IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
Archives
(PRELIMS + MAINS FOCUS)
Airports Economic Regulatory Authority of India (AERA) Amendment Bill
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-II – Policies and interventions and GS-III – Infrastructure
In news: AERA Amendment Bill, 2021, was recently passed in Lok Sabha.
About the Bill
- It seeks to amend the Airports Economic Regulatory Authority of India Act, 2008.
- The 2008 Act established the Airport Economic Regulatory Authority (AERA).
- AERA regulates tariffs and other charges (such as airport development fees) for aeronautical services rendered at major airports in India.
- The 2008 Act designates an airport as a major airport if it has an annual passenger traffic of at least 35 lakh. The central government may also designate any airport as a major airport by a notification.
- The amendment Bill adds that the central government may group airports and notify the group as a major airport.
News Source: TH
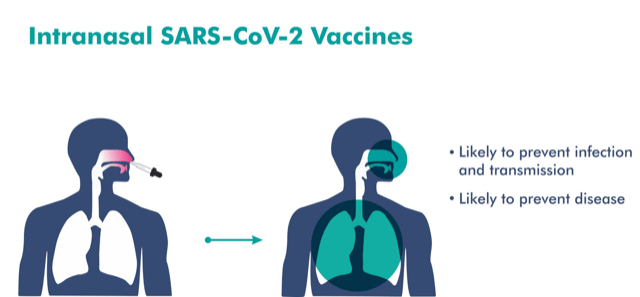
Intranasal Vaccine
Part of: GS Prelims and GS – II – Health
In news: In another two to two-and-a-half months, Bharat Biotech is going to have significant data on its intranasal COVID-19 vaccine whose clinical trials are under way.
- New vaccine being developed by Hyderabad based Bharat Biotech is BBV154 – A novel adenovirus vectored, intranasal vaccine for COVID-19
- Intranasal vaccine is a vaccine administered to a person via the nose and does not require a needle.
Source: Bharat Biotech
What are the benefits of intranasal vaccine?
- It promises to be more effective, since it is expected to generate immune responses at the site of infection (respiratory mucosa)
- Non-invasive, Needle-free.
- Ease of administration – does not require trained health care workers.
- Elimination of needle-associated risks (injuries and infections).
- High compliance (Ideally suits for children’s and adults).
- Scalable manufacturing – able to meet global demand. It can produce 100 million doses a month.
Also Read: Approaches to vaccine making
News Source: TH
Reservation in Medical Seats
Part of: Prelims and GS -II – Education
In news The Union Health Ministry has announced 27% reservation for the OBCs (Other Backward Classes) and 10% quota for the Economically Weaker Sections (EWS) in the all-India quota (AIQ) scheme for undergraduate and postgraduate medical and dental courses from 2021-22.
- This decision would benefit every year nearly 1,500 OBC students at the undergraduate level (MBBS) and 2,500 such students at the postgraduate level
Background:
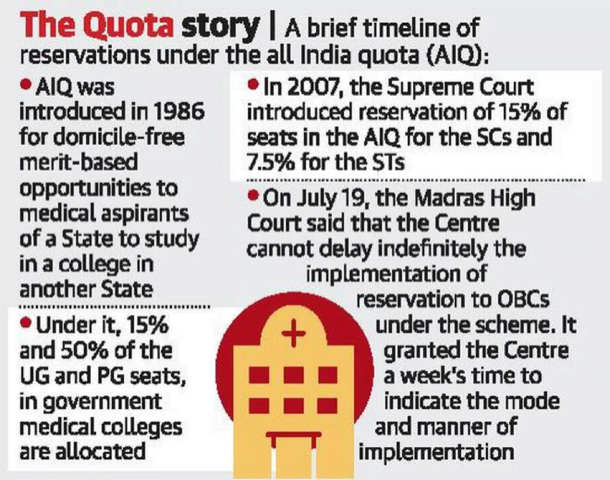
- The AIQ was introduced in 1986 under the directions of the Supreme Court to provide for domicile-free merit-based opportunities to students from any State aspiring to study in a medical college located in another State.
- AIQ comprises 15% of the UG seats and 50% of the PG seats in government medical colleges.
- Initially, there was no reservation in the AIQ.
- In 2007, the SC introduced reservation of 15% for SCs and 7.5% for STs in the scheme.
- When the Central Educational Institutions (Reservation in Admission) Act became effective that year, providing for uniform 27% reservation to the OBCs, the same was implemented in all the Central educational institutions.
News Source: TH
Global Conservation Assured|Tiger Standards (CA|TS)
Part of: GS Prelims and GS – III – Environment; Biodiversity; Ecosystem
In news: In a recently held event, the 14 Tiger Reserves in India received the accreditation of the Global Conservation Assured|Tiger Standards (CA|TS).
- The 14 accredited tiger reserves are:
- Assan: Manas, Kaziranga and Orang
- Madhya Pradesh: Satpura, Kanha and Panna
- Maharashtra: Pench
- Bihar: Valmiki Tiger Reserve
- Uttar Pradesh: Dudhwa,
- West Bengal: Sunderbans
- Kerala: Parambikulam
- Karnataka: Bandipur Tiger Reserve
- Tamil Nadu: Mudumalai and Anamalai Tiger Reserve.
About Conservation Assured | Tiger Standards (CA|TS)
- Officially launched in 2013, it sets minimum standards for effective management of target species and encourages assessment of these standards in relevant conservation areas.
- CA|TS is a set of criteria which allows tiger sites to check if their management will lead to successful tiger conservation.
- CA|TS has been agreed upon as accreditation tool by the global coalition of Tiger Range Countries (TRCs) and has been developed by tiger and protected area experts.
Additional Info
- The Environment Minister also released the report ‘Status of Leopards, Co-predators and Megaherbivores-2018’ which showed that conservation of tigers leads to the conservation of entire ecosystem.
- The overall leopard population in tiger range landscape of India in 2018 was estimated at 12,852. This is a significant increase from the 2014, figure that was 7,910 in forested habitats of 18 tiger bearing states of the country.
- National Tiger Conservation Authority (NTCA) felicitated some of the forest frontline workers as ‘BaghRakshaks’, to recognize their outstanding contribution towards the protection of tigers and forests during the pandemic.
- The event also saw the release of a special edition of National Tiger Conservation Authority’s (NTCA) quarterly newsletter ‘STRIPES’, commemorating Global Tiger Day (29th July)
News Source: PIB
Geo-imaging satellite “EOS-03”
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-III – Space
In news: Geo-imaging satellite“EOS-03”is scheduled for launch in the third quarter of 2021 by ISRO.
About EOS-3 Satellite
- EOS-03 is Earth Observation Satellite that would enable near-real time monitoring of natural disasters like floods & cyclones.
- Earth observation is the gathering of information about Earth’s physical, chemical and biological systems.
- Other earth observation satellites launched by ISRO include RESOURCESAT- 2, 2A, CARTOSAT-1, 2, 2A, 2B, RISAT-1 and 2, OCEANSAT-2, Megha-Tropiques, SARAL and SCATSAT-1, INSAT-3DR, 3D, etc.
- EOS-03 is capable of imaging the whole country 4-5 times daily.
- In addition to natural disasters, EOS-03 would also enable monitoring of water bodies, crops, vegetation conditions, forest cover changes etc.
Other development: SSLV
- The first developmental flight of the Small Satellite Launch Vehicle or SSLV is scheduled in the fourth quarter of 2021 from Satish Dhawan Space Centre, Sriharikota.
- SSLV is to be developed as a cost-effective, three stage, all-solid launch vehicle with a payload capability of 500 kg to 500 km planar orbit or 300 kg to Sun Synchronous Polar Orbit.
- SSLV is ideal for on-demand, quick turn-around launch of small satellites.
News Source: PIB
Non-Bank PSPs to Join Centralised Payment System
Part of: GS Prelims and GS -III – Economy
In news Recently, the RBI allowed non-bank Payment System Providers (PSPs) to participate in Centralised Payment Systems (CPS – RTGS and NEFT), as direct members.
- Presently, only banks and select non-banks such as NABARD and Exim Bank are allowed access to CPS – NEFT and RTGS.
Key features
- Allowed in a Phased Manner: In the first phase, PSPs such as Prepaid Payment Instruments (PPIs), card networks and White Label ATM (WLA) operators will be allowed access.
- Separate IFSC to Non-Banks: It means allotment of a separate Indian Financial System Code (IFSC) to non-banks, opening a current account with the RBI in its core banking system (e-Kuber) and maintaining a settlement account with the RBI.
What is the Significance?
- Direct access for non-banks to CPS lowers the overall risk in the payments ecosystem.
- Reduction in cost of payments
- Mitigating failure or delay in fund execution
- Increasing efficiency and better risk managemen
News Source: IE
Kanjeevaram Silk Sari: Tamil Nadu
Part of: GS Prelims and GS III – Indian Art forms
In news National award winning artisan weaver, B Krishnamoorthy, has created a repository with samples of all the designs, patterns and motifs traditional to Kanjeevaram silk sari weaving, preserving fine pieces for next generation.
About Kanjeevaram Sarees:
- Traditionally, the Kanjeevaram is a sari that is usually handwoven in mulberry silk and has pure gold or silver zari that renders it a festive quality.
- Originating from the village ‘Kanchipuram’ in Tamil Nadu, Kanjeevaram is considered the queen of silk sarees.
- The temple architecture of south India and especially around Kanchipuram has historically served as a mood board for design inspiration for the traditional Kanjeevaram motifs.
- One can spot motifs such as the mythical creature called the Yali (an elephant-lion fusion), the Ganda Berunda (a two-headed majestic mythical bird) and the ubiquitous temple border called reku.
- It traces its long and rich history from the Chola Dynasty
- Kanchipuram silk has also received GI Tag in 2005-06.
About Silk Production in India
- India is the second largest producer of silk in the world, producing around 18% of the world’s total silk.
- There are five major types of silk of commercial importance, obtained from different species of silkworms. These are Mulberry, Oak Tasar & Tropical Tasar, Muga and Eri.
- Except mulberry, other non-mulberry varieties of silks are wild silks, known as vanya silks.
- India has the unique distinction of producing all these commercial varieties of silk.
- South India is the leading silk producing area of the country and is also known for its famous silk weaving enclaves like Mysore, Kancheepuram, Dharmavaram, Arni, etc.
- The Government of India in 2017 launched a scheme called “Silk Samagra” for the development of sericulture in the country.
News Source: TH
(Mains Focus)
INTERNATIONAL/ EDUCATION
Topic:
- GS-2: Education & Governance
- GS-2: Effect of policies and politics of developed and developing countries on India’s interests.
Shared values: On India and the U.S
Context: Recent visit of U.S. Secretary of State Antony Blinken to Delhi. The visit was meant to prepare the way for more substantive meetings in Washington later this year, including
- US -India “2+2” of Foreign and Defence Ministers
- Quad (India, US, Australia, Japan) summit of its leaders
- Bilateral meeting between PM Modi and U.S. President Joseph Biden.
Key Takeaways of the Blinken’s Visit
Most of the conversations were focused on Quad cooperation in the Indo-Pacific, Afghanistan and on the state of democracy and rights.
- On Quad: US & India showed full convergence
- On Afghanistan: India said that there were “more convergences than divergences” on the common positions that there is no military solution to conflict, and that neither country would recognise a Taliban regime that takes Kabul by force.
- On Democratic freedom: Both sides maintained there were “shared values” but points of friction existed between two.
What are the divergences between India & USA on Afghanistan?
- U.S. withdrawal will mean a less secure region that also impacts India’s security interests in the region.
- U.S. continues to engage the Taliban in talks for a power-sharing arrangement, despite the Taliban leadership’s refusal to enforce a ceasefire, and stop attacks against civilians in areas they take over. This embolden Taliban who has close ties with Pakistan (against India’s interests)
- Taliban is also trying to squeeze trade and financial supply chains to the Afghanistan government and US is not holding Taliban accountable for its actions.
- Perhaps the greatest worry for India is the U.S.’s refusal to hold Pakistan to account for having given shelter to the Taliban, as this will only embolden Islamabad if the Taliban advance in Afghanistan.
- Another cause of worry is the recent U.S.’s announcement of a new “Quad” with Uzbekistan-Afghanistan-Pakistan on connectivity.
What were the points of friction on Democratic freedoms?
- Mr. Blinken met with a “civil society roundtable” wherein internal Indian issues such as minority rights, religious freedoms and curbs on the media and dissent were discussed. This was done in the wake of international criticism against Citizenship Amendment Act, 2019 & abrogation of Article 370.
- India’s Minister of External Affairs however countered the allegation of “backslide” in India’s democracy by reiterating that the same standards apply for the U.S. and India and actions by government like CAA & Article 370 was taken to “right historical wrongs”
Conclusion
Despite the attempt from both sides to paper over the cracks, Democratic freedoms is an issue that they will grapple with in the future even as they build upon the strong “Comprehensive Global Strategic Partnership” that the world’s oldest and most populous democracies continue to share.
Connecting the dots :
HEALTH/ GOVERNANCE
Topic:
- GS-2: Government policies and interventions for development in various sectors and issues arising out of their design and implementation.
- GS-2: Functions and responsibilities of the Union and the States
In the interest of the public: Meghalaya HC order on Compulsory Vaccination
Context: Recently, Meghalaya government had had ordered shopkeepers, local taxi drivers and others to get the COVID-19 vaccines before they resume economic activities in the wake of lock down relaxation post second wave. This was appealed in Meghalaya High Court
In Registrar General vs. State of Meghalaya, the Meghalaya High Court ruled that the State government’s order is violative of the right to privacy, life, personal liberty, and livelihood.
Significance of the case: It raises important questions of how the government can overcome widespread vaccine hesitancy and bring the pandemic to an end.
What was the Court’s reasoning?
- The court reasoned that forcing people to vaccinate themselves vitiates the “very fundamental purpose of the welfare attached to it”.
- It ruled that the government’s order intrudes upon one’s right to privacy and personal liberty as it deprives the individual of their bodily autonomy and bodily integrity, even though the intrusion is of minority intensity.
- It ruled that the government’s order affects an individual’s right “significantly” more than affecting the general public.
- It found that the government’s order is not maintainable in law as there is no legal mandate for mandatory vaccination.
- It relied on the Central government’s frequently asked questions, which specify that COVID-19 vaccination is voluntary.
- The court felt that the consequences of non-compliance with the order (i.e., non-resumption of economic activities) was excessive.
- The court concluded that the State, rather than adopting coercive steps, must persuade the people to get themselves inoculated.
Counter-arguments to Meghalaya High Court’s order
- Precedence Exists: Compulsory vaccination has often been deployed in India and abroad. The Vaccination Act, 1880, allowed the government to mandate smallpox vaccination among children in select areas.
- International Judicial Orders: Compulsory vaccination has passed the muster of judicial review in several national and international courts abroad. In a recent judgment in Vavřička and Others v. Czech Republic, the European Court of Human Rights (ECtHR) said that the compulsory COVID-19 vaccination scheme is consistent with the right to privacy and religion.
- No right is absolute: Right to Privacy is not absolute rather rights are subject to reasonable restrictions.
- Public health takes priority: Violations of rights from mandatory administration of a vaccine cannot be termed so grave so as to override the health rationale underlying the government’s order.
- Compulsory Vaccination can also pass the three-pronged test laid out in Justice Puttaswamy v. Union of India case, when any restriction is being imposed on rights
- First, the restriction must be provided in the law: State governments have the authority to mandate vaccines under the Epidemic Diseases Act, 1897, which allows them to prescribe regulations to prevent the spread of an epidemic disease
- Second, the restriction must have a legitimate aim. Compulsory vaccination pursues the legitimate aim of protecting the public from COVID-19.
- Third, the restriction must be proportional to the object pursued. With more than four lakh reported deaths and a looming third wave, the current scenario counts as a pressing social need.
Conclusion
The Court could have ordered the government to replace the existing order with less stringent consequences, such as a moderate fine.
Connecting the dots:
(TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE)
Model questions: (You can now post your answers in comment section)
Note:
- Correct answers of today’s questions will be provided in next day’s DNA section. Kindly refer to it and update your answers.
Q.1 What are the possible monitoring benefits of Geo imaging satellite EOS-03 which is scheduled for launch in the third quarter of 2021?
- Floods
- Cyclones
- Water bodies
- Crops
- Forest cover changes
Select the correct statements
- 1, 2 and 3 Only
- 2 and 5 only
- 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5 only
- 1 and 2 only
Q.2 Consider the following statements regarding All-India quota (AIQ) scheme:
- The AIQ was introduced in 1986 under the directions of the Central government.
- It comprises 15% of the UG seats and 50% of the PG seats in government medical colleges.
Select the correct statements
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Q.3. Kanjeevaram Sarees originated in which of the following state of India?
- Andhra Pradesh
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Tamil Nadu
ANSWERS FOR 29th July 2021 TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE (TYK)
| 1 | C |
| 2 | B |
| 3 | A |
Must Read
On Cyber Crimes:
On Police Reforms:
On Anti-trafficking:











