IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
Archives
(PRELIMS + MAINS FOCUS)
COVID-19 vaccine export to resume
Part of: Prelims and GS II – International Relations
Context India will resume the export of COVID-19 vaccines under its ‘Vaccine Maitri’ programme to fulfil the commitment towards COVAX (COVID-19 Vaccines Global Access).
What is COVAX (COVID-19 Vaccines Global Access)?
- The COVAX program is led by the vaccine alliance GAVI, WHO and the Coalition for Epidemic Preparedness Innovations (CEPI) in partnership with UNICEF, vaccine manufacturers and the World Bank, among others.
- Aim: To ensure equitable distribution of COVID-19 vaccines globally
- It is supposed to be the largest vaccine procurement and supply operation in history.
- The program wants to vaccinate roughly 20 percent of the population in the 92 Advance Market Commitment (AMC) countries, which include middle and lower-income nations that cannot afford to pay for COVID-19 vaccines.
- Countries with a Gross National Income (GNI) per capita of less than US $4000 and some other countries eligible under the World Bank International Development Association (IDA) shall be given top priority.
What is Gavi, the Vaccine Alliance?
- It was Created in 2000.
- Gavi is an international organisation – a global Vaccine Alliance, bringing together public and private sectors with the shared goal of creating equal access to new and underused vaccines for children living in the world’s poorest countries.
- Its core partners include the WHO, UNICEF, the World Bank and the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation.
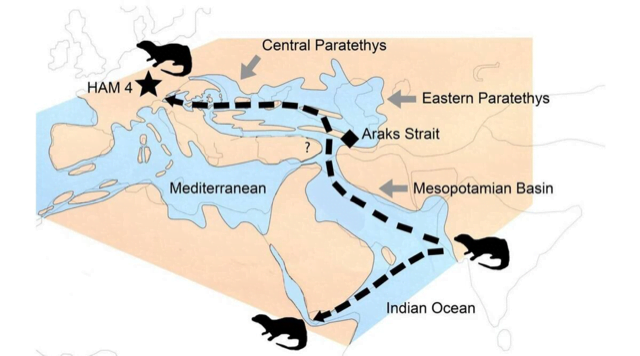
Vishnuonyx
Part of: Prelims and GS-III- Biodiversity
Context Newly found fossils of Vishnuonyx have been found in the area of Hammerschmiede, which is a fossil site in Bavaria, Germany.
- Between 12.5 million and 14 million years ago, members of a genus of otters called Vishnuonyx lived in the major rivers of southern Asia.
Key takeaways
- Fossils of these now extinct otters were first discovered in sediments found in the foothills of the Himalayas.
- Now, the newly found fossil indicates it had travelled as far as Germany.
- The newly discovered fossils have been named Vishnuonyx neptuni, meaning ‘Neptune’s Vishnu’.
- This is the first discovery of any member of the Vishnuonyx genus in Europe.
- It is also its most northern and western record till date.
About Vishnuonyx
- Vishnuonyx were mid-sized predators that weighed, on average, 10-15 kg.
- Before this, the genus was known only in Asia and Africa.
- Vishnuonyx depended on water and could not travel long distances over land.
How did it travel as far as Europe?
- According to the researchers, its travels over 6,000 km were probably made possible by the geography of 12 million years ago, when the Alps were recently formed.
- These Alps and the Iranian Elbrus Mountains were separated by a large ocean basin, which would have made it easier for the otters to cross it.
Plant Discoveries 2020: The Botanical Survey of India
Part of: Prelims and GS III – environment
Context The Botanical Survey of India, in its new publication Plant Discoveries 2020 has added 267 new taxa/ species to the country’s flora.
- An assessment of the geographical distribution of these newly discovered plants reveals that 22% of the discoveries were made from the Western Ghats.
About Botanical Survey of India (BSI)
- It is the apex research organization under the Ministry of Environment and Forests (MoEFCC)
- It carries out taxonomic and floristic studies on wild plant resources of the country.
- It was established in 1890
- It has nine regional circles
- Headquarter: Kolkata, West Bengal.
Rail Kaushal Vikas Yojana
Part of: Prelims and GS – II – policies and interventions
Context Recently, the Ministry of Railways launched Rail Kaushal Vikas Yojana (RKVY) under Pradhan Mantri Kaushal Vikas Yojana (PMKVY).
