IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis

Archives
(PRELIMS + MAINS FOCUS)
Financial Action Task Force (FATF) decides to keep Pakistan on its grey list
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-II – International Relations
In news
- The Financial Action Task Force (FATF) decided to keep Pakistan on its “grey list”.
- According to FATF, Pakistan has failed to act on six key mandates.
- It urged Pakistan to complete an internationally agreed action plan by February 2021.
Important value additions
Financial Action Task Force (FATF)
- The FATF is a global watchdog.
- It was founded to tackle money laundering initially but its role became prominent after the 9/11 terror attacks.
- It expanded its operations and included terror financing under its purview after 9/11.
- Its membership includes 39 jurisdictions.
- It maintains two lists – a blacklist and a grey list.
- Countries on its blacklist are those that FATF deems non-cooperative in the global effort to curb money laundering and terror-financing.
- The grey list is officially referred to as ‘Jurisdictions under Increased Monitoring.’
- It constitutes those nations that present significant risks of money laundering and terror-financing but which have committed to working closely with the FATF in the development and implementation of action plans that address their deficiencies.
- If the country is not actively tackling money laundering or terror funding, it is then blacklisted.
- So far, only two countries have been blacklisted – Iran and North Korea.
North Korea warns its citizens of Yellow Dust
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-II – International Relations; Health & GS-III – Environment
In news
- North Korea has urged its citizens to remain indoors to avoid contact with a mysterious cloud of ‘yellow dust’ which is blowing in from China.
- This cloud could bring Covid-19 with it.
Important value additions
Asian Dust
- It is also known as yellow dust, yellow sand, yellow wind or China dust storms.
- It is actually sand from deserts in China and Mongolia that high speed surface winds carry into both North and South Korea during specific periods every year.
- The sand particles tend to mix with other toxic substances such as industrial pollutants.
- Thus, it is known to cause a number of respiratory ailments.
Industry 4.0 Technology jointly developed by IIT Kharagpur and TCS
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-III – Industry; Innovation; Science and Technology
In news
- IIT Kharagpur and Tata Consultancy Services (TCS) have jointly developed a novel Industry 4.0 Technology.
- It is developed for remotely controlled factory operations and real-time quality correction during industrial production so as to deliver quality output at low costs.
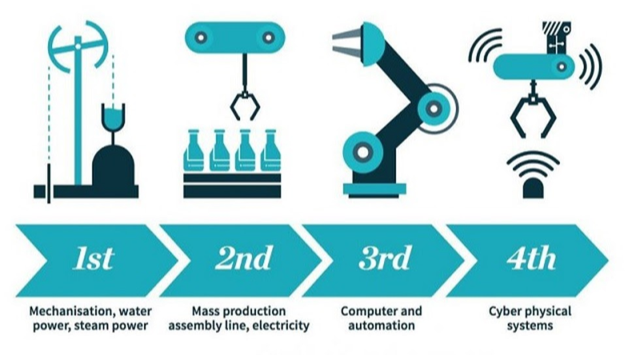
Important value additions
Industrial Revolution 4.0
- Klaus Schwab, founder and executive chairman of the Geneva-based WEF, published a book in 2016 titled “The Fourth Industrial Revolution” and coined the term at the Davos meeting in the same year.
- It refers to how technologies like artificial intelligence, autonomous vehicles and the internet of things are merging with humans’ physical lives.
- Examples: Voice-activated assistants, facial ID recognition or digital health-care sensors.
- There is a common theme among each of the industrial revolutions: the invention of a specific technology that changed society fundamentally.
- Major invention of The First Industrial Revolution: The steam engine. The steam engine enabled new manufacturing processes, leading to the creation of factories.
- Major inventions of the Second Industrial Revolution: Light bulb, telephone and internal combustion engine
- Major inventions of the Third Industrial Revolution: The semiconductor, personal computer and the Internet. This is also referred to as the “Digital Revolution.”
- The Fourth Industrial Revolution is different from the third for two reasons: the gap between the digital, physical and biological worlds is shrinking, and technology is changing faster than ever.
Kisan Suryodaya Yojana launched
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-II – Policies and interventions
In news
- Indian Prime Minister launched the Kisan Suryodaya Yojana in Gujarat.
- Under the scheme, 16 hours of power supply shall be provided to farmers.
Key takeaways
- Objective: To provide day-time power supply for irrigation.
- Under this scheme, farmers will be able to avail power supply from 5 AM to 9 PM.
- The state government has allocated a budget of Rs.3500 crore for installing transmission infrastructure under this scheme by 2023.
- 234 ‘66-Kilowatt’ transmission lines will be established under the project, in addition to 220 KV substations.
- Districts to be covered in initial phase: Dahod, Patan, Mahisagar, Panchmahal, Chhota Udepur, Kheda, Tapi, Valsad, Anand and Gir-Somnath have been
- The remaining districts will be covered in a phase-wise manner by 2022-23.
Hong Kong BNO Passports not to be considered by China as valid travel documents
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-II – International Relations
In news
- Chinese foreign ministry said that it will consider not recognizing Hong Kong British national overseas (BNO) passports as valid travel documents.
- Recently, the British government had announced new visa rules for British National Overseas citizens in HK.
Key takeaways
New visa rules
- Britain will start to process BNO visa applications for residents in the Hong Kong Special Administrative Region (HKSAR) from January 31, 2021.
- As per new visa rule, BNO Visa holders will have the right to work and study in the UK for a period of five years. They can apply for citizenship after the sixth year.
Important value additions
BNO Passport
- The British National (Overseas) passport, commonly referred to as the BN(O) passport, is a British passport for persons with British National (Overseas) (BN(O)) status.
- The passport was first issued in 1987 after the Hong Kong Act 1985 from which this new class of British nationality was created.
- Holders of BN(O) passports are permanent residents of Hong Kong who were British Dependent Territories citizens until 30 June 1997 and had registered as BN(O)s.
Historic ceasefire announced in LIBYA
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-II – International Relations
In news
- Rival parties in Libya announced a historic ceasefire followed by five days of the 5+5 Libyan Joint Military Commission (JMC) talks in Geneva.
- This gives way to the possibility that the long-drawn conflict might be coming to an end.
Key takeaways
New Ceasefire Agreement
- As per this new agreement facilitated by the UN, all foreign mercenaries and armed forces will have to withdraw within the next 90 days.
- The parties also agreed that any violations in the ceasefire will be dealt by a joint military force, which will be under a unified command.
- The agreement has also established a Joint Police Operations room that will implement and propose special arrangements to secure the areas that are cleared of military units and armed groups.
- Further, the 5+5 have also agreed to open the land and air routes that connect the regions and cities of Libya.
Khadi being manufactured in the region of Oaxaca
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-II – International Relations
In news
- Indian Prime Minister made a reference to the region of Oaxaca (pronounced O-aa-ha-ka) in Mexico where Khadi was being manufactured.
Key takeaways
- Khadi Oaxaca is a farm-to-garment collective which comprises around 400 families.
- They live and work on traditional farms and homesteads in the Oaxaca region of southern Mexico
- It uses cotton produced and cultivated on the Oaxaca coast, and produces chemical-free clothing, relying on locally harvested plant-based dyes.
International Snow Leopard Day
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-III – Biodiversity
In news
- International Snow Leopard Day is observed on 23rd October.
Key takeaways
- Aim: To raise awareness on conservation and protection of snow leopards.
- International Snow Leopard Day came into being on 23rd October, 2013 when Bishkek Declaration was adopted by 12 countries on the conservation of snow leopards.
- The 12 countries included: India, Nepal, Bhutan, China, Mongolia, Russia, Pakistan, Afghanistan, Kyrgyzstan, Kazakhstan, Tajikistan, and Uzbekistan.

Important value additions
Snow Leopard
- It is also known as Ghost of the mountains.
- They are positioned as the top predator in the food web.
- It acts as an indicator of the health of the mountain ecosystem in which they live.
- Habitat: Higher Himalayan and trans-Himalayan landscape in J&K, Himachal Pradesh, Uttarakhand, Sikkim, and Arunachal Pradesh.
- India is home to 5 big cats: Snow Leopard, Lion, Tiger, Common Leopard, and Clouded Leopard.
- Snow Leopard capital of the world: Hemis, Ladakh.
- Threat: Reduction in prey populations, illegal poaching and increased human population infiltration into the species habitat and illegal trade of wildlife parts and products
- IUCN Red List: Vulnerable
- CITES: Appendix I
- Convention on Migratory Species (CMS): Appendix I
- Indian Wildlife (Protection) Act 1972: Schedule I
- Conservation Efforts by India: (1) HimalSanrakshak: It is a community volunteer programme, to protect snow leopards, launched on 23rd October 2020; (2) In 2019, First National Protocol was also launched on Snow Leopard Population Assessment; (3) SECURE Himalaya: Global Environment Facility (GEF)-UNDP funded project on conservation of high altitude biodiversity; (4) Project Snow Leopard launched in 2009; (5) Snow Leopard is in the list of 21 critically endangered species for the recovery programme of the Ministry of Environment Forest & Climate Change.
Do you know?
- Hemis National Park is the biggest national park of India and also has a good presence of Snow Leopard.
Miscellaneous
Girnar Ropeway
-
Indian Prime Minister recently launched the world’s longest temple ropeway project at Girnar in Junagadh.
- Girnar ropeway project consists of a total of 25 cabins.
- It operates at a capacity of 800 passengers per hour and 8000 per day.
- It will attract more tourists and pilgrims to this historical place which will boost employment opportunities.
- Mount Girnar is a major igneous plutonic complex which intruded into the basalts towards the close of the Deccan Trap period.
Dhammachakra Pravartan Day
- Dhammachakra Pravartan Day (DhammaChakra Anupravartan Din) is a day to celebrate the Buddhist conversion of B. R. Ambedkar and approximately 600,000 followers in October 1956 at Deekshabhoomi on the occasion of Vijayadashami.
- It is primarily celebrated at Deeksha Bhoomi every year.
- Deekshabhoomi is a sacred monument of Navayana Buddhism located at Nagpur city in Maharashtra where B. R. Ambedkar embraced Buddhism.
(MAINS FOCUS)
SOCIETY/ GOVERNANCE
Topic: General Studies 1,2:
- Issues relating to poverty and hunger.
- Mechanisms, laws, institutions and Bodies constituted for the protection and betterment of these vulnerable sections.
Global Hunger Index
Context: India has been ranked 94 on the 2020 Global Hunger Index (GHI), lower than neighbours like Bangladesh and Pakistan.
The number of young children in India who are very short and thin, reflecting severe undernutrition, puts it alongside the poorest African nation
What is the Global Hunger Index, and what determines its ranking?
- The GHI is an annual peer-reviewed publication by Concern Worldwide and Welthungerhilfe.
- It aims to track hunger at global, regional and national levels. It uses four parameters to calculate its scores.
- One third of the score comes from the level of undernourishment in a country, which is the share of the population with insufficient caloric intake, and uses Food and Agriculture Organization data.
- A third of the score comes from child mortality rate (under the age of five years), which often reflects the fatal mix of inadequate nutrition and unhealthy environments.
- The remaining third of the score is based on child wasting, which is the share of children who have low weight for their height, reflecting acute undernutrition, and child stunting, which is the share of children who have low height for their age, reflecting chronic undernutrition.
What data is used for calculating the Index?
- The above parameters use information from the World Health Organization, the World Bank and the United Nations
- All these international organisations draw from national data, which, in India’s case, includes the National Family Health Surveys (NFHS).
- There is always a time lag in such data, so the 2020 scores are based on data from 2015-19.
- This results in a 100-point scale, with zero meaning no hunger at all.
How does India fare on the different parameters in comparison to other countries?
- In 2020, India falls in the ‘serious’ category on the Index, with a total score of 27.2.
- India is tied at the 94th rank out of 107 countries, sharing the rank with Sudan.
- This is a definite improvement from the situation two decades ago, when it scored 38.9 and fell into the ‘alarming’ category.
- China and Brazil both scored under five, and are considered to have very low levels of hunger. South Africa is ranked 60 with a score of 13.5, indicating moderate levels of hunger.
- Overall undernourishment, 14% of India’s population does not get enough calories, an improvement from almost 20% in 2005-07.
- Child mortality rate is 3.7%, a significant drop from 9.2% in 2000.
- Child Stunting: Almost 35% of Indian children are stunted, and although this is much better than the 54.2% rate of 2000.
- Child Wasting: 17.3% of Indian children under five are wasted, which is the highest prevalence of child wasting in the world. There is no change from two decades ago, when it was 17.1%.
What is the main cause for such high levels of child stunting and wasting in India?
- African babies are usually healthy at birth, but as they grow up into their toddler years, undernourishment starts to kick in.
- In contrast, South Asian babies show very high levels of wasting during early years of lives, particularly during the first six months
- This is because of poor maternal health in South Asian countries like India. Mothers are too thin, too short and too undernourished themselves before they become pregnant and this affects new-born’s health aspects as well.
- Almost 42% of adolescent girls aged 15 to 19 have a low body mass index (BMI), while 54% have anaemia
- Social Factors like Early Marriage: Many women in India and South Asian Countries start their pregnancies in their late teens which impacts not only their health but also that of child born
- Poor sanitation, leading to diarrhoea, is another major cause of child wasting and stunting. Only 36% of households disposed of children’s stools in a safe manner. One in 10 children under the age of five suffer from diarrhoea.
How do different Indian States compare?
- Almost one in three children in Jharkhand show acute undernutrition, with a 29% rate of wasting
- Other large States such as Tamil Nadu, West Bengal, Madhya Pradesh, Chhattisgarh and Karnataka have one in five children who are wasted.
- Interestingly, other States that usually fare poorly on development indices, such as Bihar, Rajasthan and Odisha, actually do better than the national average, with 13-14% rates of wasting.
- Uttarakhand and Punjab, along with several north-eastern States, have levels of child wasting below 10%.
- In terms of stunting, Bihar performs the worst, with 42% of children too short for their age.
- At the national level, among social groups, the prevalence of stunting is highest amongst children from the Scheduled Tribes (43.6 percent), followed by Scheduled Castes (42.5 percent) and Other Backwards Castes (38.6 percent).
What needs to be done?
- Although India has overall food security with record levels of foodgrain production in recent years, access to healthy food is still difficult for poor households.
- Food insecurity, poor sanitation, inadequate housing, limited access to healthcare — all result in maternal distress that leads to the kind of slow, chronic wasting seen in Indian children. All these needs to be addressed for improving the malnutrition among Children.
- Every kind of household deprivation that makes life difficult for women needs to be dealt with. The focus needs to be on healthy mothers.
(TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE)
Model questions: (You can now post your answers in comment section)
Note:
- Correct answers of today’s questions will be provided in next day’s DNA section. Kindly refer to it and update your answers.
- Comments Up-voted by IASbaba are also the “correct answers”.
Q.1 Which of the following countries are blacklisted by Financial Action Task Force (FATF)?
- North Korea
- Iran
- Iraq
- Pakistan
Select the correct code:
- 1 and 2 only
- 1 and 4 only
- 3 and 4 only
- 1 and 3 only
Q.2 Consider the following statements regarding Kisan Suryodaya Yojana:
- It was launched in Rajasthan.
- Under the scheme, 24 hours of power supply shall be provided to the farmers.
Which of the above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
ANSWERS FOR 24th October 2020 TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE (TYK)
| 1 | D |
| 2 | B |
| 3 | D |
| 4 | D |
Must Read
About interpretation of residence rights for women in Domestic Violence Act:
About gender gap in unpaid domestic maintenance and care work:











