IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
IASbaba’s Daily Current Affairs (Prelims + Mains
Focus)- 16th August 2018
Archives
(PRELIMS+MAINS FOCUS)
PM Narendra Modi’s Independence Day speech: Highlights
Part of: GS Prelims and Mains
In news:
72nd anniversary of India’s Independence
Important Highlights: PM speaks about
- Passage of the Bill to create an OBC Commission
- 100th anniversary of Jallianwala Bagh massacre
- India’s space mission – In 2022 (on the occasion of India’s 75th Independence Day), India to unfurl the tri-colour in the space.
- Subramania Bharati vision of India – Subramania Bharati (great Tamil poet) had said India will not only rise as a great nation, but will also inspire the others. India will show the way to the entire world to unshackle the bonds.
- Pradhan Mantri Jan Arogya Abhiyaan – to be launched on 25th September 2018 (birth anniversary of Pandit Deendayal Upadhyay)
- India’s farming sector – ‘Beej Se Bazar Tak’ approach ; double farmer incomes by 2022
- On women empowerment – Practice of Triple Talaq to be ended; Women officers commissioned in short service will get opportunity for permanent commission.
- On government schemes and policies – Thirteen crore ‘mudra loans’; Ujjwala and Saubhagya Yojana; GST; Swachh Bharat mission
Kerala reels under its worst floods
Part of: GS Prelims and Mains I and III – Indian Geography and Disaster Management
In news:
- The 2018 Kerala floods were a result of the unusually severe amount of southwest monsoon rains.
- It is the first time in its history all five gates of the Idukki Dam were opened at the same time and also 35 out of 39 reservoirs in the state were opened.
Concern:
- There is no proper flood water warning system in place, people also lack awareness in various disaster management procedures is also a major concern.
- Local authorities should have inspected and given warnings in several hilly regions, where various land slide deaths could have been prevented.
What do you mean by “Flood”?
It is a temporary inundation of large regions as a result of an increase in reservoir, or of rivers, flooding their banks because of heavy rains, high winds, cyclones, storm surge along coast, tsunami, melting snow or dam bursts.
Types of Floods
Flash floods:
- It is defined as floods which occur within six hours of the beginning of heavy rainfall , and are usually associated with cloud bursts, storms and cyclones requiring rapid localized warning and immediate response if damage is to be mitigated. In case of flash floods, warning for timely evacuation may not always be possible.
River floods:
- Such floods are caused by precipitation over large catchment areas. These floods normally build up slowly or seasonally and may continue for days or weeks as compared to flash floods.
Coastal floods:
- Some floods are associated with the cyclonic activities like hurricanes, tropical cyclone etc. Catastrophic flooding is often aggravated by wind-induced storm surges along the coast.
Causes of Flood:
- Excessive rainfall in river catchments or concentration of runoff from the tributaries and river carrying flows in excess of their capacities
- Back movement of water in tributaries at their confluence with the main river
- Synchronization of flood peaks of the main rivers and tributaries
- Landslides causing obstruction to flow and change in the river course
- Poor natural drainage
- Cyclone and very intense rainfall
- Intense rainfall when river is flowing full
- Climate change is responsible for abrupt rainfall and a high variability in rainfall.
- Melting of glacier due to increase in mean global temperature.
Approach to Flood Management/Prevention
Structural Measures: Attempts to Modify Flood
- Dams and Reservoirs
- Embankment
- Drainage Improvements
- Channel Improvements
- Diversion of Flood Waters
- Using Natural Detention Basin
Non- Structural Measures: Attempts to modify susceptibility of Flood
- Flood plain zoning: – It aims to regulate the developments in the flood plains, so that it is compatible with Flood Risk. It recognises the basic fact that the flood plains are essentially the domain of the river, and as such all developmental activities must be compatible with the flood risk involved
- Flood forecasting :- Involves observing and collecting hydrological and meteorological data, transmission and then processing the data with a view to work out the likely level to be achieved at a particular site, i.e. to give advance warning
- Flood Proofing:- It is essentially a combination of structural change and emergency action without evacuation. A programme of the flood proofing provides the raised platforms for flood shelter for men and cattle and raising the public utility installations above flood levels.
- Attempts to modify loss burden by way of Disaster relief, Flood fighting, Flood insurance
Main Mitigation Strategies for Flood Disaster Management
- Mapping of flood prone areas is a primary step involved in reducing the risk of the region.
- Historical records give the indication of flood inundation areas and the period of occurrence and the extent of the coverage.
- The basic map is combined with other maps and data to form a complete image of the flood-plain.
- Warning can be issued looking into the earlier marked heights of the water levels in case of potential threat. In the coastal areas, the tide levels and land characteristics will determine areas liable to inundation.
- Flood hazard mapping will give the proper indication of water flow during floods.
Government Policy response:
- Enactment of National disaster management act 2005 and NDRF
- Setting up of National Flood commission and Task Force on Flood Management/ Erosion Control to study India’s flood control measures.
- Central Water Commission (CWC) –apex body for flood and water management
- National Water Policy ( 1987/ 2002/2012)
The Sendai Framework for disaster risk reduction(2015-2030) must be implemented completely involving adopting integrated and inclusive institutional measures so as to work towards preventing vulnerability to disaster, increase preparedness for response and recovery and strengthen resilience by inclusion of private sector and local population to prevent such mishaps in the future.
India-UK: Cultural Diplomacy
Part of: GS Mains II – International Relations; India and the World
In news:
- British police returned 12th century bronze Buddha statue to India
- The 12th century icon was stolen from Nalanda museum
- Example of Britain’s “cultural diplomacy”
Cyber attack: Pune-based Cosmos Cooperative Bank
Part of: GS Mains III – Challenges to internal security through communication networks; Cyber Security
In news:
- Recent incident of cyber attack in Pune-based Cosmos Cooperative Bank caused ₹90-crore loss.
- There has been rising menace of financial frauds.
- Cyber security is an important arena of internet when the country is moving forward towards a cashless society and digitization.
- Security becomes a challenge as now privacy is a fundamental right as per SC verdict and the rise in cybercrimes can lead to violation of private space and liberty of expression.
Do you know?
- Global Conference on Cyberspace (GCCS) was conducted in India for first time where the theme for the conference was Cyber4All: A Secure and Inclusive Cyberspace for Sustainable Development.
- The IT act is not sufficient to deal with cyber security.
- The government is yet to bring a digital payment bill to strengthen legal framework and enhance surveillance to check cybercrimes in finance sector including frauds, targeting cards and e-wallets.
For mindmap on Cyber security – https://iasbaba.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/05/Cyber-Security-IASbaba.jpg
Pink Ballworm and Fall Armyworm
About:
- Earlier we had read about – Fall Armyworm
Fast recap:
- ICAR had sounded alarm after the invasive agricultural pest, Fall Armyworm was discovered in Karnataka.
- Fall Armyworm is a major maize pest.
- It can also feed on around 100 different crops, such as vegetables, rice, and sugarcane.
In news:
- The pink bollworm is an insect known for being a pest in cotton farming.
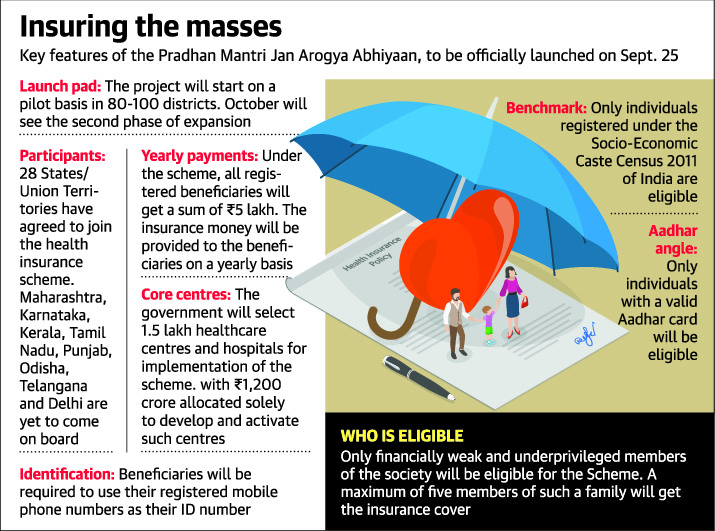
Pradhan Mantri Jan Arogya Abhiyaan
Part of: GS Prelims and Mains II – Government schemes and policies; Health issue
In news:
- Yesterday we read about Ayushman Bharat
- Pradhan Mantri Jan Arogya Abhiyaan is also known as Ayushman Bharat or the National Health Protection Mission (AB-NHPM)
- It will be launched on September 25 (birth anniversary of Pandit Deendayal Upadhyay)
https://d39gegkjaqduz9.cloudfront.net/TH/2018/08/16/DEL/Delhi/TH/5_11/f03944e2_2323003_101_mr.jpg
Gaganyaan: human space flight programme
In news:
- Gaganyaan, the human space flight programme was green-flagged and is set for 2022 by Prime Minister Narendra Modi.
- ISRO said the mission is achievable, as most of the critical technologies are ready
- The mission is estimated at ₹9,000 crore.
Do you know?
- When it achieves the mission, India would be the fourth nation to circle Earth after the Soviets, the Americans and the Chinese.
- In 1984, India’s first astronaut Wing Commander (retd.) Rakesh Sharma orbited Earth as part of a Soviet mission.
- Department of Space and ISRO are directly under the Prime Minister.

https://d39gegkjaqduz9.cloudfront.net/TH/2018/08/16/DEL/Delhi/TH/5_11/f03944e2_2323004_101_mr.jpg
(MAINS FOCUS)
NATIONAL
TOPIC:General Studies 3
- Various security forces and agencies; their mandate
Amendment to Delhi Special Police Establishment Act
Introduction:
- Parliament passed certain amendments to laws on corruption, which could have a far reaching effect.
- The two important aspects of Amendment are: one requiring prior approval for initiating investigation into allegations of corruption against public servants, and the other requiring prior sanction for prosecution of public servants.
Need for approval
- Section 6A of the Delhi Special Police Establishment Act has been amended, reinterring the requirement of prior approval for initiating investigation of corruption cases not only against Joint Secretaries and above, but all categories of public servants.
- The only exception to this are cases of traps in which such public servants are caught red-handed while taking bribe.
- Till now under Section 19 of the Prevention of Corruption Act, 1988, previous sanction of the competent authority was required to prosecute public servants, under various sections of the Act. This safeguard has been extended to retired public servants.
- As per amendment, prior approval of the government is required even to initiate an investigation by CBI into allegations of corruption against public servants.
Political interference:
- It first came in the shape of the Single Directive under the Rajiv Gandhi government, which was confined to senior officers only.
- A long legal battle was fought before the Supreme Court, challenging the legality of the directive. The court eventually set it aside, in the Vineet Narain case.
- But even after the Directive was set aside, the political class brought it back in the Central Vigilance Commission Act of 2003. This led to protests and was challenged before the court. In 2014, the Supreme Court set aside this provision of the Act.
Provisions of the law of the land:
- Under the law of the land, the police has unfettered jurisdiction to initiate investigation into a crime or acts of corruption, once it gets credible information.
- Under the scheme of the criminal justice system and the rule of law, the police and the CBI are bound by the law and the Constitution to investigate a crime reported to them, if there is credible information.
- They have jurisdiction as per law and that the power to register and proceed with the investigation must remain unhindered.
- Once the investigation is complete and the police or the CBI is ready with the report on the investigation, other authorities come into play.
Supreme Court observations:
- Supreme Court had held that the Single Directive was liable to be quashed as irrational in law.
- Court held that all the powers of the Minister are subject to the condition that none of them would extend to permit the Minister to interfere with the course of investigation and prosecution in any individual case.
- SC also held that it is the duty of Police to enforce the law of the land, in this he is not servant of anyone except the law itself.
- The court had observed that the very power of CBI to enquire and investigate into the allegations of bribery and corruption against a certain class of public servants and officials is subverted and impinged by Section 6A.
Conclusion:
The recent amendment, therefore, is regressive in nature and is likely to be quashed if contested in the apex court.
Connecting the dots:
- The CBI plays a pivotal role in the criminal justice delivery but it is being handicapped by the recent amendments. Comment while suggesting reforms to the CBI.
NATIONAL
TOPIC:
General Studies 2
- Government policies and interventions for development in various sectors and issues arising out of their design and implementation.
General Studies 3
- Science and Technology; Bio technology
Ban on Oxytocin: Unreasonable
Introduction:
- Oxytocin, which is considered to be a critical drug in maternal health care, is made primarily by the private sector.
- The decision to restrict the manufacture of oxytocin only to the public sector unit has sparked fears of shortages and a disruption of supplies of this drug.
- The restriction is because of alleged misuse of the drug by dairy farmers on milch cattle to stimulate milk production.
- The Health Ministry now hopes to control distribution channels and prevent misuse.
About Ban and Criticism
- The allegations regarding misuse have been made by the Union Minister for Women and Child Development, Maneka Gandhi, for over a decade.
- According to the medical and veterinary sciences who advised the DTAB that oxytocin is required in the treatment of both humans and animals.
- Two studies by the Central government, by the Indian Council of Medical Research and the National Dairy Research Institute, conclude that the use of oxytocin does not have an adverse effect on either people or animals.
- With cattle, the danger of misuse is that it may cause addiction, in which case cattle do not react to normal milk ejection stimuli.
So why has the Health Ministry restricted the manufacture of the drug to only the KAPL?
- The High Court of Himachal Pradesh initiated a public interest litigation (PIL) after it came across newspaper reports of oxytocin misuse.
- After hearing the matter for two years, the court passed a judgment in 2016 blaming oxytocin for a number of diseases, including breast and uterine cancers, male impotence, excessive hair growth in women and balding for men.
- However, the court did not cite a single scientific study to support these claims.
- It appeared to be unaware of the scientific studies commissioned by the Central government.
- Towards the end of its judgment, the court directed the State government to consider the feasibility of restricting manufacture to the public sector.
- While the State government appears to have ignored these directions, the Central government, for some reason, decided to adopt the judgment as the basis of its order restricting manufacture to the public sector.
- The fact is that the High Court sought a study of the feasibility of restricting manufacture to the public sector; it never ordered the restriction to be imposed.
- From a reading of the government’s order, it appears that the government has gone ahead to restrict manufacture without conducting any kind of feasibility study.
Going forward
- An order restricting manufacture of a crucial drug such as oxytocin on the grounds of alleged misuse will have to be based on a study of the degree of misuse, the demand for the drug, the manner in which the proposed restriction will affect the supply of the drug, and also its impact on public health.
- The government has not conducted such a study.
- The Delhi High Court, which is hearing a challenge against the government’s order, should signal to the government that regulation of drugs has to be rigorous and reasoned. It cannot resemble policy quackery.
Connecting the Dots:
- The case for restricting the manufacture of oxytocin is neither rigorous nor reasoned. Comment
(TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE)
Model questions: (You can now post your answers in comment section)
Note:
- Featured Comments and comments Up-voted by IASbaba are the “correct answers”.
- IASbaba App users – Team IASbaba will provide correct answers in comment section within 24 hours. Kindly refer to it and update your answers.
Q.1) Which of the following are the potential impacts of climate change on water situation in India?
- Increased summer flows in river streams.
- Frequent changes in river courses.
- Changes in rainfall pattern.
Select the correct answer using code below
- 1 and 2
- 1 and 3
- 2 and 3
- 1, 2 and 3
Q.2) Gaganyaan is associated with which of the following agencies?
- DRDO
- CSIR
- ISRO
- Clean Ganga Mission
Q.3) Consider the following events:
- Kheda Satyagraha
- Champaran Satyagraha
- Jallianwala Bagh Massacre
- Non Cooperation
Their correct chronological sequence is
- 2 – 1 – 3 – 4
- 1 – 2 – 4 – 3
- 2 – 4 – 1 – 3
- 1 – 2 – 3 – 4
MUST READ
Questioning a crackdown
Making NHPM work: On Ayushman Bharat
The roadmap to military reform
Probing an amendment
Gaganyan: How to send an Indian into space
A Law Past Its Sell-by Date
Why theatre commands is an unnecessary idea











