IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis

Archives
(PRELIMS + MAINS FOCUS)
Promotion of Buddhist Sites under Swadesh Darshan & PRASHAD
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-I – Indian Heritage Sites
In news
- Development of tourism related infrastructure and facilities at various Buddhist Sites in India under flagship schemes of Swadesh Darshan & PRASHAD has been undertaken.
- Ministry: Ministry of Tourism
Steps Taken
- Swadesh Darshan Scheme has included Buddhist circuit and Spiritual circuit among its 13 thematic circuits.
- 30 projects for development of infrastructure have also been undertaken under the PRASHAD Scheme.
- Buddhist Sites at Bodhgaya, Ajanta & Ellora have been identified to be developed as Iconic Tourist Sites.
- Buddhist Conclave is organised every alternate year with the objective of promoting India as a Buddhist Destination.
- Signages have been installed in Chinese language at buddhist monuments in Uttar Pradesh and in Sinhala language at Sanchi monuments in Madhya Pradesh.
Important value additions
PRASHAD Scheme
- The ‘National Mission on Pilgrimage Rejuvenation and Spiritual Augmentation Drive’ (PRASAD).
- Launched by: Ministry of Tourism (2014-15).
- It was changed from PRASAD to “National Mission on Pilgrimage Rejuvenation and Spiritual, Heritage Augmentation Drive (PRASHAD)” in October 2017.
- Objective: (1) Holistic development of identified pilgrimage destinations; (2) Rejuvenation and spiritual augmentation of important pilgrimage and heritage sites; (3) Follow community-based development and create awareness among the local communities; (4) Strengthen the mechanism for bridging the infrastructural gaps.
Swadesh Darshan Scheme
- It is a Central Sector Scheme launched in 2014 -15.
- Objective: (1) Integrated development of theme based tourist circuits in the country; (2) To position the tourism sector as a major engine for job creation
- The Ministry of Tourism provides Central Financial Assistance (CFA) for infrastructure development of circuits.
Graphene Mask Inactivates Coronaviruses
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-III – Science & Technology
In news
- Recently, the researchers from the City University of Hong Kong have produced a laser-induced form of graphene masks that inactivate the coronavirus species.
- The researchers are also planning to test this mask on the Covid-19 (SARS-Cov-2) virus.
Key takeaways
- All carbon-containing materials, such as cellulose or paper, can be converted into graphene.
- The researchers described the production of laser-induced graphene as a “green technique.”
- Benefits: (1) It is reusable; (2) Can also be produced at low cost
Important value additions
Graphene
- It is a single layer (monolayer) of carbon atoms.
- It is the building-block of Graphite.
- It is the strongest known material.
- Other Properties: (1) High thermal stability; (2) High elasticity; (3) High electrical conductivity; etc.
- Uses: It can be used in miniaturised electronics to biomedical devices like computers, solar panels, etc.
Do you know?
- Diamond, graphite and fullerenes are the important allotropes of pure carbon.
- Allotropy: Property of some chemical elements to exist in two or more different forms, in the same physical state.
- Graphene is also known for antibacterial properties.
Study on biogenic methane hydrate in the Krishna-Godavari (KG) Basin conducted
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-I – Mineral & Energy Resources
In news
- Recently, a study on biogenic methane hydrate in the Krishna-Godavari (KG) Basin was conducted by the researchers at the Agharkar Research Institute (ARI).
- They have identified the methanogens that produced the biogenic methane trapped as methane hydrate.
- Methane hydrate can be a significant source of energy.
- This study revealed maximum methanogenic diversity in the KG basin in comparison to the Andaman and Mahanadi basins.
Important value additions
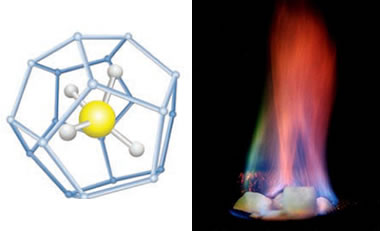
Methane Hydrate
- Methane hydrate is a crystalline solid that consists of a methane molecule surrounded by a cage of interlocking water molecules.
- It only occurs naturally as ‘ice’ in subsurface deposits where temperature and pressure conditions are favourable for its formation.
- It becomes unstable if the ice is removed from its environment.
- Other names: Methane clathrate, methane ice, fire ice, natural gas hydrate, and gas hydrate.
- Most methane hydrate deposits also contain small amounts of other hydrocarbon hydrates.
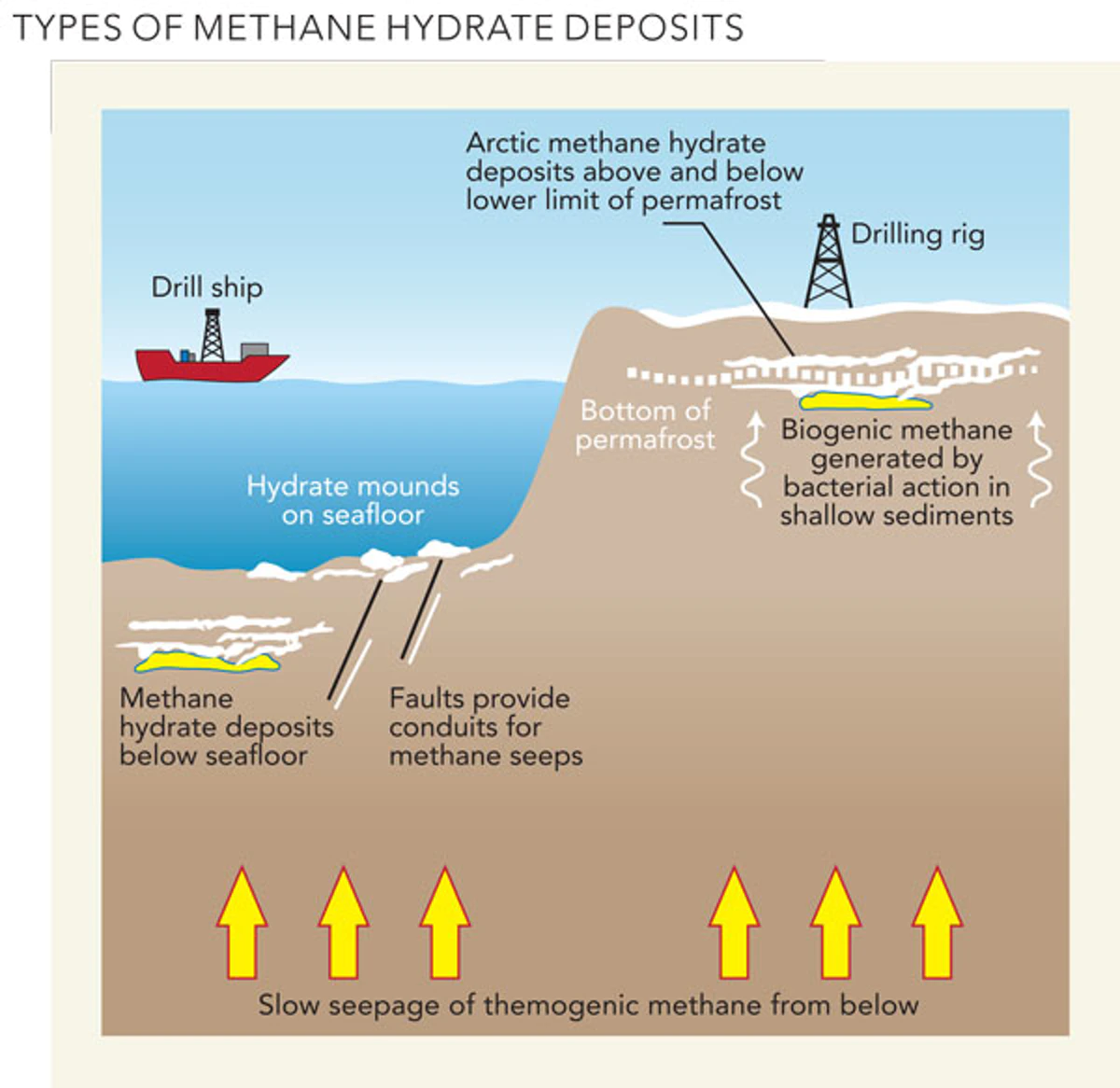
Krishna-Godavari Basin
- It is an extensive deltaic plain formed by two large east coast rivers, Krishna and Godavari
- Location: Andhra Pradesh and the adjoining areas of Bay of Bengal.
- The site is known for the D-6 block with the biggest natural gas reserves in India.
- The first gas discovery was made in 1983 by ONGC.
- The basin is home to the Olive Ridley Sea Turtle (IUCN Status: Vulnerable).
Do you know?
- Biogenic Methane is the methane produced from the metabolic activities of living organisms.
- Methane is a clean and economical fuel.
- Even the lowest estimate of methane present in the methane hydrates in the KG Basin is twice that of all fossil fuel reserves available worldwide.
USA Sanctions against ICC Officials
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-II – Global Groupings
In news
- The USA had announced sanctions, including asset freezes and visa bans, against two officials of the International Criminal Court (ICC) for their investigation into alleged war crimes by the USA forces and the Central Intelligence Agency (CIA) in Afghanistan since 2003.
Important value additions
International Criminal Court
- It is an intergovernmental organization and international tribunal.
- Headquarter: The Hague, Netherlands.
- It is a criminal court.
- Jurisdiction: Prosecute individuals for the international crimes of genocide, crimes against humanity, and war crimes.
- When a state’s legal system collapses or when a government is a perpetrator of heinous crimes, the ICC can exercise jurisdiction.
- India is not a party to ICC.
Green Strategic Partnership between India and Denmark launched
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-II – International Relations
In news
- India and the Kingdom of Denmark have launched the Green Strategic Partnership for delivering sustainable solutions to India.
- The Ministry of Commerce and Industry has also signed a Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) for Intellectual Property (IP) Cooperation with Denmark.
Key takeaways
Green Strategic Partnership
- The Partnership will focus on expanding economic ties, green growth, and cooperation on global challenges such as climate change.
- Danish companies with niche technologies and expertise have offered to help India in meeting its air pollution control targets, Covid-19 pandemic and cooperation in water efficiency and water loss.
- The creation of India-Denmark energy parks in areas with large numbers of Danish firms and an India-Denmark skill institute to train Indian manpower has been proposed.
Intellectual Property Cooperation
- The MoU aims at increasing IP co-operation between the two countries through exchange of information and best practices on processes for disposal of applications for patents, trademarks, Geographical Indications, and cooperation in the field of protection of Traditional Knowledge.
- It will be a landmark step forward in India’s journey towards becoming a major player in global innovation and further the objectives of the National Intellectual Property Rights Policy, 2016
Do you know?
- Green growth is a term to describe a path of economic growth that uses natural resources in a sustainable manner.
Congo Fever Alert in Maharashtra raised
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-II – Health
In news
- There might be a possible spread of the Congo fever in the Maharashtra districtof Palghar.
Important value additions
Crimean-Congo Haemorrhagic Fever (CCHF)
- Cause: It is caused by a tick-borne virus (Nairovirus) of the Bunyaviridae family.
- Transmission: It is transmitted through bite of Hyalomma tick, an external parasite, living by feeding on the blood of mammals, birds etc.
- Human-to-human transmission: Close contact with the blood, secretions, organs or other bodily fluids of infected persons.
- Virus can lead to epidemics, with a high case fatality ratio (10-40%).
- CCHF is endemic in all of Africa, the Balkans, the Middle East and in Asia.
- Symptoms: Fever, bodyache, dizziness, sore eyes and photophobia (sensitivity to light).
- Treatment: (1) The antiviral drug ribavirin has been used to treat CCHF infection with apparent benefit; (2) There are no vaccines widely available for human or animal use.

EPFO’s New Facility on UMANG App started
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-II – E-Governance & GS-III – Employment
In news
- Recently, the Employees’ Provident Fund Organisation (EPFO) has started a facility on the Unified Mobile Application for New-age Governance (UMANG) App which enables members of the Employees’ Pension Scheme (EPS) 1995 to apply online for Scheme Certificates.
Key takeaways
- Scheme Certificate is issued to members who withdraw their Employees’ Provident Fund (EPF) contribution but wish to retain their membership with EPFO, to avail pension benefits on the attainment of retirement age.
- Members become eligible for pension only if they have been, cumulatively, a member of the EPS, 1995 for at least 10 years.
- Upon joining a new job, Scheme Certificate ensures that previous pensionable service is added to pensionable service rendered with the new employer
- It is also useful for family members to avail family pension
Important value additions
UMANG App
- It is a unified, secure, multi-channel, multi-platform, multi-lingual, multi-service mobile app.
- Developed by: Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY) and National e-Governance Division (NeGD)
- Objective: To drive mobile governance under Digital India.
Employees’ Provident Fund Organisation (EPFO)
- It is a government organisation that manages the provident fund and pension accounts for the workforce engaged in the organized sector in India.
- It implements the Employees’ Provident Fund and Miscellaneous Provisions Act, 1952.
- Administered by: Ministry of Labour and Employment.
Do you know?
- EPS is a social security scheme that was launched in 1995 and is provided by EPFO.
- It makes provisions for pensions for the employees in the organised sector after the retirement at the age of 58 years.
RAISE 2020 to be organised
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-III – Artificial Intelligence
In news
- Global Virtual Summit on Artificial Intelligence (AI), RAISE 2020- ‘Responsible AI for Social Empowerment 2020,’ shall be held from October 5-9, 2020.
- Organised by: The Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY) and NITI Aayog
- Inaugurated by: Indian Prime Minister
Key takeaways
- It is a first of its-kind, global meeting of minds on Artificial Intelligence to drive India’s vision for social transformation through responsible AI.
- Global industry leaders, key opinion makers, Government representatives and academia shall participate in the event.
Do you know?
- Industry analysts predict that AI could add up to USD 957 billion to India’s economy by 2035.
ASCON Phase IV Network launched
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-III – Defence; Science & technology
In news
- The Cabinet Committee on Security had approved the proposal for establishment of Army Static Switched Communication Network, ASCON Phase IV Network.
Key takeaways
- Implemented by: M/s ITI, a Public Sector Undertaking
- Implementation schedule: 36 months from the date of signing of the contract.
- It is a strategic and theatre area communication network.
- It will upgrade the existing Asynchronous Transfer Mode Technology to Internet Protocol, Multi-Protocol Label Switching Technology.
- Optical Fibre Cable, Microwave Radio and Satellite will be used as communication media.
- It will provide better survivability, responsiveness and high bandwidth in any operational scenario and enhance the communication coverage of the network closer to International Border, Line of Control and Line of Actual Control.
Ambedkar Social Innovation & Incubation Mission launched
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-II – Issues related to SCs and STs & GS-III – Innovation; Entrepreneurship
In news
- The Ambedkar Social Innovation and Incubation Mission under Venture Capital Fund for Scheduled Castes (SCs) was recently launched.
- Ministry: Ministry of Social Justice
- Objective: To promote innovation and enterprise among SC students studying in higher educational institutions.

Key takeaways
- Under the initiative, 1,000 SC youth will be identified in the next four years with start-up ideas through the Technology Business Incubators in various higher educational institutions.
- They will be funded 30 lakh rupees in three years as equity funding to translate their start-up ideas into commercial ventures.
- Successful ventures would further qualify for venture funding of up to five Crore rupees from the Venture Capital Fund for SCs.
Important value additions
Venture Capital Fund for SCs:
- Launched by: The Social Justice Ministry
- Year: 2014-15
- Aim: To develop entrepreneurship amongst the SC and Divyang youth and to enable them to become job-givers.
- Objective: To provide concessional finance to the entities of the SC entrepreneurs.
- Under this fund, 117 companies promoted by SC entrepreneurs have been sanctioned financial assistance to set up business ventures.
Miscellaneous
Bharati Script
- Bharati is a simple and unified script which can be used to write most major Indian languages.
- It is designed using simplest shapes, often borrowing simple characters from various Indian languages/scripts and English.
- Scripts supported are: Hindi/Marathi (Devanagari), Tamil, Telugu, Gujarati, Punjabi (Gurmukhi), Bengali, Oriya, Kannada and Malayalam.
- Developed By: Srinivasa Chakravathy’s team at IIT Madras.
- Documents can be read in Bharati script using a multi-lingual Optical Character Recognition (OCR) scheme.
- Finger-spelling Method can be used to generate a sign language for hearing-impaired persons.
- It is in line with ‘One Nation, One Script’.
- It is an ideal script for languages like Konkani or Tulu that don’t have their own script.
- It can serve as a writing system for the innumerable tribal languages of India, and languages of the NorthEast.
Pakur Honey launched
- The Ministry of Tribal Affairs will launch Pakur Honey on the occasion of Gandhi Jayanti.
- Pakur Honey is 100% natural honey which is Multi Floral and Forest Fresh.
- It is gathered by Santhal Tribals and Vulnerable Pahadhiya tribes from Pakur, Jharkhand.
- Natural Multiflora honey is a good source of antioxidants and antiseptic vitamins, nutrients, enzymes and other herbal properties that no other super-food can provide.
(MAINS FOCUS)
SOCIETY/ GOVERNANCE
Topic: General Studies 2:
- Role of civil Society in a democracy. Formal/informal associations and their role in the Polity.
- Important International actors and their functioning
Constraining critique: On Amnesty halting India operations
Context: Amnesty’s decision to close its operations in India
What is Amnesty International?
- Amnesty International is a worldwide human rights organization (International NGO) founded in 1961 by the British lawyer Peter Benenson
- It is independent of all governments and all financial players and had won the Nobel Peace Prize way back in 1977.
- Amnesty has taken up human rights causes such as minority rights, ending torture, abolition of the death penalty and refugee rights, globally.
Why did Amnesty halt its operation in India?
Its working had been made difficult due to government actions in recent years for ex:
- Freezing of its bank accounts by government of India in early September 2020.
- Constant harassment by government agencies including the Enforcement Directorate from past two years
- Intrusive scrutiny from state agencies
- Critical reporting of abrogation of Article 370 was viewed by Union Government as interference in Domestic Politics of India
As a result of all these constraints, the NGO decided to close its functioning in India
What is the government’s argument for taking action against NGO?
- Non-Compliance with Indian Laws: Amnesty International Foundation and its three subsidiaries — Amnesty India Private Limited, Indians for Amnesty International Trust and Amnesty International South Asia Foundation — are not registered under the Foreign Contribution Regulation Act, 2010 (FCRA), a pre-requisite for civil society groups, associations and NGOs to receive foreign donations.
- It made use the “prior permission” route, which meant applying to the government each time it wanted to accept a foreign donation.
- Flouting Financial Laws: Having failed to receive registration under the FCRA, the Amnesty had taken the “commercial route” and accepted funds through Foreign Direct Investment, which Ministry of Home affairs (MHA) said is a contravention of the Foreign Exchange Management Act (FEMA).
- Interference in Domestic Politics: MHA also stated that India does not allow interference in domestic political debates by entities funded by foreign donations, in a pointed reference to Amnesty’s reports on alleged human rights violations in Jammu & Kashmir
- Not an Isolated Case: The action against AI including freezing their funds is part of the government’s scrutiny of more than 20 international NGOs including Greenpeace, Compassion International, and Ford Foundation, over the past few years.
- Long History of monitoring: The enquiry into Amnesty International had been undertaken by both the UPA and the NDA regimes over the past decade. The UPA government had blocked over ₹5 crore foreign funds to Amnesty between 2010 and 2013 after receiving allegedly adverse intelligence reports
Criticism of government’s action
- Against Democratic Spirit: The freedom of civil society organisations to operate underpins any functioning democracy. Curbing the activities of NGOs through excessive State interference is considered as moving backwards in Democracy.
- Climate of Fear: Treating human rights organisations like criminal enterprises and dissenting individuals as criminals will stoke a climate of fear and dismantle the critical voices in India
- Fundamental Rights Impacted: Such witch-hunting by government agencies violates people’s basic rights to freedom of speech and expression, assembly, and association guaranteed by the Indian Constitution and international human rights law
- Intolerance to Criticism: Freezing of account is akin to freezing dissent
Way Ahead
- View as Constructive Criticism: Democratic regimes that are bound by constitutionalism should not consider critical activism by groups such as Amnesty as being adversarial, but instead view it as constructive critique of their functioning
- Adopt Soft Actions: If the critique of such groups is not reasoned, the state can rebut it through communiqués and responses, but should not restrict freedom of expression through intimidation or restraining actions.
- Build on Democratic gains: For India to aspire to become a leading Power and a just nation, it must build on its strengths such as its demographic dividend and the procedural institutions that have been built over decades
Conclusion
It is to be hoped Amnesty’s decision to halt operations is therefore temporary and that it would be able to function within India’s regulatory framework.
Connecting the dots:
MODERN HISTORY/ ETHICS
Topic: General Studies 2:
- The Freedom Struggle —important contributors
- Contributions of moral thinkers and philosophers from India and world.
Mahatma as an intercultural Indian
Context: There is a tendency in today’s world to think that Gandhi’s ideal of non-violence is a noble idea but impractical and unrealistic. The odd thing about this thought is that it tends to sanctify Gandhi while rejecting his principles.
Gandhi’s Idea of non-violence
- Gandhi’s idea of non-violence was not a dream; it was a realistic hope, armed with a dose of practical idealism; that of the global welcoming of the law of love.
- With Gandhi, the philosophy of non-violence turned into an instrument of public dissent and a pragmatic tool of the powerless against the powerful.
- While being an instrument of conflict resolution and universal harmony, non-violence was also an essentially moral exercise.
- He viewed non-violence essentially as an ethical commitment and a constructive political action.
- For Gandhi, the ethical and the political were the same. Therefore, for him, the struggle against violence and fanaticism was at the same moral level as disobeying unjust laws.
What was Gandhiji’s vision of Democracy?
- Gandhi said that it would not be possible to understand the concept of democracy without having some understanding of the philosophical tradition of a critique of violence in which it is nurtured. Therefore, democracy and non-violence as two sides of the same reality
- Gandhi’s idea of democracy also hinges on moral growth in humankind, where an undisciplined and unrestrained individualism gives its place to an empathetic humanism
- Gandhi considered democracy as a dynamic element in the ethical becoming of human civilisation.
- The entire Gandhian thought in the realm of citizenship and democracy revolves around the establishment of a just society
- Gandhi’s repeated emphasis on service to all human beings from all traditions of thought was the essence of his non-violent democratic theory.
How was Gandhiji’s approach ahead of his time?
- His non-violent democratic theory as a philosophy of inter-cultural dialogue is still far ahead of our time, several generations after his death.
- Gandhi was not a dogmatic nationalist but essentially a pathfinder towards a common ground among different cultures and diverse mentalities.
- Therefore, his philosophy of democracy remains neither mono-cultural nor essentialist. It is essentially pluralistic and empathetic.
- More importantly, his attachment to politics is more ethical than religious. Consequently, religion for him is identified with ethics rather than theology.
What was Gandhiji’s idea of Indianness?
- Gandhiji was well aware of the fact that politics is a fragile concept and is vulnerable to nationalist justifications of violence and war.
- That is the reason why he refused to define India in terms of ethnic purity or linguistic unity or some other unifying religious attribute.
- More than rallying Indians to combat various “others,” Gandhi’s philosophy of democracy introduced an anti-monistic and pluralistic dimension into a primarily territorial rootedness of Indianness.
- For Gandhi, there was no sentiment of loving one’s country (namely India) without loving the culture of the other.
- Gandhi’s appeal to fraternity was based on an inclusive and dialogical idea of living together which disapproved all forms of national or religious self-centredness.
Conclusion
Gandhiji believed profoundly in the possibility of introducing humanity to the principle of non-violence. In this era of Nationalistic rivalries and impending Cold war-II, it is all the more necessary to follow Gandhi’s ideal in spirit.
(TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE)
Model questions: (You can now post your answers in comment section)
Note:
- Correct answers of today’s questions will be provided in next day’s DNA section. Kindly refer to it and update your answers.
- Comments Up-voted by IASbaba are also the “correct answers”.
Q.1 Which of the following Ministry is responsible for PRASHAD Scheme?
- Ministry of Social Justice and Empowerment
- Ministry of Culture
- Ministry of Tourism
- Ministry of Planning
Q.2 Consider the following statements regarding Swadesh Darshan Scheme:
- It is a Central Sector Scheme.
- Theme based tourist circuits are developed under this scheme.
Which of the above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Q.3 Consider the following statements regarding Graphene:
- It is the strongest known material.
- It is one of the allotropes of pure carbon.
Which of the above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Q.4 Headquarter of International Criminal Court is situated at?
- Washington
- Paris
- Netherlands
- United Kingdom
ANSWERS FOR 1st October 2020 TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE (TYK)
| 1 | C (2 and 3) |
| 2 | A |
Must Read
A debate on whether online gambling should be regulated or not:
About Strategic dealing with China:
About conflict between Azerbaijan and Armenia:












