IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
Archives
(PRELIMS + MAINS FOCUS)
IPCC’s Sixth Assessment Report, “Climate Change 2021: The Physical Science Basis”
Part of: GS Prelims and GS- III – Climate change
In news UN Secretary-General Antonio Guterres and the United Nations Framework Convention for Climate Change (UNFCCC) said that the IPCC report, released recently, underscored that “there is no time for delay and no room for excuses”.
What are the key observations of the IPCC report?
- Heat waves and humid heat stress will become more intense and frequent over Southeast Asia during the 21st century.
- Both summer and annual monsoon precipitation will increase, with enhanced inter annual variability over Southeast Asia.
- Heat extremes have increased while cold extremes have decreased and these trends will continue over the coming decades.
- Glacier run-off in the Asian high mountains will increase upto mid 21st century and subsequently run-off may decrease due to the loss of Glacier storage.
- Relative sea level around Asia increased faster than global average, with coastal area loss and shoreline retreat. Regional mean sea level will continue to rise.
What is Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC)?
- It is an international body set up in 1988 by the World Meteorological Organization (WMO) and United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) to provide policymakers with
- Regular assessments of the scientific basis of climate change
- Impacts and future risks associated with Climate Change
- Options for adaptation and mitigation for Climate Change
- Membership of the IPCC is open to all members of the WMO and the UNEP.
- IPCC assessments provide a scientific basis for governments at all levels to develop climate-related policies and also underlie climate negotiation at International level.
- The main objective of UNFCCC is to stabilize greenhouse gas concentrations in the atmosphere at a level that would prevent dangerous anthropogenic interference with the climate system.
News Source: TH
The Constitution (Scheduled Tribes) Order (Amendment) Bill, 2021
Part of: Prelims and GS – II – Government policies and interventions
In news The Constitution (Scheduled Tribes) Order (Amendment) Bill, 2021 has recently been passed in both the houses of the Parliament.
- The Bill amends the Constitution (Scheduled Tribes) Order, 1950.
- The Bill has been introduced to give effect to modifications proposed by the state of Arunachal Pradesh.
- The Bill removes the Abor tribe from the list of identified STs in Arunachal Pradesh.
- Further, it replaces certain STs with other tribes.
Proposed changes in list of STs in Arunachal Pradesh under the Bill
| Original list | Proposed changes under the Bill |
| Abor | Deleted from the list |
| Khampti | Tai Khamti |
| Mishmi, Idu, and Taroan | Mishmi-Kaman (Miju Mishmi), Idu (Mishmi), and Taraon (Digaru Mishmi) |
| Momba | Monpa, Memba, Sartang, and Sajolang (Miji) |
| Any Naga Tribes | Nocte, Tangsa, Tutsa, and Wancho |
Do you know?
- The Constitution under Article 342 empowers the President to specify the Scheduled Tribes (STs) in various states and union territories.
- Further, it permits Parliament to modify this list of notified STs.
News Source: TH
National Mission on Edible Oil-Oil Palm (NMEO-OP)
Part of: GS Prelims and GS- III – Food processing and related industries in India
In news Indian Prime Minister recently announced National Mission on Edible Oil-Oil Palm (NMEO-OP) initiative on palm oil production to help increase farm incomes.
- Rs. 11,000 crores over five year period will be invested in the edible oil ecosystem through this mission
What are the key features of the Scheme?
- Objective: To ensure self-sufficiency in edible oil production.
- Aim: To reduce import dependence from 60% to 45% by 2024-25, by increasing domestic edible oil production from 10.5 million tonnes to 18 million tonnes which is a 70% growth target.
- Farmers will get all needed facilities, from quality seeds to technology.
- Along with promoting the cultivation of oil palm, this mission will also expand the cultivation of our other traditional oilseed crops.
What is the need for such schemes?
- India is the largest consumer of vegetable oil in the world.
- India’s Palm oil imports are almost 60% of its total vegetable oil imports.
- Recently, India’s dependence on expensive imports has driven retail oil prices to new highs.
- In India, 94.1% of its palm oil is used in food products, especially for cooking. Thus, palm oil is extremely important to India’s edible oils economy.
- The oil is used in food manufacturing, in beauty products, and as biofuel.
- Palm oil accounted for about 33% of global oils produced from oil crops in 2014.
- Top consumers: India, China, and the European Union (EU).
Do you know?
- The NMEO-OP’s predecessor was the National Mission on Oil Seeds and Oil Palm.
- In May 2020, oilseed production had grown 35% from 27.5 million tonnes in 2014-15 to 37.3 million tonnes by 2020-21.
News Source: TH
Tribals in Rajasthan seek more panchayats in scheduled areas
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-II – Panchayati Raj Institutions
In news The tribal outfits in Rajasthan have demanded inclusion of over 165 village panchayats of seven districts in the scheduled areas under the Tribal Sub-Plan (TSP).
- The tribal groups said the population of Scheduled Tribes in these panchayats had crossed 50%, making them eligible to be declared as scheduled areas.
- The objective of the demand is to facilitate the control of local communities over minor minerals and minor forest produce as well as development activities in the region.
- It will also ensure statutory protection of the tribal population.
- Consequently, the provisions of the Panchayats (Extension to Scheduled Areas) Act, 1996, will apply to these areas.
- The Provisions of the Panchayats (Extension to Scheduled Areas) Act, 1996 or PESA is a law enacted by the Government of India for ensuring self-governance through traditional Gram Sabhas for people living in the Scheduled Areas of India.
- The tribal groups have also been spearheading a movement for creation of a separate State, Bhil Pradesh, to be carved out of the tribal-dominated areas of Rajasthan, Gujarat, Madhya Pradesh and Maharashtra.
News Source: TH
Permanent Forum of People of African Descent
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-II – International relations
In news Recently, the UN General Assembly approved a resolution establishing a Permanent Forum of People of African Descent.
About the UN United Nations Permanent Forum of People of African Descent.
- It would serve as “a platform for improving the safety and quality of life and livelihoods of people of African descent” and ensure the full political, economic and social inclusion in the societies where they live.
- It would provide expert advice and recommendations, to Human Rights Council & UN agencies, on addressing the challenges of racism, racial discrimination, xenophobia and intolerance.
- Forum’s first session will take place in 2022.
- The forum will consist of 10 members — five elected by the General Assembly from all regions and five appointed by the Human Rights Council following consultations with regional groups and organizations of people of African descent.
- The resolution also calls for annual reports to the assembly and the council on the forum’s activities, and an evaluation of its operation by the General Assembly after four sessions, based on an evaluation by the Human Rights Council.
Do you know?
- Recently, the International Decade for People of African Descent was also established by the General Assembly, which began on January 1, 2015, and ends on December 31, 2024.
- The decade is focusing on the themes of recognition, justice and development.
- Member States of the UN adopted the texts at the World Conference against Racism, Racial Discrimination, Xenophobia and Related Intolerance, held in 2001 in Durban, South Africa and is called Durban declaration.
About The Human Rights Council
- It is an inter-governmental body within the United Nations system made up of 47 States responsible for the promotion and protection of all human rights around the globe.
- It has the ability to discuss all thematic human rights issues and situations that require its attention throughout the year.
- It meets at the UN Office at Geneva.
News Source: TH
(News from PIB)
“Seekho Aur Kamao” Scheme
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-II- Government Schmes
About Seekho Aur Kamao scheme
- It is a skill development Central sector scheme for minorities (youth of 14 – 35 years age group) and aimed at providing employment and employment opportunities, improving the employability of existing workers, school dropouts etc.
- In the last 7 years appx. 3.92 lakh persons have been benefitted under this employment-oriented scheme.
- The scheme ensures 75% placement, out of which 50% should be in organized sector.
- Post placement support of Rs. 2000/- per month is provided to placed trainees for two months as placement assistance.
Some of the schemes for growth and development of MSME Sector in the country are:
| Prime Minister’s Employment Generation Programme (PMEGP) |
|
| Scheme of Fund for Regeneration of Traditional Industries (SFURTI) |
|
| A Scheme for Promoting Innovation, Rural Industry & Entrepreneurship (ASPIRE) |
|
| Credit Guarantee Fund Scheme for Micro and Small Enterprises (CGMSE) |
|
| Credit Linked Capital Subsidy and Technology Upgradation Scheme (CLCS-TUS) |
|
Contribution of MSMEs to GDP (will be useful for Mains)
- As per the information received from Central Statistics Office, Ministry of Statistics & PI, Share of MSME Gross Value Added (GVA) in All India Gross Domestic Product at current prices (2011-12) for the year 2018-19 and 2019-20 were 30.5% and 30.0% respectively.
- The share of the MSME manufacturing in All India manufacturing gross value output during the year 2018-19 and 2019-20 were 36.9% and 36.9% respectively.
- Further, as per the information received from Directorate General of Commercial Intelligence and Statistics, the share of export of specified MSME related products to All India exports during 2019-20 and 2020-21 was 49.8% and 49.5% respectively.
- As per 73rd Round of NSS Report on Unincorporated Non-Agricultural Enterprises’ (July 2015- June 2016) conducted by Ministry of Statistics & PI, estimated number of workers in MSME sector was 11.10 crore.
- Under the Prime Minister’s Employment Generation Programme (PMEGP), the estimated employment generated (number of persons) in micro enterprises during the year 2020-21 and 2021-22 (as on 01.07.2021) are 5.95 lakh and 1.19 lakh respectively.
Indian Institute of Heritage
Part of: GS Prelims and Mains GS-I- Culture
In news: Indian Institute of Heritage would be a world-class and standalone Institution of its type in the country: Union Culture Minister.
Key highlights:
- The government has decided to set up the ‘Indian Institute of Heritage’ at Noida, Gautam Buddha Nagar.
- It will be a world-class university that would focus on the conservation and research in India’s rich tangible heritage, while offering research, development and dissemination of knowledge associated with heritage.
- It would also offer Masters and Ph. D courses in History of Arts, Conservation, Museology, Archival Studies, Archaeology, Preventives Conservation, Epigraphy and Numismatics, Manuscriptology etc. as well as conservation training facilities to in-service employees and the students of the Indian Institute of Heritage.
- This would be a standalone Institution of its type in the country and will have positive impact on higher education and research in the fields related to rich Indian heritage and its conservation.
News Source: Pib
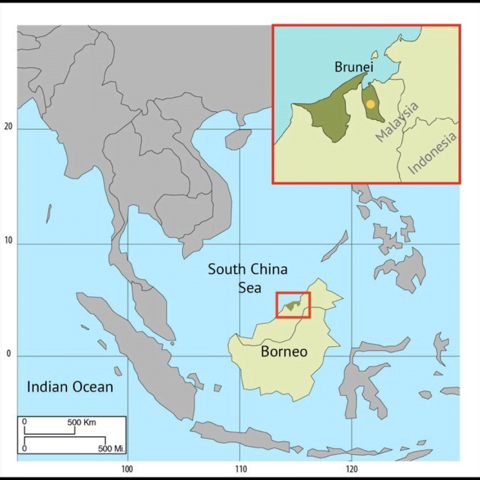
Indian Naval Ships Shivalik and Kadmatt at Brunei to enhance Bilateral Ties
Part of: GS Prelims
In news: Indian Naval Ships Shivalik and Kadmatt at Brunei to enhance Bilateral Ties
- During the stay at Muara, Brunei, the crew of both the ships will participate in various bilateral professional interactions with Royal Brunei Navy.
- The exercise will provide an opportunity to both the navies to enhance inter-operability, gain from best practices and develop common understanding of procedures for Maritime Security Operations.
- The harbour interactions and exercises at sea aim to consolidate the strong bond shared by the two navies and would be another step towards strengthening India-Brunei defence relations.
Indian Navy Ships Shivalik and Kadmatt
- Indian Navy Ships Shivalik and Kadmatt are the latest indigenously designed and built, multi-role Guided Missile Stealth Frigate and Anti-Submarine Corvette respectively, and form part of the Indian Navy’s Eastern Fleet based at Visakhapatnam under the Eastern Naval Command.
- The two ships are equipped with a versatile array of weapons and sensors, can carry multi-role helicopters, and represent the maturation of India’s warship-building capabilities.
News Source: Pib
(Mains Focus)
WOMEN/GOVERNANCE
- GS-1: Role of women and women’s organization, population and associated issues, poverty and developmental issues, urbanization, their problems and their remedies.
- GS-2: Mechanisms, laws, institutions and Bodies constituted for the protection and betterment of these vulnerable sections
Misinformation through a feminist lens
Context: The online world amplifies the social norms of the physical world. Women face aggressive and offensive trolling on the Internet, designed to undermine and discredit them professionally and shame them into silence.
Feminism & misinformation on Social Media
- Position does not matter: Woman’s position of power does not shield her from vulgar misinformation. 95 female politicians out of 724 received nearly one million hateful mentions on Twitter between March and May, 2021 (Amnesty International Report)
- Inter-sectional challenges: Organised disinformation and sexism intersect with Islamophobia, castetism, religious bigotry and other forms of discrimination to threaten vocal women
- Responsibility on Women: The harassment is so rampant that more often than not, women are asked to either ignore the abusers or block such handles. As always, women are expected to take precautionary measures instead of men being asked to behave.
- Misusing Sexuality: While on the one hand women are targeted with sexist attacks, on the other, their sexuality is used to further misinformation. There are multiple fake Facebook accounts posing as a woman and “posting provocative comments that could hurt social harmony”.
- Political attempt to silence Feminist Voices: A recent report by UNESCO on online harassment faced by women journalists says that political actors instigate and fuel online violence campaigns against women journalists.
- Misinformation and sexism have a symbiotic relationship: Misinformation piggybacks on sexism to discredit vocal women and sexism uses misinformation to reinforce patriarchal norms.
- Gendered misinformation threatens Democracy: A healthy democracy is participatory and promotes gender inclusiveness. Sexism and misinformation intimidate women from taking vocal stands and are antithetical to a progressive society.
Conclusion
While social media gives a platform for women to raise issues, repeated abuse takes away that freedom. Social media, the place that bolstered the #MeToo movement, is the same place used to shut women down.
Connecting the dots:
- Intersectionality
- Rape & Sexual Crimes Law in India
- Punitive Responses to Sexual Violence Need Rethink
- Sexual Harassment at workplaces
- Disha Act of Andhra Pradesh
ECONOMY/ GOVERNANCE
Topic:
- GS-2: Government policies and interventions for development in various sectors
- GS-3: Indian Economy and challenges with regard to resource mobilization
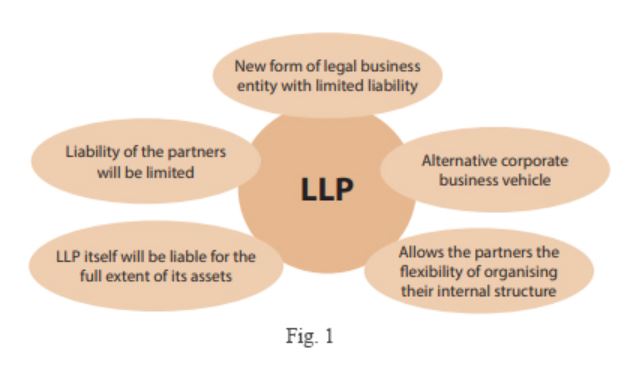
The Limited Liability Partnership (Amendment) Bill, 2021
In news The Limited Liability Partnership (Amendment) Bill, 2021 has been recently passed in both the Houses of the Parliament.
- The Bill seeks to amend the Limited Liability Partnership Act, 2008.
- A limited liability partnership (LLP) is a partnership in which some or all partners have limited liabilities.
- It therefore can exhibit elements of partnerships and corporations. In an LLP, each partner is not responsible or liable for another partner’s misconduct or negligence
- Under LLP, a partner’s liabilities are limited to their investment in the business.
What are Key features of the Bill?
- Certain offences decriminalised: The Bill decriminalises provisions and imposes a monetary penalty: (i) changes in partners of the LLP, (ii) change of registered office, (iii) filing of statement of account and solvency; (iv) arrangement between an LLP and its creditors or partners, and reconstruction or amalgamation of an LLP.
- Change of name of LLP: The Bill empowers the central government to allot a new name to such an LLP instead of levying a fine.
- Punishment for fraud: Under the Bill, if an LLP or its partners carry out an activity to defraud their creditors, every person party to it knowingly is punishable with maximum term of imprisonment up to five years
- Non-compliance of orders of Tribunal: Bill has removed the offence of non-compliance with an order of the National Company Law Tribunal (NCLT)
- Compounding of offences: The Bill provides that a regional director (or any officer above his rank), appointed by the central government, may compound such offences which are punishable only with a fine. The amount imposed must be within the minimum and maximum fine for the offence.
- Adjudicating Officers: Under the Bill, the central government may appoint adjudicating officers for awarding penalties under the Act. These will be central government officers not below the rank of Registrar.
- Special courts: The Bill allows the central government to establish special courts for ensuring speedy trial of offences under the Act.
- Appeals to Appellate Tribunal: Appeals against orders of the NCLT lie with the National Company Law Appellate Tribunal (NCLAT). Also, the appeals cannot be made against an order that has been passed with the consent of the parties. Appeals must be filed within 60 days (extendable by another 60 days) of the order.
- Small LLP: The Bill provides for formation of a small LLP where: (i) the contribution from partners is up to Rs 25 lakh (may be increased up to five crore rupees), (ii) turnover for the preceding financial year is up to Rs 40 lakh (may be increased up to Rs 50 crore). The central government may also notify certain LLPs as start-up LLPs.
- Standards of accounting: Under the Bill, the central government may prescribe the standards of accounting and auditing for classes of LLPs, in consultation with the National Financial Reporting Authority.
News Source: TH
(AIR – SPOTLIGHT)
Spotlight 28 July, 2021: AIR NEWS EXCLUSIVE- Discussion on India’s presidency and its quest for an expanded UN Security Counsil
INTERNATIONAL/ GOVERNANCE
- GS-2: India Foreign Policy
- GS-2: International Organisation, their structure & functioning.
India’s presidency and its quest for an expanded UN Security Council
- India’s two-year tenure as a non-permanent member of the Security Council began on January 1, 2021.
- India will take over the Presidency of the United Nations Security Council (UNSC) on August 1 and is set to host signature events in three major areas of maritime security, peacekeeping and counterterrorism during the month.
- External Affairs Ministry said, India’s vision has been steered by Dialogue and Cooperation, mutual respect and commitment to international law.
- In its presidency, India will be guided by the principles of Transparency, credibility, accountability and effectiveness. Maritime security, peacekeeping and counter-terrorism will be the focus areas for India during its presidency.
- The Ministry said, as a founding member of the UN, India is committed to multilateralism, Rule of Law, and Fair and equitable international system.
India and UN Security Council
- India was offered seat at UNSC way back in 1950 by USA (the US had begun mounting pressure on India for a permanent seat as early as 1950, wanting her to take the place of China.)
- The 1955 offer was made by USSR to India for a permanent seat in the UN (at a time when the USSR and China’s alliance had reached a certain height).
- China has been stonewalling India’s efforts to become member of the UN’s powerful body for years, pointing to the lack of consensus even though the other four permanent members, the US, the UK, France and Russia have expressed backing for New Delhi’s membership.
India’s Bid for Permanent Seat In UNSC
- India has basically followed two strategies for the expansion of the Security Council. “The first focuses on a narrow major-power claim, which emphasizes India’s capabilities and contributions to the UNSC as the basis for permanent membership”.
- The second approach basically focuses on the “problem of representation in the UNSC and makes the case for expanding both permanent and non-permanent categories of membership with a view to ensuring that the world’s foremost organization for international peace and security reflects the dramatically altered distribution of power since 1945.
Issues India need to overcome in Getting a Permanent Seat at UNSC
- Although it may seem like a simple process, it is made difficult by the objections of certain permanent members of the Security Council. China, in particular, has been blocking India’s push for a permanent seat at the Council. China believes that granting India a permanent seat at the UNSC will lead to Indian interests being of paramount importance in the geopolitics of the subcontinent, a sentiment echoed by its ally, Pakistan.
- In addition to this, India is also seen as a proliferating nuclear power. Analysts believe that this is the single most factor that is being a roadblock for India’s UNSC dreams.
- India should make effort to counter terrorism and should ensure it end once and for all and that we have in place a global convention on counter terrorism. All parts of world are suffering from this issue and India is making good efforts already.
- The recent discussions on the global counter-terrorism strategy which India adopted has strengthened the efforts to combat terrorism, for example in the financing of terrorism and the use of new technology like artificial intelligence, drones etc.
Criticism of UNSC
- Unlike the General Assembly which truly represents the interests of all the member states, the Security Council represents the interest and domination of only the five permanent members which includes China, France, Russia, the United Kingdom and the United States of America.
- Another criticism of the UNSC includes the veto power exercised by the five permanent members. For passing any resolution, the approval of all the five permanent members is necessary and even if one of the members says no the resolution cannot be passed. This right to veto has been misused by the members.
Can you answer this question now?
Discuss the structure and functioning of UNSC. Also mention the issues India need to overcome in Getting a Permanent Seat at UNSC.
(TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE)
Model questions: (You can now post your answers in comment section)
Note:
- Correct answers of today’s questions will be provided in next day’s DNA section. Kindly refer to it and update your answers.
Q.1 Abor tribe recently seen in news belongs to which of the following state of India?
- Odisha
- Tamil Nadu
- Assam
- Arunachal Pradesh
Q.2 Palm oil is used in the manufacturing of which of the following products?
- Detergents
- Plastics
- Cosmetics
- Biofuels.
Select the correct statements:
- 1 and 2 only
- 3 only
- 1 and 4 only
- 1, 2, 3 and 4
Q.3 Permanent Forum of People of African Descent was recently established to address which of the following?
- Unemployment
- Poverty
- Political instability
- Racism
ANSWERS FOR 9th August 2021 TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE (TYK)
| 1 | A |
| 2 | None of the above |
| 3 | C |
Must Read
On Labour Law reforms:
On Pegasus Scandal and Surveillance State:
On Privatising PSBs:











