IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
Archives
(PRELIMS + MAINS FOCUS)
World Youth Skill Day Programme
Part of: GS Prelims and GS -III – Skill development
In news Indian Prime Minister recently addressed World Youth Skill Day Programme.
Key notes from the address
- Skill development of the new generation is a national need and is the foundation of Aatmnirbhar Bharat
- More than 1.25 crore youth have been trained under ‘Pradhanmantri Kaushal Vikas Yojna’
- India providing smart and skilled man-power solutions to the world should be at the core of our strategy of skilling our youth
- Mission of skilling, re-skilling and up-skilling the youth should go on relentlessly
- Skill India Mission is fulfilling visionary dream of Dr Babasaheb Ambedkar by skilling weaker sections
Skill Development Programmes of India
| Name | Year | Type | Objective |
| Industrial Training Centres (ITIs) | 1950 | Central Sector | To expand and modernize the existing Long-Term Training ecosystem in India. |
| Pradhan Mantri Kaushal Vikas Yojana (PMKVY) | 2015 | Central Sector | To provide free skill training avenues to youths of India. |
| National Career Service Project | 2015 | Central Sector | To offer free online career skills training through its National Career Service (NCS) project for job-seekers registered with it. |
| Skills Strengthening for Industrial Value Enhancement (STRIVE) | 2016 | World Bank assisted-Government of India project | To improve the performance of ITIs. To improve the relevance and efficiency of skills training provided through Industrial Training Institutes (ITIs) and apprenticeships. |
| Pradhan Mantri YUVA Yojana (Yuva Udyamita Vikas Abhiyan) | 2016 | Centrally sponsored | To create an enabling ecosystem for Entrepreneurship development through Entrepreneurship education and training; Advocacy and easy access to entrepreneurship support network and Promoting social enterprises for inclusive growth. |
| Skills Acquisition and Knowledge Awareness for Livelihood (SANKALP) | 2018 | Centrally Sponsored Scheme collaborated with the World Bank. | District-level skilling ecosystem through convergence and coordination. |
| Scheme for Higher Education Youth in Apprenticeship and Skills (SHREYAS) | 2019 | Central sector | To provide industry apprenticeship opportunities to the general graduates exiting in April 2019 through the National Apprenticeship Promotion Scheme (NAPS). |
| Atma Nirbhar Skilled Employee Employer Mapping (ASEEM) | 2020 | To help skilled people find sustainable livelihood opportunities. | |
| Skill Management and Accreditation of Training Centres (SMART) | It provides a single window IT application that focuses on the accreditation, grading, Affiliation and Continuous monitoring of the Training Centres (TC) in the skill ecosystem. |
News Source: PIB
School Innovation Ambassador Training Program
Part of: GS Prelims and GS -II – Education
In news Union Education Minister and Tribal Affairs Minister will jointly launch the ‘School Innovation Ambassador Training Program’ for 50,000 School Teachers.
- It is innovative and one of its kind training program for School Teachers.
- Aim: Training 50,000 school teachers on Innovation, Entrepreneurship, IPR, Design Thinking, Product development, Idea generation etc.
- The training will be delivered in online mode only.
- Designed by: Innovation Cell of the Ministry of Education and AICTE for School Teachers.
- The All India Council for Technical Education (AICTE) is a statutory body established by AICTE Act, 1987 for proper planning and co-ordinated development of a technical education system throughout the country and regulation & proper maintenance of norms and standards in the technical education system
News Source: PIB
Cloud Computing
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-III – Information Technology
In news Google Cloud announced expanding its footprint in India with its second ‘Cloud Region’ in the country.
- It will be located in Delhi-NCR.
- With this new region, Google Cloud customers operating in India will benefit from low latency and high performance of their cloud-based workloads.
What is Cloud Computing?
- Simply put, cloud computing is the delivery of computing services—including servers, storage, databases, networking, software, analytics, and intelligence—over the Internet (“the cloud”)
- It is the pool of shared resources such as networks, servers, storage, applications, and services that can be provided to the consumer rather than the consumer managing them on her own which is costly and time-consuming.
- Rather than owning their own computing infrastructure or data centres, companies or individuals can rent access to storage (or application or services) from a cloud service provider.
- Advantages
- Low capital expenditure
- Flexible resources
- Economies of scale
- Improved disaster recovery and reliability
Do You Know about Edge Computing?
- Edge computing is a distributed IT architecture in which client data is processed at the periphery of the network, as close to the originating source as possible.
- It doesn’t mean the cloud will disappear. It means the cloud is coming to you.
- It means running fewer processes in the cloud and moving those processes to local places, such as on a user’s computer or an edge server.
- In edge computing data is analysed locally, closer to where it is stored, in real-time without latency.
- Edge Computing allows data from internet of things devices to be analysed at the edge of the network before being sent to the data centre or cloud
- The global edge computing market is forecasted to reach more than $ 8 Billion by 2025 valued growing at more than 32% between 2019-2025.
News Source: TH
UV-C technology
Part of: GS Prelims and GS -III – Science & Technology
In news Ultraviolet-C or UV-C Disinfection Technology will soon be installed in Parliament for the “mitigation of airborne transmission of SARS-COV-2’’.
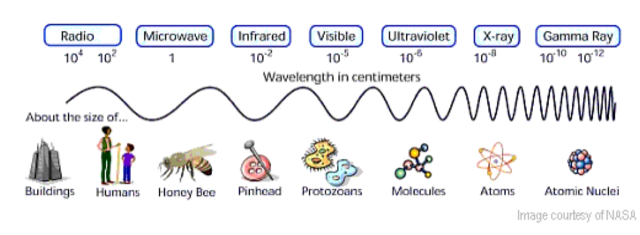
What is UV radiation?
- UV radiation is the portion of the Electromagnetic spectrum between X-rays and visible light.
- The most common form of UV radiation is sunlight, which produces three main types of UV rays: UVA, UVB and UVC.
- UVA rays have the longest wavelengths, followed by UVB, and UVC rays which have the shortest wavelengths.
- While UVA and UVB rays are transmitted through the atmosphere, all UVC and some UVB rays are absorbed by the Earth’s ozone layer.
- So, most of the UV rays you come in contact with are UVA with a small amount of UVB.
How is it being used?
- UV radiations are normally used to kill microorganisms.
- Particularly, UV-C, also known as Ultraviolet germicidal irradiation (UVGI) is a disinfection method that uses short-wavelength ultraviolet light to kill or inactivate microorganisms by destroying their nucleic acids and disrupting their DNA, leaving them unable to perform vital cellular functions and stops their replication.
- UVGI is used in a variety of applications, such as food, air, and water disinfection.
- UVC lamps used for disinfection purposes may pose potential health and safety risks depending on the UVC wavelength, dose, and duration of radiation exposure.
- Direct exposure of skin and eyes to UVC radiation from some UVC lamps may cause painful eye injury and burn-like skin reactions.
- Some UVC lamps generate ozone. Ozone inhalation can be irritating to the airway.
- However, studies have shown that far-UVC light (207–222 nm) does not harm mammalian skin as they have a very limited range and cannot penetrate through the outer dead-cell layer of human skin
About the UV-C air duct disinfection system
- Developed by CSIR-CSIO (Central Scientific Instruments Organisation).
- The system is designed to fit into any existing air-ducts and the UV-C intensity can be calibrated according to the existing space.
- The virus will get deactivated in any aerosol particles by the calibrated levels of UV-C light.
- It can be used in auditoriums, malls, educational Institutions, AC buses, and in railways.
News Source: IE
Commission to examine the issue of Sub-categorization
Part of: GS Prelims and GS -I – Social empowerment, communalism, regionalism & secularism.
In news Cabinet approves Extension of term of the commission constituted under Article 340 of the constitution to examine the issue of Sub-categorization within other Backward Classes in the Central List.
What is the background?
- National Commission for Backward Classes (NCBC) proposed the sub-categorisation of Other Backward Classes (OBCs) back in 2015.
- In October 2017, President Ram Nath Kovind, in exercise of the powers conferred by Article 340 of the Constitution, appointed a commission to examine the issue of sub-categorisation of OBCs, chaired by retired Justice G. Rohini, to ensure social justice in an efficient manner by prioritising the Extremely Backward Classes (EBCs).
What is Article 340?
- It lays down conditions for the appointment of a Commission to investigate the conditions of the backward classes.
- The President may by order appoint a Commission consisting of such persons as he thinks fit to investigate the conditions of socially and educationally backward classes within the territory of India.
What is National Commission for Backward Classes (NCBC)?
- Two Backward Class Commissions were appointed under Kaka Kalelkar in 1953 and under B.P. Mandal in 1979.
- In Indra Sawhney case of 1992, Supreme Court had directed the government to create a permanent body to entertain, examine and recommend the inclusion and exclusion of various Backward Classes for the purpose of benefits and protection.
- In pursuant to these directions parliament passed NCBC Act in 1993 and constituted the NCBC (statutory body under the Ministry of Social Justice and Empowerment)
- 102nd Constitution Amendment Act, 2018 provided constitutional status to NCBC. The amendment act also inserted new Articles 338 B and 342 A.
- Article 338B provides authority to NCBC to examine complaints and welfare measures regarding socially and educationally backward classes.
- Article 342A empowers President to specify socially and educationally backward classes in various states and union territories. He can do this in consultation with Governor of concerned State. However, law enacted by Parliament will be required if list of backward classes is to be amended.
What is the Need for sub- categorization?
- Sub categorization of the OBCs will ensure that the more backward among the OBC communities can also access the benefits of reservation for educational institutions and government jobs.
- At present, there is no sub-categorisation and 27% reservation is a monolithic entity.
News Source: PIB
Special Livestock Sector Package
Part of: GS Prelims and GS – III – Economics of Animal Rearing
In news The Cabinet Committee on Economic Affairs (CCEA) has approved implementation of a special livestock sector package.
About the Package
- Aim: To boost growth in the livestock sector and thereby making animal husbandry more remunerative to 10 crore farmers engaged in Animal Husbandry Sector.
- The Central government will spend Rs. 9,800 crore on livestock development over the next five years
- All the schemes of the Department will be merged into three broad categories as:
- Development Programmes: It includes Rashtriya Gokul Mission, National Programme for Dairy Development (NPDD), National Livestock Mission (NLM) and Livestock Census and Integrated Sample Survey (LC & ISS) as sub-schemes.
- Disease Control Programme: It is renamed as Livestock Health and Disease Control (LH & DC) which includes the present Livestock Health and Disease Control (LH & DC) scheme and National Animal Disease Control Programme (NADCP).
- Infrastructure Development Fund: it includes the Animal Husbandry Infrastructure Development fund (AHIDF), the Dairy Infrastructure Development Fund (DIDF), scheme for support to Dairy Cooperatives and Farmer Producer Organizations engaged in Dairy activities
About Animal Husbandry in India
- It supports the livelihood of almost 55% of the rural population.
- As per the Economic Survey-2021, the contribution of Livestock in total agriculture and allied sector Gross Value Added (at Constant Prices) has increased from 24.32% (2014-15) to 28.63% (2018-19).
- India is the highest livestock owner of the world.
News Source: TH
(Mains Focus)
GEOGRAPHY/ SCIENCE
Topic:
- GS-2: Fundamental Rights & Democracy
- GS-2: Government policies and interventions for development in various sectors and issues arising out of their design and implementation.
A strong Indian state must be humane too
Context: Father Stan Swamy passed away in a Mumbai hospital recently while his case for bail was going on in the Bombay High Court.
- He 84-year-old Jesuit priest and a tribal rights activist based in Jharkhand.
- He was arrested by the National Investigation Agency (NIA) under the Unlawful Activities (Prevention) Act (UAPA), in the Bhima Koregaon case.
- NIA had alleged that he was a CPI (Maoist) cadre which is a banned organisation and carrying on activities to overthrow the democracy of the nation”
Criticism
- International Ire: The Indian system’s treatment of Fr. Swamy has attracted substantial and pointed criticism from significant international quarters like UNHRC, US & EU.
- Government’s refusal to engage with liberal opinion: Indian diplomatic engagement with international liberal opinion on Stan Swamy’s death was wooden and inflexible assertions of general principles only. There was expectation of sensitivity in the response which was belied.
- Red-Tapism in Indian Prisons: There are criticism that it took almost a month for the jail authorities to provide a straw, sipper and winter clothes to Fr. Swamy, as Parkinson’s disease made it difficult for him to hold cups or glasses.
- The stringent nature of UAPA renders it difficult for one held under it to obtain bail.
- Under Section 43D(5) of UAPA Act, bail cannot be granted to a suspect if the court is of the opinion that there are reasonable grounds to believe that the charges are prima facie true.
- A Supreme Court judgment on this has clarified that this meant that the court considering bail should not examine the evidence too deeply, but must go by the prosecution version based on broad probabilities.
- This means that the onus is on the accused to show that the case is false but without inviting the court to evaluate the available evidence.
- UAPA presumes a person is guilty until proven innocent, contrary to the spirit of Constitution.
- This is why human rights defenders feel that the provision is draconian, virtually rendering it impossible for anyone to obtain bail until the completion of the trial.
Way Ahead
- A strong and effective state can and must also be a humane state, which it hardly was in the case of Fr. Swamy.
- Government needs to be reminded that the principle to achieve development in India should not through an authoritarian polity but a democratic and liberal one.
- Superior judiciary needs to redress the situation of misuse of UAPA through an audit of such cases. Fr. Stan Swamy’s case should provide an impetus to put such an audit machinery in place.
Conclusion
Yes, special laws were, and continue to be required to meet the challenges that arise from violence that cannot be confronted under the ordinary criminal statute. Their application, however, requires constant review
Connecting the dots:
- Misuse of UAPA: Delhi HC bail to student activists
- Delhi Riots & SC on Public Protests
- Sedition Law & the debate
ENVIRONMENT/ INTERNATIONAL
Topic:
- GS-2: Effect of policies and politics of developed and developing countries
- GS-3: Conservation, environmental pollution and degradation
Amazon forests are no longer acting as a carbon sink
Context: The Amazon forests in South America, which are the largest tropical forests in the world, have started emitting carbon dioxide (CO2) instead of absorbing carbon emissions
The Amazon basin
- Covering over 6 million square kilometres, it is nearly twice the size of India.
- The Amazon rainforests cover about 80 per cent of the basin
- Also, it is home to nearly a fifth of the world’s land species and about 30 million people including hundreds of indigenous groups and several isolated tribes.
- The basin produces about 20% of the world’s flow of freshwater into the oceans
What changes are being witnessed in recent times?
Over the last few years, the forest has been under multiple threat
- Forest fires have doubled since 2013. One reason that they happen is when farmers burn their land to clear it for the next crop. In 2019, fires in the Amazon were visible from space.
- Deforestation in the Brazilian Amazon, which comprises about two-thirds of the area of the rainforest, started in the 1970s and 1980s when large-scale forest conversion for cattle ranching and soy cultivation began
- State policies that encourage economic development, such as railway and road expansion projects have led to “unintentional deforestation” in the Amazon and Central America.
- Amazon is therefore teetering on the edge of functional destruction
New Research Findings
- Over the years as fossil-fuel emissions across the world have increased, the Amazon forests have absorbed CO2 from the atmosphere, helping to moderate the global climate.
- However, the eastern Amazon forests are no longer carbon sinks, whereas the more intact and wetter forests in the central and western parts are neither carbon sinks nor are they emitters.
- Another reason for the eastern region not being able to absorb as much CO2 as it did previously is the conversion of forests into agricultural land, which has caused a 17% decrease in the forest cover, an area that is almost the size of continental US.
- In the southeast region, which forms about 20 per cent of the Amazon basin and has experienced about 30% of the deforestation in the last four decades, scientists have recorded
- 25% reduction in precipitation
- Temperature increase of at least 1.5 degrees Celsius during the dry months of August, September and October.
- Not only the Amazon rainforests, some forests in Southeast Asia have also turned into carbon sources in the last few years as a result of formation of plantations and fires.
Conclusion
The study shows that if the ability of tropical forests to act as carbon sinks is to be maintained, fossil fuel emissions need to be reduced and temperature increases need to be limited as well.
Connecting the dots:
(TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE)
Model questions: (You can now post your answers in comment section)
Note:
- Correct answers of today’s questions will be provided in next day’s DNA section. Kindly refer to it and update your answers.
Q.1 TRIFED comes under which of the following Ministry?
- Ministry of Agriculture
- Ministry of Tribal Affairs
- Ministry of Commerce
- Ministry of Skill Development
Q.2 Consider the following statements regarding UV radiation
- UV radiation is the portion of the Electromagnetic spectrum between X-rays and visible light.
- The most common form of UV radiation is sunlight
Select the correct statements
- 1 Only
- 2 Only
- Both 1 and 2 only
- Neither 1 nor 2
Q.3 SMART, SHREYAS, SANKALP are schemes related to which of the following field/sector?
- Education
- Skill Development
- Tribal Products
- Information Technology
ANSWERS FOR 15th July 2021 TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE (TYK)
| 1 | C |
| 2 | D |
| 3 | A |
Must Read
On Social Justice & Caste:
On India-China relations:
On Unorganised Workers:











