IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
Archives
(PRELIMS & MAINS Focus)
Syllabus
- Prelims – Art and Culture
Context: Recent initiatives to refashion Telangana’s woollen gongadi shawls into shoes for farmers have been observed.
About Telangana’s woollen gongadi shawls:-
- Gongadi is the traditional woollen blanket woven by the indigenous Kuruma communities.
- It is made from the wool of the indigenous Deccani sheep, which is locally known as Nalla gorrae.
- Nalla gorrae: it is a breed of sheep found in the Deccan Plateau region. (UPSC MAINS: Landform formation due to volcanic eruptions)
- The blanket is famous for its durability and versatility. It lasts for more than a decade due to its unique hand weaving. (UPSC CSE: Textile Industry in India)
- Unique natures of gongadi = it does not fade but grows darker in time.
- The traditional gongadi is produced organically, without using any dyes either natural or synthetic.
- Sizing of the strings is done using the paste of soaked and cooked tamarind seeds.
MUST READ: Hyderabad lac bangles set to get GI tag
SOURCE: THE HINDU
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) Consider the following pairs: (2018)
Crafts Heritage of
- Puthukkuli Shawls Tamil Nadu
- Sujni Embroidery Maharashtra
- Uppada Jamdani saris Karnataka
Which of the pairs given above is /are correct?
- 1 only
- 1 and 2
- 3 only
- 2 and 3
Q.2) Kalamkari painting refers to (2015)
- a hand-painted cotton textile in South India.
- a handmade drawing on bamboo handicrafts in NorthEast India.
- a block-painted woollen cloth in the Western Himalayan region of India.
- a hand-painted decorative silk cloth in North-Western India.
Syllabus
- Prelims –Governance
Context: According to recent reports the Tele-Law programme has achieved a new milestone with 40 lakh beneficiaries across the country.
About the Tele-Law programme:-
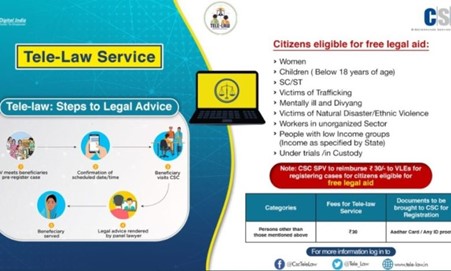
IMAGE SOURCE: CODESSLIDE.IN
- The Tele-Law programme was launched in (UPSC CSE: Tele-Law)
- Ministry/ministries: Ministry of Law and Justice and Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY).
- Objective: the programme connects the disadvantaged section with a panel of lawyers through an e-interface platform.
- It uses video conferencing facilities and telephone services to connect lawyers to litigants who need legal advice.
- It is to facilitate the delivery of legal advice through a panel of lawyers stationed at the State Legal Services Authorities (SALSA) and CSC (Common service centres). (UPSC CSE: NALSA)
- The service is free for those who are eligible for free legal Aid under Section 12 of the Legal Services Authority Act, 1987. For all others, a nominal fee is charged.
MUST READ: Citizens’ Tele-Law Mobile App
SOURCE: AIR
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) Which of the following is/are the aim/aims of the “Digital India” Plan of the Government of India? (2018)
- Formation of India’s own Internet companies like China did.
- Establish a policy framework to encourage overseas multinational corporations that collect Big Data to build their large data centres within our national geographical boundaries.
- Connect many of our villages to the Internet and bring Wi-Fi to many of our schools, public places and major tourist centres.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
- 1 and 2 only
- 3 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
Q.2) Regarding Digi Locker’, sometimes seen in the news, which of the following statements is/are correct? (2016)
- It is a digital locker system offered by the Government under Digital India Programme.
- It allows you to access your e-documents irrespective of your physical location.
Select the correct answer using the code given below.
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Syllabus
- Prelims –Environment and Ecology
Context: Recently, a rare mouse deer was caught on a camera trap set up at Kanger Valley National Park.
About Kanger Valley National Park:-
IMAGE SOURCE: SLIDESHARE
- Kanger valley national park is situated in Jagdalpur,
- It was established as a national park in the year (UPSC CSE: Eco-sensitive Zones (ESZ) )
- It derives its name from the Kanger River that flows through it.
- The Cuddapah group of rock formations, as well as the Vindhyan group of rock formations, are the most prevalent rock formations in the park.
- The state bird of Chattisgarh, the Bastar Hill Myna, is the most famous species in this area.It can imitate human voices.
- Kutumbasar, Kailash, and Dandak are three caves in the park, known for their geological features of stalagmites and stalactites.
- Fauna: Tigers, Leopards, Mouse Deer, Rhesus Macaque, Sloth Bear, Flying Squirrel, Chital, Sambar, Barking Deer, Pythons, Cobra, Snakes etc. (UPSC CSE: Chhattisgarh’s state animal, Wild buffalo, close to extinction)
- Flora: Teak, Haldu, Sal, Tendu, Mahua, Saja, Bija, Dhavara, Tinsa, , Mahulbel, Amarbel, Bandha etc.
MUST READ: Indravati Tiger Reserve
SOURCE: THE TIMES OF INDIA
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) Which of the following Protected Areas are located in the Cauvery basin? (2020)
- Nagarhole National Park
- Papikonda National Park
- Sathyamangalam Tiger Reserve
- Wayanad Wildlife Sanctuary
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
- 1 and 2 only
- 3 and 4 only
- 1, 3 and 4 only
- 1, 2, 3 and 4
Q.2) Which one of the following protected areas is well-known for the conservation of a sub-species of the Indian swamp deer (Barasingha) that thrives well on hard ground and is exclusively graminivorous? (2020)
- Kanha National Park
- Manas National Park
- Mudumalai Wildlife Sanctuary
- Tal Chhapar Wildlife Sanctuary
Syllabus
- Prelims –Science and Technology
Context: A Foucault’s Pendulum, was installed in the new Parliament building inaugurated recently.
About Foucault’s Pendulum:-
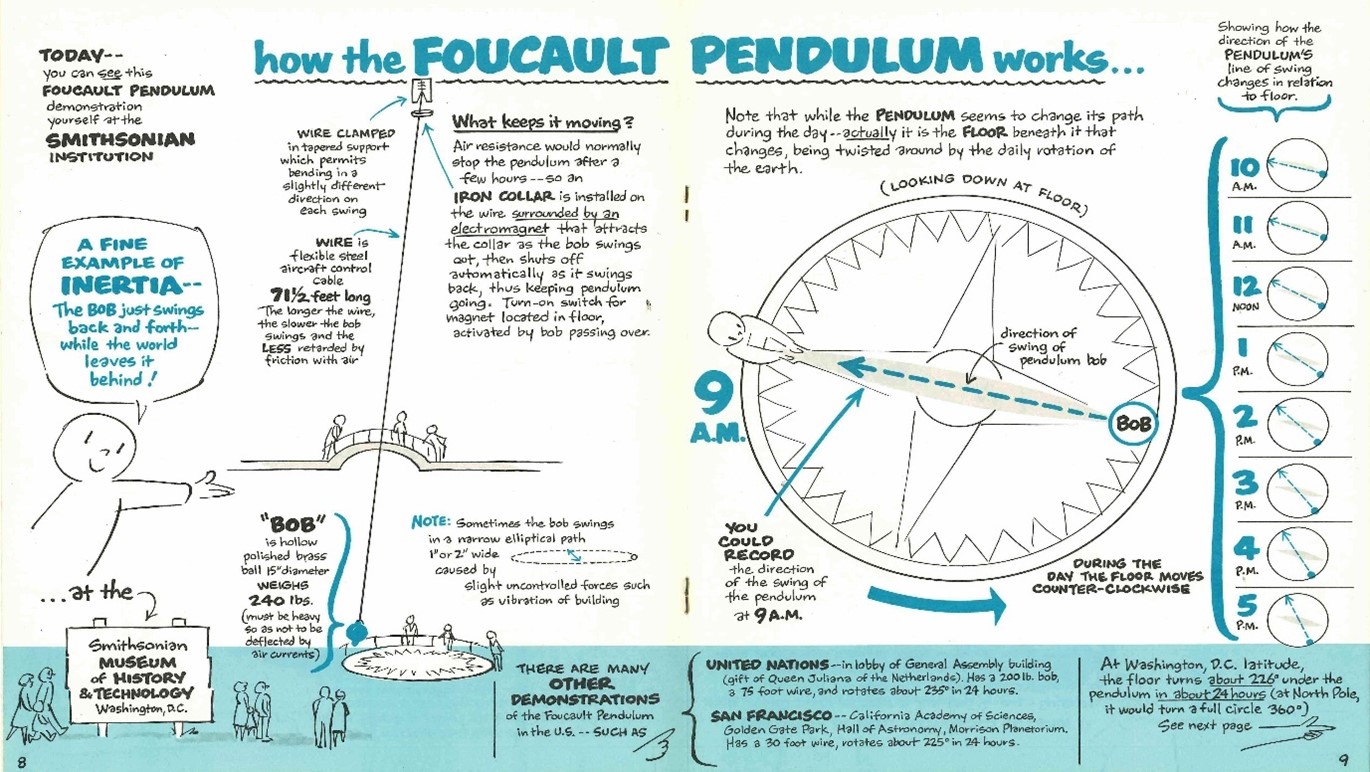
IMAGE SOURCE: si.edu
- The Foucault pendulum is a device that proves the Earth’s rotation.
- A French scientist, Leon Foucault invented the Foucault pendulum.
- Historical Context: In 1851, the Foucault pendulum experiment conclusively demonstrated the Earth’s rotation, settling debates about the planet’s movement. (UPSC MAINS: What is Geomagnetism?)
- Working: The pendulum consists of a heavy iron ball suspended by a steel wire and swings in a plane, mimicking the Earth’s rotation on its axis.
- A Foucault pendulum always rotates clockwise in the Northern Hemisphere.
- The rate of rotation depends on the latitude. (UPSC CSE: Climate change causing a shift in Earth’s axis)
- The rate becomes slower as the pendulum’s location approaches the Equator.
- At the Equator, 0° latitude, a Foucault pendulum does not rotate.
- In the Southern Hemisphere, rotation is counter-clockwise.
MUST READ: NavIC
SOURCE: THE INDIAN EXPRESS
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) Which one of the following statements best reflects the idea behind the “Fractional Orbital Bombardment System” often talked about in media? (2022)
- A hypersonic missile is launched into space to counter the asteroid approaching the Earth and explode it in space.
- A spacecraft lands on another planet after making several orbital motions.
- A missile is put into a stable orbit around the Earth and deorbits over a target on the Earth.
- A spacecraft moves along a comet with the same surface. speed and places a probe on it.
Q.2) Which one of the following is a reason why astronomical distances are measured in light-years? (2021)
- Distance among stellar bodies does not change.
- Gravity of stellar bodies does not change.
- Light always travels in a straight line.
- Speed of light is always the same.
Syllabus
- Prelims –Important Institutions
Context: Recently, the government announced dropping the plans to host the Shanghai Cooperation Organisation summit in Delhi.
About India and Shanghai Cooperation Organisation:-
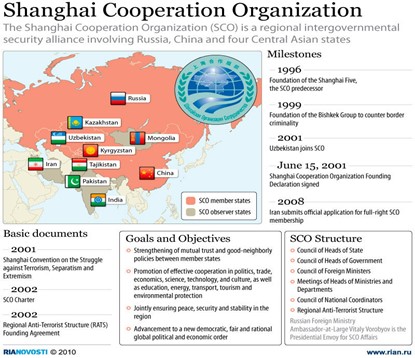
IMAGE SOURCE: BLOGSPOT.COM
- The Shanghai Cooperation Organisation is a permanent intergovernmental international organisation.
- It was created in 2001. (UPSC PRELIMS: Shanghai Cooperation Organization (SCO))
- The SCO Charter was signed in 2002 and entered into force in 2003. (UPSC MAINS: What are India’s stakes in the Shanghai Cooperation Organisation (SCO))
- Objectives: It aims to maintain peace, security and stability in the region.
- SCO’s official languages: Russian and Chinese.
India and SCO:-
- India’s membership in SCO can help in achieving the following goals:-
- Security:-
- India through RATS can improve its counterterrorism abilities by working toward intelligence sharing, law enforcement and developing best practices and technologies.
- It will also help India to work on anti-drug trafficking and small arms proliferation
- Energy:-
- SCO can provide India with an opportunity to meet its energy requirements through regional diplomacy.
- For example, Talks on the construction of stalled pipelines like the TAPI (Turkmenistan-Afghanistan-Pakistan-India) pipeline; IPI (Iran-Pakistan-India) pipeline can get a much-needed push through the SCO.
- Trade:-
- SCO provides India with direct access to trade in Central Asia.
- Central Asian countries provide India with a market for its IT, telecommunications, banking, finance and pharmaceutical industries.
- Geopolitical:-
- It will India to fulfil its aspiration of playing an active role in its extended neighbourhood as well as checking the ever-growing influence of China in Eurasia.
- It is also a platform for India to simultaneously engage with its traditional friend Russia as well as its rivals, China and Pakistan.
MUST READ: Significance of SCO Summit
SOURCE: THE HINDU
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) Consider the following pairs: (2020)
International agreement set-up Subject
- Alma-Ata Declaration Healthcare of the people
- Hague Convention Biological and Chemical Weapons
- Talanoa Dialogue Global Climate Change
- Under2 Coalition Child Rights
Which of the pairs given above is/are correctly matched?
- 1 and 2 only
- 4 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 2,3 and 4 only
Q.2) In which one of the following groups are all four countries members of G20? (2020)
- Argentina Mexico, South Africa and Turkey.
- Australia Canada, Malaysia and New Zealand
- Brazil, Iran, Saudi Arabia and Vietnam
- Indonesia Japan Singapore and South Korea
Syllabus
- Prelims – International Relations
Context: Recently, India and Indonesia have completed a joint feasibility study on developing the Sabang port.
About Sabang Port:-
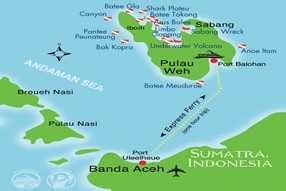
IMAGE SOURCE:BLUEWATERDIVETRAVEL.COM
- Sabang Port is located in the Aceh Province of Indonesia. (UPSC MAINS: India-Indonesia relationship)
- It is roughly 700 km from the Andaman and Nicobar Islands.
- Sabang is at the entrance of the Strait of Malacca.
- Malacca Straits: a narrow stretch of the sea between Indonesia and Malaysia.
- It is considered a key global choke point.
- The successful development of this vital port would allow India easier access to the Malacca Straits.
- It could bolster India’s military position vis-a-vis China in the Indian Ocean.
- During Prime Minister Narendra Modi’s visit to Indonesia in 2018:-Both countries had decided to cooperate in connectivity between Andaman & Nicobar Island and Aceh Province of Indonesia.
- It was also decided to set up a joint task force for undertaking projects for port-related infrastructure around the Sabang. (UPSC CSE: Indian Ports Association )
MUST READ: Indo-Pacific Relations
SOURCE: THE MINT
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) Consider the following countries: (2018)
- Australia
- Canada
- China
- India
- Japan
- USA
Which of the above are among the ‘free-trade partners’ of ASEAN?
- 1, 2, 4 and 5
- 3, 4, 5 and 6
- 1, 3, 4 and 5
- 2, 3, 4 and 6
Q.2) Consider the following in respect of the Indian Ocean Naval Symposium (IONS): (2017)
- Inaugural IONS was held in India in 2015 under the chairmanship of the Indian Navy.
- IONS is a voluntary initiative that seeks to increase maritime cooperation among navies of the littoral states of the Indian Ocean Region.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Syllabus
- Prelims –Geography
Context: Recently, an underwater volcano erupting with mud and fluids from Earth’s interior was discovered in the Barents Sea.
About Barents Sea:-
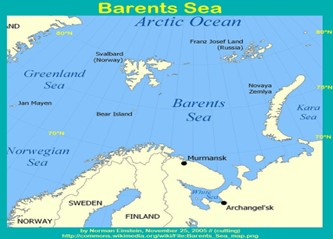
IMAGE SOURCE: RCLUTZ.COM
- The Barents Sea is a marginal sea of the Arctic Ocean.
- It is located along the northern coasts of Norway and Russia.
- It borders the Norwegian and Greenland Seas in the west, the Arctic Sea in the north and the Kara Sea in the east.
- The Barents Sea is divided between Russia and Norway by the United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea (UNCLOS).
- The sea was known to Vikings and medieval Russians as the Murmean Sea.
- The current name of the sea is after the historical Dutch navigator Willem Barentsz.
- Boundary with island landforms:-
- It is bounded by the Svalbard archipelago in the northwest, Franz Josef Land islands in the northeast, the Novaya Zemlya archipelago in the east, the Norwegian Sea and the Greenland Sea in the west, and the Kola Peninsula in the south. (UPSC MAINS: landforms formed by Volcanic eruption)
- It is separated from the Kara Sea by the Kara Strait and the Novaya Zemlya archipelago.
- The sea’s deepest point is 600 m at the Bear Island Trench. (UPSC MAINS: What is volcanism)
MUST READ: India – Russia Relations
SOURCE: INDIA TODAY
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) Consider the following pairs: (2020)
Rivers Flows into
- Mekong Andaman Sea
- Thames Irish Sea
- Volga Caspian Sea
- Zambezi Indian Ocean
Which of the pairs given above is/are correctly matched?
- 1 and 2 only
- 3 only
- 3 and 4 only
- 1, 2 and 4 only
Q.2) With reference to Ocean Mean Temperature (OMT), which of the following statements is/are correct? (2020)
- OMT is measured up to a depth of 26°C isotherm which is 129 meters in the southwestern Indian Ocean during January — March.
- OMT collected during January — March can be used in assessing whether the amount of rainfall in the monsoon will be less or more than a certain long-term mean.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Toy Industry of India
Syllabus
- Mains – GS 3 (Economy)
Context: India has recently turned a net exporter of toys, during 2020-21 and 2021-22, ending decades of import dominance.
Toy Industry in India:
- Presently, the Indian toy industry is only 5% of the global industry size indicating a large potential growth opportunity.
- The domestic toy demand forecasted to grow at 10-15% against the global average of 5%.
- The report ‘State of play: India’s toy story- Unboxing fun and beyond’ said India could also target a 2% share of global exports by 2025.
- There is high growth potential for India in exports of plastic toys and board games in the US, EU, and the Middle East among other markets.
Growth of India’s Toy Industry:
- Indian Toys Industry is estimated to be US$ 1.5 billion making up 0.5% of global market share.
- The toy manufacturers in India are mostly located in the NCR, Maharashtra, Karnataka, Tamil Nadu and clusters across central Indian States.
- The sector is fragmented with 90% of the market being unorganized and 4,000 toy industry units from the MSME sector.
- According to a joint report by industry body FICCI and KPMG, the India’s toy industry is expected to double from US$ 1 billion in 2019-20 to US$ 2 billion by 2024-25.
- A share of 0.5% of the global toy industry shows indicates large potential growth opportunity.
- The domestic toy demand is forecasted to grow at 10-15% against the global average of 5%.
- According to the Ministry of Commerce and Industry, the import of toys into India has declined sharply from US$ 304 million in 2018-19 to US$ 36 million in 2021-22.
- On the other hand, exports have increased from US$ 109 million in 2018-19 to US$ 177 million in 2021-22.
Factors driving growth of India’s Toy Industry:
- Huge consumer base: India’s population stands at around 1.4 billion, with approximately 26.62% of the population falling into the 0-14 age category.
- Rising disposable income: India has experienced strong GDP growth rates for the last several years, and the middle-class population has experienced strong growth.
- Rise in online purchases: Online sales channels have witnessed a boom in India with the evolution of smartphones and other digital media.
- Shifting preferences: According to the Toy Association report in 2018, parents believe in STEM-focussed toys as their primary way to encourage science and math development in young children.
- Disincentivising imported toys: The Indian government has increased the basic customs duty on toys from 20% to 60%, reduced availability of imported toys and enhanced demand for the domestic toy industry.
Challenges associated with the toy industry:
- India’s toy industry is minuscule and during the one-and-half decades between 2000 and 2016, industry output was halved in real terms (net of inflation) with job losses.
- Imports accounted for up to 80% of domestic sales until recently.
- Between 2000 and 2018-19, imports rose by nearly three times as much as exports.
- India hardly figures in the global toy trade, with its exports at a mere half a percentage point.
- Between 2014-19, the Indian toy industry witnessed negative productivity growth.
- India followed an inward-oriented industrial policy in the Planning era, which sheltered domestic production by providing a “double protection” — by import tariffs and reservation of the product for exclusive production in the small-scale sector — known as the “reservation policy”.
- Toy manufacturing remained stagnant, archaic, and fragmented, even as imports of modern, safe, and branded toys boomed.
- The output of the informal or unorganised sector shrank, though it continues to account for the majority of establishments and employment.
- ‘Make in India’ had a negligible effect on strengthening toy production and exports on a sustained basis.
Steps taken by the Government to aid growth of Toy Industry:
- Call to the Start-ups: The Government has called upon start-up entrepreneurs to explore the toy sector.
- The Government has also urged industry players to support local toys and reduce reliance on foreign goods.
- Educational institutions have been asked to organise hackathons for students to innovate in toy technology and design, including online games, to reflect Indian ethos and values.
- Increase in Custom Duty: The Government has increased basic customs duty from 20% to 60%.
- It is likely to result in toy importing brands to explore manufacturing in India, especially for the Indian market.
- It has also increased demand of toys manufactured by domestic toy industry.
- Mandatory Quality Certification: The Government has made toy quality certification mandatory to revive the indigenous industry.
- The Government began enforcing quality control for imported toys from September 1, 2020, to ensure that only products conforming to standards enter the country.
- Programmes Boosting the Toy Industry: The Government has chalked out a plan to promote traditional toys manufactured in the country by creating Toy Labs (a national toy fair for innovative Indian-themed toys).
- A plan to establish networks of toy labs such as Atal Tinkering Labs is also in the works to provide support for physical toys and for children to learn, play and innovate.
- Such labs will also be a way of specialised toy marking for quality certification and original design.
Source: The Hindu
Syllabus
- Mains – GS 3 (Environment)
Context: More than 50 percent of the world’s largest lakes and reservoirs have shrunk over the past three decades primarily due to climate change and human activities, according to a new study.
Highlights of the study:
- From these water bodies, approximately 600 cubic km of water was lost between 1992 and 2020 — an amount equivalent to the total water used in the United States for the entire year of 2015.
- The researchers found that out of the 1,052 natural lakes that were examined, 457 had significant water losses in the past three decades.
- They attributed 57 per cent of the net decline in the water quantity in natural lakes to human activities, such as unsustainable consumption of water, and increasing temperature and potential evapotranspiration (PET) with the latter two indicating the role of climate change.
- Contrary to previous studies, natural lakes located in humid tropics and high altitudes are experiencing water shortages.
- Two-thirds of all reservoirs across the globe have experienced significant storage declines.
- Reservoirs, however, showed a net global increase in water levels, owing to 183 recently filled reservoirs.
- The main reason behind the drop in water levels is sedimentation — the process of particles such as sand and stones settling to the bottom of a body of water.
Findings of the Study:
- The study also pointed out the worst affected largest lakes across the world and why they are shrinking in size.
- For instance, the Aral Sea in Central Asia, Lake Mar Chiquita in Argentina, the Dead Sea in the Middle East, and the Salton Sea in California have mainly dried due to unsustainable water consumption.
- Whereas, increasing temperature and (potential evapotranspiration)PET caused the complete disappearance of Lake Gowd-e-Zareh in Afghanistan, Toshka lakes in Egypt, and marked drying of Lake Kara-Bogaz-Gol in Turkmenistan, Lake Khyargas in Mongolia, and Lake Zonag in China.
- Notably, lakes have shrunk or disappeared completely across 82 percent of the Arctic’s lake-rich regions in the past 20 years.
- In India, more than half of the reservoirs located in peninsular India have witnessed substantial water storage decline, mainly due to sedimentation.
- Moreover, among the worst affected natural lakes in the country is Ladakh’s Tso Morari.
Reasons for Shrinking of Lakes:
- Human Activities: 57 percent of the net decline in the water quantity in natural lakes to human activities, such as unsustainable consumption of water.
- Climate Change: The Arctic lakes have shrunk because of a “combination of changes in precipitation, runoff, temperature, and potential evapotranspiration (PET) — loss of water due to both evaporation and transpiration, which are likely a concurrent result of natural variability and climate change.
- Sedimentation: The main reason behind the drop in water levels is sedimentation — the process of particles such as sand and stones settling to the bottom of a body of water.
Consequences of shrinking lakes:
- Nearly two billion people, one-quarter of the global population in 2023, will be affected as they live in basins with large water bodies that have witnessed a significant drop in their water levels in the past three decades.
- Many of these drying lakes have been identified as important sources of water and energy.
- The reduced size of these lakes not only results in freshwater decline and environmental degradation but also disrupts the water and carbon cycles.
- Widespread water shortage in these water bodies, “particularly accompanied by rising lake temperatures, could reduce the amount of absorbed carbon dioxide and increase carbon emissions to the atmosphere given that lakes are hotspots of carbon cycling.”
Way Forward:
There is a need to manage them in an integrated manner. Steps like restrictions on water consumption and climate mitigation to bring down global temperatures are some of the ways to conserve them.
This will also help in reducing sedimentation in reservoirs as the rate of sedimentation is linked to climate change — it increases when there is extreme precipitation, as well as land disturbance such as wildfires, landslides and deforestation.
Source: Indian Express
ANSWERS FOR 31st May – Daily Practice MCQs
Q.1) – c
Q.2) – c
Q.3) -d














