for regulators to keep up with the latest developments and effectively regulate a technology that is constantly evolving.
- Deepfakes: These are the synthetic media that generative AI models can create by manipulating or combining existing images, videos, or audio.
- Deepfakes can be used for malicious purposes such as spreading disinformation, impersonating people, or blackmailing.
- Increased costs and competition: Compliance with regulations may impose additional costs on businesses, particularly smaller companies and startups, limiting their ability to compete in the AI market.
- The burden of regulatory compliance could disproportionately affect smaller players.
- Accountability: Determining responsibility and liability when AI systems cause harm or make erroneous decisions can be challenging.
- Clarifying the legal frameworks and accountability structures surrounding AI is crucial for effective regulation.
- Cybersecurity: Generative AI models can be used by hackers to create new and complex types of malwares, phishing schemes, or other cyberattacks that can evade conventional security measures.
- Such attacks can have serious consequences such as data breaches, financial losses, or reputational damage.
- International cooperation: AI regulation requires international cooperation and collaboration to address global challenges, harmonize standards, and prevent regulatory arbitrage.
- Developing consensus among different countries with varying interests and priorities can be a complex task.
Artificial Intelligence across the globe:

- India: The Ministry of Information Technology and Electronics is working on framing the draft Digital India Act, which will replace the existing IT Act.
- India has established a National AI Programme to promote the efficient and responsible use of AI.
Overall generative AI has the potential to enable efficiency and productivity across multiple industries and applications at scale. However, if not designed and developed responsibly with appropriate safeguards, Generative AI can create harm and adversely impact society through misuse, perpetuating biases, exclusion, and discrimination.
Source: TH
Syllabus
- Mains – GS 3 (Economy)
Context: The National Bank for Agriculture and Rural Development (NABARD) has issued India’s first ‘AAA’ rated Indian Rupee-denominated Social Bonds.
About Social bonds:
- Social bonds, also known as social impact bonds (SIB), are the type of bond where the bond issuer is gathering funds for a project that had some socially beneficial implications.
- Similar to any other bond, social bonds imply that the bond issuer owes a debt to the bondholder.
- The Pimpri Chinchwad Municipal Corporation (PCMC) in Maharashtra’s Pune and United Nations Development Programme (UNDP) in 2020 co-created India’s first Social Impact Bond (SIB).
Sustainability Bond Framework
- NABARD recently announced a Sustainability Bond Framework which seeks to finance and refinance new or existing eligible green and social projects.
- Eligible social projects: Includes affordable basic infrastructure, access to essential services, affordable housing, employment generation, food security, socioeconomic advancement, and empowerment.
- Projects that promise energy efficiency including green buildings, energy storage, and smart grids.
Key features of Social Bonds:
- Designed for social cause: These bonds are raised to improving healthcare access, advancing education, providing affordable housing, alleviating poverty, and promoting environmental sustainability.
- The defining characteristic of social bonds is their commitment to generating tangible and positive societal outcomes.
- Broad spectrum of issuers: They are not limited to government entities but can be issued by a diverse array of organizations.
- This includes governments at various levels. international multilateral organizations, financial institutions and corporations.
- This diversity of issuers underscores a collective commitment to addressing social issues and leveraging financial markets to do so.
- Certification and reporting: The certification ensures that the bond’s proceeds are used exclusively for the intended social projects and adhere to predefined social goals.
- Issuers are obligated to provide regular and transparent reporting on the progress and impact of the projects financed.
- This reporting helps investors, regulators, and the public assess whether the social bonds are fulfilling their intended purpose.
Challenges associated with the social bonds:
- Complexity of identifying projects: Identifying suitable social projects that can effectively absorb the capital raised through social bonds can be a complex task.
- This challenge arises from the need to align the projects with the specific criteria and goals of social bonds.
- Therefore, careful project selection and prioritization are critical to the success of social bond issuances.
- Measuring Impact: As it generate tangible and positive social outcomes, measuring the social impact of projects can be intricate, as it often involves assessing complex and multifaceted social variables.
- Robust monitoring and evaluation systems are necessary to track progress and demonstrate the impact of financed projects.
- Lack of awareness and education: To foster broader adoption of social bonds, there is a need to increase awareness among both investors and issuers about their benefits and mechanisms.
- Many potential stakeholders may not fully understand the unique attributes of social bonds, including their potential for positive social impact. Education campaigns and targeted outreach efforts can help bridge this knowledge gap and encourage more participation in the market.
Way Forward:
Therefore, issuance of social bonds is a significant development in the Indian financial market, providing an avenue for financing projects that have a positive impact on society and addressing social issues. The strong investor response reflects growing interest in socially responsible investing and sustainable finance in India.
Source: THB
Practice MCQs
Q1) Consider the following pairs:
| Indices | Organization |
| 1.Child Development Index | Save the Children |
| 2.Corruption Perceptions Index | Transparency International |
| 3.Education Index | UNDP |
How many of the above pairs are correctly matched?
- Only one
- Only two
- All three
- None
Q2) Consider the following statements
Statement-I:
Protection of Children from Sexual Offences (POCSO) Act does not recognize boys as the victims of sexual abuse.
Statement-II:
The Act forbids the disclosure of the victim’s identity.
Which one of the following is correct in respect of the above statements?
- Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and Statement-II is the correct explanation for Statement-I
- Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and Statement-II is not the correct explanation for Statement-I
- Statement-I is correct but Statement II is incorrect
- Statement-I is incorrect but Statement II is correct
Q3) With reference to diabetes, consider the following statements:
- Its symptoms include blurred vision and feeling tired.
- The blood glucose levels are higher than normal but not high enough to be officially diagnosed with Type 2 diabetes in gestational diabetes.
- Diabetes only affects people of old age (above 60yrs).
How many of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 1, 2 and 3 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 1 and 2 only
Mains Practice Questions
Q.1) Analyse the potential benefits and challenges of generative AI for India’s development and security. Suggest some measures that India should take to harness the opportunities and mitigate the risks of generative AI. (250 words)
Q.2) Discuss the potential benefits and disadvantages of social impact bonds (SIBs). Explains NABARD’s Sustainability Bond Framework with examples. (250 words)
Comment the answers to the above questions in the comment section below!!
ANSWERS FOR ’ 2023 – Daily Practice MCQs’ will be updated along with tomorrow’s Daily Current Affairs.st
ANSWERS FOR 30th September – Daily Practice MCQs
Q.1) – b
Q.2) – b
Q.3) – c











