IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis

Archives
(PRELIMS + MAINS FOCUS)
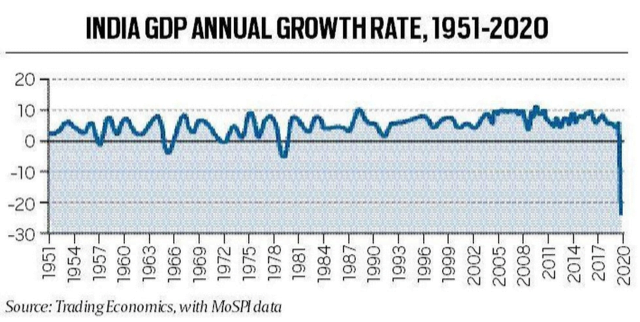
India enters phase of technical recession: RBI
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-III – Economy
In news
- In RBI’s monthly bulletin of November, it has started “nowcasting” or “the prediction of the present or the very near future of the state of the economy”.
Key takeaways
- The very first “nowcast” predicts that India’s economy will contract by 8.6% in the second quarter (July, August, September) of the current financial year.
- This pace of contraction is considerably slower than the 23.9% decline in the real GDP during the first quarter.
- However, the contraction of Q2 is crucial because it implies that India has entered a “technical recession” in the first half of 2020-21— for the first time in its history.
Important value additions
Recessionary phase
- It is a phase when the GDP contracts from one quarter to another.
Recession
- When a recessionary phase sustains for long enough, it is called a recession.
- During a recession, a significant decline in economic activity spreads across the economy and can last from a few months to more than a year.
Technical recession
- When real GDP has declined for at least two consecutive quarters.
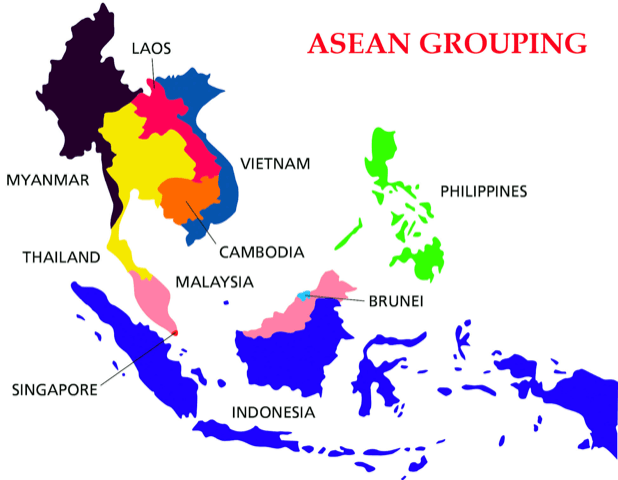
17th ASEAN-India Summit held
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-II – International Relations
In news
- Recently, India participated in the 17th ASEAN-India Virtual Summit.
- The current Chair of ASEAN is Vietnam.
Key takeaways
- The summit focused on measures to recover from the economic turmoil triggered by the Covid-19 pandemic and ways to further broad-base strategic ties.
- India placed the ASEAN at the centre of India’s Act East policy.
- It held that a cohesive and responsive ASEAN is essential for security and growth for all in the region.
- India highlighted the importance of strengthening convergence between India’s Indo-Pacific Oceans Initiative (IPOI) and the ASEAN Outlook on Indo-Pacific, to ensure a free, open, inclusive and rules-based region.
- It also highlighted the importance of cooperation by ASEAN for the Security And Growth for All in the Region (SAGAR) Vision.
- India would explore ways to increase trade despite its exit from the 15-nation RCEP agreement in 2019.
- India affirmed the importance of maintaining and promoting peace in the South China Sea.
- It also underscored the importance of cooperation and regular exchanges in the field of traditional medicines as a source of healthy and holistic living.
- India called for an early review of ASEAN-India Trade in Goods Agreement (AITIGA), which is pending for a long time.
Important value additions
Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN)
- It is a regional grouping that promotes economic, political, and security cooperation.
- It was established on 8th August 1967 in Bangkok, Thailand with the signing of the ASEAN Declaration (Bangkok Declaration).
- Founding members: Indonesia, Malaysia, Philippines, Singapore and Thailand.
- Present Ten Members: Brunei, Cambodia, Indonesia, Laos, Malaysia, Myanmar, the Philippines, Singapore, Thailand, and Vietnam.
- Chairmanship rotates annually, based on the alphabetical order of the English names of Member States.
- It is India’s 4th largest trading partner with about USD 86.9 billion in trade.
New Species of frog in Andaman found
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-III – Biodiversity
In news
- Recently a group of scientists has reported a new genus of treefrog from the Andaman Islands called Striped Bubble-nest frog.

Important value additions
Striped Bubble-nest frog
- Biological name: Rohanixalus vittatus
- It belongs to the genus of the Old World treefrog family Rhacophoridae.
- This is the first report of a tree frog species from the Andaman Islands.
- They are also known as Asian Glass Frog or see through frogs
- The female (mother) attends the egg clutches until hatching and assists in release of the tadpoles into the water.
- A large number of egg clutches (over 50) of different developmental stages may be found on a single leaf or plant.
- Multiple females usually attend such clutches in a behaviour termed as ‘community’ egg attendance.
- Frequent male-male combats involving pushing, kicking and dislodging to mate with a female were also reported.
Miscellaneous
Spacex’s Crew Dragon Spacecraft
-
Recently, SpaceX’s Crew Dragon spacecraft will lift off carrying a crew of four people to the International Space Station (ISS) on a six-month-long mission.
- The mission is part of NASA’s Commercial Crew Program.
- Objective: To make access to space easier in terms of its cost, so that cargo and crew can be easily transported to and from the ISS, enabling greater scientific research.
- At the ISS, the Crew-1 team will conduct microgravity studies and deliver new science hardware and experiments that they will carry with them to space aboard the Crew Dragon spacecraft.
- It is the first spacecraft certified by NASA. This means SpaceX can now operate regular flights to the space station.
- Earlier in May, NASA’s SpaceX Demo-2 test flight lifted off for the ISS, becoming the first crewed flight to launch from American soil since the conclusion of the space shuttle era in 2011.
(MAINS FOCUS)
ECONOMY/ INTERNATIONAL
Topic: General Studies 2,3:
- Effect of policies and politics of developed and developing countries on India’s interests.
- Indian Economy and issues relating to planning, mobilization, of resources, growth, development and employment.
Digital taxation & OECD: On a weak pillar
Context: The tax challenges pertaining to the digitalisation of the economy have been a contentious issue over the past decade.
In recognition of this, OECD identified it as one of the main areas of focus of the OECD/G20 Base Erosion and Profit Shifting (BEPS) Project, leading to the 2015 BEPS Action 1 report.
What is Base erosion and profit shifting (BEPS)?
- BEPS refers to tax planning strategies used by multinational enterprises that exploit gaps and mismatches in tax rules to avoid paying tax.
- Although some of the schemes used are illegal, most are not
- BEPS practices cost countries USD 100-240 billion in lost revenue annually.
- Working together within OECD/G20 Inclusive Framework on BEPS, over 135 countries and jurisdictions are collaborating on
- The implementation of 15 measures to tackle tax avoidance,
- Improve the coherence of international tax rules
- Ensure a more transparent tax environment.
What are the concerns with BEPS?
- Reduced Tax Revenue: Developing countries’ higher reliance on corporate income tax means they suffer from BEPS disproportionately.
- Disproportionately impacts domestic small firms: Such tax planning strategies undermines the fairness and integrity of tax systems because businesses that operate across borders can use BEPS to gain a competitive advantage over enterprises that operate at a domestic level.
- Sets wrong precedent: Moreover, when taxpayers see multinational corporations legally avoiding income tax, it undermines voluntary compliance by all taxpayers
What is 2015 BEPS Action 1 report?
In 2015, when the OECD released Action Plan 1 report, that contained the pillars that should guide taxation of the digital economy. It recognised
- Neutrality
- Efficiency
- Certainty and simplicity
- Effectiveness and fairness
- Flexibility
OECD, Taxation on digitalisation and BEPS
- The debate and focus on taxing digital companies peaked when countries started implementing uncoordinated, unilateral measures.
- In January 2019, the OECD released a policy note that said the renewed international discussions will focus on two central pillars: Pillar One and Pillar Two.
- Pillar One will address the broader challenges related to the digitalisation of the economy and will focus on the allocation of taxing rights.
- The aim of Pillar One is to reach a global agreement on adapting the allocation of taxing rights on business profits in a way that expands these rights for market jurisdictions.
- The OECD Blueprint on Pillar one provides a solid foundation for a future agreement that would adhere to the concept of net taxation of income, avoid double taxation and be as simple and easy to administer as possible.
- Pillar Two will sort out the remaining BEPS concerns (collectively, BEPS 2 project)
Concerns
- Changes in International Rules: The reallocation of taxing rights under Pillar One could lead to significant changes in the international tax rules under which multinational businesses operate and could have important consequences on the overall tax liability of businesses and tax revenues of the countries.
- Policy Note lacks Consensus: The Blueprint recognises that it is not a consensus document and that there are several key features of the solution that can only be resolved through political decisions.
- Requires further Political Action: The Blueprint notes that political decisions are required on several issues, including the amount of residual profit to be allocated under the new taxing right, the scope of mandatory binding dispute resolution etc.
- Short on Principles: The Blueprint falls short on a number of principles detailed in 2015 Action 1 report by OECD.
Conclusion
In the absence of a consensus, the uncertainty caused by the unilateral measures is expected to add to the tax woes of multinationals.
Connecting the dots:
ECONOMY/ GOVERNANCE
Topic: General Studies 2,3:
- Government policies and interventions for development in various sectors and issues arising out of their design and implementation
- Indian economy and mobilization of resources
Calibrated Economic Package (Atmanirbhar Bharat 3.0) – Part 1
Context: On 12th November, the Union Finance Ministry made a series of announcements comprising the third stimulus package that includes additional expenditure of Rs 2.65 lakh crore.
About Previous Packages
- The first stimulus focused on containing the damage of the lockdowns by addressing the cash-flow mismatch. This was done using emergency credit facilities, macro-prudential policies, deferred taxes and regulatory forbearance. The objective was to prevent massive bankruptcies
- The second stimulus was given to primarily the government employees as they did not witness an income shock as such, with the objective of incentivising them to spend.
- Additionally, the government reiterated its commitment towards maintaining its expenditure and pushed state governments to keep up with their expenditure commitments, including those on capital outlays.

Image Source: Livemint
About the Third Package
- Atmanirbhar Bharta Rozgar Yojana: The new employees hired by the EPFO-registered organisations will receive benefits during COVID-19. If the EPFO registered establishments take in new employees or those who lost jobs earlier will get benefits from government.
- Emergency Credit Line Guarantee Scheme (ECLGS) for MSMEs, businesses, MUDRA borrowers and individuals (loans for business purposes), has been extended till March 31, 2021.
- New Credit Guarantee Scheme: A credit guarantee support scheme for health care sector and 26 sectors stressed due to COVID-19 pandemic was also launched. Under this new credit scheme, banks will be able to lend to stressed companies from 26 sectors identified by the K.V. Kamath committee earlier this year.
- Production-Linked Incentive: The PLI scheme worth ₹ 1.46 lakh crore is being offered to 10 champion sectors which will help boost the efficiency and competitiveness of domestic manufacturing. A total amount of ₹ 1.5 lakh crore has been earmarked across sectors, for the next five years.
- Pradhan Mantri Awaaz Yojana Urban: An additional outlay of ₹ 18,000 crore over budget estimate towards PM Awaaz Yojana Urban has been announced which will help ground 12 lakh houses and complete 18 lakh houses. This will create additional 78 lakh jobs and improve the production and sale of cement and steel.
- Income Tax Relief for Developers and Home Buyers for houses up to ₹ 2 crore which provides an incentive to the middle class to buy homes.
- Equity Investment in Debt Platform by NIIF: The government will make ₹ 6,000 crore equity investment in debt platform of National Investment and Infrastructure Fund (NIIF), which will help NIIF raise ₹ 1.1 lakh crore by 2025 for financing infrastructure project
- Total Support: It comes at a time when the worst seems to be over and the economy seems to be transitioning from the normalisation of economic activity stage to the growth recovery stage. The support totalled ₹2.65 trillion.
The analysis of the package will be covered in Part-2 of the article.
(TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE)
Model questions: (You can now post your answers in comment section)
Note:
- Correct answers of today’s questions will be provided in next day’s DNA section. Kindly refer to it and update your answers.
- Comments Up-voted by IASbaba are also the “correct answers”.
Q.1 Consider the following statements:
- A recession is a period of declining economic performance across an entire economy that lasts for several months.
- Depressions are often identified as recessions lasting longer than three years or resulting in a drop in annual GDP of at least 10%.
Which of the above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Q.2 Which of the following is not a founding member of ASEAN?
- Indonesia
- Malaysia
- Philippines
- Brunei
ANSWERS FOR 13th November 2020 TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE (TYK)
| 1 | B |
| 2 | B |
Must Read
About The Western bias in science:
About Criticism of Judiciary’s action in Arnab Goswami Bail case:














