IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
Archives
(PRELIMS + MAINS FOCUS)
International Financial Services Centres Authority (Banking) Regulations, 2020 approved
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-III – Economy
In news
- The International Financial Services Centres Authority (IFSCA) approved the International Financial Services Centres Authority (Banking) Regulations, 2020.
Key takeaways
The salient aspects of the Banking Regulations include
- Laying down the requirements for setting up IFSC Banking Units (IBUs)
- Permitting persons resident outside India (having net worth not less than USD 1 Million) to open foreign currency accounts in any freely convertible currency at IFSC Banking Units (IBUs)
- Permitting persons resident in India (having net worth not less than USD 1 Million) to open foreign currency accounts in any freely convertible currency at IBUs to undertake any transaction under the Liberalised Remittance Scheme (LRS) of the RBI.
- Laying down the permissible activities of IBUs including credit enhancement, credit insurance, and sale, etc.
- Permitting the Authority to determine business that a Banking Unit may be permitted to conduct in INR with persons resident in India and persons resident outside India.
- The above mentioned regulations will be notified by the Government of India in due course.
Production-Linked Incentive (PLI) Scheme approved for 10 more sectors
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-III – Economy
In news
- The Union Cabinet has given its approval to introduce the Production-Linked Incentive (PLI) Scheme in the following 10 key sectors for Enhancing India’s Manufacturing Capabilities and Enhancing Exports.
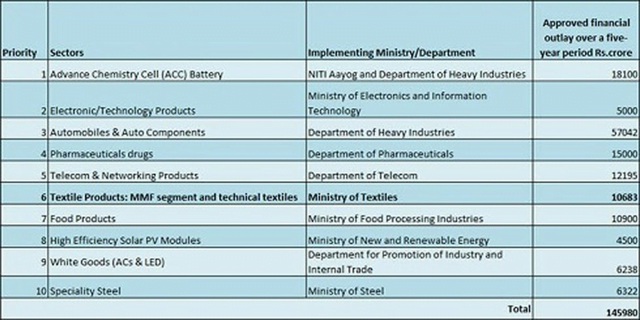
Sectors and Implementing Ministry/Department are as follows
- Advance Chemistry Cell (ACC) Battery: NITI Aayog and Department of Heavy Industries
- Electronic/Technology Products: Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology
- Automobiles & Auto Components: Department of Heavy Industries
- Pharmaceuticals drugs: Department of Pharmaceuticals
- Telecom & Networking Products: Department of Telecom
- Textile Products (MMF segment and technical textiles): Ministry of Textiles
- Food Products: Ministry of Food Processing Industries.
- High Efficiency Solar PV Modules: Ministry of New and Renewable Energy.
- White Goods (ACs & LED): Department for Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade.
- Speciality Steel: Ministry of Steel.
Do you know?
Notified PLI schemes are already available in the following sectors:
- Mobile Manufacturing and Specified Electronic Components: MEITY.
- Critical Key Starting materials/Drug Intermediaries and Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients: Department of Pharmaceuticals.
- Manufacturing of Medical Devices: Department of Pharmaceuticals
Religion in news: Sarna Religion
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-I – Culture
In news
- The Jharkhand government has passed a resolution to send the Centre a letter to recognise Sarna religion and include it as a separate code in the Census of 2021.

Important value additions
Sarna religion
- The followers of Sarna faith believe in praying to nature.
- The motto of the faith is “Jal, Jungle, Zameen”.
- Its followers pray to the trees and hills while believing in protecting the forest areas.
Do you know?
- It is believed that 50 lakhs tribals in the entire country put their religion as ‘Sarna’ in the 2011 census, although it was not a code.
- Jharkhand has 32 tribal groups of which 8 are from Particularly Vulnerable Tribal Groups.
Kalvari-Class Submarine INS Vagir launched
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-III – Defence & Security
In news
- Indian Navy’s fifth Kalvari-class Diesel Electric attack submarine INS Vagir was launched at Mazgaon Dock in Mumbai.

Key takeaways
- Indian Naval Ship (INS) Vagir is the fifth among the six Kalvari-class submarines.
- The other vessels in the class are INS Kalvari, INS Khanderi, INS Karanj, INS Vela and INS Vagsheer.
- Of these Kalvari and Khanderi have been commissioned in 2017 and 2019.
- Vela and Karanj are undergoing sea trials.
- Vagsheer is under construction.
Technical details
- The design of Kalvari class of submarines is based on Scorpene class of submarines.
- This class of submarines have Diesel Electric transmission systems.
- These are primarily attack submarines or ‘hunter-killer’ type which means they are designed to target and sink adversary naval vessels.
- It can reach the highest speeds of 11 knots when surfaced and 20 knots when submerged.
- These submarines have the Air Independent Propulsion (AIP) which enables non-nuclear submarines to operate for a long time without access to surface oxygen.
Do you know?
- Like Kalvari (which means Tiger Shark), Vagir has been named after a Sand Fish, a predatory marine species.
- Khanderi has been named after an Island Fort built by Chhatrapati Shivaji.
- Karanj has also been named after an Island located South of Mumbai.
Aatmanirbhar Bharat Rozgar Yojana
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-II – Policies and interventions & GS-III – Economy
In news
- Union Minister for Finance announced a new scheme of AATMANIRBHAR BHARAT ROZGAR YOJANA to incentivize job creation during COVID-19 recovery
Key takeaways
- If EPFO-registered establishments take in new employees without EPFO registration or those who lost jobs earlier, the Yojana will benefit these employees.
- Beneficiaries / New Employees under the scheme would be:
- any new employee joining employment in EPFO registered establishments on monthly wages less than Rs.15,000
- EPF members drawing monthly wage of less than Rs.15,000 who exited from employment during COVID Pandemic from 1st March to 30th September, 2020 and is employed on or after 1st October, 2020.
- Central Govt. will provide subsidy for two years in respect of new eligible employees engaged on or after 1st October, 2020 at following scale:
- Establishments employing up to 1000 employees: Employee’s contributions (12% of Wages) & Employer’s contributions (12% of wages) totalling 24% of wages
- Establishments employing more than 1000 employees: Only Employee’s EPF contributions (12% of EPF wages)
- The scheme will be effective from October 1, 2020 and operational till 30th June 2021.
Finance Minister Announces Measures On Aatmanirbhar Bharat 3.0
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-II – Policies and interventions & GS-III – Economy
In news
- Union Minister for Finance announced various measures, as part of Government of India’s stimulus to the economy, under AatmaNirbhar Bharat 3.0.
Key takeaways
- Emergency Credit Line Guarantee Scheme for MSMEs, businesses, MUDRA borrowers and individuals (loans for business purposes), has been extended till March 31, 2021.
- 10 more Champion Sectors will be covered under the Production Linked Incentives Scheme to help boost competitiveness of domestic manufacturing.
- A sum of Rs 18000 crore is being provided for PM Awaas Yojana – Urban over and above Rs. 8000 Crore already allocated this year.
- Support for Construction & Infrastructure – Relaxation of Earnest Deposit Money & Performance Security on Government Tenders
- To provide ease of doing business and relief to contractors whose money otherwise remains locked up, performance security on contracts has been reduced from 5-10% to 3%.It will also extend to ongoing contracts and Public Sector Enterprises.
- Differential between circle rate and agreement value in real estate income tax under Section 43 CA of IT Act has been increased from 10% to 20%.
- Government will make ₹6,000 Crore equity investment in debt platform of National Investment and Infrastructure Fund (NIIF), which will help NIIF provide a debt of ₹ 1.1 Lakh Crore for infrastructure projects by 2025.
- Additional outlay of ₹10,000 Crore is being provided for PM Garib Kalyan Rozgar Yojana to provide rural employment. This will help accelerate rural economy.
- Around ₹3,000 Crore boost is being provided to EXIM Bank for promoting project exports under Indian Development and Economic Assistance Scheme (IDEAS Scheme).
- ₹900 Crore is being provided to Department of Biotechnology for Research and Development of Indian COVID Vaccine.
(MAINS FOCUS)
GOVERNANCE/ RIGHTS/ ECONOMY
Topic: General Studies 2,3:
- Government policies and interventions for development in various sectors and issues arising out of their design and implementation
- Awareness in the field of IT
Media regulation that is quite over the top
Context: The government in its latest move has brought online news and current affairs portals along with “films and audio-visual programmes made available by online content providers” under the Ministry of Information and Broadcasting.
In other words, the Union government has brought Over The Top (OTT) platforms, or video streaming service providers such as Netflix, Amazon Prime and others, under the ambit of the Ministry of Information and Broadcasting.
Do You Know?
- The Press Council of India regulates the print media,
- News Broadcasters Association (NBA) represents and regulates the news channels,
- Advertising Standards Council of India regulates advertising,
- Central Board of Film Certification (CBFC) monitors films.
- However, there is no law or autonomous body governing digital content.
Brief Background to the issue
- From time to time, the government had indicated the necessity to monitor these platforms.
- In October 2019, the government had indicated that it will issue “negative” list of don’ts for the video streaming services like Netflix and Hotstar.
- Government also wanted the platforms to come up with a self-regulatory body on the lines of the News Broadcasting Standards Authority.
- Anticipating the government’s intervention, in January 2019, eight video streaming services had signed a self-regulatory code that laid down a set of guiding principles for content on these platforms
What was the self-regulatory Code adopted by OTT platforms?
The code adopted by the OTTs prohibited five types of content. This includes
- Content that deliberately and maliciously disrespects the national emblem or national flag
- Any visual or story line that promotes child pornography
- Any content that “maliciously” intends to outrage religious sentiments
- Any content that “deliberately and maliciously” promotes or encourages terrorism
- Any content that has been banned for exhibition or distribution by law or court.
The government had refused to support this code.
Implication of the Bringing digital media under the I&B Ministry
- No more unregulated: This will give the government control over OTT platforms, which were unregulated till now
- Treats to freedom of speech: Such regulatory powers would arm the executive with control over the free press, thereby essentially making it unfree.
- Matter is being heard in Supreme Court: Passing such executive orders hijacks public interest litigation in the Supreme Court relating to content on “Over The Top” (OTT) platforms
- It seeks to divide and rule the press by creating an artificial distinction between the new-age digital media (the stand-alone news portals which are already struggling to stay afloat) — which is the media of the future, the media of the millennial generation — and the older print and TV news media.
- Disincentives Innovation: The fate of the digital media under the control of the Ministry of Information and Broadcasting leaves little scope for hope, and dooms the sector for both the media practitioner and the media entrepreneur and for the startups that have been the new vibrant face of contemporary journalism.
- Not in Democratic Spirit: The move is tantamount to nipping in the bud a promise of combative journalism. It makes our democracy the poorer for it.
Conclusion
Government should walk a tight rope to ensure that content on digital medium doesn’t affect the Nation’s & Society’s interest but should also make sure that regulations don’t stifle the freedom of speech & expression.
Connecting the dots:
- Sudarshan TV Case: Click here
- Net Neutrality
- Shreya Singhal Case
INTERNATIONAL/ ECONOMY
Topic: General Studies 2:
- International Politics
UK-Japan: A deal for the post-Brexit era?
Context: The trade agreement was sealed between the U.K. and Japan, marking the UK’s first big post-Brexit deal on trade.
Key features of the trade deal
- Britain has said the deal meant 99% of its exports to Japan would be tariff-free, and that it could increase trade by 15.2 billion pounds ($19.9 billion) in the long run, compared with 2018.
- The deal removes Britain’s tariffs on Japanese cars in stages to zero in 2026, which is the same as in the Japan-EU trade agreement.
- Britain’s has expressed its interest in joining the 11-member Comprehensive and Progressive Agreement for Trans-Pacific Partnership (CPTPP) free trade deal. Japan has welcomed Britain’s eagerness to join this trade deal.
- Japan is already a member of the CPTPP, which also links Canada, Australia, Brunei, Chile, Malaysia, Mexico, New Zealand, Peru, Singapore and Vietnam.
Significance of the deal
- UK will now be able to access Japan’s agricultural market, which was earlier done under the ambit of European Union.
- The trade deal is modelled on the EU-Japan Economic Partnership Agreement, that provides for smooth trade between the nations with reduced duties & procedures
- Japan’s auto industry will get benefitted in the wake of intense competition unleashed by electric automotive industry of USA.
- The agreement has some flexibility on rules of origin and data sharing, besides recognition for additional number of geographical indications
- The deal gives UK the breathing space when it exits the European Union (EU) on December 31, 2020.
- UK wants to make an example of this trade deal with Japanese so to strike accords with other countries.
- Britain views the trade pact with Japan as a gateway for London’s entry into the 11-member CPTPP
Challenges in the deal
- Absence of preferential trading terms in agriculture: U.K. has not won major concessions compared to the EU on farm quotas from Japan.
- Slow Opening of UK auto sector: Tokyo has not been able to secure the elimination of British tariffs on cars sooner than (in 2026) under the deal with the EU.
- Stakes on UK-EU deal: The Japanese have emphasised the considerable stakes in an EU-U.K. deal, as the country’s businesses based in the U.K. rely on European supply chains.
- Similar demands from EU: In relation to rules on government aid for ailing companies and subsidies, the U.K. would face pressure from the EU to extend similar conditions in a future relationship
- Modest Benefit for UK: As per the assessment of the trade deal between UK & Japan, of the £15.66 billion increase in bilateral trade, 83% of the projected benefits would accrue to Japan. In any case, the overall gain from the pact is a modest 0.07% boost to the U.K.’s GDP, compared to loss of trade after leaving the EU.
Conclusion
The Trade deal reflects UK government’s recognition of the new and complex reality, wherein Britain must strike out on its own as it engages with countries around the world.
(TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE)
Model questions: (You can now post your answers in comment section)
Note:
- Correct answers of today’s questions will be provided in next day’s DNA section. Kindly refer to it and update your answers.
- Comments Up-voted by IASbaba are also the “correct answers”.
Q.1 Sarna religion was in news recently. It is associated with which of the following state of India?
- Madhya Pradesh
- Jharkhand
- Chhattisgarh
- Bihar
Q.2 which of the following Kalvari-class Diesel Electric attack submarine was recently launched?
- INS Kalvari
- INS Vagir
- INS Khanderi
- INS Karanj
ANSWERS FOR 12th November 2020 TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE (TYK)
| 1 | A |
| 2 | D |
Must Read
About criticism of Supreme Court’s decision to grant bail to Arnab Goswami:
About right to work:
About need to tap the demographic dividend:











