IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
Archives
(PRELIMS + MAINS FOCUS)
First Colombo Security Conclave
Part of: Prelims and GS-II -International Relations
Context: The first Colombo Security Conclave Virtual Workshop on “Developing Regional Cyber Security Capabilities on Defensive operations, Deep/Dark Web handling and Digital Forensics” was hosted recently.
Key takeaways
- Hosted by: National Security Council Secretariat (NSCS) in association with National Forensics Science University, Gandhinagar (Gujarat) and the Secretariat of the Colombo Security Conclave
- Delegates from Member and Observer States of the Colombo Security Conclave (CSC) including Sri Lanka, Maldives, India, Mauritius, Seychelles, and Bangladesh participated in the workshop.
- Members and Observer States had agreed on four pillars of cooperation
- Maritime Safety and Security,
- Terrorism and Radicalization,
- Trafficking and Organized Crime and Cyber Security and
- Protection of Critical Infrastructure.
What is Colombo Security Conclave?
- The decision to establish Colombo Security Conclave was taken in November 2020 at the NSA-level meeting of India, Sri Lanka, and the Maldives to forge closer cooperation on maritime and security matters among the three Indian Ocean countries.
- The idea of ‘Colombo Security Conclave’ was initiated by President Gotabaya Rajapaksa in 2011.
News Source: ANI
‘Sea to Sea ’ Variant Of BrahMos Missile
Part of: Prelims and GS-III Defence and Security
Context: India successfully tested advanced sea to sea variant of BrahMos Supersonic Cruise missile from INS Visakhapatnam.
Indian Navy’s newest indigenously-built guided missile destroyer represents a twin achievement:
- Certifies the accuracy of the ship’s combat system and armament complex
- Validates a new capability the missile provides the Navy and the Nation
About BrahMos Supersonic Cruise Missile
- BrahMos, deployed by the Navy on its warships first in 2005, has the capability to hit sea-based targets beyond radar horizon.
- Capable of being launched from land, sea, sub-sea and air against surface- and sea-based targets
- The missiles, fired at a speed of 2.8 Mach or nearly three times the speed of sound, significantly increase the capability of the ships in engaging long-range targets.
- The name BrahMos is a portmanteau formed from the names of two rivers, the Brahmaputra of India and the Moskva of Russia.
- It is the world’s fastest anti-ship cruise missile currently in operation.
- BrahMos missiles are designed and developed by BrahMos Aerospace, a joint venture company set up by Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) and Mashinostroyenia of Russia
News Source: The Hindu
India’s passport rank improves to 83 from 90
Part of: Prelims and GS-II – International Relations
Context: India’s passport power has improved this quarter compared to 2021.
- Japan and Singapore top the index.
- India ranks at 83rd position in the Henley Passport Index, climbing seven places from 90th rank last year.
Do you know?
- Since 2005, Henley Passport Index ranks world’s passports according to the number of destinations their holders can access without prior visa and is based on data from International Air Transport Association (IATA).
Growing disparity
- India now has visa-free access to 60 destinations worldwide with Oman and Armenia being the latest additions.
- India has added 35 more destinations since 2006.
- The overall increase marks a growing disparity between countries in the global north and those in the global south.
News Source: The Hindu
Transgender Prisoners
Part of: GS-I – Social issues
Context: The Ministry of Home Affairs (MHA) has written to all States to ensure separate accommodation for transgender persons in prisons.
Key takeaways
- Advised the States and the Union Territories that the prison admission register may be suitably revised to include “transgender” as a category other than male and female gender.
- Similar provision may be made in the Prison Management System in maintaining electronic records.
- The government enacted the Transgender Persons (Protection of Rights) Act in 2019 and the advisory was sent to ensure their safety and to protect them against any form of exploitation in the context of prisons and correctional facilities.
- However, while making provision for a separate enclosure for transgender prisoners, due care may be taken by the prison authorities that this may not result in their complete isolation or propagate social stigma among such prisoners.
- There should also be adequate preservation of right to privacy and dignity in regard to separate toilets for transmen and transwomen as well as shower facilities.
- Physical search of a transgender person may be conducted by a person of their preferred gender or by a trained medical professional or a paramedic.
- At the stage where the search procedure requires stripping, it must be done in a private room or partition.
News Source: The Hindu
(News from PIB)
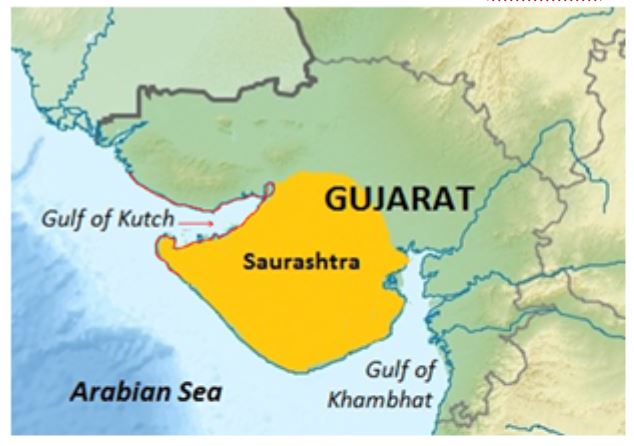
Deendayal Port:
Crosses the 100 Million Mark
- Kandla, officially Deendayal Port, is a seaport and town in Kutch district of Gujarat state, located on the Gulf of Kutch.
About Gulf of Kutch
- An inlet of the Arabian Sea along the west coast of India, in the state of Gujarat
- Divides Kutch and the Kathiawar peninsula regions of Gujarat; the Rukmavati River empties into the Arabian Sea nearby. Gulf of Khambhat lies in south and the Great Rann of Kutch is located in north of the gulf.
- Renowned for extreme daily tides thus, making it a region with highest potential of tidal energy generation.
- Is referred to in the Periplus of the Erythraean Sea, a travelogue written in about 50 CE, as the Gulf of Baraca
- One of the four major coral reef areas – the first coral garden will be set up near Mithapur in the Gulf of Kutch
- Facing incidences of coral bleaching
- Bleached corals are likely to have reduced growth rates, decreased reproductive capacity, increased susceptibility to diseases and elevated mortality rates]
- Coral bleaching and associated mortality not only have negative impacts on coral communities, but they also impact fish communities and the human communities that depend on coral reefs and associated fisheries for livelihoods and wellbeing.
- Coral colonies provide a source of food and shelter for countless reef-associated organisms and their health is of critical importance to the ecology of the reef community.
- Dugong (Vulnerable), also called the sea cow, is found here
- Issues being faced: Extraction of corals and sands by cement industries, increased turbidity of water, oil refineries, chemical industries and mechanized fishing boats.
Map link: https://medcraveonline.com/IJAWB/images/IJAWB-03-00108-g001.png
News Source: PIB
India – South Korea Trade Talks
Part of: Mains GS-2: India and its neighbourhood- relations.
Context: India-Republic of Korea (RoK) relations has made great strides in recent years and has become truly multidimensional, spurred by a significant convergence of interests, mutual goodwill and high level exchanges.
- India Korea aim to achieve the trade target of USD 50 Billion before 2030.
- Both the countries have agreed to
- Impart fresh momentum to the discussions on CEPA up-gradation negotiations and address difficulties expressed by industry from both sides
- Promote extensive B2B interactions on trade and investment between the Industry leaders of the two countries.
- Highlighted the difficulties the bovine meat exports are facing in South Korea.
A brief history of India-South Korea Relation
- During the Korean War (1950- 53), India has played a major role in cease-fire agreement signed between both the warring sides and the ceasefire was declared on 27 July 1953.
- The relationship did not move much till 1990s due to South Korea’s closeness to US and India either following non-aligned or under Russian influence
- The economic relation between India and South Korea grew after economic reforms in India which led to signing of Comprehensive Economic Partnership Agreement (CEPA) in 2010
- Relations between India and South Korea was raised to the level of Strategic Partnership in January 2010 and upgraded to Special strategic partnership in 2015
- India has a major role to play in South Korea’s Southern Policy under which Korea is looking at expanding relations beyond its immediate region.
- Similarly, South Korea is a major player in India’s Act East Policy under which aims to promote economic cooperation, cultural ties and develop strategic relationships with countries in the Asia-Pacific.
Comprehensive Economic Partnership Agreement (CEPA)
- A free trade agreement between two countries
- Covers negotiation on the trade in services and investment, and other areas of economic partnership such as trade facilitation and customs cooperation, competition, and Intellectual Property Rights.
- CEPA also looks into the regulatory aspect of trade and encompasses an agreement covering the regulatory issues.
News Source: PIB
(Mains Focus)
ECONOMY/ GOVERNANCE
- GS-3: Economy, development & its challenges
- GS-2: Governance & its challenges
Planetary Pressure Adjusted HDI
Context: The 2020 Human Development Report of UNDP, titled “The Next Frontier – Human Development and the Anthropocene” proposed a planetary pressure-adjusted Human Development Index (HDI).
- Ever since the UNDP took up computation of the HDI driven by the vision of Mahbub ul Haq and articulated by Amartya Sen in 1990, there have been adjustments such as inequality-adjusted HDI.
- Besides, there was computation of several other indices such as Gender Development Index, Gender Inequality Index, and Multidimensional Poverty Index to flag the issues that warranted the attention of policymakers.
What is the purpose of Planetary Pressure Adjusted HDI (PHDI)?
- The environment is one such issue now considered to be an essential component to be factored in to measure human development.
- The concept of the planetary boundary was introduced by a group of scientists across the world, led by J. Rockström of the Stockholm Resilience Centre in 2009.
- It is how established that human-induced environmental change can irrevocably destabilise the long-term dynamics of the earth system, thereby disrupting the life-supporting system of the planet.
- Both global and local evidence indicate that biodiversity loss, climate change, land system/land-use change, disruption of biogeochemical cycles, and scarcity of freshwater availability are a threat and increase the vulnerability of society.
- The purpose of the planetary pressure adjusted HDI, or PHDI, is to communicate to the larger society the risk involved in continuing with existing practices in our resource use and environmental management, and the retarding effect that environmental stress can perpetuate on development.
What will be the impact on country rankings due to PHDI?
- When planetary pressure is adjusted, the world average of HDI in 2019 came down from 0.737 to 0.683. This adjustment has been worked out by factoring per capita carbon dioxide (CO2) emission (production), and per capita material footprint.
- The average per capita global CO2 emission (production) is 4.6 tonnes and the per capita material footprint is 12.3 tonnes.
- The global ranking of several countries was altered, in a positive and negative sense, with adjustment of planetary pressure.
- Switzerland is the only country in the group of high human development countries whose world rank has not changed with adjustment of planetary pressure, although the HDI value of 0.955 has come down to 0.825 after the necessary adjustment.
- Among 66 very high human development countries, 30 countries recorded a fall in rank values. It succinctly brings out the nature of planetary pressure generated by the developed countries and indirectly indicates their responsibility in combating the situation.
- In the case of India, the PHDI is 0.626 against an HDI of 0.645 with an average per capita CO2 emission (production) and material footprints of 2.0 tonnes and 4.6 tonnes, respectively.
- India gained in global rankings by eight points (131st rank under HDI and 123rd rank under PHDI), and its per capita carbon emission (production) and material footprint are well below the global average.
What are the challenges in India?
- India’s natural resource use is far from efficient, environmental problems are growing, and the onslaught on nature goes on unabated.
- At the same time, India has 27.9% people under the Multidimensional Poverty Index ranging from 1.10% in Kerala to 52.50% in Bihar, and a sizable section of them directly depend on natural resources for their sustenance.
- The twin challenges of poverty alleviation and environmental safeguarding that former Prime Minister Indira Gandhi first articulated in her lecture during the Stockholm conference on the human environment in 1972 still remain unattended. In fact, the situation is much more complex now.
- Any standalone environmental safeguarding actions are not sufficient to navigate the Anthropogenic caused planetary pressures.
- It is now well established that there are interdependencies of earth system processes including social processes, and their relationships are non-linear and dialectic.
- Therefore, the central challenge is to nest human development including social and economic systems into the ecosystem, and biosphere building on a systematic approach to nature-based solutions that put people at the core.
What should be the way forward?
- It is now essential to consider people and the planet as being a part of an interconnected social-ecological system.
- Social and environmental problems cannot be addressed in isolation anymore; an integrated perspective is necessary.
- This can be conceived and addressed at the local level, for which India has constitutional provisions in the form of the 73rd and 74th Amendments.
- What is required is a reorientation of the planning process, adoption of a decentralised approach, a plan for proper institutional arrangements, and steps to enable political decisions.
Connecting the dots:
(TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE)
Model questions: (You can now post your answers in comment section)
Q.1. Which of the following is/are true regarding Colombo Security Conclave?
- The decision to establish Colombo Security Conclave was taken between countries India, Sri Lanka, and the Maldives to forge closer cooperation on maritime and security matters among the three Indian Ocean countries.
- The idea of ‘Colombo Security Conclave’ was initiated by Indian Prime Minister Manmohan Singh in 2011.
Select the correct answer:
- Only 1
- Only 2
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Q.2 Consider the following statements regarding ‘Sea to Sea’ Variant Of BrahMos Missile:
- This version of the missile has been designed to launch either in a vertical or a horizontal mode from moving/stationary assets to target both land and sea targets.
- The missiles, fired at a speed of 2.8 Mach, significantly increase the capability of the ships in engaging long-range targets.
Which of the above is or are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Q.3 National Portal for Transgender Persons is launched by which of the following?
- Ministry of Home Affairs
- Ministry of Social Justice & Empowerment
- National Human Rights Commission
- NITI Aayog
ANSWERS FOR 12th Jan 2022 TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE (TYK)
| 1 | A |
| 2 | C |
| 3 | B |
Must Read
On vigilante justice:
On extending GST compensation:
On Hate Speech:











