IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
IAS UPSC Prelims and Mains Exam – 9th May 2020
Archives
(PRELIMS + MAINS FOCUS)
National Infrastructure Pipeline proposes to set up National Land Management Corporation
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-III – Infrastructure
In News:
- The task force on National Infrastructure Pipeline has recommended setting up a National Land Management Corporation
- This corporation would help in monetising state-owned surplus land assets in a systematic manner.
Key takeaways:
- Such a corporation should be set up under Companies Act.
- It would act as a facilitator for land monetisation and an asset manager for lands owned by the government and public enterprises.
- The Corporation should have representation from:
- Finance Ministry
- Department of Public Enterprises
- Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs
- Independent directors from finance and real estate industry.
- The Corporation will be able to raise capital from the equity market, based on the value of its leased assets.
Important value additions:
National Infrastructure Pipeline (NIP)
- It is the investment plan unveiled by the Central Government for enhancing infrastructure in identified sectors for a period of five years from 2020-25.
- $1.4 trillion have been allotted to NIP.
- It will help India to become the $5 trillion economy by 2025.
- The funding will be jointly made by the Centre, states and the private sector in the proportion of 39:39:22 ratio.
Changes brought to Labour laws by U.P and M.P governments
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-III – Employment
In News:
- The Uttar Pradesh government has approved an Ordinance exempting businesses from all the labour laws except few for the next 3 years.
- Madhya Pradesh government has also suspended many labour laws for the next 1000 days.
Key takeaways:
Uttar Pradesh:
- Laws related to the following have become defunct:
- Settling industrial disputes
- Occupational safety
- Health and working conditions of workers
- Trade unions, contract workers, and migrant labourers
- No relaxation in laws related to the following:
- Bonded labour
- Deployment of women and children
- Timely payment of salaries
- These changes will apply to both the existing businesses and the new factories being set up in the state.
Madhya Pradesh
- Few important amendments are:
- Employers can increase working hours in factories from 8 to 12 hours.
- The factory registration will be done within a day, instead of 30 days.
- The licence renewal will be done after 10 years, instead of a year.
- Industrial Units will be exempted from majority of the provisions of the Industrial Disputes Act, 1947.
- Contractors employing less than 50 workers will be able to work without registration under the Contract Labour (Regulation and Abolition) Act, 1970.
- Reasons for change in labour laws in both states:
-
- To attract investment.
- To encourage industrial activity.
- To protect the existing employment.
- To provide employment to workers. who have migrated back to their respective States.
- To increase the revenue of states which have fallen due to closure of industrial units during Covid-19 lockdown.
- The changes could lead to denying the rights of workers which is a violation of human and fundamental rights.
- It may create insecurity among the workers.
- The changes may lead to desperate conditions for workers.
Important value additions:
The Industrial Disputes Act, 1947
- It was enacted to promote industrial peace by providing appropriate machinery for amicable settlement of disputes arising between employers and employees.
Luhman 16: Binary Brown Dwarf System
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-III – Space
In News:
- Recently, a group of astrophysicists have found that the closest known brown dwarf, Luhman 16A.
- It also shows signs of cloud bands similar to those seen on Jupiter and Saturn.
Key takeaways:
- They used polarimetry technique to determine the properties of atmospheric clouds.
- They have found the actual structure of the clouds (not only their presence) in case of Luhman 16A.
Important value additions:
Luhman 16
- Luhman 16A is part of a binary system (Luhman 16) containing a second brown dwarf, Luhman 16B.
- This pair orbits each other.
- It is situated at a distance of about 6.5 light years from the Sun and
- It is the third closest system to the Sun after Alpha Centauri and Barnard’s star.
Brown Dwarfs
- They are also called failed stars.
- Their masses are heavier than planets but lighter than stars.
Binary Stars System
- Binary stars are two stars orbiting a common center of mass.
- Calculations of their orbits allow the masses of their component stars to be directly determined.
Polarimetry
- It is the study of polarization.
- It is a property of light.
- It represents the direction in which the light wave oscillates.
- When light is reflected off of particles it can favor a certain angle of polarization.
- By measuring the angle from a distant system, astronomers can deduce the presence of clouds.
Miscellaneous
FlytNow
- It is an Internet of Drones (IoD) platform that allows seamless integration of intelligent fleets of drones with cloud-based business applications.
- It can assist the Police officials to stream live multi-video feeds from multiple drones to their control room which shall enable them to respond quickly to emergencies.
- It is developed by FlytBase, an enterprise drone automation company.
Rath Yatra at Jagannath Puri
- The Ministry of Home Affairs (MHA) has allowed the construction of chariots for the annual Rath Yatra at Jagannath temple, Puri in Odisha.
- It is a Hindu festival associated with Lord Jagannath.
- During the festival, the three holy chariots carrying idols of Lord Jagannath, his brother Balaram and sister Subhadra are pulled by devotees.
- The temple is believed to be constructed in the 12th century by King Anatavarman Chodaganga Deva of the Eastern Ganga Dynasty.
- The temple was called the “White Pagoda” and is a part of Char Dham pilgrimages (Badrinath, Dwaraka, Puri, Rameswaram).
‘AYUSH Sanjivani’ App
- Recently, it was launched by the Government.
- It is developed by the Ministry of AYUSH and the Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MEITY).
- It intends to generate data on usage of AYUSH (Ayurveda, Yoga & Naturopathy, Unani, Siddha, Sowa-rigpa and Homoeopathy) medicines and measures among the population and its impact in prevention of Covid-19.
- It targets to reach out to 50 lakh people in the country.
(MAINS FOCUS)
INTERNATIONAL RELATIONS
Topic: General Studies 3:
- India and its neighbourhood
- Effect of policies and politics of developed and developing countries on India’s interests, Indian diaspora.
India amidst challenging geopolitical situation
Context:
Today, India is in the midst of a new geopolitical situation:
- The world is moving in the direction of multi-polarity which may turn into a US-Chinese bipolar system in the long run.
- The world faces a destabilising power transition as China seeks to demonstrate international power in a world so far dominated by the U.S.
- “America First” attitude of the United States President has also caused rapid shifts in the balance of power.
- China-U.S. strategic contention is growing despite both countries being economically dependent on each other.
- Indo-Pacific Region (IPR), including countries of Indonesia, South Korea and Vietnam, is gradually turning into one of the world’s primary regions.
The geopolitical aspect of relations between India, China and the United States is thus becoming increasingly complex and multifaceted.
What should be India’s response in such a scenario?
- The current Indian government has set itself ambitious, long-term goals aimed at strengthening the country’s international standing as a “serious global player.
- To counter unstoppable growth of China, many experts advocate that India should enter into an alliance with the U.S.
- However, an alliance seems to be the wrong answer for India’s growth quests which may harm its development ambitions.
- Strategic autonomy has been the pursuit for India since many decades. Hence, this is the most opportune time for India to not get entangled in contention concerning other countries which might affect India’s national interests.
- India must follow diplomacy and flexibility, and adjust itself to the fast-changing balance of power and correlation of forces around it.
- The experts also believe that India can gain a full-fledged status of a great power only if it creates multilateral organizations independently that would safeguard its interests and express its values.
- India must develop a strategy of counterbalancing China.
- India is already trying to counterbalance the USA by strengthening and diversifying ties with Russia.
- Europe, though equally burdened by its own problems, could also play its part by recognizing and supporting India’s growth.
- India’s investment needs are increasing like never before. Thus, India must come up with such a foreign policy that could lure investors from both China and the United States, without getting involved in their politics.
- India should also retain for itself maximum freedom of maneuver and flexibility in international relations and uphold its claim to be the system-forming power of South Asia.
- High-level strategic dialogue between these countries about their core interests, red differences and areas of convergence should take place.
Way forward
- The world also knows that without India’s participation neither USA’s IPR project, nor Beijing’s “Community of Common Destiny” concept can be fully implemented.
- On the other hand, India may not become a developed country if it continues business and politics as usual, or tries to imitate China’s experience in the last 40 years.
- It must adapt and manage its internal social and political situations better.
Conclusion
- Today, India is more dependent on the outside world than ever before.
- It relies on the world for energy, technology, essential goods like fertilizer and coal, access to markets, and capital.
- Thus, the most important improvement that India needs to make involves its national security structures and their work.
Connecting the dots:
- India – China relations are of global significance
- India’s participation is significant for USA’s India-Pacific Region project
ECONOMY
Topic: General Studies 3:
- Indian Economy and issues relating to planning, mobilization, of resources, growth, development and employment.
- Government policies and interventions for development in various sectors.
To sustain growth, India needs fiscal stimulus
Context:
We are aware that the impact of COVID-19 will debilitate or weaken the global as well as the Indian economies.
- Various institutions have assessed India’s growth prospects for 2020-21 ranging from 0.8% (Fitch) to 4.0% (Asian Development Bank).
- IMF has projected India’s growth at 1.9%, China’s at 1.2%, and the global growth at (-) 3.0%.
India was already facing a persistent economic downslide before it slid into the novel coronavirus crisis.
- There was a sustained fall in the saving and investment rates especially with unutilised capacity in the industrial sector.
- 2019-20 Centre’s gross tax revenues also showed contraction.
All these trends would continue to trouble the Indian economy in this crisis.
2019-20 India’s economic growth
- Central Statistics Office (CSO) had estimated gross value added (GVA) growth of about 4.9% for 2019-20.
- IMF’s GDP growth estimate for 2019-20 is at 4.2%.
- However, India may show real GVA growth of 4.4% for 2019-20.
India’s growth prospects for 2020-21
- GVA is divided into eight broad sectors (as shown in fig/table below) and all the sectors have been disrupted.
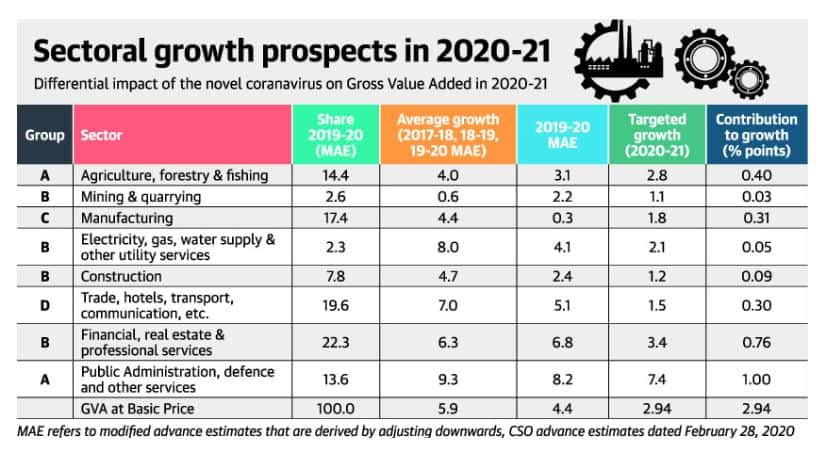
Source: The Hindu
Group A sectors
- This group comprises of two sectors – agriculture and allied sectors, and public administration, defence and other services.
- Total contribution to growth is expected to be highest as the sectors under this group have suffered only limited disruption.
Agriculture and allied sectors
- In the case of agriculture, rabi crop is currently being harvested and a good monsoon is predicted later in the year.
- Despite some labour shortage issues, this sector may show near-normal performance.
Public and defence sector
- This sector has been nearly fully active, especially with the health services at the forefront of the COVID-19 fight.
Group B sectors
- This group comprises four sectors which may suffer average disruption.
- These sectors are mining and quarrying, electricity, gas, water supply and other utility services, construction, and financial, real estate and professional services.
Group C sectors
- Manufacturing sector has suffered significantly. However, it is feasible to stimulate this sector by supporting demand.
- This sector requires strong policy support.
Group D sectors
- This group is likely to suffer maximum disruption.
- This includes, trade, hotels, restaurants, travel and tourism under the broad group of “Trade, Hotels, Transport, Storage and Communications”.
Note: Considering these four groups together, a GVA growth of 2.9% is estimated for 2020-21.
Measures taken:
- Monetary policy initiatives – RBI has reduced the repo rate to 4.4%, the reverse repo rate to 3.75%, and cash reserve ratio to 3%.
- RBI has also opened several special financing facilities.
- The Centre has announced a relief package of ₹1.7-lakh crore.
- Now, these measures need to be supplemented by an appropriate fiscal stimulus.
What measures are required?
The actual growth outcome for India would depend on 3 important areas –
- the speed at which the economy is opened up;
- the time it takes to contain the spread of virus, and,
- the government’s policy support.
Need for Fiscal Stimulus
Fiscal stimulus can be of three types:
- relief expenditure for protecting the poor and the marginalised;
- demand-supporting expenditure for increasing personal disposable incomes or government’s purchases of goods and services, including expanded health-care expenditure imposed by the novel coronavirus, and,
- bailouts for industry and financial institutions.
Way ahead:
- Centre’s budgeted fiscal deficit of 3.5% of GDP may have to be enhanced substantially and provide for a stimulus.
- Expenditure on construction of hospitals, roads and other infrastructure and purchase of health-related equipment and medicines require prioritisation. These expenditures will have high multiplier effects.
- Similar initiatives may be undertaken by the State governments under their respective Fiscal Responsibility Legislation/Law and to provide for the shortfall in their revenues and some stimulus.
Connecting the dots:
- Do you think India needs a strong fiscal stimulus when already its fiscal deficit poses a major challenge?
- Which sector needs major policy support and why? What measures are needed?
(TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE)
Model questions: (You can now post your answers in comment section)
Note:
- Correct answers of today’s questions will be provided in next day’s DNA section. Kindly refer to it and update your answers.
- Comments Up-voted by IASbaba are also the “correct answers”.
Q.1 With regard to National infrastructure Pipeline, consider the following statements:
- It is an investment plan in identified sectors for a period of 10 years, 2020-2030.
- The funding will be jointly made by the centre and state in the proportion of 50:50 ratio.
Which of the above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Q.2 With regard to the ordinance brought in by the Uttar Pradesh Government, consider the following statements:
- Laws related to the dispute settlement will be different for the next 3 years.
- There will be no relaxation in laws related to the bonded labour.
Which of the above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Q.3 Consider the following statements regarding the amendments brought in by the Madhya Pradesh government:
- Employers can increase the working hours in factories.
- Registration of factories will be done within 2 days instead of 30 days.
Which of the above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Q.4 Recently, signs of cloud bands were observed by astrophysicists on the brown dwarf, Luhman 16A. Which of the following planets also show signs of cloud bands?
- Jupiter and Neptune
- Saturn and Jupiter
- Mercury and Jupiter
- Mercury and Venus
Q.5 In which of the following city of Odisha is Jagannath temple situated?
- Sambalpur
- Bhubaneswar
- Puri
- Cuttack
ANSWERS FOR 8th May 2020 TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE (TYK)
| 1 | C |
| 2 | C |
| 3 | B |
| 4 | D |
| 5 | A |
| 6 | D |
Must Read
About female genital mutilation
About migrant problems












