IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
Archives
(PRELIMS + MAINS FOCUS)
Parliamentary Privileges
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-II – Parliamentary Privileges
In news: The Supreme Court recently held that lawmakers cannot indulge in criminal acts on the Parliament or Assembly floors and then take cover behind the right to free speech.
- The court refused the Kerala government’s plea to withdraw prosecution of top Left Democratic Front (LDF) leaders accused of vandalism and wanton destruction of public property on the Assembly floor during a Budget speech in 2015.
- The SC observed that Parliamentary privileges and immunities are not “gateways” for legislators to claim exemption from the law of the land, especially criminal law.
What is Parliamentary Privilege?
- Parliamentary privilege refers to rights, immunities and exemptions enjoyed by Parliament as an institution and MPs in their individual capacity, without which they cannot discharge their functions as entrusted upon them by the Constitution.
- When any of these rights and immunities are disregarded, the offence is called a breach of privilege and is punishable under law of Parliament.
- A notice is moved in the form of a motion by any member of either House against those being held guilty of breach of privilege
What are the Rules Governing Privilege?
- Article 105 mentions two privileges – freedom of speech in Parliament and right of publication of its proceedings.
- Rule No 222 in Chapter 20 of the Lok Sabha Rule Book and Rule 187 in Chapter 16 of the Rajya Sabha rulebook governs privilege.
- A member may, with the consent of the Speaker or the Chairperson, raise a question involving a breach of privilege either of a member or of the House.
- The rules mandate that any notice should be relating to an incident of recent occurrence and should need the intervention of the House.
News Source: TH
Lithium Exploration
Part of: GS Prelims and GS – III – Economy; Sci and tech
In news: Geological Survey of India (GSI) has taken up 7 projects on lithium exploration in Arunachal Pradesh, Andhra Pradesh, Chhattisgarh, Jharkhand, Jammu & Kashmir and Rajasthan.
- However, resource of lithium has not yet been augmented by GSI.
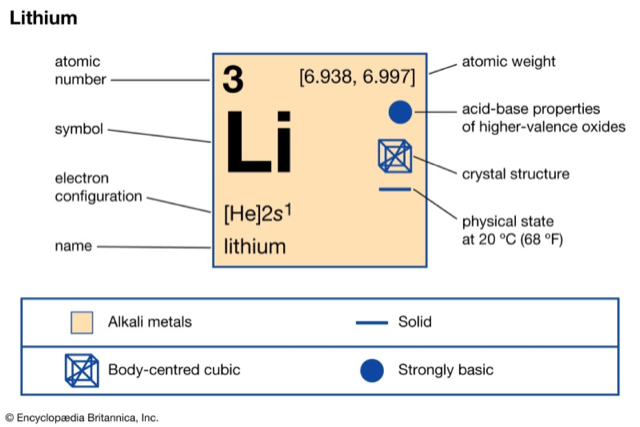
What is Lithium?
- Lithium (Li), chemical element of Group 1 (Ia) in the periodic table, the alkali metal group, lightest of the solid elements.
- The metal itself—which is soft, white, and lustrous—and several of its alloys and compounds are produced on an industrial scale.
- The most important use of lithium is in rechargeable batteries for mobile phones, laptops, digital cameras and electric vehicles.
- Lithium is also used in some non-rechargeable batteries for things like heart pacemakers, toys and clocks.
What is Geological Survey of India?
- It was set up in 1851 primarily to find coal deposits for the Railways.
- Over the years, it has attained the status of a geo-scientific organisation of international repute.
- Main function: Creation and updation of national geo-scientific information and mineral resource assessment.
- Headquarter: Kolkata
- Six regional offices: Lucknow, Jaipur, Nagpur, Hyderabad, Shillong and Kolkata.
- Every state also has a state unit.
- Presently, GSI is an attached office to the Ministry of Mines.
News Source: PIB
King Chilli ‘Raja Mircha’
Part of: Prelims and GS -III – Economy
In news
- In a major boost to exports of Geographical Indications (GI) products from the north-eastern region, a consignment of ‘Raja Mircha’ also referred as king chilli from Nagaland was today exported to London via Guwahati under assistance from APEDA.
- The consignment was sourced from Tening, part of Peren district, Nagaland.
- Exporting fresh King Chilli posed a challenge earlier because of its highly perishable nature.
About King Chilli
- King Chilli is considered as the world’s hottest based on the Scoville Heat Units (SHUs).
- is constantly on the top five in the list of the world’s hottest chilies based on the SHUs.
- It is also referred to as Bhoot Jolokia and Ghost pepper.
- It got GI certification in 2008.
- It belongs to genus Capsicum of family Solanaceae.
What is Agricultural and Processed Food Products Export Development Authority (APEDA)?
- It is an apex body under the Union Ministry of Commerce and Industry responsible for the export promotion of agricultural products.
- It was established under the APEDA Act of 1985.
- Functions
- Promotion of exports of agricultural and processed food products.
- Promotion of export oriented production and development of the Scheduled products.
- To make Improvement in areas such as packaging
- Setting standards and specifications for the scheduled products
- Financial assistance, reliefs and subsidies to the related industries.
- Provide training in the related areas
Do you know?
- APEDA has facilitated exports of Jackfruits from Tripura to London and Germany, Assam Lemon to London, Red rice of Assam to the USA and Leteku ‘Burmese Grape’ to Dubai.
News Source: PIB
Academic Credit Bank
Part of: GS Prelims and GS – III – Infrastructure
In news On the first anniversary of the National Education Policy (NEP), the Central government shall officially roll out some initiatives promised in the policy, such as a credit transfer system that will allow multiple entry and exit options in higher education, as well as engineering programmes in regional languages.
- However, other promised reforms such as the Higher Education Commission of India (HECI), the four-year undergraduate degree, and the common university entrance test, have been delayed due to COVID-19 pandemic.
What are the initiatives that will be rolled out?
- The Academic Bank of Credit will be rolled out for students in over 290 top institutions from the current academic year 2021-22 onwards. All institutions in the top 100 of the National Institutional Ranking Framework as well as those who have achieved an A grade under the NAAC will be allowed to participate in the credit transfer system, which will also allow multiple entry and exit options for students.
- Multidisciplinarity will be issued with guidelines to allow the merger of institutes to give students the choice of taking subjects such as social sciences, music and sports while pursuing engineering, or to get a minor degree in emerging areas while majoring in a different subject.
- Engineering degrees in regional languages in about 14 smaller institutions.
- Establishment of the National Digital Education Architecture and National Education Technology Forum.
- Vidya Pravesh, a three-month play-based school preparation module for Class 1 students which gains greater importance now since pre-schools, nurseries and anganwadis are closed due to COVID-19 pandemic.
- A competency-based assessment framework for Classes 3, 5 and 8 will also be announced for students of the CBSE.
News Source: TH
Tea Board
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-III – Economy
In news The United Planters’ Association of Southern India (UPASI) has termed as ‘retrograde’ the recent circular issued by Tea Board India.
The Association said the mode of sale of tea should be left to the choice of the producers.
About the circular
- The circular had directed manufacturers to comply with the order of mandatory sale of 50% of the total output through public auctions.
- In 2001, the government repealed the mandatory routing of tea through auctions in line with the policy of economic liberalisation and free trade. However, this was again amended in 2015.
- Tea producers have, during this period, developed a domestic market where they get better prices.
- According to the Tea Board, its order will make the auction system robust and bring stability to prices.
- But, tea auctions in India have a finite load- handling capacity.
- Also, there is no guarantee that the manufacturers will get fair prices to cover even the cost of production.
- Routing of teas through auction increases the transaction cost too.
About Tea Board
- It is a statutory body under the Ministry of Commerce.
- The Board is constituted of 31 members (including Chairman) drawn from Members of Parliament, tea producers, tea traders, tea brokers, consumers, and representatives of Governments from the principal tea producing states, and trade unions.
- The Board is reconstituted every three years.
- Functions:
-
- Rendering financial and technical assistance for cultivation, manufacture and marketing of tea.
- Export promotion
- Research and Development activities
- Extend financial assistance in a limited way to the plantation workers and their wards through labour welfare schemes.
- Collection and maintenance of Statistical data and publication.
News Source: TH
Factoring Regulation (Amendment) Bill 2020
Part of: GS Prelims and GS -II – Policies and interventions
In news The Bill was recently passed by the Lok Sabha. The Bill seeks to widen the scope of entities that can engage in factoring business.
What is factoring?
- Factoring is a transaction where an entity (like MSMEs) ‘sells’ its receivables ( dues from a customer) to a third party ( a ‘factor’ like a bank or NBFC) for immediate funds (partial or full).
- Currently, seven non-bank finance companies called NBFC factors do the majority of the factoring through the principal business condition
What are its Key Provisions?
- The Bill has done away with the threshold for NBFCs to get into the factoring business.
- It widens the scope of financiers and to permit other non-banking finance companies also to undertake factoring business and participate on the Trade Receivables Discounting System platform for discounting the invoices of micro, small and medium enterprises.
- It reduces the time period for registration of invoice and satisfaction of charge upon it, in order to avoid possibility of dual financing.
- It empowers the Reserve Bank of India to make regulations with respect to factoring business
What is its Significance?
- Allowing non-NBFC factors and other entities to undertake factoring is expected to increase the supply of funds available to small businesses.
- This may result in bringing down the cost of funds and enable greater access to the credit-starved small businesses, ensuring timely payments against their receivables.
- Steps like integration with GSTN, mandatory listing of the government dues and direct filing of charges will improve the operational efficiency and acceptability of the platforms among the financiers.
News Source: TH
Exercise INDRA-21
Part of: GS Prelims and GS II – International relations
In news The 12th Edition of Indo-Russia joint military Exercise INDRA will be held at Volgograd, Russia in August 2021.
About Exercise INDRA
- The exercise will entail conduct of counter terror operations under the United Nations mandate by a joint force against international terror groups.
- The INDRA series of exercises began in 2003 and was conducted as a bilateral naval exercise alternately between the two countries. However, the first joint Tri-Services Exercise was conducted in 2017.
- The last joint, tri-services exercise between India and Russia was conducted in India in December 2019. It was held simultaneously at Babina (near Jhansi), Pune, and Goa.
Major Indian Maritime Exercises
| Name of the Exercise | Name of the Country |
| SLINEX | Sri Lanka |
| Bongosagar and IN-BN CORPAT | Bangladesh |
| JIMEX | Japan |
| Naseem-Al-Bahr | Oman |
| Indra | Russia |
| Za’ir-Al-Bahr | Qatar |
| Samudra Shakti | Indonesia |
| Indo-Thai CORPAT | Thailand |
| IMCOR | Malaysia |
| SIMBEX | Singapore |
| AUSINDEX | Australia |
| Malabar Exercise | Japan, and the USA |
News Source: PIB
(Mains Focus)
INTERNATIONAL/ EDUCATION
Topic:
- GS-2: Education & Governance
- GS-2: Effect of policies and politics of developed and developing countries on India’s interests.
Japanese education spells holistic development
Investment in education yields both private and social returns.
- Private returns, like wages, accrue to individuals.
- Social returns accrue to society: For when educated people follow rules such as queuing, using washrooms, washing hands, protecting public property, etc. the collective returns from such actions generate a huge social value such as cleaner, healthier and disciplined societies.
The novel coronavirus pandemic has given us an opportunity to re-evaluate how our schools should expand our capabilities.
- While academic prowess in math, science and language is essential, moral & value education is missing in India’s education system
- Japanese Education system provides important lessons for India to make our Education system human-centric in nature.
What is Japanese Model of Education?
Japanese curriculum emphasis on both cognitive & non-cognitive elements.
- Moving Beyond Academic Prowess
-
- ‘Chi-Toku-Tai’ is the defining features of Japanese schooling.
- Chi, which translates to ‘know’ lay an emphasis on building strong academic abilities.
- Toku, translates to ‘virtue’ and refers to mindfulness, self-discipline, and cooperative abilities.
- Tai, translates to ‘body, and refers to physical and mental well-being.
- This philosophy focuses on holistic ability extending beyond academic prowess to include ‘kansei’ which roughly translates to ‘sensitivity’.
- This approach aims at developing a knowledgeable mind which can appreciate beauty and nature, hold a sense of justice, and respect life and labour.
- ‘Chi-Toku-Tai’ is the defining features of Japanese schooling.
- Shaping Social Behaviour
-
- The elementary school curriculum is supplemented with subjects, namely moral education, integrated studies and special activities. This plays a tremendous role in building courteous and mindful societies.
- Moral education includes norms that define socially responsible and considerate behaviour towards everyone including nature.
- Students as young as first graders take turns to clean their classrooms, washrooms, serve school lunches, and water the plants at school.
-
- Such a system reaps several benefits. As students do various chores, it builds respect for labour, humility at a young age and encourages responsible and mindful behaviour towards the community.
- Experiential learning
-
- Integrated studies encompass experiential learning and independent thinking where students identify problems in their local communities and think of solutions.
- For example, children may create a disaster preparedness map based on their own research. Activities such as these integrate schools with community.
- If we can train our children in identifying problems in their local communities such as health ailments, pollution, waste disposal, etc. and coach them in developing solution road maps, the gains to both sides can be immense.
- Any solution & analysis inculcates the practise of ‘kaizen’ — the Japanese philosophy of continuous improvement.
- Emphasis on Unity
-
- Another notable aspect that defines Japanese society and education system is ‘collectivism’.
- Unlike the West, Japan is a collectivist society. Working as a group and group harmony is fundamental to this society
- The belief that one wins only when the group wins, generates equitable and united societies.
- Education includes activities which promotes the idea of Unity & Collectivism.
Conclusion
- The Japanese education philosophy transitioned from an extremely examination-focused, rote memorisation-based approach to the ‘Chi-Toku-Tai’ approach in the 1970s.
- The results are visible with high Civic Consciousness among Japanese as well as top rank in the Programme for International Student Assessment (PISA).
- It is time India learn from this model.
Connecting the dots:
ECONOMY/ GOVERNANCE
Topic:
- GS-3: Indian Economy and issues relating to planning, mobilization, of resources, growth, development and employment.
- GS-2: Government policies and interventions for development in various sectors and issues arising out of their design and implementation.
Resolution ‘pre-packs’ for MSMEs
Context: The Insolvency and Bankruptcy Code (Amendment) Bill, 2021, passed by Lok Sabha on Wednesday has proposed ‘pre-packs’ as an insolvency resolution mechanism for Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises (MSMEs).
What are ‘pre-packs’?
- A pre-pack envisages the resolution of the debt of a distressed company through a direct agreement between secured creditors and the existing owners or outside investors, instead of a public bidding process.
- Under the pre-pack system, financial creditors will agree to terms with the promoters or a potential investor, and seek approval of the resolution plan from the National Company Law Tribunal (NCLT).
- The approval of at least 66% of financial creditors that are unrelated to the corporate debtor would be required before a resolution plan is submitted to the NCLT.
- The NCLTs will be required to either accept or reject an application for a pre-pack insolvency proceeding before considering a petition for a Corporate Insolvency Resolution Process (CIRP).
- This system of insolvency proceedings has become an increasingly popular mechanism for insolvency resolution in the UK and Europe over the past decade
How are pre-packs better than CIRP?
- One of the key criticisms of the CIRP has been the time it takes for resolution.
- At the end of March 2021, 79% of the 1,723 ongoing insolvency resolution proceedings had crossed the 270-day threshold. A major reason for the delays is the prolonged litigation by erstwhile promoters and potential bidders.
- The pre-pack in contrast, is limited to a maximum of 120 days with only 90 days available to stakeholders to bring a resolution plan for approval before the NCLT.
- Another key difference between pre-packs and CIRP is that the existing management retains control in the case of pre-packs; in the case of CIRP, a resolution professional takes control of the debtor as a representative of financial creditors. This ensures minimal disruption of operations relative to a CIRP.
Is that the reason why the pre-pack has been introduced?
- Pre-packs are largely aimed at providing MSMEs with an opportunity to restructure their liabilities and start with a clean slate while still providing adequate protections so that the system is not misused by firms to avoid making payments to creditors.
- Currently, only corporate debtors themselves are permitted to initiate a Pre-Insolvency Resource Package (PIRP) after obtaining the approval of 66% of their creditors.
- The pre-pack mechanism does however, allow for a ‘Swiss challenge’ to any resolution plan that provides less than full recovery of dues for operational creditors.
- Under the Swiss challenge mechanism, any third party would be permitted to submit a resolution plan for the distressed company, and the original applicant would have to either match the improved resolution plan or forego the investment.
What challenges can pre-packs bring?
- The timeline for PIRP may be difficult to meet for lenders and distressed firms,
- Ordinarily where haircuts are involved, forensic/transaction audits become imperative, and a negative report may become a roadblock in resolution involving the same management.
- If a firm restructures its outstanding debt through a PIRP with the existing management retaining control, the NPA status of the company’s account with lenders may not be automatically upgraded under RBI guidelines.
- There is a need for the IBBI and RBI to find middle ground on these regulations to make the PIRP more attractive
- Also, debtor-in-possession model may militate against the Swiss challenge option, as the existing management may create hurdles for an outside investor seeking information to potentially invest in the company.
- Under CIRP, a resolution professional is in charge of running the company and providing information to potential investors.
Conclusion
Experts have noted that the pre-pack mechanism is effective in arriving at a quick resolution for distressed companies, and that the regime should be rolled out to all corporations over time as legal issues are settled through case law.
Connecting the dots:
(TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE)
Model questions: (You can now post your answers in comment section)
Note:
- Correct answers of today’s questions will be provided in next day’s DNA section. Kindly refer to it and update your answers.
Q.1 Consider the following statements about Tea Board
- It is a statutory body under the Ministry of Commerce.
- The Board is reconstituted every three years.
Select the correct statements
- 1 Only
- 2 Only
- Both 1 and 2 only
- Neither 1 nor 2
Q.2 Naseem-Al-Bahr Military exercise is held between which of the following two countries?
- Qatar and Saudi Arabia
- India and Oman
- Pakistan and China
- China and Pakistan
Q.3 World’s hottest Chilli based on the Scoville Heat Units (SHUs) is found in which of the following country?
- India
- Myanmar
- USA
- Malaysia
ANSWERS FOR 28th July 2021 TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE (TYK)
| 1 | A |
| 2 | C |
| 3 | A |
Must Read
On post-pandemic economic strains:
On GST Compensation issue:
On Farm reforms:











