IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
Archives
(PRELIMS + MAINS FOCUS)
Repeal of UAPA demanded
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-II – Policies and interventions
In news
- Major Opposition parties have demanded the repeal of the Unlawful Activities (Prevention) Act (UAPA), 1967.
- This came after the arrest of Stan Swamy, a tribal rights activist, in the Bhima Koregaon case.
Important value additions
Unlawful Activities (Prevention) Act (UAPA), 1967
- UAPA was passed in 1967.
- It aims at effective prevention of unlawful activities associations in India.
- The Act assigns absolute power to the central government. If the Centre deems an activity as unlawful then it may declare it so.
- It has death penalty and life imprisonment as highest punishments.
- Under UAPA, both Indian and foreign nationals can be charged.
- It will be applicable to the offenders in the same manner, even if crime is committed on a foreign land, outside India.
- The 2004 amendment added terrorist act to the list of offences to ban organisations for terrorist activities, under which 34 outfits were banned.
Do you know?
- In August 2019, Parliament cleared the Unlawful Activities (Prevention) Amendment Bill, 2019 to designate individuals as terrorists if the individual commits or participates in acts of terrorism, prepares for terrorism, promotes terrorism or is otherwise involved in terrorism.
- The Act empowers the Director General of National Investigation Agency (NIA) to grant approval of seizure or attachment of property when the case is investigated by the said agency.
Mobile Application for Geo Tagging launched by Ministry of Jal Shakti
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-II – E-governance; Policies and interventions
In news
- A mobile application for geo-tagging of the components of projects under Pradhan Mantri Krishi Sinchayee Yojana (PMKSY) was recently launched. .
- Ministry: Ministry of Jal Shakti
- Developed By: Bhaskaracharya National Institute of Space Applications & Geo-informatics (BISAG-N).
Key takeaways
- Objective: To track the pace of work and actual status of the projects.
- The mobile application can be used to capture the image of the project component along with other details.
- The captured information can be submitted by the user for geo-tagging on the geographic information system (GIS) portal.
- It can be operated in both online & offline mode.
Important value additions
Pradhan Mantri Krishi Sinchayee Yojana (PMKSY)
- PMKSY is a centrally sponsored scheme
- Launched in: 2015
- Motto: Har Khet Ko Paani
- Objectives: (1) To expand cultivated areas with assured irrigation, reduce wastage of water and improve water use efficiency; (2) To create protective irrigation by harnessing rainwater at micro level; (3) To enhance recharge of aquifers
Do you know?
- Geo-tagging is the process of adding geographical identification data to various media such as websites, SMS messages, QR Codes.
- This data usually consists of latitude and longitude coordinates, altitude, accuracy data, etc.
- A GIS is a framework for gathering, managing, and analyzing geography related data.
UDAN Day observed
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-II –Policies and interventions & GS-III – infrastructure
In news
- Recently, 4th anniversary of the UDAN (Ude Desh Ka Aam Naagrik) Scheme was observed by the Ministry of Civil Aviation
Important value additions
Ude Desh Ka Aam Naagrik (UDAN)
- It was launched as a regional connectivity scheme (RCS) in 2016
- Ministry: Ministry of Civil Aviation.
- Aim: (1) To develop the regional aviation market; (2) To provide affordable and profitable air travel on regional routes to the common man.
- It envisages providing connectivity to un-served and under-served airports of the country through the revival of existing airstrips and airports.
- Implemented by: Airports Authority of India (AAI) and is operational for a period of 10 years.
COVIRAP: A Quick Covid-19 Test approved by ICMR
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-III – Scientific innovation and discoveries
In news
- Recently, Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR) has approved a new Covid-19 diagnostic method named COVIRAP.
- Developed by: Indian Institute of Technology (IIT), Kharagpur
Key takeaways
- Benefit of COVIRAP Process: (1) It is a cheaper process; (2) The test is completed within an hour; (3) Simpler to Handle; (4) Reusable; (5) Efficient; (6) High Accuracy
- It can also be used in influenza, malaria, dengue, Japanese encephalitis, TB etc, which are under the category of isothermal nucleic acid-based tests.

India Invited to Join the Blue Dot Network
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-II – International relations
In news
- A group of the US Senators has asked India to join the Blue Dot Network (BDN) in a letter.
Important value additions
Blue Dot Network
- The BDN was announced in 2019 at the Indo-Pacific Business Forum in Bangkok, Thailand.
- It is led by the USA along with Japan and Australia.
- It is a multi-stakeholder initiative to bring together governments, the private sector and civil society to promote high-quality, trusted standards for global infrastructure development.
- It is expected to serve as a globally recognized evaluation and certification system for roads, ports and bridges with a focus on the Indo-Pacific region.
- It does not offer public funds or loans for the project.
- Blue Dot certification shall serve as a globally recognized seal of approval for major infrastructure projects.
Life in Miniature Project launched
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-I – Art & Culture
In news
- “Life in Miniature” project was recently launched
- Ministry: Ministry for Culture and Tourism
- It is collaboration between the National Museum, New Delhi, Ministry of Culture, and Google Arts & Culture.
Key takeaways
- Under the project, several miniature paintings from the National Museum, New Delhi can be viewed online on Google Arts & Culture by people around the world.
- The project uses technologies like machine learning, augmented reality and digitization with high-definition robotic cameras, to showcase the paintings.
Base year for CPI-Industrial Workers (CPI-IW) revised
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-III – Economy
In news
- The labour ministry has revised the base year of the Consumer Price Index-Industrial Workers (CPI-IW) from 2001 to 2016.
- It has given more weight to spending on housing, education and health in inflation index calculation.
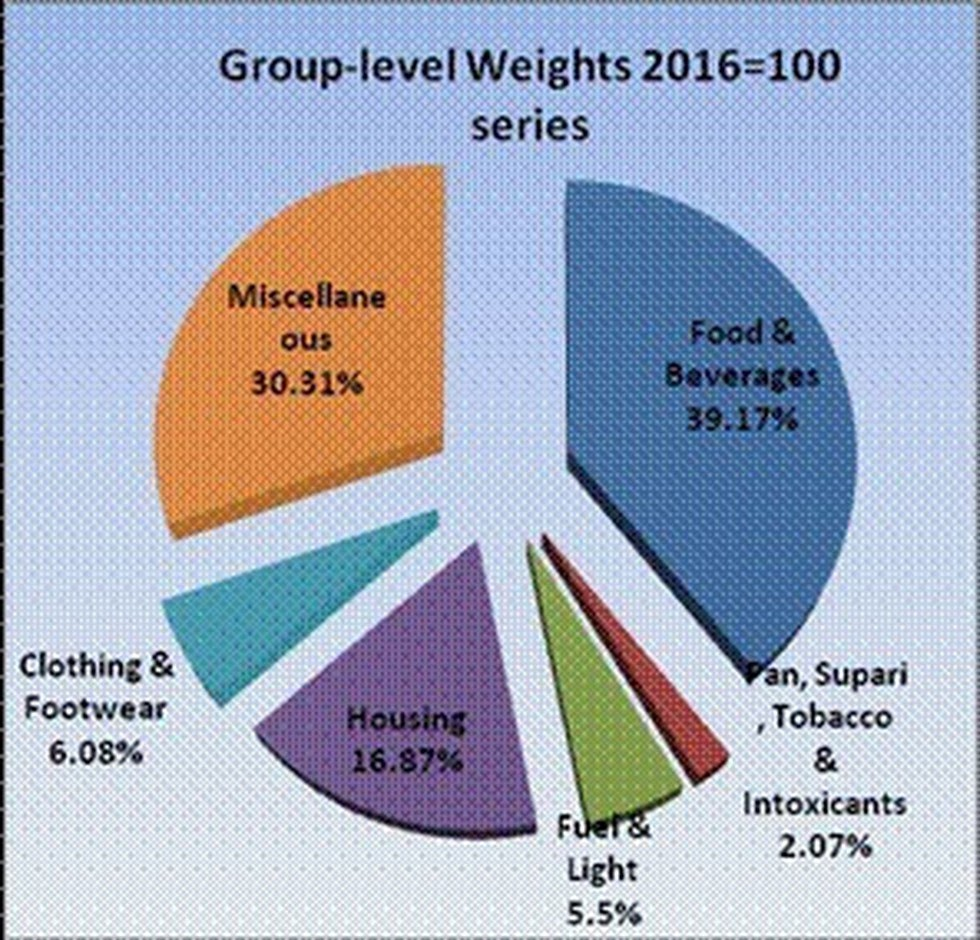
Key takeaways
- The revision in base year will reflect changing consumption pattern of the working-class population over the years.
- Following the change in base year, the index will give 39% weight to food and beverage consumption of workers now as against 46.2% earlier.
- In contrast, spending on housing will get almost 17% weight compared to 15.2% earlier.
Important value additions
CPI-Industrial Workers (CPI-IW)
- It is used as a benchmark for calculating dearness allowance for government employees, dearness relief for pensioners and wages for industrial workers in some sectors.
- Though it may not impact the salary of industrial workers and DA of government staff immediately, it will have a cascading impact on salary, DA and DR of workers, and pensioners.
G-20 Anti-Corruption Working Group Meeting
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-II – International Relations
In news
- Recently, Saudi Arabia hosted the first-ever Ministerial Meeting of the G-20 Anti-Corruption Working Group (ACWG) virtually.
- Currently, Saudi Arabia holds the presidency of G-20.
- It is the first Arab nation to do so.
Important value additions
G-20 Anti-Corruption Working Group
- It was established in June 2010 at the Toronto Summit of G-20.
- The year 2020 marks its 10th anniversary.
- Objective: To prepare comprehensive recommendations on how the G20 could continue to make practical and valuable contributions to international efforts to combat corruption.
- It actively works with the World Bank Group, the Organisation for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD), and other important Organisations
G-20
- It is an informal group of 19 countries and the European Union (EU), with representatives of the IMF and the World Bank.
- The G20 membership comprises a mix of the world’s largest advanced and emerging economies.
- It represents about two-thirds of the world’s population, 85% of global GDP, 80% of global investment and over 75% of global trade.
- The G20 operates as a forum and not as an organisation. Therefore, it does not have any permanent secretariat or headquarter.
- Members: Argentina, Australia, Brazil, Canada, China, France, Germany, India, Indonesia, Italy, Japan, Republic of Korea, Mexico, Russia, Saudi Arabia, South Africa, Turkey, the UK, the USA, and the EU.
- One nation holds the chair every year, known as the ‘G20 Presidency’.

(MAINS FOCUS)
INTERNATIONAL/ GOVERNANCE
Topic: General Studies 1,2:
- Contemporary World History (UN)
- Important International institutions, agencies and fora- their structure, mandate.
India’s UN journey
Context: The 75th anniversary of the founding of the United Nations (UN) is an opportunity to look at the major trends, patterns and future challenges as far as India is concerned.
India’s Membership at UN during three phases
- Seven and a half decades of India at the UN may be viewed with reference to roughly three distinct phases.
- First phase until the end of the Cold War in 1989
-
- Moderating Force: India had learnt the ropes of exploring and enhancing its diplomatic influence as a moderating force in easing armed conflicts in Asia and Africa by disentangling them from the superpower rivalry (Non-Aligned Movement)
- Unresolved Kashmir Dispute: The Indian leadership learned the hard way that the UN could not be relied upon to impartially resolve vital security disputes such as Jammu and Kashmir (US reliance on Pakistan in its Afghanistan war)
- Moral Values based Foreign Policy: India strove to utilise the UN only to focus on common causes such as anti-colonialism, anti-racism, nuclear disarmament, environment conservation and equitable economic development.
- Championed Nuclear Disarmament: India, in a clever way, seemed to claim the moral high ground by proposing, in 1988, a bold, but obviously impractical, three-phase plan to eliminate nuclear weapons from the surface of earth.
- Impact of 1962 war: India resisted attempts by neighbouring countries to raise bilateral problems. A loss of face for India in the 1962 border war against China meant a definitive redesign of the country’s diplomatic style to privilege bilateral contacts over the third party role by the UN.
- Decade of 1990s: Turbulent and Transition Phase
-
- Sudden Changes: The years were marked by the sudden end of the Cold War, the disintegration of the Soviet Union and the resultant emergence of the United States as the unrivalled power in world politics.
- Domestic Factors hindered active role at UN: The uncertain political climate caused by unstable coalition governments along with the balance of payments crisis constrained the country’s capability to be active in UN.
- Pragmatic Foreign policy: To cite a few examples, India showed pragmatism in enabling the toughest terms on Iraq even after eviction from occupied Kuwait, or in reversing the hitherto stated position on Zionism as racism.
- Internationalisation of Kashmir Issue: Growing militancy in Kashmir in the early 1990s emboldened Pakistan to internationalise the dispute with accusations about gross human rights violations by India. Clearly, India had to work hard to seek favours from Iran and China in the Human Rights Commission to checkmate Pakistan.
- India stood against major powers to safeguard its security interest: India resolutely stood against indefinite extension of the Non-Proliferation Treaty in 1995, and it stoutly rejected the backdoor introduction for adoption of the Comprehensive Test Ban Treaty in 1996.
- Emerged as Nuclear Power: The growing power politics in World pushed India to surprise the world in 1998 with its Pokhran nuclear weapon tests, ignoring the likely adverse reaction from the nuclear club.
- The Third phase with onset of 21st Century
-
- Economics Enhanced India’s Profile: The impressive economic performance in the first decade, thanks to economic liberalisation and globalisation policies, helped a great deal in strengthening India’s profile. This was aided by its reliable and substantial troop contributions to several peacekeeping operations of UN
- Responsible Stakeholder: India has emerged as a responsible stakeholder in non-traditional security issue areas such as the spread of small and light weapons, the threat of non-state actors acquiring weapons of mass destruction, and the impact of climate change.
- India’s growing popularity: This is evident in the successful electoral contests for various prestigious slots in the UNSC, the Human Rights Council, the World Court, and functional commissions of the Economic and Social Council, at times defeating the nominees of China and the United Kingdom.
- Two major initiatives of India stuck: The first relates to the draft Comprehensive Convention on International Terrorism it drafted and revised with the hope of helping consensus. The other is the question of equitable expansion of the UNSC to enable India to acquire Permanent position at UNSC
What are the prospects of Permanent Seat at UNSC?
- India has been lobbying with world powers to attain permanent membership along with other claimants from Asia, Africa and Latin America.
- The move has been stuck for more than 25 years because of a lack of unity among the regional formations.
- It also includes stout opposition from some 30 middle powers such as Italy and Pakistan which fear losing out to regional rivals in the event of an addition of permanent seats.
- Although India enjoys by far the greatest support, the only realistic possibility seems to settle for a compromise, i.e. a new category of members elected for a longer duration than the present non-permanent members without veto power.
Challenges for India at UN – Increased Volatility
- Unabated economic slowdown
- Trump administration’s disdain towards multilateral institutions
- The changing U.S.-China equation
- China’s growing political isolation on account of the spread of the novel coronavirus
- China’s aggressive territorial forays in eastern Ladakh and the South China Sea.
Way Ahead
India will soon begin its two-year term as a non-permanent UNSC member (January 1, 2021). Its areas of priority will continue to be
- Upholding of Charter principles
- Mounting effective punitive measures against those who support, finance and sponsor terrorists
- Striving for securing due say to the troop contributing countries in the management of peace operations.
Conclusion
As a non-permanent UNSC member now, it needs to uphold the Charter principles in the backdrop of a turbulent world
Connecting the dots:
- SAARCH and BIMSTEC
- RCEP and Why India did not join it?
ECONOMY/ GOVERNANCE/ SCIENCE & TECH
Topic: General Studies 3:
- Awareness in the fields of IT
- Challenges to internal security through communication networks, role of media and social networking sites in internal security challenges, basics of cyber security
US sues Google in biggest anti-trust case
Context: The United States Department of Justice (DoJ) has sued Google alleging that the company had abused its dominant position in a way that had harmed its competitors as well as customers.
What is the lawsuit about?
- Google has maintained its monopoly power through exclusionary practices that harm competition. So the Justice Department has determined that an antitrust response is necessary to benefit consumers.
- Antitrust refers to a group of businesses that team up or form a monopoly in order to dictate pricing in a particular market.
- Antitrust laws exist to promote competition among sellers, limit monopolies, and give consumers more options
What led to the lawsuit?
- A US House of Representatives panel had submitted the report of a bipartisan investigation into the working of Amazon, Apple, Google and Facebook.
- The probe had started in July 2019.
- These companies have been on the radar of governments in many countries for being big spenders and trying to steamroll competition by either buying out their rivals or pushing vendors to avoid working with these rivals.
- The panel said each of these companies was now acting as a “gatekeeper” over a key channel of distribution, which meant that they had full control over what went on in their respective domains
- The report called for the big technology companies to be broken up and for a “presumptive prohibition against future mergers and acquisitions by the dominant platform”.
Why is the lawsuit important?
- The lawsuit marks the first time there has been a bipartisan effort — involving both the Democratic and the Republican parties — to look into the monopolistic powers of Google.
What is the Challenge for Google?
- Although the lawsuit by a US Federal body is the first of its kind, it is unlikely that there will be any swift action on the company in the near term
- The challenge for Google would be continued scrutiny into its biggest revenue generating segment, which is advertising gained from its search engine and affiliate websites.
- In the April-June quarter, the company had earned nearly $38 billion, mainly from advertisements.
- Apart from increased federal scrutiny, big tech companies are also likely to face more questions and probes from states in the US
When was the last time Google faced legal action?
- The last time Google faced legal action for allegedly abusing its dominance in the search market was almost a decade ago — in 2011- when the Federal Trade Commission (FTC) was acting on a complaint filed by a Washington-based non-profit research agency, Electronic Privacy Information Center.
- Although the five commissioners eventually voted not to pursue a case, Google had to implement a strict user data security policy and agree to independent privacy audits for the next 20 years
What are the allegations that Google faces in India?
- Over the last three years, Google has had multiple run-ins with the CCI (Competition Commission of India) for alleged abuse of its dominant position in the market.
- In 2019, CCI had held Google guilty of misuse of its dominant position in the mobile Android market and said the company had imposed “unfair conditions” on device manufacturers to prevent them from using other operating systems.
- In February 2018, the CCI had fined Google Rs 136 crore for unfair business practices in the online search market. It said that Google had “allocated disproportionate real estate” for its affiliates, to the disadvantage of other companies that were trying to gain market access.
- Google has challenged the CCI findings in forums such as the National Company Law Appellate Tribunal and the Supreme Court.
What lies ahead for Google?
- Google may argue before the courts that it is being singled out from amongst the other companies, or try to explain why it does not really abuse its dominance in any market segments.
- In coming years, as India plans to regulate the use of personal and non-personal data, these tech companies could face scrutiny over how they manage and use the data they collect from users in India
- Amazon and Facebook, which are trying to enter the retail space in India, are also likely to be under the lens for the way they price their products and the space they give/deny to their competition
Conclusion
Free and Fair market is needed to balance the need for innovation and to protect the rights of people & society
Connecting the dots:
- Should India also launch Joint Parliamentary committee to investigate whether these tech giants are indulging in anti-competitive trade practices in India?
- If these tech giants are broken up, would it impact the digital revolution which is witnessed around the globe and also in India?
(TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE)
Model questions: (You can now post your answers in comment section)
Note:
- Correct answers of today’s questions will be provided in next day’s DNA section. Kindly refer to it and update your answers.
- Comments Up-voted by IASbaba are also the “correct answers”.
Q.1 Consider the following statements regarding Unlawful Activities Prevention Act:
- It includes punishment only against associations carrying out unlawful activities.
- It is applicable to Indians only.
Which of the above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Q.2 Consider the following statements regarding Pradhan Mantri Krishi Sinchai Yojana:
- It is a state sponsored scheme.
- One of the objectives of the scheme is to enhance recharge of aquifers.
Which of the above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Q.3 Consider the following statements link regarding UDAN (Uday Desh Ka Aam Nagrik) scheme:
- It is implemented by Ministry of Civil Aviation.
- It is operational for a period of 50 years.
Which of the above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Q.4 Consider the following statements regarding G20:
- Every member of G20 holds the presidency for two years.
- Its headquarter is in New York, USA.
Which of the above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
ANSWERS FOR 23rd October 2020 TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE (TYK)
| 1 | B |
| 2 | B |
| 3 | A |
| 4 | D |
| 5 | A |
Must Read
About states rejecting farm laws:
About On U.S. B-1 business visa curbs:
About factors that cause Delhi’s air quality to dip this time of the year:











