IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
Archives
(PRELIMS + MAINS FOCUS)
Delhi Master Plan 2041
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-II – Policies and Interventions & GS-III – Pollution; Climate Change
In news
- Recently, the Delhi Development Authority (DDA) has decided to hold public consultations for the preparation of the Master Plan for Delhi 2041.
- It is a vision document for Delhi’s development.
Key takeaways of 2041 Master Plan:
- Focus: Sustainability, inclusivity and equity, blue-green infrastructure, cycling infrastructure, walking circuits for pedestrians, removal of all sources of pollution and unauthorised colonies
- Objective: To be proactive and forward-looking
- Features: Spaces for yoga, active sports, open air exhibitions, museums and information centres, and other low impact public uses.
- It will fulfil various provisions of Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) like: (1) SDG 6 – Clean water and sanitation; (2) SDG 11 – Sustainable cities and communities; (3) SDG 14 – Life below water; (4) SDG 15 – Life on land.
Administration of Assam Rifles
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-III – Various Security Forces and Agencies and their Mandate.
In news
- Recently, the Delhi High Court has directed the Centre to take a decision on the issue of bringing Assam Rifles out of the dual control of the Ministry of Home Affairs (MHA) and the Ministry of Defence (MoD).
- The administrative control of the Assam Rifles is with the MHA.
- Its operational control rests with the MoD.
- This duality of control leads to problems of coordination.
Key takeaways of the High Court’s Direction
- The issue has been pending for nearly three years.
- The Centre should resolve it within 12 weeks with cooperation from all the stakeholders.
- The matter involves servicemen/ex-servicemen and others whose interests are paramount as proclaimed from various platforms of the Government
Important value additions
Assam Rifles
- Assam Rifles is a Central Paramilitary Force under the Central Armed Police Forces (CAPF).
- It came into being in 1835, as a militia called the ‘Cachar Levy’.
- Initial Objective: To primarily protect British Tea estates and their settlements against tribal raids.
- In November 2019, MHA proposed to merge it with the Indo-Tibetan Border Police (ITBP).
- ITBP is a specialized mountain force, raised in October 1962.
- It is deployed on border guarding duties from Karakoram Pass in Ladakh to Jachep La in Arunachal Pradesh covering 3,488 km of Indo-China Border.
Gap in Vaccination of Children reported
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-II – Health
In news
- ‘Health in India’ report was recently published.
- Published by: National Statistical Organisation (NSO)
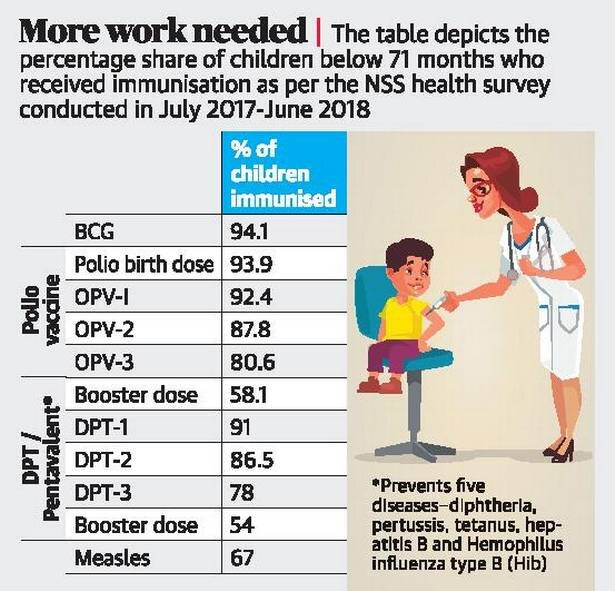
- Major finding: Full immunisation programme is not completed among 40% of the children.
- The report is based on the 75th round of the National Sample Survey (July 2017-June 2018) on household social consumption related to health.
Key takeaways from the report about children under five years:
- Fully immunised: 59.2%
- Received at least one vaccination (mostly BCG or the first dose of OPV at birth): About 97%
- Protected against measles: 67%
- Polio booster dose: 58%
- DPT booster dose: 54%
- Best Performance under full immunisation: Manipur (75%), Andhra Pradesh (73.6%) and Mizoram (73.4%)
- Poor Performance: Nagaland (12%), Puducherry (34%) and Tripura (39.6%).
Bamboo Clusters launched
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-II – Policies and Interventions & GS-III – Major Crops
In news
- Recently, 22 bamboo clusters in 9 states were virtually inaugurated
- States covered: Gujarat, Madhya Pradesh, Maharashtra, Odisha, Assam, Nagaland, Tripura, Uttarakhand and Karnataka.
- Ministry: Union Ministry for Agriculture and Farmers’ Welfare
- A logo for the National Bamboo Mission (NBM) has also been released.

Important value additions
Government’s Efforts
- India is the world’s second-largest cultivator of bamboo after China, with 136 species and 23 genera spread over 13.96 million hectares, according to the State of Environment report 2018.
- The National Bamboo Mission, under the Ministry of Agriculture & Farmers’ Welfare, has been initiated to provide a boost to livelihood and environmental acreage.
- Additionally, in 2017, Parliament ‘declassified’ bamboo as ‘a tree’ on non-forest lands.
- Similarly, a scheme called SFURTI (Scheme of Fund for Regeneration of Traditional Industries) is being implemented by the Ministry of Micro, Small, and Medium Enterprises (MSME) in order to boost traditional industries and bamboo artisans.
- Amendment has been brought about in the 100 year old Indian Forest Act brought about by the Central government in 2017, as a result of which, home grown bamboo has been exempted from it in order to enhance livelihood opportunities through bamboo.
- Bamboo Technology Parks were also set up in Jammu & Kashmir and Ladakh.
Hybrid Data Warfare by China
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-II – International relations & GS-III – Cybersecurity
In news
- The Chinese company Zhenhua Data Information Technology Co. Limited is monitoring over 10,000 Indian individuals and organisations in its global database of foreign targets.
Key takeaways
- Zhenhua monitors the digital footprint of its targets using Artificial Intelligence tools across social media platforms, maintains an information library.
- The library includes content from news sources, forums, papers, patents, bidding documents and positions of recruitment.
- Targets: Individuals and institutions in politics, government, judiciary, art and sports, business, technology, media, and civil society.
- The Company counts the Chinese government, intelligentsia and military among its clients. However, the Chinese government has denied this.
- Threat: This information can be used for strategic and intelligence services of China for hybrid warfare.
Important value additions
Hybrid Warfare
- It refers to using non-military tools to achieve dominance or damage, subvert or influence.
- These tools include information pollution, perception management and propaganda.
- Hybrid warfare was used in the 2006 Israel-Lebanon War by the Hezbollah group.
- It was also used by Russia against Ukraine in the 2014 annexation of Crimea
India & China agree on Five Point Plan
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-II – International relations & GS-III – Cybersecurity
In news
- Recently, India and China have agreed on a five points plan to disengage troops and reduce tensions along the Line of Actual Control (LAC).
- Indian and Chinese troops have been engaged in a four and a half month long stand-off.
- The talks were held on the margins of a Shanghai Cooperation Organisation (SCO) meeting in Russia.
Five Point Plan
- Both sides should take guidance from Wuhan and Mahabalipuram summits on developing India-China relations. Differences should not be allowed to become disputes.
- Border troops should continue their dialogue, quickly disengage, maintain proper distance and ease tensions.
- The two sides shall abide by all the existing agreements and protocols on China-India boundary affairs and avoid any action that could escalate matters.
- Continuing communications through the Special Representatives mechanism, and meetings of the Working Mechanism for Consultation and Coordination (WMCC) on border affairs.
- Working to conclude new confidence-building measures.
Do you know?
- The Special Representatives (SRs) on the Boundary Question was established in 2003.
- It provided important guidance for ensuring peace and tranquility in border areas in a challenging situation.
- WMCC was established in 2012.
Miscellaneous
Typhoon Maysak and Typhoon Haishen
- Recently, Korean Peninsula and Japan were hit by two typhoons named Maysak and Haishen.
- The Maysak typhoon takes its name from a Cambodian word for a type of tree.
- While, Haishen means Sea God in Chinese.
Background of Naming
- In Japan, the first typhoon to occur after January 1st of the year is called typhoon number 1.
- In the USA, hurricanes are referred to by English names.
- The intergovernmental organisation called the Typhoon Committee which has 14 members including Japan, USA and China uses Asian names for typhoons that are contributed by the member countries.
- Haishen was a name recommended by China, while Maysak is a Combodian name.
Shikshak Parv
- Shikshak Parv is being celebrated from 8th-25th September 2020 to felicitate the teachers and to take New Education Policy (NEP) 2020 forward.
- Under the initiative, the Ministry of Education is organizing a series of webinars on NEP and its implementation.
- Teachers’ Day is celebrated on 5th September every year throughout India in memory of Dr. Sarvapalli Radhakrishnan’s birth anniversary.
(MAINS FOCUS)
NATIONAL/ENVIRONMENT
Topic: General Studies 3:
- Conservation, environmental pollution and degradation, environmental impact assessment
Loss of forest and tree cover: Conserving through Cash for Conservation System
Context:
The unprecedented breadths of the wildfires over three western states of the US, combined with their intensity, scale, speed and duration, have greatly complicated the ability to bring them under control. The 500,000-acre fire is the largest ever recorded blaze in California.
Impact of wildfires:
While natural fires have regenerative properties, large-scale anthropogenic fires have a devastating environmental impact.
- Wildfires can have long-term effects on the quality of rivers and lakes, and on storm water runoff channels. As ash-dry soil with organic matter that hasn’t rotted becomes hydrophobic and prevents the absorption of water.
- Wildfires emit carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gases that will continue to warm the planet well into the future. They damage forests that would otherwise remove CO2 from the air.
- Biodiversity gets impacted hugley.
Grim situation around the world:
- In 2019, the world lost a football field of rainforest every six seconds.
- 11.9 million hectares of tree cover was lost in 2019. This is about 1.8 gigatonnes of released carbon dioxide, or the annual emission equivalent of 400 million cars (the world’s total number of cars is estimated at 1 billion).
- Brazil, the Democratic Republic of Congo and Indonesia have lost the most tropical primary forest cover in recent years.
- The massive wildfires during the latest Australian summer resulted in the worst tree loss ever recorded in Australia, along with the loss of hundreds of millions of animals.
India’s situation:
India has about 31 million hectares, or 11% of its area under forest cover. Over the past 20 years, India has lost 328,000 hectares of humid primary forest.
Deforestation and destruction of wetlands are among the leading causes of annual floods in heavily urbanized areas in Kerala and the cities of Mumbai and Chennai.
Silver lining:
- Some countries like Colombia and Costa Rica have been able to slow forest loss.
- While on the one hand contributing to forest loss, China, the US, Ethiopia, and India have also planted billions of trees over the last decade.
- The Billion Tree Campaign inspired by Kenyan Nobel Laureate Wangari Maathai has morphed into a Trillion Tree Campaign.
Environmentalists estimate that planting a trillion trees can cancel out the deleterious effects of a decade of anthropogenic emissions.
“Cash for conservation” or Payment for Ecosystem Services (PES):
- Populations living on the periphery of forests often see an advantage in cultivating the forest land or using it for pasture, resulting in high rates of deforestation.
- One solution to the alarming loss of forest cover is to compensate marginalized populations on the periphery of forests and incentivize them not to flatten forests.
- PES was pioneered in Costa Rica, and has been successfully used in Mexico.
- The world’s longest running PES programme is the US Conservation Reserve Program, which pays out about $1.8 billion a year to the farmers to refrain from cultivating environmentally sensitive land.
- The contract requires these farmers to plant resource-conserving covers to manage soil-erosion, improve water quality, and enhance biodiversity.
- China’s Grain-for-Green scheme hands out nearly $4 billion a year to conserve sloping plots (greater than 25 degrees) that are prone to soil erosion by giving out grain and cash. One of the programme’s goals is to reduce the annual silt deposits in the Yangtze and Huang He rivers.
Word of caution:
PES systems are complicated to design and implement because they have to be very specific to micro-climatic conditions as well as to the practices of local populations.
Conclusion:
Even as the world tries to give up fossil fuels, reduce material consumption, work more from home and turn vegetarian, afforestation and PES programmes can add significant strength to the fight against climate change.
India should set up an ambitious goal of first retaining and then increasing its forest cover.
Connecting the dots:
- Payment for ecosystem services (PES) can be an effective way to check deforestation. Comment.
- What is a wildfire? What are its impacts?
GOVERNANCE/ ECONOMY/ SOCIETY
Topic: General Studies 2:
- Government policies and interventions for development in various sectors
- Indian Economy and issues relating to planning, mobilization, of resources
Shrinking Economy and Urban Jobs
Context:
As per the economy and employment’s recent data on the contraction of the economy, the shrinking sectors that have been affected the most — construction (–50%), trade, hotels and other services (–47%), manufacturing (–39%), and mining (–23%) — are those that create the maximum new jobs in the economy.
Given the contraction and lack of demand in the economy, there would be a significant dip in urban employment generation.
Vulnerable employment in India:
- Vulnerable employment is characterised by inadequate earnings, low productivity and difficult conditions of work that undermine the basic rights of workers.
- It is higher in India than that of the world or the South Asia region. According to the International Labour Organization, 75% of the labour force in India in 2019 will have poor quality jobs.
India presents a curious case as capital and labour are moving from low value added activities in a sector to another sector, but not to higher value added activities. This leads to a situation where a large proportion of the jobs being created are of poor quality.
Multi pronged strategy to tackle the issue of urban jobs:
- Given the scale of urbanisation, the focus on urban employment generation programmes should be in coordination with local governments. Actors at the local level need to have more resources at their disposal.
- Employment intensive investment policies should embrace both private entrepreneurs as well as by the government. Private investments need to be facilitated by conducive contractual relations between labour and capital. Small and micro enterprises need extra support to balance the interests between labour and capital.
- Prioritising labour intensive urban infrastructure: A labour intensive approach to building municipal infrastructure can be a cost effective alternative to capital intensive approach as wage rates are low. Infrastructure investments will generate employment and earnings. Construction of low cost housing, building large scale medical, health and sanitation infrastructure in cities and towns across India can be carried out using labour intensive methods.
- While MGNREGA or its substitutes will not be able to absorb a significant proportion of workers (given millions of workers have returned to their home States due to a loss of livelihoods during the pandemic situation), MGNREGA needs to be strengthened and their capacity increased. It can be expanded by both increasing the budgetary allocations and the guaranteed minimum number of days of work.
Conclusion:
For workers in urban areas more jobs need to be generated and vulnerabilities need to be reduced by providing decent wages and some form of job security.
Connecting the dots:
- What do you mean by vulnerable employment? With India having one of the highest poor quality jobs tackling the issue of urban jobs becomes important. Comment.
- Recent data highlights the contraction of the Indian economy. In this light tackling the issue of urban jobs requires multi-pronged strategy. Comment.
(TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE)
Model questions: (You can now post your answers in comment section)
Note:
- Correct answers of today’s questions will be provided in next day’s DNA section. Kindly refer to it and update your answers.
- Comments Up-voted by IASbaba are also the “correct answers”.
Q.1 Which of the following Sustainable Development Goal (SDG) deals with Clean water and sanitation?
- SDG 6
- SDG 11
- SDG 14
- SDG 8
Q.2 ‘Health in India’ report was recently published. Consider the following statements regarding the same:
- Manipur has shown the poorest performance under full immunisation.
- Only 59.2% of the children below five years were fully immunised all over India.
Which of the above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Q.3 Bamboo Technology Parks were set up by which of the following Ministry?
- Ministry of Agriculture
- Ministry of Development of North Eastern Region
- Ministry of Urban Affairs
- Ministry of Information technology
Q.4 Consider the following statements:
- National Bamboo Mission was launched by the Ministry of Micro, Small, and Medium Enterprises (MSME).
- Scheme of Fund for Regeneration of Traditional Industries (SFURTI) was launched by the Ministry of Agriculture & Farmers’ Welfare.
Which of the above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
ANSWERS FOR 13th September 2020 TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE (TYK)
| 1 | D |
| 2 | B |
| 3 | C |
| 4 | A |
Must Read
Changing geopolitics in Afghanistan and Arabia:
About NEP 2020:
About right to information for citizens:











