IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
Archives
(PRELIMS + MAINS FOCUS)
Annual Status of Education Report (ASER) 2021
Part of: Prelims and GS II – Education
Context Annual Status of Education Report (ASER) 2021 was recently released.
- The ASER survey was facilitated by the NGO, Pratham.
Key findings of the report
- Pandemic effect: The percentage of rural children who were not enrolled in school doubled during the pandemic.
- Increase in enrolment: Government schools saw an increase in enrolment at the expense of private schools.
- Government school enrolment spiked significantly from 64.3% in 2018 to 70.3% in 2021, while private school enrolment dropped from 32.5% to 24.4% over the same period.
- Reasons for enrolment shift: Financial distress, the closure of affordable private schools and the movement of migrants to rural areas
-
- Never attended school: Over a third of children enrolled in Classes 1 and 2 have never attended school in person.
- Lack of learning resources: While 92% of children had textbooks for their grade, only one third of them had access to any other learning resources or support.
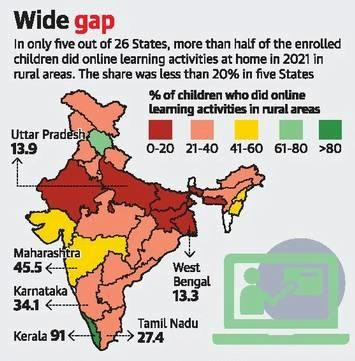
- Limited smartphone availability: With smartphone availability and access limited, online learning was restricted to a quarter of students.
- Varied experiences: 91% of students from Kerala and almost 80% from Himachal Pradesh had online education, but only 10% from Bihar and 13% from West Bengal.
- Private tuition: 40% of the school children are now opting for private tuition classes compared to 30% in 2018. This proportion has increased across both sexes and all grades and school types. The incidence of tuition has increased across all States except Kerala.
Suggestions
- Government schools and teachers are equipped and given the necessary resources for this surge in enrolment.
Sabz Burj
Part of: Prelims and GS-I – Medieval history; Art and culture
Context Sabz Burj, one of Delhi’s earliest Mughal-era monuments, has been conserved and restored over the last four years using traditional materials and building-craft techniques favoured by 16th century craftsmen.
About Sabz Burj (“Green Dome”)
- It is an octagonal tomb situated beside Humayun’s Tomb, New Delhi.
- Some Mughal historians consider the Sabz Burj tomb constructed to be for Fahim Khan, who died in 1626 A.D. He was an attendant to Abdur Rahim Khan during 4th Mughal emperor Jahangir’s reign. But others have opined that it was made in 1530–40.
- The Archaeological Survey of India (ASI) has renovated the structure.
- The structure is crowned with a blue dome and it is popularly known as the Neeli (“Blue”) chhatri
- It is of immense significance due to the ceiling on its double dome structure painted in pure gold and lapis and revealed after conservation efforts began. It is thought to be the earliest surviving painted ceiling for any monument in India.

India to hold first 2+2 with Russia
Part of: Prelims and GS-II – International relations
Context India and Russia shall hold their first “2+2” format talks in December.
- A number of agreements on defence, science and technology and trade are expected to be announced.
- A “fundamental change” in the defence relationship since 2018 has taken bilateral contracts from $2-3 billion per year to $9-10 billion, making Russia India’s “top defence partner”.
Significance
- The 2+2 format is particularly significant since India conducts joint foreign and defence ministerial meetings only with its closest ‘Quad’ partners — the U.S., Japan and Australia.
- The 2+2 is also expected to look further afield in building India’s ties with Central Asia and Russia’s engagement in the Indo-Pacific.
Russian 2+2
- Russia thus far has the 2+2 format for “problem solving” with countries such as Japan, France and earlier with the U.S.
Defence deals awaiting conclusion
- Two major defence deals awaiting conclusion are the AK-203 assault rifles and the Igla-S very short range air defence systems.
- India and Russia are expected to sign the Reciprocal Exchange of Logistics Support Agreement and a Navy-to-Navy cooperation MoU.
World Bank’s STARS project
Part of: Prelims and GS-II – Education
Context Performance of World Bank aided project STARS was reviewed recently.
What is STARS?
- STARS stands for Strengthening Teaching-Learning and Results for States Program (STARS).
- It is a new Centrally Sponsored Scheme
- Ministry: Department of School Education and Literacy, Ministry of Education.
- Objective: To improve the quality and governance of school education in six Indian states.
- Six states are– Himachal Pradesh, Kerala, Madhya Pradesh, Maharashtra, Odisha, and Rajasthan.
- Beneficiaries: Some 250 million students (between the age of 6 and 17) in 1.5 million schools, and over 10 million teachers will benefit from the program.
Reform initiatives under the project include
- Focusing more directly on the delivery of education services by providing customized local-level solutions.
- Addressing demands from stakeholders, especially parents, for greater accountability; giving special attention to students from vulnerable section.
- Equipping teachers to manage this transformation.
- Recognizing that teachers are central to achieving better learning outcomes.
- Investing more in developing India’s human capital needs by strengthening foundational learning for children.
Norovirus
Part of: Prelims and GS-II – Health
Context Recently, several cases of Norovirus have been reported in the state of Kerala.
About Norovirus
- It is the most common cause of gastroenteritis.
- It is a bug similar to the diarrhoea-inducing rotavirus and it infects people across age groups.
- Disease outbreaks typically occur aboard cruise ships, in nursing homes, dormitories, and other closed spaces.
- The initial symptoms: vomiting and/or diarrhoea, which show up one or two days after exposure to the virus.
- Nausea, abdominal pain, fever, headaches and body aches.
- In extreme cases, loss of fluids could lead to dehydration.
- It normally lasts only two or three days.
- It is highly contagious, and can be transmitted through contaminated food, water, and surfaces. The primary route is oral-faecal.
- It is resistant to many disinfectants and heat up to 60°C. The virus can also survive many common hand sanitisers.
- About one out of every five cases of acute gastroenteritis worldwide is caused by Norovirus.
- Diagnosis is done by real-time reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction.
- No vaccines are available for the disease.
(News from PIB)
NaVIC
Part of: GS Prelims
Navigation with Indian Constellation (NAVIC) is India’s indigenous global navigation satellite system.
- NAVIC consists of a constellation of three geostationary, four geosynchronous and two on-standby satellites.
- NAVIC will facilitate accurate real-time positioning and timing services over India and the region around it extending to 1,500 km.
Applications of NAVIC
- Terrestrial, aerial and marine navigation
- Disaster management
- Vehicle tracking and fleet management
- Integration with mobile phones
- Precise timing, mapping and geodetic data capture
- Terrestrial navigation aid for hikers and travelers
- Visual and voice navigation for drivers
News Source: PIB
USOF scheme
Part of: GS Prelims
In News: The Union Cabinet has given its approval for provisioning of mobile services in Uncovered Villages of Aspirational Districts across five States of Andhra Pradesh, Chhattisgarh, Jharkhand, Maharashtra & Odisha.
- The Project envisages to provide 4G based mobile services in the 7,287 uncovered villages of 44 Aspirational Districts across five States of Andhra Pradesh, Chhattisgarh, Jharkhand, Maharashtra & Odisha
- The project would be funded by Universal Service Obligation Fund (USOF)
- The work related to provision of 4G mobile services in identified uncovered villages will be awarded through open competitive bidding process as per extant USOF procedures.
Key benefits:
- Enhance digital connectivity useful for self-reliance,
- Facilitate learning,
- Dissemination of information and knowledge,
- Skill upgradation and development,
- Disaster management,
- E-Governance initiatives,
- Establishment of enterprises & e-commerce facilities,
- Provision of adequate support to educational institutes for knowledge sharing
- Availability of job opportunity
- Fulfilling the vision of Digital India promoting domestic manufacturing
- Fulfilling the objectives of Atmanirbhar Bharat
News Source: PIB
(Mains Focus)
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY/ INTERNATIONAL
- GS-2: Science and Technology- developments and their applications and effects in everyday life
- GS-2: Effect of policies and politics of developed and developing countries on India’s interests.
Russian ASAT test and its implications
Context: Russia has carried out an Direct-Ascent Anti-Satellite (DA-ASAT) test by shooting down an old satellite which has created a huge debris in the low earth orbit, according to the U.S. space command.
What is the test and its significance?
- According to the US space command, Russia has conducted the DA-ASAT test to shoot down an old Soviet Tselina-D SIGINT satellite, Kosmos-1408, which was launched in 1982 and had been dead for a long time.
- The test so far has generated more than 1,500 pieces of trackable orbital debris and will likely generate hundreds of thousands of pieces of smaller orbital debris.
- While Russia has previously tested ASAT weapons, the DA-ASAT is more advanced and similar to the ones the US has in its inventory.
- ASAT weapon gives the capability to destroy satellites in orbit disrupting the communications and surveillance capabilities of adversaries.
- Only a handful of countries have successfully demonstrated ASAT capability – China, India, Russia and U.S.
What is the assessment and the reaction?
- US condemned Russia’s reckless test of a direct-ascent anti-satellite missile against its own satellite, creating space debris that risks astronauts’ lives, the integrity of the International Space Station, and the interests of all nations.
- The debris created by Russia’s DA-ASAT will continue to pose a threat to activities in outer space for years to come, putting satellites and space missions at risk, as well as forcing more collision avoidance maneuvers.
- Initial assessment by USSPACECOM is that the debris will remain in orbit for years and potentially for decades, posing a significant risk to the crew on the International Space Station and other human spaceflight activities, as well as multiple countries’ satellites.
- US also stated that Space activities underpin our way of life and such kind of behaviour is being considered as irresponsible.
- US attacked Russia by stating that Russia is developing and deploying capabilities to actively deny access to and use of space by the United States and its allies and partners.
What is the threat to the International Space Station?
- Due to the debris generated by the “destructive” Russian test, ISS astronauts and cosmonauts undertook emergency procedures for safety, National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) Administrator Bill Nelson said in a statement. There are currently seven astronauts on the ISS.
- National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) Administrator stated that “With its long and storied history in human spaceflight, it is unthinkable that Russia would endanger not only the American and international partner astronauts on the ISS, but also their own cosmonauts”.
- Their actions are reckless and dangerous, threatening as well the Chinese space station and the taikonauts on board.
- However, Russian Astronaut Anton Shkaplerov currently on the ISS tweeted “Friends, everything is regular with us! We continue to work according to the program.”
Connecting the dots:
- Space Exploration in the era of Privatisation
- IN-Space: Growing Private role
- UN Outer Space Treaty
- Gaganyaan Mission of ISRO
ECONOMY/ GOVERNANCE
- GS-3: Energy
- GS-2: Government policies and interventions for development in various sectors and issues arising out of their design and implementation.
Decarbonisation of India’s Power Sector
Context: Prime Minister Narendra Modi’s announcement of enhanced targets for climate action by India, particularly for achieving net-zero emissions by 2070, has highlighted the importance of long-term planning for decarbonising the economy.
What precautions needs to be taken to achieve net-zero emission goal by 2070?
- By 2070, there will be many changes in technology, environmental conditions, and the economy.
- The planning horizon of about 50 years will need to be broken up into shorter periods so that new knowledge about emerging technologies can be incorporated into plans.
- In addition, plans will need to be monitored so that the course can be corrected to respond to any unforeseen problems. Five years, as the UK has used, seems like a reasonable “Goldilocks ideal.”
- For setting interim targets and monitoring progress, an autonomous and technically credible agency, like the Climate Change Committee (CCC) in the UK, should be set up.
- The agency would provide independent advice to the government on setting and meeting both long-term and interim (five-year) targets that are ambitious but also achievable. It would also monitor progress and annually report and suggest mid-course corrections.
Decarbonisation of Power Sector
- Decarbonisation is the process of reducing the amount of carbon, mainly carbon dioxide (CO2), sent into the atmosphere.
- The shorter-term targets announced by the PM to be reached by 2030 refer mostly to the power sector. This is appropriate because it is the biggest source of GHG emissions and also the easiest one to decarbonise.
- In order to decarbonise the power sector, it would be best to have a single emissions-related objective so that an optimal strategy can be developed to achieve the objective at the lowest cost.
- Reducing emission intensity is a good overarching objective; increased use of RE or non-fossil-fuel generation is a means to that end.
- Setting permissible emission intensity in terms of grammes of carbon dioxide equivalent per kWh of electricity sold, applied to all load-serving entities, would be a good option for targets in the power sector.
- There is a profusion of separate targets for almost every resource used to generate electricity. Such an approach reduces the flexibility of distribution companies to select resources to meet their loads, resulting in a non-optimal resource mix, and a higher cost of electricity.
Conclusion
The use of five-year interim targets for permissible emission intensity and the establishment of an autonomous and credible agency to advise the government on targets and policies and to monitor progress will greatly facilitate an effective, economic, and smooth transition to decarbonisation of the power sector first, and the Indian economy later by 2070.
Connecting the dots:
(All India Radio: Azaadi ka Safar)
Nov 16: Birsa Munda – https://youtu.be/Od6nKnUWzTs
TOPIC:
- GS-1: Freedom fighters
Context: As India celebrates Azadi Ka Amrit Mahotsav, one name stands tall among the galaxy of stars who fearlessly worked for the freedom of the motherland against the oppressive British Raj — Bhagwan Birsa Munda. Birsa Munda lived a short — just 25 years — but valiant life. His life story, full of gallant efforts to fight injustice and oppression, represents a strong voice of resistance against colonialism.
- 5th of November is the birth anniversary of the fearless freedom fighter and tribal hero, Birsa Munda.
- The state of Jharkhand was created on his birth anniversary in the year 2000.
Background
- Born at Ulihatu village in Khunti district of Jharkhand on 15 November, 1875.
- Birsa belonged to the ‘Munda’ tribe of Chota Nagpur region.
- Birsa received his education in Salga under the guidance of his teacher Jaipal Nag. Later, Birsa converted into a Christian to join the German Mission School but soon dropped out after finding out that Britishers were aiming to convert tribals to Christianity through education.
- After dropping out of school, Birsa Munda created a faith called ‘Birsait’.
- Members of the Munda community soon started joining the faith which in turn became a challenge for the British conversation activities.
Birsa’s beliefs and his fight against Britishers
Fondly called ‘Dharti Abba’ or Father of the Earth, he encouraged his followers to get back to their tribal roots and follow their traditions. Birsa believed that self-rule is the only way to protect tribal rights. He raised the slogan “Abua raj seter jana, maharani raj tundu jana” which means ‘Let the Kingdom of the Queen be ended and create our own kingdom’. It became one of the famous slogans which helped to organise Birsa’s guerrilla army and attack the British army in different parts of Chota Nagpur region.
Though he lived a short span of life, Birsa Munda is known to have mobilised the tribal community against the British and had also forced the colonial officials to introduce laws protecting the land rights of the tribals.
Spearheaded movement against British oppression giving a call for ‘Ulgulan’ or the Great Tumult (Revolution).
Munda Revolt: In the late 1890s, Birsa set out to abolish the feudal system that the British had introduced in the Adivasi forest land.
- Under this system, the British invited migrants from other states to take over work on tribal land, while they usurped all the profits. Thus, the original owners were left bereft of their land and any means of livelihood.
- In March 1900, while fighting the British alongside his guerilla army, Birsa was arrested in Jamkopai forest in Chakradharpur. A few months later, he passed away in custody. The icon of India’s Independence struggle attained martyrdom on 9 June at the age of 24.
- Almost a decade after his death, the British introduced the Chhotanagpur Tenancy Act (CNT), which prohibits the transfer of tribal land to non-tribal parties.
Birsa’s achievements as a young tribal revolutionary has continued to be celebrated over decades now and he has successfully carved out a space for himself in popular and folk literature, academia, and mass media.
Janjatiya Gaurav Divas: 15th November, the birth anniversary of Bhagwan Birsa Munda
- The declaration acknowledges the glorious history and cultural heritage of tribal communities.
- The day will be celebrated every year and would recognize the efforts of the tribals for preservation of cultural heritage and promotion of Indian values of valour, hospitality and national pride.
Birsa Munda museum: In Ranchi
Can you answer the following question:
- Contribution of Birsa Munda to India’s freedom struggle
(TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE)
Model questions: (You can now post your answers in comment section)
Note:
- Correct answers of today’s questions will be provided in next day’s DNA section. Kindly refer to it and update your answers.
Q.1 The structure of the monument is crowned with a blue dome and it is popularly known as the Neeli (“Blue”) chhatri. It is of immense significance due to the ceiling on its double dome structure painted in pure gold and lapis which is thought to be the earliest surviving painted ceiling for any monument in India.
Which of the following monument is mentioned above?
- Humayun Tomb
- Safdarjung Tomb
- Bibi ka Maqbara
- Sabz Burj
Q.2 World Bank’s STARS project is associated with Which of the following?
- Exploration to Mars
- Education
- Tribal welfare
- Poverty alleviation
Q.3 Consider the following statements regarding Norovirus:
- It is the rarest cause of gastroenteritis.
- Vaccine is given at infancy to prevent the disease.
Select the correct answer from the following codes:
- Only 1
- Only 2
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
ANSWERS FOR 17th Nov 2021 TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE (TYK)
| 1 | B |
| 2 | B |
| 3 | C |
Must Read
On Private sector and Healthcare:
On criticism of Collegium system:
On Digital Divide in Education:












