IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
Archives
(PRELIMS & MAINS Focus)
Syllabus
- Prelims –Economy
Context: Recent reports suggest that Small Finance Banks have revolutionised banking services in rural and semi-urban areas.
About Small Finance Banks:-

IMAGE SOURCE: tnpscthervupettagam.com
- Small Finance Banks are the financial institutions, which provide financial services to the unserved and unbanked region of the country.
- They are registered as a public limited company under the Companies Act, 2013.
- Minimum paid-up capital– 100 cr.
- Capital adequacy ratio – 15% of risk-weighted assets.
- Foreign shareholding capped at 74% of paid capital.
- Foreign Portfolio investment ( FPIs) cannot be more than 24%.
- Priority sector lending requirement of 75% of total adjusted net bank credit. (UPSCE MAINS: Micro finance has the ability to unleash rural India’s entrepreneurial zeal.)
Eligibility Criteria:-
- Resident individuals/professionals, having at least 10 years of experience in banking and finance can start Small Finance Banks with the approval of RBI.
- Existing Non-Banking Finance Companies (NBFCs), Micro Finance Institutions (MFIs), and Local Area Banks (LABs) in the private sector. (UPSC CSE: Digital Banks)
- Indian residents and have a successful record of accomplishment of running their businesses for at least a period of five years must control these.
- Joint ventures for setting up small finance banks are not permitted.
Functions:-
- Take small deposits and disburse loans.
- Distribute mutual funds, insurance products and other simple third-party financial products.
- Lend 75% of their total adjusted net bank credit to priority sector. (Revised Priority Sector Lending Guidelines).
- Maximum loan size would be 10% of capital funds to single borrower, 15% to a group.
- Minimum 50% of loans should be up to 25 lakhs.
MUST READ: Inclusive Growth
SOURCE: THE PRINT
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) In India, the Central Bank’s function as the “lender of last resort” usually refers to which of the following? (2020)
- Lending to trade and industry bodies when they fail to borrow from other sources
- Providing liquidity to the banks having a temporary crisis
- Lending to governments to finance budgetary deficits
Select the correct answer using the code given below
- 1 and 2
- 2 only
- 2 and 3
- 3 only
Q.2) With reference to Urban Cooperative Banks in India, consider the following statements: (2021)
- They are supervised and regulated by local boards set up by the State Governments.
- They can issue equity shares and preference shares.
- They were brought under the purview of the Banking Regulation Act, of 1949 through an Amendment in 1996
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
Syllabus
- Prelims –Governance
Context: Recently, the Union Cabinet approved a programme for “world’s largest grain storage”.
About World’s largest grain storage plan:-
- This scheme intends to construct grain storage facilities in the cooperative sector.
- Every block will have a dedicated godown with a capacity of 2,000 tonnes.
- Objective: to revolutionize the storage and distribution of food grains, ensuring their preservation and availability across the country.
- Supervision of the scheme: an inter-ministerial committee will oversee implementation.
Schemes identified for convergence under the Plan:-
- Ministry of Agriculture and Farmers Welfare:-
- Agriculture Infrastructure Fund (AIF)
- Agricultural Marketing Infrastructure Scheme (AMI)
- Mission for Integrated Development of Horticulture (MIDH)
- Sub Mission on Agricultural Mechanization (SMAM)
- Ministry of Food Processing Industries:-
- Pradhan Mantri Formalization of Micro Food Processing Enterprises Scheme (PMFME)
- Pradhan Mantri Kisan Sampada Yojana (PMKSY)
- Ministry of Consumer Affairs, Food and Public Distribution:-
- Allocation of food grains under the National Food Security Act
- Procurement operations at Minimum Support Price
Benefits:-
- The plan aims to address not just the shortage of agricultural storage infrastructure. (UPSC MAINS: Evaluate the storage mechanism for agricultural produce in India. )
- Functioning as Procurement centres for State Agencies/ Food Corporation of India (FCI)
- Creation of decentralised storage capacity- it would reduce food grain wastage and strengthen the food security of the country.
- Providing various options to the farmers-, it would prevent the distressed sale of crops, thus enabling the farmers to realise better prices for their produce.
- Reduce the cost incurred in the transportation of food grains to procurement centres.
MUST READ: Free Foodgrain Scheme
SOURCE: THE HINDUSTAN TIMES
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) Which of the following factors/policies were affecting the price of rice in India in the recent past? (2020)
- Minimum Support Price
- Government’s trading
- Government’s stockpiling
- Consumer subsidies
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
- 1, 2 and 4 only
- 1, 3 and 4 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1, 2, 3 and 4
Q.2) In India, which of the following can be considered as public investment in agriculture? (2020)
- Fixing Minimum Support Price for agricultural produce of all crops
- Computerization of Primary Agricultural Credit Societies
- Social Capital Development
- Free electricity supply to farmers
- Waiver of agricultural loans by the banking system
- Setting up cold storage facilities by the governments.
In India, which of the following can be considered as public investment in agriculture?
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
- 1, 2 and 5 only
- 1, 3, 4 and 5 only
- 2, 3 and 6 only
- 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 and 6
Syllabus
- Prelims –Science and Technology
Context: Recently, scientists developed a diagnostic test for Chytridiomycosis.
About Chytridiomycosis:-

IMAGE SOURCE: SLIDESERVE.COM
- Chytridiomycosis is a fungal disease in frog populations. (UPSC CSE: White fungus)
- It has caused severe declines in over 500 frog species and led to 90 extinctions, making it the deadliest animal disease known. (UPSC CSE: Mucormycosis )
- How does it infect?
- It infects frogs skin.
- This damages their ability to balance water and salt levels.
- Origin- the disease originated in Asia.
- It spread globally through amphibian trade and travel.
- Mortality rate- extremely high.
- Natural immunity:-
- Some amphibian species have some form of natural immune resistance and do not become sick when they carry the fungus.
- This Immunity might come from anti-microbial chemicals within the skin, symbiotic bacteria on the skin, white blood cells and antibodies in the blood, or combinations of these mechanisms.
- So far, no clear trend has been found between resistance and immune function.
MUST READ: World Health Organization(WHO) releases first-ever list of health-threatening fungi
SOURCE: THE NEW INDIAN EXPRESS
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) Certain species of which one of the following organisms are well known as cultivators of fungi? (2022)
- Ant
- Cockroach
- Crab
- Spider
Q.2) Which of the following is not a bird? (2022)
- Golden Mahseer
- Indian Nightjar
- Spoonbill
- White Ibis
Syllabus
- Prelims –Economy
Context: Recently, the Kerala High Court held that an education loan application should not be rejected based on a low Credit Information Bureau India Ltd (CIBIL) score.
About Credit Information Bureau India Ltd (CIBIL):-

IMAGE SOURCE: SLIDESHARE.NET
- Credit Information Bureau (India) Limited is one of the Credit Information Companies in India.
- It is involved in keeping the documentation of every credit-related action of individuals and companies.
- Different financial institutions and the banks, submit their individual information to CIBIL.
- CIBIL provides CIR (Credit Information Report) and the credit scores.(UPSC CSE: Credit Rating agencies)
- The reports on CIBIL accommodate the information in detail about the credits an individual is taking like car loans, credit cards, home loans, personal loans, etc.
- Two types of CIBIL reports are available:-
- CIBIL Report on Company Credit– CIBIL CCR is a record of your company’s credit history. This is created from data submitted to CIBIL by lending institutions across India. The past payment behaviour of a company is a strong indication of its future behaviour
- Credit Information Report– it is created for individuals and contains in-depth information about credit behaviour in past and a score of CIBIL.
Importance of Credit Rating:
For Lenders;
- Better Investment Decision: No bank or money lending companies would like to give money to a risky customer. With credit rating, they get an idea about the creditworthiness of a company (that is borrowing the money) and the risk factor attached with them. By evaluating this, they can make a better investment decision.
- Safety Assured: High credit rating means an assurance about the safety of money and that it will be paid back with interest on time.
For Borrowers;
- Easy Loan Approval: With a high credit rating, you will be seen as a low/no risk customer. Therefore, banks will approve your loan application easily.
- Competitive Rate of Interest: You must be aware of the fact that every bank offers loans in a particular range of interest rates. One of the major factors that determine the rate of interest on the loan you take is your credit history. Higher the credit rating, lower the rate of interest.
Credit Information Companies (CICs):-
- At present, there are four CICs.
- They are provided with a Certificate of Registration.
- These include Equifax Credit Information Services Private Limited, CRIF High Mark Credit Information Services Private Limited, Credit Information Bureau (India) Limited, and Experian Credit Information Company of India Private Limited.
- Credit Information Companies in India are licensed by the Reserve Bank of India and governed by the Credit Information Companies Regulation Act, 2005.
MUST READ: Financial Services Institutions Bureau (FSIB)
SOURCE: TIMES OF INDIA
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) Consider the following statements: (2022)
- In India, credit rating agencies are regulated by the Reserve Bank of India.
- The rating agency popularly known as ICRA is a public limited company.
- Brickwork Ratings is an Indian credit rating agency.
Which of the statements given above is correct?
- 1 and 2 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
Q.2) With reference to the ‘Banks Board Bureau (BBB)’, which of the following statements is correct? (2022)
- The Governor of RBI is the Chairman of BBB.
- BBB recommends the selection of heads for Public Sector Banks.
- BBB helps Public Sector Banks develop strategies and capital-raising plans.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
- 1 and 2 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
Syllabus
- Prelims –Environment and Ecology
Context: Recent reports show that encroachment is pushing Himalayan brown bears into Kashmir’s villages.
About Himalayan brown bears:-

IMAGE SOURCE: ROUND.GLASS.COM
- Distribution:Northwestern and central Himalaya, including India, Pakistan, Nepal, the Tibetan Autonomous Region of China and Bhutan.
- Habitat:High altitude open valleys and pastures.
- Conservation Status:-
- IUCN Red List- Critically endangered
- CITES – Appendix I (UPSC CSE: CITES COP 19)
- Indian Wildlife (Protection) Act of 1972 – Schedule 1 (UPSC CSE: Wildlife Institute of India (WII))
- Food:Omnivorous
- Threat: Human-animal conflict, rapid habitat loss, poaching for fur, claws and organs and, in some rare cases, bear baiting.
MUST READ: Asiatic Black Bear
SOURCE: DOWN TO EARTH
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) Consider the following animals (2021)
- Hedgehog
- Marmot
- Pangolin
To reduce the chance of being captured by predators, which of the above organisms rolls up/roll up and protects/protects its/their vulnerable parts?
- 1 and 2
- 2 only
- 3 only
- 1 and 3
Q.2)Which one of the following is a filter feeder? (2021)
- Catfish
- Octopus
- Oyster
- Pelican
Syllabus
- Prelims –Economy
Context: Recently, the shares of Coal India dropped 5% as offer-for-sale kicked off.
About Offer-for-sale:-
- Under the offer-for-sale method, securities are not issued directly to the public but are offered for sale through intermediaries like issuing houses or stockbrokers.
- The OFS mechanism was originally developed and implemented by the Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) in 2012.
- Objective: to make it simpler for founders of publicly traded firms to reduce their shareholding and conform to the required public shareholding standard.
- Unique conditions under which an OFS turns out to be a suitable option:-
- The issued shares are reserved for retail investors in an amount of at least 10%.
- A minimum of 25% of the available shares are reserved for mutual funds and insurance firms.
- Sponsors can sell firm shares straightaway through an Offer for Sale rather than being required to pause for an IPO. (UPSC CSE: IPO)
- Initial Public Offering (IPO): it is issued by a business to raise money from the stock markets, for the inaugural period. (UPSC CSE: FPO)
- The Offer for Sale is open to shareholders with greater than 10% ownership of a corporate entity.
- The trading hours, from 15 AM to 3 PM, are available for placing an OFS.
- Any allocations will not be made if the offer value falls below the prevailing market price.
- Before the OFS, the organization must notify the stock markets at least 2 days in advance.
MUST READ: Open Offer
SOURCE: BUSINESS
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) With reference to the Indian economy, what are the advantages of “Inflation-Indexed Bonds (IIBs)”? (2022)
- Government can reduce the coupon rates on its borrowing by way of IIBs.
- IIGs provide protection to investors from uncertainty regarding inflation.
- The interest received as well as capital gains on IIBs are not taxable.
Which of the statements given above is correct?
- 1 and 2 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
Q.2) With reference to the Indian economy, consider the following statements: (2022)
- A share of the household’s financial savings goes towards government borrowings.
- Dated securities issued at market-related rates in auctions form a large component of internal debt.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Syllabus
- Prelims –Important Institutions
Context: Recently, the Asian Development Bank (ADB) stated that it would contribute to India’s urban-focused flagship programmes and schemes.
About Asian Development Bank (ADB):-
IMAGE SOURCE: CORPORATEFINANCEINSTITUTE.COM
- Asian Development Bank (ADB) is a regional development bank. (UPSC MAINS: Differences between the World Bank and the Asian Development Bank (ADB). )
- It was established in
- First President: Takeshi Watanabe
- HQ: Manila, Philippines
- Objective: to promote social and economic development in Asia. (UPSC CSE: Multi-tranche financing facility)
- Membership:-
- The bank admits members of the United Nations Economic and Social Commission for Asia and the Pacific (UNESCAP) and non-regional developed countries.
- From 31 members at its establishment in 1966, ADB has grown to encompass 68 members
- 49 of these are within Asia and the Pacific.
- Shareholders: Japan and the United States (each with 15.6% of total shares), the People’s Republic of China (6.4%), India (6.3%), and Australia (5.8%).
- Voting rights: votes are distributed in proportion with members’ capital subscriptions.
- ADB is official United Nations Observer.
- Roles and functions:-
- It is dedicated to reducing poverty in Asia and the Pacific through inclusive economic growth, environmentally sustainable growth, and regional integration.
- Key Publications:-
- ADB Annual Report 2022
- Asian Development Outlook April 2023
- Asian Economic Integration Report 2023: Trade, Investment, and Climate Change in Asia and the Pacific
- Key Indicators for Asia and the Pacific 2022
India and ADB
- India is a founding member of ADB.
- India is the bank’s fourth largest shareholder.
- ADB operations promote private sector development, gender empowerment, regional integration, knowledge solutions, and capacity development.
- ADB supports India’s priorities for robust, climate resilient, and inclusive growth, aligned with ADB’s Strategy 2030 and the forthcoming country partnership strategy, 2023–2027.
- ADB Projects in India:-
- Visakhapatnam-Chennai Industrial Corridor Development Program (Tranche 2)
- Himachal Pradesh Subtropical Horticulture, Irrigation, and Value Addition Project
- Nhava Sheva Container Terminal Financing Project
- Strengthening Vocational High Schools in South Asia
- Olam Global Agri Food Security Support Project
- Improving Bengaluru’s Livability Through Transit-Oriented Development
- Proposed projects:-
- State Road Safety Incentive Program
- Manipur State Road Connectivity Investment Program
- Nashik Metro Neo Project
- Road Sector Development in Tripura
- Promoting Disaster Risk Insurance
MUST READ: Loan Agreements between Govt & Asian Development Bank to Boost the infrastructure sector in India
SOURCE:
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) “Rapid Financing Instrument” and “Rapid Credit Facility” are related to the provisions of lending by which of the following: (2022)
- Asian Development Bank
- International Monetary Fund
- United Nations Environment Programme Finance Initiative
- World Bank
Q.2) With reference to the “G20 Common Framework”, consider the following statements: (2022)
- It is an initiative endorsed by the G20 together with the Paris Club.
- It is an initiative to support Low-Income Countries with unsustainable debt.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Recusal by Judges
Syllabus
- Mains – GS 2 (Polity and Governance) and GS 4 (Ethics – Conflict of Interest)
Context: Recently, there have been various instances of judges recusing themselves from hearing cases.
About Judge Recusal:
- When there is a conflict of interest, a judge can withdraw from hearing a case to prevent creating a perception that she carried a bias while deciding the case.
- The conflict of interest can be in many ways — from holding shares in a company that is a litigant to having a prior or personal association with a party involved in the case.
- Another instance for recusal is when an appeal is filed in the Supreme Court against a judgement of a High Court that may have been delivered by the SC judge when she was in the HC.
- The practice stems from the cardinal principle of due process of law that nobody can be a judge in her own case.
Rule for Recusal:
- There are no formal rules governing recusals, although several SC judgments have dealt with the issue.
- In Ranjit Thakur v Union of India (1987), the SC held that the test of the likelihood of bias is the reasonableness of the apprehension in the mind of the party.
- The judge needs to look at the mind of the party before him, and decide that he is biased or not.
Causes of Recusal:
- The decision to recuse generally comes from the judge himself or herself as it rests on the conscience and discretion of the judge to disclose any potential conflict of interest.
- Conflict of interest could be:
- Judge’s Interest in the subject matter, or relationship with someone who is interested in it;
- Judge’s Background or experience, such as the judge’s prior work as a lawyer;
- Judge’s Personal knowledge about the parties or the facts of the case;
- Judge’s Ex parte communications with lawyers or non-lawyers;
- Judge’s Rulings, comments or conduct;
- In some circumstances, lawyers or parties in the case bring it up before the judge.
- If a judge recuses, the case is listed before the Chief Justice for allotment to a fresh Bench.
Process of Recusal:
- The decision to recuse generally comes from the judge himself as it rests on the conscience and discretion of the judge to disclose any potential conflict of interest.
- Some judges orally convey to the lawyers involved in the case their reasons for recusal, many do not. Some explain the reasons in their order.
- In some circumstances, lawyers or parties in the case bring it up before the judge. Once a request is made for recusal, the decision to recuse or not rests with the judge.
- While there are some instances where judges have recused even if they do not see a conflict but only because such an apprehension was cast, there have also been several cases where judges have refused to withdraw from a case.
- If a judge recuses, the case is listed before the Chief Justice for allotment to a fresh Bench.
Concerns:
- Undermining Judicial Independence: It allows litigants to cherry-pick a bench of their choice, which impairs judicial fairness.
- In addition, the purpose of recusal in these cases undermines both independence and impartiality of the judges.
- Different Interpretations: As there are no rules to determine when the judges could recuse themselves in these cases, there are different interpretations of the same situation.
- Delays the Process: Some requests for recusal are made with the intent to intimidate the court or to get better of an ‘inconvenient’ judge or to obfuscate the issues or to cause obstruction and delay the proceedings or in any other way frustrate or obstruct the course of justice.
Way Forward:
Recusal is also regarded as the abdication of duty. Maintaining institutional civilities are distinct from the fiercely independent role of the judge as an adjudicator. It is the constitutional duty, as reflected in one’s oath, to be transparent and accountable, and hence, a judge is required to indicate reasons for his recusal from a particular case.
Source: The Hindu
Syllabus
- Mains – GS 3 (Environment)
Context: The government has recently invited bids for 50 GW of renewable energy capacity annually for the next five years.
About Renewable Energy:
- Renewable energy is energy derived from natural sources that are replenished at a higher rate than they are consumed.
- Sunlight and wind, for example, are such sources that are constantly being replenished. Renewable energy sources are plentiful and all around us.
- On the other hand, Fossil fuels – coal, oil and gas, are non-renewable resources that take hundreds of millions of years to form.
- Fossil fuels, when burned to produce energy, cause harmful greenhouse gas emissions, such as carbon dioxide.
Renewable energy capacity in India:
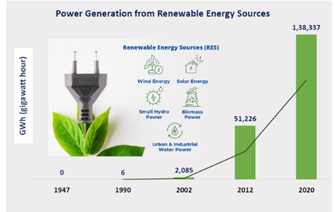
Source: pib
- India currently has a total renewable energy capacity of 168.96 GW (as on February 28, 2023) with about 82 GW at various stages of implementation and about 41 GW at tendering stage.
- This includes 64.38 GW Solar Power, 51.79 GW Hydro Power, 42.02 GW Wind Power and 10.77 GW Bio Power.
- Today, India is the world’s third largest producer of renewable energy, with 40% of its installed electricity capacity coming from non-fossil fuel sources.
Advantages of Renewable Energy:
A Fuel Supply That Never Runs Out:
- Renewable energy is created from sources that naturally replenish themselves – such as sunlight, wind, water, biomass, and even geothermal (underground) heat.
- While fossil fuels are becoming harder and more expensive to source – resulting in the destruction of natural habitats and significant financial losses – renewable energy never runs out.
Zero Carbon Emissions
- There are no greenhouse gasses or other pollutants created during the process.
- Coal power plants on the other hand create around 2.2 pounds of CO2 for every kilowatt-hour of electricity.
- As we race to decarbonize our world and embrace energy sources that do not contribute to global warming, renewables are helping to provide us with emission-free energy.
Cleaner environment
- Burning fossil fuels causes global warming and causes pollution.
- Coal power stations, for example, release high volumes of carbon dioxide (CO2) and nitrous oxide (N2O) directly into the atmosphere – two of the most potent greenhouse gasses.
- On the other hand, renewable energy creates no pollution, waste, or contamination risks to air and water.
A Cheaper Form of energy:
- With the rapid growth of renewable energy over the last ten years, solar and wind power are now the cheapest sources of energy in many parts of the world.
- In the United Arab Emirates, a new sun farm recently secured the world’s lowest price of solar energy at just 1.35c per kilowatt-hour.
- Whereas green energy was once a “clean-but-expensive” alternative – it is now helping to reduce energy bills for people in many parts of the world.
Renewable Energy Creates New Jobs:
- With an increasing focus on global warming and many governments, setting ambitious carbon-reduction goals Renewable Energy has quickly become a major source of new job growth.
Challenges of Renewable Energy in India:
- High initial cost of installation: While the development of a coal-based power plant requires around Rs 4 crore per MW, the investment required a wind-based plant, with a capacity utilization of 25%, which requires an investment of Rs 6 crore per MW.
- Reliability: By their very nature, solar and wind energy are variable in availability both spatially as well as geographically.
- Hence, they need to be supported by conventional sources of power.
- Creation of storage infrastructure: To overcome the variable nature of renewable sources of energy, it is vital to invest in affordable batteries of large capacity.
- Poor DISCOM’s condition: An important challenge for further scaling up renewables in India is the poor financial condition of power distribution companies (discoms), most of which are owned by state governments and are reeling under heavy debts.
- Low Social acceptance: renewable-based energy system is still not very encouraging in urban India. Despite heavy subsidies being provided by the government for the installation of solar water heaters and lighting systems, its penetration is still very low.
- Weak domestic manufacturing capability: It is important to set up manufacturing capacity in India to decrease imports and promote Aatmanirbhar Bharat.
- It would also aid in the creation of multiple manufacturing jobs.
- Sustainability: that is, how to expand reliable energy access and use while maintaining affordability for consumers and financial stability for the DISCOMs.
- Integration into the national grid: that is how to integrate increasing shares of renewable energy securely and reliably into the national electricity grid.
Govt schemes to promote RE:
- National Solar Mission (NSM) (Solar energy in India)
- Pradhan Mantri Kisan Urja Suraksha evam Utthaan Mahabhiyan (PM-KUSUM).
- Atal Jyoti Yojana (AJAY) Phase-II:
- The Ministry of New and Renewable Energy (MNRE) launched to illuminate dark regions through establishment of solar street lights.
- It is a sub scheme under off –grid and decentralized solar application scheme of Ministry of New and Renewable Energy (MNRE), Govt. of India.
- The Phase II is being implemented during 2018-19 and 2019-20.
- Solar Parks Scheme
Way Forward:
India’s switch from coal to clean power is a win-win and a promising step towards meeting the country’s net zero emissions target by 2070. Governments and private sector organizations need to collaborate and work together to develop innovative solutions and strategies that can help to overcome these obstacles.
India’s energy demand is expected to increase more than that of any other country in the coming decades due to its sheer size and enormous potential for growth and development. Therefore, it is imperative that most of this new energy demand is met by low-carbon, renewable sources.
Source: The Hindu
Practice MCQs
Q1. Consider the following statements about the Asian Development Bank (ADB):
- China is the largest shareholder in the ADB.
- The membership of the ADB is open to only poor and least developed countries across Asia and Africa.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
- Only 1
- Only 2
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Q2. Consider the following statements about the Himalayan Brown bear:
- Himalayan Brown bear is Vulnerable as per the IUCN red list.
- Its distribution is restricted to India, Pakistan, Nepal, the Tibetan Autonomous Region of China and Bhutan.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
- Only 1
- Only 2
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Q3. Consider the following statements about Primary Agricultural Credit Societies:
- PACS confer equal rights to all its members without considering their holding of share and their social standing.
- PACS provides long-term loans to its members.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
- Only 1
- Only 2
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Comment the answers to the above questions in the comment section below!!
ANSWERS FOR ’ 2nd June 2023 – Daily Practice MCQs’ will be updated along with tomorrow’s Daily Current Affairs.st











