IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
Archives
(PRELIMS + MAINS FOCUS)
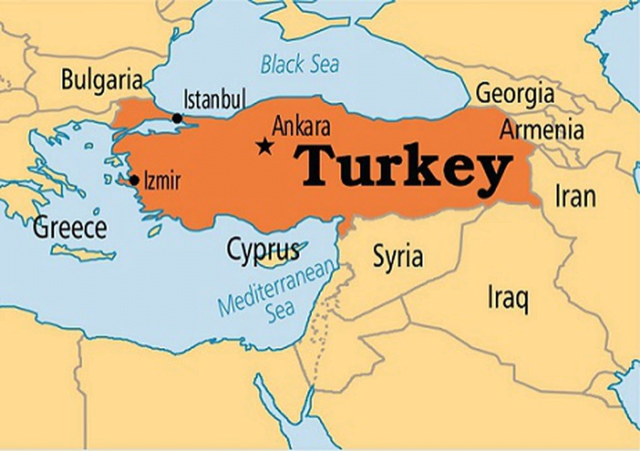
Preventing Financing Of Proliferation Of Weapons Of Mass Destruction bill passed by Turkey
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-II –Internatioanal Relations
In news
- The Turkish parliament passed a bill called “Preventing Financing of Proliferation of Weapons of Mass Destruction”.
- It would increase the monitoring of civil society groups.
Key takeaways
- The Bill was passed following the 2019 report on Turkey prepared by the intergovernmental body Financial Action Task Force (FATF) meant to fight money laundering and terror financing.
- The bill consists of 43 articles and has made changes to seven laws on Turkey’s Law of Associations.
- It is meant to keep Turkey from being blacklisted by the Paris-based watchdog of terror financing.
- The Bill gives the Turkish government the power to appoint trustees to NGOs, to suspend their activities, seize their assets and monitor their sources of funding.
- Critics believe that it violates the provisions under the Turkish constitution since it interferes with the right to freedom of association.
National Summit On Good, Replicable Practices And Innovations In Public Healthcare Systems In India
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-II –Health
In news
- Union Minister of Health and Family Welfare digitally inaugurated the 7th National Summit on Good, Replicable Practices through a video conference.
Key takeaways
- The first one was held in 2013 at Srinagar.
- The summit is held to recognize, showcase and document various best practices and innovations in public healthcare system.
- Union Minister of Health also launched New Health Management Information System (HMIS) along with the Operational Guidelines for TB services at AB-HWCs and the Operational Guidelines 2020 on Active Case Detection and Regular Surveillance for Leprosy.
Do you know?
- Indian Prime Minister has set a bold target of a TB-free India by 2025, five years ahead of the SDG targets of 2030.
Eye Cancer therapy in the form of the first indigenous Ruthenium-106
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-III – Sci & Tech
In news
- Bhabha Atomic Research Centre (BARC), Mumbai has developed Eye Cancer therapy in the form of the first indigenous Ruthenium 106 Plaque for treatment of Ocular Tumours.
Key takeaways
- The handling of plaque is very convenient for the Surgeon and it has been acknowledged to be at par with the international standards.
- So far the BARC plaques made in India through the Department of Atomic Energy have been used for seven cases for Ocular Cancer.
- Ocular tumours are tumours inside the eye. They are collections of cells that grow and multiply abnormally and form masses.

Important value additions
Ruthenium-106
- Ruthenium-106 is a radioactive form of the rare heavy metal ruthenium, which is a “platinum group” metal similar to platinum.
- Ruthenium-106 is produced from the fission or splitting of uranium-235, the type of uranium used in nuclear fission reactors, so it’s found in spent nuclear fuel.
- It’s used in medicine for cancer radiation therapy, especially for eye and skin tumours.
- It’s also used in radioisotope thermoelectric generators that power satellites.
PM to lay Foundation Stone of Light House Projects under GHTC-India
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-III –Infrastructure
In news
- Prime Minister will lay the foundation stone of Light House Projects (LHPs) under Global Housing Technology Challenge-India (GHTC-India) at six sites across six States
- Prime Minister will also announce winners under Affordable Sustainable Housing Accelerators – India (ASHA-India) and give out annual awards for excellence in implementation of Pradhan Mantri Awas Yojana – Urban (PMAY-U) Mission.
- The Prime Minister will also release a certificate course on innovative construction technologies named NAVARITIH (New, Affordable, Validated, Research Innovation Technologies for Indian Housing) and a compendium of 54 innovative housing construction technologies identified through GHTC-India.
Key takeaways
- The Light House Projects (LHPs) showcase the best of new-age alternate global technologies, materials and processes in the construction sector for the first time in India at such a large scale.
- They are being constructed under GHTC-India which envisages to provide an ecosystem for adoption of innovative technologies in the housing construction sector in a holistic manner.
- The LHPs are being constructed at Indore (Madhya Pradesh), Rajkot (Gujarat), Chennai (Tamil Nadu), Ranchi (Jharkhand), Agartala (Tripura) and Lucknow (Uttar Pradesh).
- They comprise about 1000 houses at each location along with allied infrastructure facilities.
- These projects will demonstrate and deliver ready to live houses at an expedited pace within twelve months, as compared to conventional brick and mortar construction, and
- They will be more economical, sustainable, of high quality and durability.
Important value additions
Affordable Sustainable Housing Accelerators – India (ASHA-India)
- It aims to promote domestic research and entrepreneurship by providing incubation and acceleration support to potential future technologies.
- Under ASHA-India initiative, five ASHA-India Centers have been set up for providing incubation and acceleration support.
- The technologies, processes and materials identified through this initiative will provide a major fillip to young creative minds, start-ups, innovators and entrepreneurs.
PMAY-U Mission
- Pradhan Mantri Awas Yojana – Urban (PMAY-U) Mission has been designed to achieve the vision of “Housing For All by 2022”.
- In order to recognize the outstanding contribution by States, UTs,Urban Local Bodies and beneficiaries, the Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs has introduced annual awards for excellence in implementation of PMAY-Urban.
34th PRAGATI interaction held
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-II –Policies and Interventions
In news
- Indian Prime Minister chaired the thirty-fourth PRAGATI interaction.
- In the meeting, various projects, programmes and grievances were reviewed
Important value additions
Pro-Active Governance And Timely Implementation (PRAGATI)
- It is a unique integrating and interactive platform.
- The platform is aimed at addressing common man’s grievances, and simultaneously monitoring and reviewing important programmes and projects of the Central and State Governments
- It is also a robust system for bringing e-transparency and e-accountability with real-time presence and exchange among the key stakeholders.
- The PRAGATI platform uniquely bundles three latest technologies: Digital data management, video-conferencing and geo-spatial technology.
- It is a three-tier system (PMO, Union Government Secretaries, and Chief Secretaries of the States).
- The system has been designed in-house by the PMO team with the help of National Informatics Center (NIC).
Cabinet Approves Export of Akash Missile System
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-III –Trade; Defence and Security
In news
- Recently, Cabinet approved export of Akash Missile System.
- Under the Atma Nirbhar Bharat, India is growing in its capabilities of manufacturing wide variety of Defence platforms and missiles.
Key takeaways
- Akash is country’s important missile with over 96% indigenisation.
- Akash is a Surface to Air Missile with a range of 25 Kms.
- The missile was inducted in 2014 in IAF and in 2015 in Indian Army
- A Committee is created for faster approval of exports.
- This Committee would authorise subsequent exports of major indigenous platforms to various countries.
- The Committee would also explore various available options including the Government-to-Government route.
- Government of India intends to focus on exporting high value defence platforms, to achieve target of 5 Billion USD of defence export and improve strategic relations with friendly foreign countries.
- The export version of Akash will be different from System currently deployed with Indian Armed Forces.
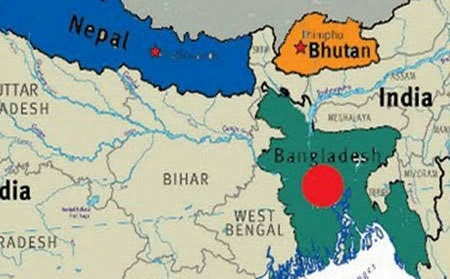
Cabinet approves MoU between India and Bhutan on Cooperation in the peaceful uses of outer space
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-II –International relations
In news
- The Union Cabinet chaired by Prime Minister approved Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) between the India and Bhutan on Cooperation in the peaceful uses of outer space.
Key takeaways
- This MoU shall enable India and Bhutan to pursue cooperation in potential interest areas, such as remote sensing of the earth; satellite communication and satellite based navigation; Space science and planetary exploration; use of spacecraft and space systems and ground system; and application of space technology.
- This MoU would lead to set up a Joint Working Group which will further work out the plan of action including the time-frame and the means of implementation
- The signed MoU will provide Impetus to explore cooperation possibilities in the field of remote sensing of the earth; satellite communication; satellite navigation; space science and exploration of outer space.
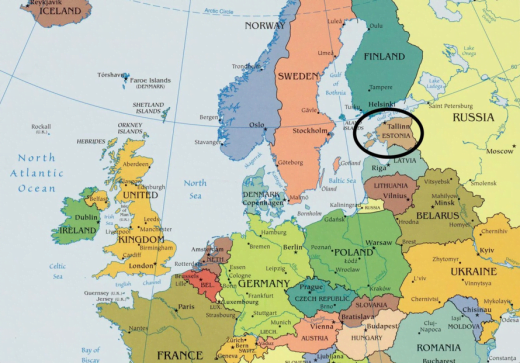
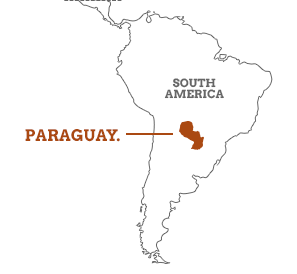
Cabinet approves Opening of 3 Indian Missions in Estonia, Paraguay and Dominican Republican
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-III – International Relations
In news
- The Union Cabinet chaired by Prime Minister approved the opening of 3 Indian Missions in Estonia, Paraguay and Dominican Republic in 2021.
- Opening of Indian Missions in these countries will help expand India’s diplomatic footprint, deepen political relations, enable growth of bilateral trade, investment and economic engagements, facilitate stronger people-to-people contacts, bolster political outreach in multilateral fora and help garner support for India’s foreign policy objectives.
- Indian mission in these countries will also better assist the Indian community and protect their interests.
(Mains Focus)
ECONOMY/ GOVERNANCE
Topic: General Studies 2,3:
- Indian Economy and issues relating to planning, mobilization, of resources, growth, development.
- Government policies and interventions for development in various sectors and issues arising out of their design and implementation
PM SVANidhi scheme for street vendors
Context: The PM Street Vendor’s AtmaNirbhar Nidhi (PM SVANidhi) scheme was launched in June amid the pandemic.
What is the scheme all about?
- It is a micro-credit facility that provides street vendors a collateral-free loan of Rs 10,000 with low rates of interest for a period of one year.
- So far (Dec 2020), the scheme – part of the AtmaNirbhar Bharat package – has received 31.6 Lakh applications from across the country (except from Sikkim, which is officially not taking part in it).
- Of the total applications, 16.7 Lakh have been sanctioned and 12.17 Lakh have been disbursed.
Why was this scheme rolled out?
- To deal with Impact of Pandemic & Lockdown: The COVID-19 pandemic and the nationwide lockdown disrupted the business cycle and left daily wage workers & street vendors out of work. The scheme aims at aiding the vendors at getting back on their feet financially.
- Establishing Credit Score & Digital Record: In the long term, it aims at establishing a credit score for the vendors as well as creating a digital record of their socio-economic status, so that they can avail the Central government schemes later.
- Prevents Debt Trap: Many vendors belong to what we call the informal economy, and often borrow from private lenders which charge them exorbitant rates of interest. This loan charges below 12% rate of interest, and helps prevent street vendors from falling into debt trap.
- Formalisation of Economy: The scheme also attempts to formalise the informal sector of the economy and provide them safety nets and a means of availing loans in the future.
Which vendors are eligible for the loan, and how do they apply for it?
- All vendors who have been vending from or before March 24, 2020 and with a certificate of vending can avail the loan.
- As per the Street Vendors Act of 2014, the Town Vending Committees (which comprises the local authorities and vendors from an area) issue a certificate of vending after a survey has been conducted of all the vendors.
- But since many states and cities have not conducted the survey yet, many vendors are unable to provide any such certificate of vending. Instead, as per scheme, the urban local bodies – in this case, the municipalities – shall provide a Letter of Recommendation (LOR) for every vendor who wishes to avail the loan.
- If the vendor is a member of a vendor association, he or she can apply,
- These documents, including the identification proof, are uploaded on a special portal made for the scheme, and the loans are sanctioned by banks and disbursed, ideally, in 10-15 days.
Does the scheme legitimise vending of the applicants if the city has not conducted a Town Vending Committee survey as per the Act?
- Once
- Letter Of Recommendation is issued by the ULBs, its mandate lasts a month, after which the survey for the issuance of the certificate of vending should be undertaken by the ULBs.
- But since it is a state subject, the central government can only direct or sensitise the state governments on the importance of doing so, and not evicting vendors who have availed the loan but do not have a certificate.
- The LORs issued by the ULB do not give any legal authorisation or rights for vending, as this is not mentioned by the scheme
What are the various challenges that vendors are facing while applying for the loan?
Even though the scheme has received a tremendous response from vendors across the country, certain areas lag others when it comes to its implementation due to various factors.
- City-wide survey of vendors is lacking: States across the country have unevenly implemented the Street Vendors Act of 2014, which necessitates a survey of the vendors to provide them with a certificate of vending.
- Delay in issuing LORs: Due to lack of comprehensive data, the vendors must first apply for a Letter of Recommendation (LORs) from the ULBs, which tends to not only delay the entire process, but can also lead to the application being rejected. Some municipalities are also slow in issuing LORs, which has kept hundreds of vendors waiting for the loan for months
- Linkage with Aadhar: Another issue was that mobile numbers of various vendors were not linked with their Aadhar cards. To address this, various ULBs have now set up camps. Many vendor associations are also setting up camps at markets to rectify this issue and also help the vendors in the online application process.
- Mindset of local authorities against vendors: Various vendors who have received the loans are often evicted from their place by either the police or by the ULB officials, hitting their only source of income and their ability to repay the loan.
- Regional Imbalance in disbursement of loans: Telangana, Andhra Pradesh, Uttar Pradesh, and Madhya Pradesh are among the better performing states, which have provided certificates of vending either before the pandemic or in the past few months. Other states are lagging behind.
Conclusion
Even though the scheme has received a tremendous response from vendors across the country, certain areas lag others when it comes to its implementation due to various factors.
Connecting the dots:
- Atmanirbhar Bharat
ECONOMY/ GOVERNANCE
Topic: General Studies 2,3:
- Indian Economy and issues relating to planning, mobilization, of resources, growth, development.
- Government policies and interventions for development in various sectors and issues arising out of their design and implementation
Electric Vehicles
Issues
- Electric car sales as a percentage of overall car sales in India is abysmally low at less than 0.2%.
- Electric scooters fare slightly better at 0.4% of overall two-wheeler sales — a worrying sign despite incentives like reducing GST on electric vehicles to 5%, providing income tax benefits and waiving road tax.
- There are only 650 charging stations in India.
- The biggest challenge is the availability of reliable power supply at these charging stations, especially along highways.
Way Ahead
- To promote EV uptake, the government should consider waiving highway toll fees for EVs, perhaps till 2025.
- Environmental bonus for car-makers and purchase price subsidies for EV buyers.
- India has set a goal that by 2030, 30% of cars sold annually should be EVs. But to realise this goal, the buyer, government, and the industry need to play their respective parts effectively.
- The government should aggressively work on improving the public charging infrastructure through a PPP model.
- The government must incentivise and push for solar-based charging stations.
- India needs to invest in alternative technologies like induction charging.
- Any research on creating an affordable mass-market solution for highways, parking lots, etc., will revolutionise India’s EV market. Another area for research is on developing mass-market solid-state batteries for EVs.
- While FAME (Faster Adoption and Manufacturing of Hybrid and EV) schemes are a step in the right direction, the government must create a strong EV ecosystem to help India become a leading player in the EV manufacturing and components space.
(TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE)
Model questions: (You can now post your answers in comment section)
Note:
- Correct answers of today’s questions will be provided in next day’s DNA section. Kindly refer to it and update your answers.
- Comments Up-voted by IASbaba are also the “correct answers”.
Q.1 Which of the following states of India border Bhutan?
- Sikkim
- West Bengal
- Assam
- Bihar
- Arunachal Pradesh
Select the correct code:
- 1, 2, and 4 only
- 1, and 5 only
- 2, 3 and 5 only
- 1, 2, 3 and 5 only
Q.2 Which of the following statements regarding PRAGATI is incorrect?
- It is a three-tier system
- The PRAGATI platform makes use of video-conferencing and geo-spatial technology only.
- The platform is aimed at addressing common man’s grievances.
- Important programmes and projects of the Central and State Governments are reviewed through PRAGATI
Q.3 Which of the following sea borders Turkey in the north?
- Red Sea
- Black sea
- Aegean Sea
- Marmara Sea
Q. 4 Consider the following statements regarding Ruthenium-106:
- It is a radioactive form of the rare heavy metal ruthenium.
- It’s used in medicine for cancer radiation therapy, especially for eye and skin tumours.
Which of the above is or are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
ANSWERS FOR 31st December 2020 TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE (TYK)
| 1 | C |
| 2 | A |
Must Read
About India and Nepal Political Crisis:
About Delhi Police raid on Delhi riots lawyer:












