IASbaba's Press Information Bureau
IASbaba Press Information Bureau 20th to 26th May, 2018
GS-2
UGC (Online Courses) Regulations, 2018
(Topic:
- Government policies and interventions for development in various sectors and issues arising out of their design and implementation.
- Issues relating to development and management of Social Sector/Services relating to Health, Education, Human Resources)
Higher Educational Institutions can now offer Certificate, Diploma and Degree Programmes in full-fledged online mode in line with their regular programs.
- The Higher Educational Institutions will be eligible to offer Online Programmes if they have been in existence for at least five years and are accredited by the National Assessment and Accreditation Council (NAAC) with a valid minimum score of 3.26 on a 4-point scale; and should be in the top-100 in overall category in the National Institutional Ranking Framework (NIRF) for at least two years in the previous three years.
- This initiative is a big step towards attaining the targeted GER of 30% by the year 2020.
Launch of SamagraSiksha
(Topic:
- Government policies and interventions for development in various sectors and issues arising out of their design and implementation.
- Issues relating to development and management of Social Sector/Services relating to Health, Education, Human Resources)
An integrated Scheme for school education extending support to States from pre-school to senior secondary levels
- The Scheme is a paradigm shift in the conceptual design of school educationby treating ‘school’ holistically as a continuum from pre-school, primary, upper primary, secondary and senior secondary levels.
- Emphasis on Integration of two T’s – Teacher and Technology in the new scheme will help improve quality of education
- Scheme will focus on strengthening this crucial pillar by making SCERTs and DIETs the nodal agencies for teacher training. These institutions would be strengthened to emphasize the integration of in-service and pre-service training structures in States to make it need-focused and dynamic. This would strengthen the quality of teaching in schools across levels.
- “DIKSHA”- the national digital platform for teachers would put high quality teaching learning resources for ready use of teachers. The Scheme will support ‘Operation Digital Board’ in all secondary schools over a period of 5 years, so as to enhance the use of digital technology through smart classrooms, digital boards and DTH channels. The Digital initiatives like ShaalaKosh, Shagun, ShaalaSaarthi will be strengthened.
Cabinet apprised of the MoU between India and Angola: For promoting bilateral cooperation in the field of Electronics and Information Technology
Cabinet Approves
MoU signed between India and France in the field of Renewable Energy:
- Both sides aim to identify research/ demonstration/ pilot project between National Institute of Solar Energy (NISE), India and Commissariat aI’EnergieAtomique et aux Energies Alternatives (CEA), France in the mutually identified areas.
- Based on mutual agreement, both parties would work for implementation & deployment of pilot project in ISA member countries.
- Collaboration may occur through several means, including joint research projects, joint R&D, joint workshops, Research and Technology exchange including exchange of domain experts.
- The MoU also aims for exchange of expertise and networking of information.
MoU between India and Denmark on Food Safety Cooperation:
- Help deepen bilateral ties, mutual understanding and trust, eventually strengthening both sides in their capacity building efforts towards food safety
- Promote understanding of the best practices in the areas of food safety in both countries and in faster resolution of issues related to food safety.
- Help improve food safety standard setting by getting access to best practices and facilitating food trade of important commodities.
MoU between India and Morocco on India-Morocco cooperation in Renewable Energy:
- Both sides aim to establish the basis for a cooperative institutional relationship to encourage and promote technical bilateral cooperation on new and renewable energy issues on the basis of mutual benefit, equality and reciprocity.
- The MoU envisages establishing a Joint Working Committee to review, monitor and discuss matters relation to areas of cooperation.
- The MoU aims for exchange of expertise and networking of information.
MoU between India and Singapore on Cooperation in the field of Personnel Management and Public Administration:
The MoU aims at improving the current system of governance, particularly in the areas of Workforce, Workplace and Jobs, Public Service Delivery, Human Resource Management, Public Sector Reform, Leadership/ Talent Development and E-Governance/Digital Government
- Provide a framework for cooperation between India and Singapore in the field of Public Administration and Governance Reforms.
- Aims at achieving excellence in public administration, good governance and public service reform, which in turn, would ensure and promote greater public accountability
- Aims to bring about innovative best practices, so as to achieve excellence in public administration in the context of improving online public service delivery
Provision of mobile connectivity in Left Wing Extremism Areas:
- This network would be used by the security personnel deployed in LWE affected areas.
- Project will also provide the mobile services to help the residents in unconnected inhabited villages which would improve the economic activities in the region.
- It will give impetus to the e-Governance activities in the backward and LWE affected area with the availability of digital mobile connectivity.
USOF scheme for provision of mobile services in Meghalaya under CTDP for North Eastern Region: Implementation of a Comprehensive Telecom Development Plan (CTDP) for the North Eastern Region (NER) in Meghalaya
- Strengthening of telecom network will result in increased the penetration of mobile connectivity in Meghalaya resulting in affordable and equitable access of communication, information and governance to people.
- Providing access to public mobile network to hitherto unreached people of Meghalaya will empower citizens with benefits of ICTs for furthering socio-economic developments.
- The innovative skill of uncovered areas will increase through broadband and internet access.
GS-3
Model Agriculture Produce and Livestock Contract Farming and Services (Promotion & Facilitation) Act, 2018
(Topic: Major crops cropping patterns in various parts of the country, different types of irrigation and irrigation systems storage, transport and marketing of agricultural produce and issues and related constraints; e-technology in the aid of farmers)
Objective: With a view to integrate farmers with bulk purchasers including exporters, agro- industries etc. for better price realization through mitigation of market and price risks to the farmers and ensuring smooth agro raw material supply to the agro industries
Salient features of Model Contract Farming Act, 2018 are:
- The Act lays special emphasis on protecting the interests of the farmers, considering them as weaker of the two parties entering into a contract.
- In addition to contract farming, services contracts all along the value chain including pre-production, production and post-production have been included.
- “Registering and Agreement Recording Committee” or an “Officer” for the purpose at district/block/ taluka level for online registration of sponsor and recording of agreement provided.
- Contracted produce is to be covered under crop / livestock insurance in operation.
- Contract framing to be outside the ambit of APMC Act.
- No permanent structure can be developed on farmers’ land/premises
- No right, title of interest of the land shall vest in the sponsor.
- Promotion of Farmer Producer Organization (FPOs) / Farmer Producer Companies (FPCs) to mobilize small and marginal farmers has been provided
- FPO/FPC can be a contracting party if so authorized by the farmers.
- No rights, title ownership or possession to be transferred or alienated or vested in the contract farming sponsor etc.
- Ensuring buying of entire pre-agreed quantity of one or more of agricultural produce, livestock or its product of contract farming producer as per contract.
- Contract Farming Facilitation Group (CFFG) for promoting contract farming and services at village / panchayat at level provided.
- Accessible and simple dispute settlement mechanism at the lowest level possible provided for quick disposal of disputes.
- It is a promotional and facilitative Act and not regulatory in its structure
Prelims Oriented Notes:
Competition Commission of India: To eliminate practices having adverse effect on competition, promote and sustain competition, protect the interests of consumers and ensure freedom of trade in the markets of India.
Must Read: Link
Ancient Dance Drama “Ashtapadiyattam”
- It is “Gita Govindam” written by 12th century poet Jayadeva (considered the founding father and one amongst the pioneers of Bengali literature), in Guruvayur, Kerala
- Gita Govindam’s unusually wide appeal comes from the story of Sri Krishna and his love for Radha.
- Although the ‘Ashtapadiyattam’ in its original form is no longer in existence, it can be found in various parts of India in various forms- like Mohiniattamand Kathakaliin Kerala,Bharatanatyam in Tamil Nadu,Kuchipudi in Andhra Pradesh, Manipuri in Manipur and Odissi in Orissa.
- It became an essential element of Sri Chaitanya’s movement in Bengal, inspired Yakshagana dances and became the genesis of an entire genre of music called “Sopana sangeetham” as Jayadeva’s ashtapadis were sung on temple stairs.
Panchama Veda or the fifth Veda: Bharatha Muni’s Natya Shastra, composed around the 2nd century BC
“Advaita” philosophy: Adi Shankara
Mission Innovation:
- A global platform of 23 countries and European Union aimed at accelerating clean energy innovations through enhanced Government funding, greater public-private sector partnership and enhanced global cooperation.
- India is founding member of Mission Innovation and part of the Steering Committee besides co-lead of innovation challenges on smart grids, off grids and sustainable bio-fuels.
Green Good Deeds: A societal movement with joint efforts by the BASIC countries in combating climate change
- BASIC countries – A bloc of four countries – Brazil, South Africa, India and China, formed by an agreement on November 28, 2009. The four committed to act jointly at the Copenhagen climate summit.
International Day for Biodiversity (IBD)
On: 22nd May
2018 Theme: Celebrating 25 years of action on biodiversity
Common Service Centres (CSCs):
Acts as access points for delivery of various electronic services to villages in India, are set to be expanded to 2.50 lakh gram panchayats by the year end
The CSC movement had transformed into a movement of change bringing services like banking, pensions, digital literacy and telemedicine to rural and remote villages through electronic infrastructure.
- DigiGaon or Digital Village is conceptualised as a connected village where citizens can avail various e-Services of the Central Government, state Governments and private players in a rural and remote villages in the country.
- These DigiGaons are projected to be change agents, promoting rural entrepreneurship and building rural capacities and livelihoods through community participation and collective action.
- The digital villages have been equipped with solar lighting facility in their community center, LED assembly unit, sanitary napkin unit (with active participation on Asha and Anganwadi workers) and Wi-fi choupal (rural Wi-Fi infrastructure and a slew of suitable applications).
- These villages would also have the regular CSC services like banking, health, education, financial services, and a host of other services.
BrahMos: Supersonic cruise missile
- A joint venture between DRDO of India and NPOM of Russia
- Can be launched from submarine, ships, aircraft, or land.
- It is the fastest supersonic cruise missile in the world
- Has emerged as the ultimate weapon of choice in modern warfare with its unmatched speed, precision and firepower
- The name BrahMos is a portmanteau formed from the names of two rivers, the Brahmaputra of India and the Moskva of Russia.
- In 2016, as India became a member of the Missile Technology Control Regime (MTCR), India and Russia are now planning to jointly develop a new generation of Brahmos missiles with 600 km-plus range and an ability to hit protected targets with pinpoint accuracy.
Workshop on Artificial Intelligence to study the strategic implications of AI in national security perspective, in global context –
- To establish tactical deterrent in the region.
- To support its peaceful and commercial use.
- To mitigate catastrophic risk.
- To visualize potential transformative weaponry of future.
- To facilitate in keeping a check on non-state actors.
- To develop intelligent, autonomous robotic systems.
- To enhance capabilities for collection and analysis of data and also creation of data.
- To bolster cyber defence
Must Read: Link
Indian Naval Sailing Vessel Tarini (INSV Tarini): The first-ever Indian circumnavigation of the globe by an all-women crew
130 years of Indian Railways iconic station: Chhatrapati Shivaji Maharaj Terminus building:
- Was originally planned as the office of GIP (Great Indian Peninsular) Railway
- Most photographed building after Taj Mahal
- Designed by Frederick William Stevens
- Named after Queen Empress Victoria. Later in 1996, it was renamed as Chhatrapati Shivaji Terminus. It was again renamed as Chhatrapati Shivaji Maharaj Terminus in July 2017.
- In 2004, UNESCO has enlisted this building as World Heritage Site for its architectural splendour.
DigiYatra:
- An industry-led initiative coordinated by the Ministry of Civil Aviation in line with the Digital India vision to transform the nation into a digitally empowered society
- Aims to transform the flying experience for passengers and position Indian Aviation amongst the most innovative aviation networks in the world
- The passenger will have choice to opt for the facility.
Key features are:
- Digitize air-travel experience: Use of digital technology for enhanced and seamless passenger experience all the way from ticket booking to airport entry check, security check and aircraft boarding
- Single-point verification: Passengers enrol in to DigiYatra program through AirSewa, and a DigiYatra verified passenger gets hassle free entry at airport through E-Gates. The ID verification will be done by the BCAS-approved Government ID. At the entry gate a single token for the passenger is created.
- Value-added services: like ground transportation, special services at airport, in-flight, etc. and many other value added services for passengers in future will also be delivered through the DigiYatra programme.
- Enhanced security: The programme also enhances security while providing convenience to the passenger
- Technical Standards formulated: Ministry of Civil Aviation has finalized the technical standards for DigiYatra which will be published shortly. Airports such as Bangalore, Hyderabad, Kolkata, Varanasi and Vijayawada will roll out this programme in phases by January 2019.
AirSewa app: AirSewa app brings together all the stakeholders on a common platform to ensure timely and effective handling of customer grievances and to disseminate real-time data.
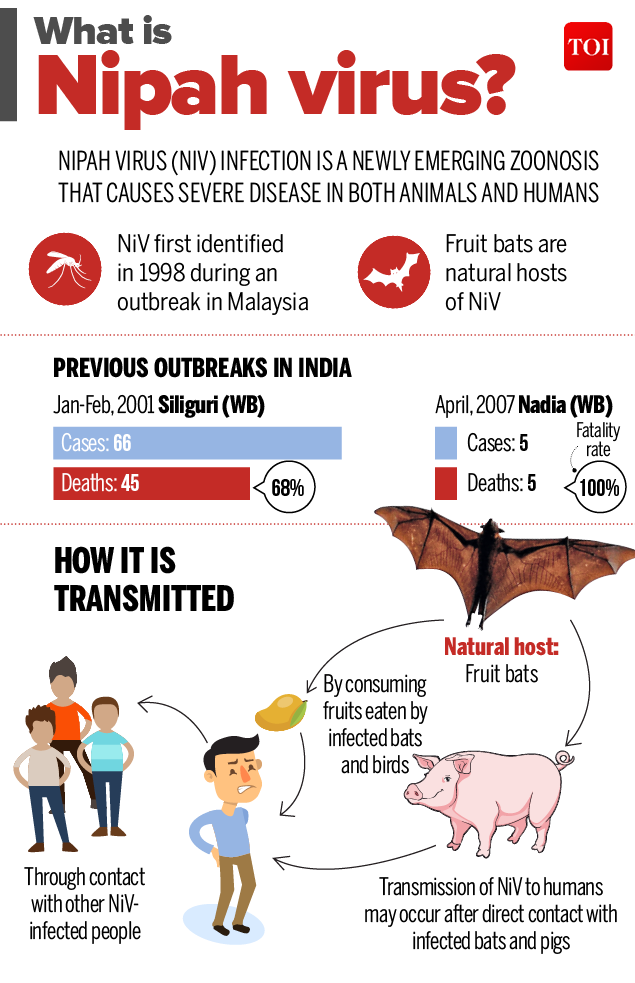
Link: https://timesofindia.indiatimes.com/india/nipah-virus-all-you-need-to-know/articleshow/64255948.cms
Quote:
Father of the nation, Gandhiji –
“I do not want my house to be walled in on all sides and my windows to be stuffed. I want the culture of all lands to be blown about my house as freely as possible. But I refuse to be blown off my feet by any”
The Vice President of India, Shri M. Venkaiah Naidu
Along with “gross national income”, we must focus on how science and technology can foster greater “happiness” and better quality of life as well as harmonious inclusive societies.
Three qualities to achieve excellence:
- First is the willingness to learn from each and every person, institution and learning resource we can access
- The second is the ability to probe, analyse and synthesize;
- The third quality is to search for a completely out of the box solution that answers the problem at hand.