What is Rail Kaushal Vikas Yojana (RKVY)?
- This is a skill development programme, where training will be provided to youth with a special focus on jobs that are relevant to the Railways.
- The training will be provided in four trades viz. Electrician, Welder, Machinist and Fitter and other trades will be added by zonal railways and Production units based on regional demands and needs assessment.
- Training will be provided to apprentices under the Apprentice Act 1961.
- Objectives:
- To impart training skills to the youth in various trades to bring qualitative improvement.
- To train 50,000 candidates over the next three years.
- Eligibility: Candidates who are 10th passed and between 18-35 years shall be eligible to apply.
- Significance: It will not only improve the employability of the youth but also upgrade the skills of employed.
What is Pradhan Mantri Kaushal Vikas Yojana?
- Launched in 2015, it is a flagship program of the Ministry of Skill Development and Entrepreneurship (MSDE).
- Aim: To mobilize youth to take up skill training with the aim of increasing productivity and aligning the training and certification to the needs of the country.
- Key Components:
-
- Short Term Training: Training as per National Skills Qualification Framework (NSQF) is provided to those who are either school/college dropouts or unemployed.
- Recognition of Prior Learning (RPL): An individual with a certain set of skills or with prior learning experience is assessed and certified under RPL with grade according to the NSQF.
- Special Projects: This component ensures training in special areas and premises of government bodies and corporate. It aims to encourage training in vulnerable and marginalized groups of society.
- Training Partners (TPs) are mandated to organize Kaushal and Rozgar Melas every six months
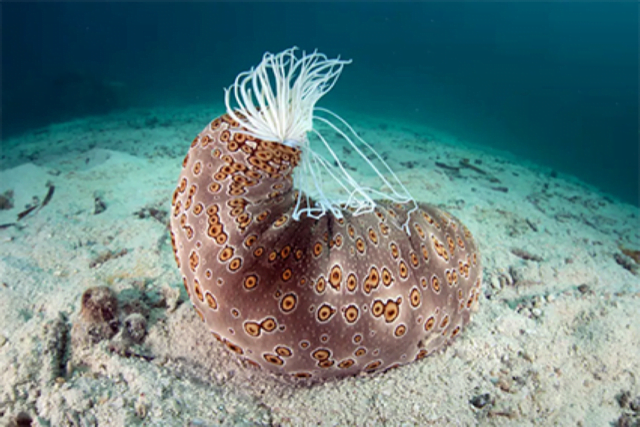
Sea Cucumber
Part of: Prelims and GS III – Conservation
Context Recently, the Indian Coast Guard (ICG) has seized two tonnes of sea cucumber, a banned marine species, in the Gulf of Mannar and Palk Bay areas in Tamil Nadu.
What is Sea Cucumber?
- Sea cucumbers are marine invertebrates that live on the seafloor found generally in tropical regions.
- They’re named for their unusual oblong shape that resembles a fat cucumber.
- Significance:
- They are crucial to maintain the balance of ocean habitats.
- The main by-products of the sea cucumbers digestion of sand is calcium carbonate and this is essential for the survival of the coral reefs.
- They act like garbage collectors of the ocean world, and they recycle nutrients
- Threats: Illegal Trading and smuggling
- Protection:
- IUCN Red List: Brown Sea Cucumber (Endangered), Blackspotted Sea Cucumber (Least Concern), Blue Sea Cucumber (Data Deficient), etc.
- Wildlife Protection Act, 1972: Schedule I.
- Conservation Efforts: In 2020, the Lakshadweep Islands administration created the world’s first conservation area – 239 sq. km – for sea cucumbers

(News from PIB)
EXERCISE ‘SAMUDRA SHAKTI’
Part of: GS-Prelims
In News: Indian Navy and Indonesian Navy Participate in Exercise ‘Samudra Shakti’.
- To strengthen the bilateral relationship
- Enhance mutual understanding and interoperability in maritime operations between the two navies
- Provide an appropriate platform to share best practices and develop a common understanding of Maritime Security Operations.
Note: Sunda Strait- the strait between the Indonesian islands of Java and Sumatra. It connects the Java Sea to the Indian Ocean.
News Source: PIB
EXERCISE SURYA KIRAN
Part of: GS-Prelims
In News: Indo-Nepal Joint Military Training Exercise Surya Kiran begins at Pithoragarh (UK)
- An Infantry Battalion each from the Indian Army and the Nepali Army will be training together to develop inter-operability and share their experience of counter terrorism operations and disaster relief operations.
News Source: PIB
Global Innovation Index 2021
Part of: GS-Prelims
- India has climbed 2 spots and has been ranked 46th by the World Intellectual Property Organization in the Global Innovation Index 2021 rankings.
- India has been on a rising trajectory, over the past several years in the Global Innovation Index (GII), from a rank of 81 in 2015 to 46 in 2021.
Global Innovation Index (GII):
- The GII provides new data and analysis on the state of global innovation, and allows readers and policy-makers to benchmark the innovation ecosystem performance of more than 130 economies.
- This year, a novel new feature, the Global Innovation Tracker, gives a snapshot on the pulse of global innovation, including throughout the Covid-19 pandemic. As the effects of the COVID-19 pandemic continue to be felt around the world, the 2021 GII assesses the impact of the crisis on global innovation performance.
Read more: The India Innovation Index
News Source: PIB
Miscellaneous
National Florence Nightingale Award 2020: Brigadier S V Saraswati; The highest national distinction a nurse can achieve for selfless devotion and exceptional professionalism.
(Mains Focus)
POLITY/ GOVERNANCE
- GS-2: Citizenship, Federalism
- GS-2: Government policies and interventions for development in various sectors and issues arising out of their design and implementation.
Done and dusted: On NRC process
Context: Foreigners’ Tribunal (FT) in Karimganj district of southern Assam, while removing the ambiguity around a man’s citizenship, has pronounced that there is no doubt that the NRC published on August 31, 2019, is the final one.
What is the background of National Register of Citizens (NRC)?
- At its core, the NRC is an official record of those who are legal Indian citizens. It includes demographic information about all those individuals who qualify as citizens of India as per the Citizenship Act, 1955.
- The register was first prepared after the 1951 Census of India and since then it has not been updated until recently.
- So far, such a database has only been maintained for the state of Assam.
- In 2014, the SC ordered the updation of the NRC in Assam.
- The main purpose for updating of the NRC in Assam was the identification of the illegal immigrants in the state who had migrated to Assam from Bangladesh during the 1971 war with Pakistan.
- One of the basic criteria for identification was that the names of the family members of the applicant should be present in the NRC prepared in 1951 or in the electoral rolls up till March 24, 1971.
- The entire updation process was executed by the Assam’s administrative machinery.
- In the run-up to the publication of the final document, Assam and the Centre had petitioned the Supreme Court for re-verification of a sample of names included in the draft NRC — 20% in the border districts and 10% elsewhere — but this was dismissed after the State NRC Coordinator, said re-verification of 27% names had been already done.
- Final NRC was published on 31st Aug 2019 (Supreme Court deadline). The list left out over 1.9 million from a list of around 33 million applicants. The citizenship of those who have been left out would be determined at the Foreigner’s Tribunals
What are the challenges post publication of NRC?
- Political Opposition: NRC publication on 31st Aug 2019 has annoyed political parties across the ideological divide, with some alleging it victimised document-less Bengali Hindus and indigenous Assamese people and others alleging that it targeted the State’s Bengali-origin Muslims.
- Re-verification demand: In May 2021, the State NRC authority has filed a petition in Supreme Court seeking re-verification of the August 31, 2019 list, citing inclusion and exclusion errors.
- Assam Chief Minister has on record stated that the State government wants 20% re-verification in the districts bordering Bangladesh and 10% in others.
- Another repetition of the NRC even on smaller scale, whether led by the judiciary or the executive, would rely on the same administrative set-up.
- Slow post-publication progress: On the execution side, the issuance of rejection slips to those left out of the NRC has not begun, a necessary step to file appeals in the Foreigner Tribunals.
- Legal Approval awaiting: Also, a Registrar General of India notification has not conferred the stamp of legality on the NRC yet.
Conclusion
Providing legal stamp on NRC and kick-starting the appeals process is perhaps the most prudent path ahead.
Connecting the dots:
- Citizenship Amendment Act, 2019
- Assam Protests against CAA, 2019
ENVIRONMENT/ INTERNATIONAL
- GS-3: Conservation, environmental pollution and degradation
- GS-2: Effect of policies and politics of developed and developing countries on India’s interests
Difficulties for India to attain Net Zero
Context: On his recent visit to India ahead of the U.N. Climate Change conference in Glasgow, U.S. Special Presidential Envoy for Climate John Kerry said he had not received any assurance that India was working to raise its ambition to cut carbon dioxide emissions.
- India, as the country with the third largest emissions, is under pressure to come up with a higher ambition on cutting CO2 emissions.
- The net zero concept, according to the United Nations, has appealed to 130 countries that have either committed themselves to carbon neutrality by 2050, or are considering that target.
The net-zero goal
- Net-zero, which is also referred to as carbon-neutrality, does not mean that a country would bring down its emissions to zero.
- Rather, net-zero is a state in which a country’s emissions are compensated by absorption and removal of greenhouse gases from the atmosphere.
- Absorption of the emissions can be increased by creating more carbon sinks such as forests, while removal of gases from the atmosphere requires futuristic technologies such as carbon capture and storage.
How are other big countries pursuing net zero?
- As the largest emitter of GHGs, China told the U.N. in 2020 that it would move to net zero by 2060. It has pledged to peak CO2 emissions before 2030 and achieve carbon neutrality three decades later.
- The U.S., as the second biggest emitter with large historical emissions, returned to the Paris Agreement under President Joe Biden with an ambitious 2050 net zero plan.
- The European Union (EU) member-states have committed themselves to reducing emissions by at least 55% by 2030 over 1990 levels. In July, the EU published a climate law that binds the bloc to its 2030 emissions target and carbon neutrality by 2050.
Why do some analysts see net zero as controversial?
- Although a global coalition has been reached around the concept, an increasingly vocal group views net zero as a distraction, useful only to score political points.
- Carbon neutrality looks to nascent technology to suck out CO2 from the atmosphere, which is expensive especially for developing countries.
- Youth movements and some scientists call this postponement, since it enables the fossil fuel industry to continue expanding. Many fossil fuel companies support net zero goals.
What is India doing to lower emissions?
- India is working to reduce its emissions and has pledged to cut the emissions intensity of GDP by 33%-35% by 2030 over the 2005 level. India also has set ambitious renewable energy targets i.e. 450 GW by 2030.
- But India has not favoured a binding commitment towards carbon neutrality. It is also not aligned with the more ambitious goal of 1.5°C temperature rise.
- Among the contentious issues India faces is heavy reliance on coal accounting 70% of electricity generation.
- Cutting greenhouse gases which heat the atmosphere and contribute to climate change involves shifting power production away from coal, greater adoption of renewables, and transforming mobility through electric vehicles.
What are India’s choices?
- Getting a stronger economic dividend for the same volume of CO2 emitted by reforming energy, industry and buildings, and achieving higher energy efficiency in all sectors can slow emissions.
- State governments must be part of such a climate plan, and climate governance institutions must be set up at the national and State levels.
Connecting the dots:
- Net Zero Carbon Emissions may not be enough
- Paris Climate Accord
- India’s Opposition to Net Zero
- China’s Climate Commitments
(AIR Spotlight)
Spotlight Sep 18: Seva aur Samarpan- Bees Saal Sushashan ke Series- Theme: Jal Jeevan Mission – https://youtu.be/xs6zwVnSuQ0
GOVERNANCE/ ECONOMY
- GS-2: Government policies and interventions for development in various sectors and issues arising out of their design and implementation.
- GS-3: Indian Economy & Challenges
Government of India has restructured and subsumed the ongoing National Rural Drinking Water Programme (NRDWP) into Jal Jeevan Mission (JJM) to provide Functional Household Tap Connection (FHTC) to every rural household i.e., Har Ghar Nal Se Jal (HGNSJ) by 2024.
- It is envisioned to provide safe and adequate drinking water through individual household tap connections by 2024 to all households in rural India.
- It envisages supply of 55 litres of water per person per day to every rural household through Functional Household Tap Connections (FHTC) by 2024.
- It also includes functional tap connection to Schools, Anganwadi centres, GP buildings, Health centres, wellness centres and community buildings
- The programme will also implement source sustainability measures as mandatory elements, such as recharge and reuse through grey water management, water conservation, rain water harvesting.
- JJM focuses on integrated demand and supply-side management of water at the local level.
- The Mission is based on a community approach to water. It looks to create a jan andolan for water, thereby making it everyone’s priority.
- It promotes and ensure voluntary ownership among local community by way of contribution in cash, kind and/ or labour and voluntary labour.
- Parent Ministry: Department of Drinking Water & Sanitation, Ministry of Jal Shakti
- Funding Pattern: The fund sharing pattern between the Centre and states is 90:10 for Himalayan and North-Eastern States, 50:50 for other states, and 100% for Union Territories.
- Four-tier implementation & monitoring of the scheme at National, State, District & village level.
- There is a Water Quality Management Information System as well which is a dedicated one-stop information portal that provides information about the quality of water. Jal Jeevan Mission emphasizes that each local village should be able to test the quality of water not only at the source but also at the delivery points. For that purpose, the National Jal Jeevan Mission with the help of states is giving training to at least five women in one village, implying out of the 6 lakh villages, 30 lakh women will be trained. So far, 6 lakh women have been trained and they are assigned the task of testing the tap water quality which they get at their village level.
Therefore, all three aspects are taken care of under the Jal Jeevan Mission.:
- The source of water and its sustainability,
- The operation maintenance and providing tap water supply to each and every household, and
- The treatment of the greywater or used water
Unburdening lives of women
For a country with 16 per cent of the world’s population, and only 4 per cent of the world’s freshwater resources, with the changing weather patterns and frequent droughts, over 250 of the 700 districts of India’s districts are now water stressed. Two hundred and fifty six of our approximately 700 districts have groundwater levels which are “critical” or “over-exploited” as per the latest data from the Central Ground Water Board (2017). To put it simply, this means that fetching water in these districts is now that much harder, as the water table has fallen that much deeper.
According to a report by the National Commission for Women, on an average, a rural woman in Rajasthan walks over 2.5 km to reach a water source. This is probably an underestimate, but the bottomline is that our women and girls spend a significant proportion of their time on fetching water.
With women playing a leadership role in managing their community’s water resources, minus the drudgery of walking for miles to fetch water for their families, the Jal Jeevan Mission will provide a massive fillip to the ease of living for women, and they will no longer be beasts of burden.
Challenges involved:
- Bigger states have bigger challenges. In water scheme though focus is village level scheme but many times support is not available very close to the villages. So, for that, there is provision of multi village scheme. Example is Rajasthan.
- Also, in the Ganga belt, water quality issues are present in the form of impurity (arsenic, sulfur, etc.) contamination or other water quality issues and hence, providing water to households in these areas does take time.
But the states have taken this mission very seriously and they are doing their best to provide water to each household.
Way Forward:
- Be it at the water conservation level, or greywater treatment, or the operation and maintenance level, all the levels require the community involvement as the main focus of the Jal Jeevan Mission is the community. Therefore, without community involvement it is not possible to successfully achieve the target.
- Earlier, all the programs were basically engineering-based programs so, most of the stress was on creating engineering water infrastructure. But this time, the emphasis is on service delivery not on infrastructure creation. Service delivery has its own challenges such as supplying adequate water, maintaining the sources, etc. Hence, all these aspects should be taken care of.
- The empowerment of capacity building of the local village communities is very important. With the involvement of not only Ph.D. engineers but also the local people, the challenges will hopefully be met.
Can you answer this question?
- Enlightened water policy needs infrastructure. But more than that, it requires institutions with local and village ownership. Analyse.
(TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE)
Model questions: (You can now post your answers in comment section)
Note:
- Correct answers of today’s questions will be provided in next day’s DNA section. Kindly refer to it and update your answers.
Q.1 consider the following statements regarding Botanical Survey of India (BSI):
- It is the apex research organization under the Ministry of Science and technology
- It carries out taxonomic and floristic studies on wild plant resources of the country.
Select the correct answer from the codes given below:
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Q.2 Pradhan Mantri Kaushal Vikas Yojana is implemented by Which of the following?
- Ministry of education
- Ministry of minority affairs
- Ministry of skill development and Entrepreneurship
- None of the above
Q.3 Which one of the following is the boundary between India and Sri Lanka ?
- Gulf of Mannar
- Palk bay
- Palk Strait
- Malacca Strait
ANSWERS FOR 20th Sept 2021 TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE (TYK)
| 1 | C |
| 2 | B |
| 3 | C |
Must Read
On Hate Speech:
On AUKUS and India:
On Earth Observation Satellites:











