IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
Archives
(PRELIMS + MAINS FOCUS)
Frontier Technologies Cloud Innovation Centre
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-III – Innovation; Science and Technology
In news
- NITI Aayog recently announced the establishment of a Frontier Technologies Cloud Innovation Centre (CIC) with Amazon Web Services (AWS).
- Objective: To address societal challenges through digital innovation
- It is the first of its kind in India.
Key takeaways
- It is a part of the AWS CIC Global Programme.
- The programme provides an opportunity for government agencies, non-profits and educational institutions, to come together on pressing challenges, apply design thinking, test new ideas, and access the technology expertise of AWS.
- The NITI Aayog Frontier Technologies CIC will be a great enabler to budding innovators and start-ups.
- It shall help in piloting state-of-the-art, cloud-centric digital innovations by making use of emerging technologies such as Artificial Intelligence, Internet Of Things, robotics, blockchain.
India’s First-Ever Multi-Modal Logistic Park in Assam
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-III – Infrastructure
In news
- The first-ever multi-modal logistic park shall come up in Assam on October 20, 2020.
- Ministry: Ministry for Road Transport and Highways
- The Rs 694 crore park will provide direct connectivity to air, road, rail and waterways to the people.
- It will be developed under the ambitious Bharatmala Pariyojana of the Government of India.
Framework For Regulatory Sandbox introduced
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-III – Economy
In news
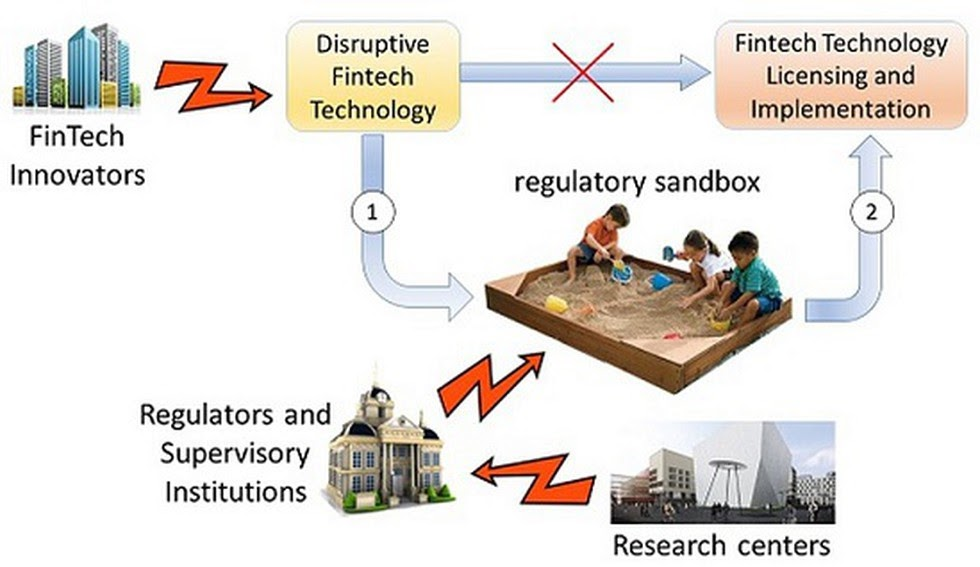
- The International Financial Services Centres Authority (IFSCA) has introduced a Framework for Regulatory Sandbox to tap into innovative FinTech solutions.
Key takeaways
- Under this Sandbox framework, entities operating in the capital market, banking and insurance and financial services space shall be granted facilities to experiment with innovative FinTech solutions in a live environment with a limited set of real customers for a limited time frame.
- These features shall be fortified with necessary safeguards for investor protection and risk mitigation.
- The Regulatory Sandbox shall operate within the IFSC located at GIFT City.
- The creation of an “Innovation Sandbox” is proposed as an additional step towards creating an innovation-centric ecosystem in the IFSC.
- The Innovation Sandbox will be managed and facilitated by the Market Infrastructure Institutions (MIIs) operating within the IFSC.
Do you know?
- IFSCA has an objective to develop a world class FinTech hub at the IFSC in GIFT City, Gandhinagar (Gujarat).
- Thus, it endeavours to encourage the promotion of financial technologies (‘FinTech’) initiatives in financial products and services across the fields of banking, insurance, securities and fund management.
- “Regulatory Sandbox” is a step towards attaining this vision.
Malabar 2020 Naval Exercise to see Australian Navy participation
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-II – International Relations
In news
- This year Malabar 2020 will see the participation of the Australian Navy as well.
- Objective: To increase cooperation with other countries in the maritime security domain; To increase defence cooperation with Australia
- The participants of Exercise Malabar 2020 shall engage to enhance safety and security in the maritime domain.
- They collectively support free, open and inclusive Indo-Pacific and remain committed to a rules based international order.
Do you know?
- The Malabar series of Naval exercises started in 1992.
- It started as a bilateral Indian Navy-US Navy exercise.
- Later on, Japan joined the Naval exercise in 2015.
- This annual exercise is expected to be held in the Bay of Bengal and the Arabian Sea later this year.
SCO Startup Forum to be launched
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-II – International Relations
In news
- The first-ever SCO Startup Forum will be launched on 27th October 2020.
Key takeaways
- The forum will lay the foundation for multilateral cooperation and engagement among the Shanghai Cooperation Organisation (SCO) Member States.
- Objective: To develop and improve startup ecosystems collectively.
- The Forum shall identify areas of cooperation by launching multiple entrepreneurial activities like startup showcases through a dedicated virtual platform, mobilizing capital for startups, sharing of best practices, procuring social innovations etc.
- Also, Innovation and Startups will be the key focus area of SCO Heads of Government meeting on 30th November 2020 to be hosted by India.
Important value additions
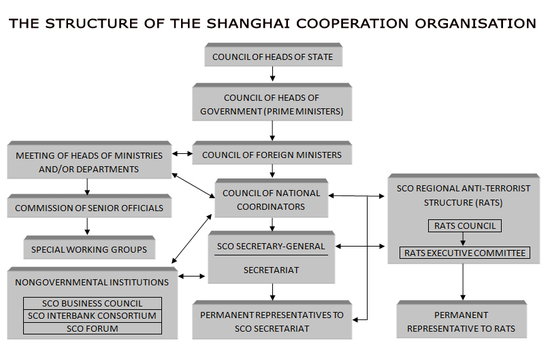
Shanghai Cooperation Organisation
- SCO or Shanghai Pact is a Eurasian political, economic, and security alliance.
- Its formation was announced on 15 June 2001 in Shanghai, China by the leaders of China, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Russia, Tajikistan, and Uzbekistan.
- Current Members: China, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Russia, Tajikistan, Uzbekistan, India and Pakistan
- Headquarters: Beijing, China
Do you know?
- India is currently the third-largest startup ecosystem in the world with over 35,000 startups.
- Close to 25% of Startups are core technology based operating in areas of AI, Robotics, Cloud Computing, IoT, Digital Health, Financial & Education Technology.
- The ‘Startup India’ has launched 10 bilateral bridges since its inception and has helped many technology-based startups to expand their businesses to global markets.
Ghar Tak Fibre Scheme inaugurated in Bihar
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-II – Government Policies and Interventions
In news
- Recently, Indian Prime Minister inaugurated ‘Ghar Tak Fibre’ scheme in Bihar.
- Implemented by: Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology
Key takeaways
- Aim: To connect all 45,945 villages of Bihar with high-speed optical fibre internet by 31st March 2021.
- Under the scheme, Bihar has to provide at least five fibre-to-the-home (FTTH) connections per village and at least one WiFi hotspot per village.
- The Scheme will lead digital services including e-Education, e-Agriculture, Tele-Medicine, and other social security schemes in Bihar.
- It shall boost the local employment generation with the implementation of Bharat Net initiative which will be done by recruiting local workers.
Dolphins make a comeback in Pearl River Estuary
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-III – Environment; Biodiversity
In news
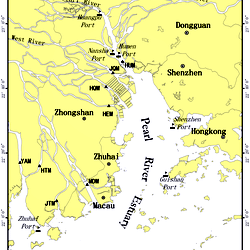
- According to a recent report, Chinese pink dolphins/Indo-Pacific humpback dolphins are making a comeback in the Pearl River Estuary (PRE).
Key takeaways
- Dolphins use echolocation to find their way in the water.
- The ships often disturb them in finding their way and even kill them.
- However, dolphin numbers in the waters between Hong Kong and Macau have seen a rebound in 2020 because Covid-19 pandemic has stopped ferries and hence reduced their traffic.
- The number of pink dolphins in the waters has roughly increased by a third according to scientists.
Important value additions
Pearl River Estuary
- It includes Hong Kong, Macau and the mainland Chinese cities of Shenzhen, Guangzhou and Dongguan.
- The Pearl River Delta is the low-lying area which surrounds the PRE where the Pearl River flows into the South China Sea.
- The Delta is one of the world’s most densely urbanised, heavily industrialised and busiest shipping lanes on Earth.
Indo-Pacific Humpback Dolphin
- Scientific Name: Sousa Chinensis.
- Habitat: Coastal waters of the eastern Indian and western Pacific Oceans.
- The World Wildlife Fund for Nature (WWF) has seen a decline in their numbers in the past 15 years by 70-80%.
- Threats: (1) Agricultural, industrial, and urban pollution; (2) Overfishing; (3) Marine construction; (4) Transport; (5) Selling into captivity at marine entertainment parks and aquariums
- IUCN Status: Vulnerable

Do you know?
- Echolocation is a technique used by bats, dolphins and other animals to determine the location of objects using reflected sound.
- This allows the animals to move around in pitch darkness, so they can navigate, hunt, identify friends and enemies, and avoid obstacles.
Zoological Survey of India lists 62 species of Skinks
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-III – Environment; Biodiversity
In news
- A recent publication by the Zoological Survey of India (ZSI) reveals that India is home to 62 species of skinks.
- Title of the publication: Skinks of India.
Key takeaways
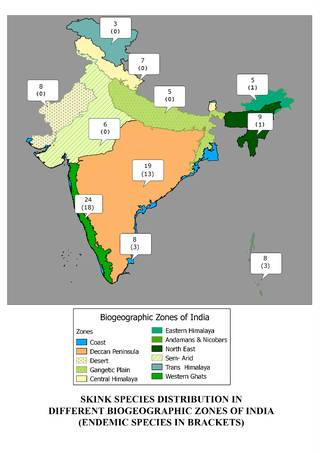
- It gives a phylogenetic (evolutionary development) and bio-geographical analysis of distribution of these species in all the 11 bio-geographic zones of India.
- India is home to less than 4% of the skinks across the globe.
- 62 species of skinks are found in India.
- About 57% of them (33 species) are endemic.
- The four genera of skinks which are endemic to India are: (1) Sepsophis punctatus is endemic to the northern part of Eastern Ghats; (2) Barkudia are limbless skinks found in the hills and coastal plains of the eastern coast; (3) Kaestlea, also known as blue-tailed ground skinks, are endemic to the Western Ghats; (4) Ristella, also known as Cat skinks, are endemic to the southern part of Western Ghats.
Important value additions
Skinks
- It is the largest family of lizards.
- There are 1,602 species of skinks across the world.
- It has long body relatively small or no legs, no pronounced neck and glossy scales.
- It is found around homes, garages, and open spaces such as sparks and school playgrounds, and around lakes.
- Skinks are non-venomous, highly alert, agile and fast moving.
- They actively forage for a variety of insects and small invertebrates.
- They have a prominent role in maintaining ecosystems.
- However, not much is known about their breeding habits, and ecology because identification of the species can be confusing.
- In India skinks are found in all kinds of habitats in the country, from the Himalayas to the coasts and from dense forests to the deserts.
Do you know?
- Barkudia insularis is believed to be found only in the Barkud Island in Chilka lake in Odisha.
- Barkudia melanosticta is endemic to Visakhapatnam.

Miscellaneous
| Important Bilateral and Multilateral Defence Exercises | |
| Indra | India-Russia Naval Exercise |
| Malabar | US-India-Japan Naval Exercise |
| Varuna | France and India Naval Exercise |
| Simbex | India and Republic of Singapore Naval Exercise |
| Ibsamar | India, Brazil and South Africa Naval Exercise |
| Konkan | India and Britain Naval Exercise |
| Ausindex | India and Australia Naval Exercise |
| Naseem Al-Bahr | India-Oman Naval Exercise |
(MAINS FOCUS)
ECONOMY/ GOVERNANCE
Topic: General Studies 2,3:
- Indian Economy and issues relating to planning, mobilization, of resources, growth, development.
- Government policies and interventions for development in various sectors and issues arising out of their design and implementation.
Transparent taxation
Context: Prime Minister launched the platform ‘Transparent Taxation—Honouring the Honest’ on August 13, 2020, comprising of faceless assessments, faceless appeals and a taxpayer’s charter.
What are the issues plaguing Tax administration in India?
- High Tax Dispute ratio
- The Receipt Budget 2020-21 indicates that the amount of taxes on income which is under dispute was Rs 8 lakh crore at the end of 2018-19. This is 5.8 times the tax amount not under dispute (Rs 1.38 lakh crore)
- Of this, the corporation tax amount under dispute at the end of 2018-19 was Rs 4.06 lakh crore—4.9 times the corporation tax amount not under dispute (Rs 0.83 lakh crore).
- High Refund:
- A significant portion of corporation tax collected during the first quarter of a financial year is used to refund previous year’s excess collection.
- It was about 48% during the first quarter of 2018-19 and 39.8% during first quarter of 2017-18.
- The CAG indicates in its 2020 report that “the possible reason for this higher refund could be exaggerated demands raised by the department during the previous financial years to meet their revenue collection targets.”
- Indiscriminate usage of Appeal Process
- When it comes to appeals, tax officers needlessly pursue these at higher levels, regardless of the outcome since there is no penalty on the ITD and its officers.
- Cases pending with the ITAT increased 2.4 times in 2018-19, to 92,205, compared to 37,572 cases in 2017-18.
- The total cases pending at higher levels (ITATs, high courts, the Supreme Court) increased to 1.35 lakh in 2018-19 compared to 0.82 lakh cases in 2017-18
- Long time to resolve Tax disputes
- Any tax dispute in India normally takes 15-20 years from the time an assessment is completed to the time the Supreme Court possibly takes a decision
- Aggressive Targets leads to Tax Terrorism
- The CBDT is known to set high tax collection targets for field officers, which forces them to be aggressive in collecting advance tax, issuing inappropriate assessment orders, leading to tax terrorism,
- As a result, demands difficult to recover have been increasing year after year, and accounted for 98.8% of the total arrears of demands in 2018-19
Significance of the Transparent Taxation initiative
- Faceless assessment and appeals aim to eliminate physical interface between taxpayers and tax authorities, thereby bringing in greater efficiency and transparency to the assessment and appeal process
- This helps in reducing tax officer’s discretion
- Tax terrorism and scope for corruption is minimised
- Faceless assessment system should reduce litigation since taxpayers will no longer be attached to a specific office or territory or jurisdiction for assessments. Instead, the National e-Assessment Centre (NeAC) will be the main gateway for communication between taxpayers and tax authorities.
Way Ahead
- Clearing Backlogs: While the faceless assessment and appeal system will address the administration issues, the CBDT should focus on resolution of the high number of pending appeals before various authorities
- Publishing Progress: The CBDT should publish on its homepage on a monthly basis a report on the total number of appeals pending at the beginning of the month, disposed of during that month and the pending appeals at month-end
- Regular Monitoring: The monthly updates to be released by CBDT needs to be reviewed every month by the FM, just as the PM reviews infrastructure projects.
- Prevent Frivolous filing of Cases: The CBDT should enhance monetary limits for filing appeals by the ITD to Rs 1 crore before ITATs, Rs 5 crore before HCs and Rs 10 crore before the SC. These enhanced limits would prevent tax officers from filing routine frivolous cases and enable judicial authorities to focus on high-value litigations.
- Ease the process for Obtaining refunds: The tax officer faces no prescribed time limit for issuing the refund. A time period of 30 days should be set for refunds consequent to such orders, and if the refund is not paid within time period interest should be levied on the refund amount
Connecting the dots:
GOVERNANCE/ ECONOMY
Topic: General Studies 3:
- Devolution of powers and finances up to local levels and challenges therein.
- e-governance and its applications
- Indian Economy and issues relating to planning, mobilization, of resources, growth, development and employment.
SVAMITVA Scheme
Context: On October 11, Prime Minister Modi launched the distribution of property cards under the SVAMITVA scheme through video conferencing.
What is the SVAMITVA card?
- The acronym SVAMITA stands for Survey of Villages and Mapping with Improvised Technology in Village Areas.
- It is a Central Sector Scheme (100% by Union Government) implemented by Union Ministry of Panchayat Raj
- It is aimed at “providing ‘record of rights’ to village household owners possessing houses in inhabited rural areas in villages and issuance of property cards to the property owners.”
- The government aims to provide such property cards to each household in the next three to four years in every village across the country.
- The plan is to survey all rural properties using drones and prepare GIS based maps for each village.
- During the current financial year, the scheme is being implemented as a pilot project in about 1 lakh villages across 8 states – Maharashtra, Karnataka, Haryana, Uttar Pradesh, Uttarakhand, Madhya Pradesh, Punjab and Rajasthan.
How is a SVAMITVA property card generated?
- MoU with States: The framework for implementation of SVAMITVA scheme provides a multi-stage process of generating a property card, which starts with signing of a memorandum of understanding between Survey of India (SoI) and respective state governments.
- Use of technology: The SoI is responsible for preparing the National Topographic database on all scales, using technology (drones, Satellite images)
- Setting up of Network: Once the MOU is done, a Continuously Operating Reference System (CORS) network is establishes that supports in establishing ground control points, which is an important activity for accurate Geo-referencing
- Public Awareness: The next step is the identification of villages to be surveyed during the pilot phase, and make people aware of the process of mapping properties.
- Preparation of GIS Database: The abadi area (residential area) of the village is demarcated and each rural property is marked with limestone (chunna). Then, drones are used for large scale mapping of rural abadi areas. Based on these images, a GIS database on 1:500 scale, and village maps — Gram Manchitra — are drawn.
- Verification: After creation of maps, a ground verification process by drone survey teams follows, on the basis of that corrections, if any, are made. At this stage, inquiry/objection process – conflict/ dispute resolution is completed
- Issuance of Property Cards: After verification, final Property Cards/Title deeds or “Sampatti Patrak” are generated. These cards will be available on digital platforms or as hard copies to the village household owners.
How will the SVAMITVA property data and maps be updated in the future?
- The framework states, “Once the GIS database is prepared encompassing the 6.62 lakh villages, state governments will be responsible for conducting future surveys and updating the GIS database.” They will also decide the update frequency of the re-survey.
Who will own the SVAMITVA data?
- According to the framework, the orthorectified base maps shall be jointly owned by the Survey of India, Ministry of Panchayati Raj and the state government. The GIS data will also be jointly owned by Centre and State.
- However, the data related to property details will be owned by the State Revenue Department as it has the authority to mutate the Right of Records (RoRs) and update the maps.
- Hence, the State Revenue Department will be the owner/host of this data and others will have a right to view
What is the benefit of issuing a SVAMITVA property card?
- Access Credit & Benefits: It will enable rural households to use their property as a financial asset for taking loans and other financial benefits.
- Tax Collection: The database will help in determination of property tax, which would accrue to the Gram Panchayats directly in states where they are empowered to collect such taxes
- Enhances Liquidity of assets: The cards will help increase liquidity of land parcels in the market and increase the financial credit availability to the village.
- Developmental Planning: The scheme will also pave the way for creation of accurate land records for rural planning. All the property records and maps will be available at Gram Panchayat, which will help in taxation of villages, construction permits, elimination of encroachments, etc.
Conclusion
- State governments and local authorities need to be enthusiastic about the scheme for it to become successful.
Connecting the dots:
- 73rd Constitutional Amendment Act
(TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE)
Model questions: (You can now post your answers in comment section)
Note:
- Correct answers of today’s questions will be provided in next day’s DNA section. Kindly refer to it and update your answers.
- Comments Up-voted by IASbaba are also the “correct answers”.
Q.1 Consider the following statements:
- India is one of the founding members of Shanghai Cooperation Organisation.
- Its headquarter is situated in Shanghai, China.
Which of the above is or are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Q.2 India’s first ever Multi-Modal Logistic Park is said to be constructed in which of the following state of India?
- Assam
- Gujarat
- Uttar Pradesh
- Karnataka
Q.3 Ghar Tak fibre scheme was recently inaugurated in which of the following state of India?
- Bihar
- Uttar Pradesh
- West Bengal
- Odisha
Q.4 Burkud Island is situated in which of the following lake of India?
- Loktak Lake
- Chilika Lake
- Wular Lake
- Pulicat Lake
ANSWERS FOR 20th October 2020 TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE (TYK)
| 1 | C |
| 2 | A |
| 3 | A |
Must Read
About AP Higher Judiciary:
On India-China relationship:
About Terror threat in today’s time:











