IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
Archives
(PRELIMS & MAINS Focus)
Syllabus
- GS-3: Infrastructure, Defence
In News: The strategically-significant Sela Tunnel project in Arunachal Pradesh is nearing completion.
- Located in
- West Kameng district of Arunachal Pradesh
- Will provide an alternate axis to the Sela pass (at 13,700 feet)
- On the BCT Road – the Balipara, Charduar and Tawang axis (more than 300 km long)
- Being executed by: Border Roads Organisation
- Includes two tunnels and a link road; Tunnel 2 will be one of the longest tunnels to have been constructed above an altitude of over 13,000 feet.
- The total length of the project, including the tunnels, the approach and the link roads, will be around 12 km.
Why does the project matter?
- All-weather connectivity to Tawang and other forward areas in the sector
- Will provide a new alignment on the axis towards the LAC, and allow movement of military and civil vehicles all through the year (Sela pass stays closed for a few winter months).
- Reduction in more than one hour of travel time from Tezpur to Tawang and travellers avoiding dangerous snow covered Sela top at a height of 13,700 feet.
All weather connectivity to Tawang would be a game-changer for the local population ahead of Sela apart from the much-required strategic edge for our security forces.
Source: Indian Express
Syllabus
- Prelims: Science & Technology
- GS-3: Security
Context: After a high-level security review for the forthcoming Amarnath Yatra, the government has decided to track all pilgrims using Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) tags. The decision has been taken amid heightened security threat to the pilgrimage.
Radio Frequency Identification
- It’s a wireless tracking system that consists of tags and readers.
- Radio waves are used to communicate information/identity of objects or people to nearby readers – devices that can be hand-held or built into fixed positions like poles or buildings.
- The tags can carry encrypted information, serial numbers and short descriptions.
- There are also high-memory tags like the ones designed for use in the aviation industry.
Types of RFID
- Active RFIDs use their own power source, mostly batteries. Active tags can ping information every few seconds like beacons, or they can get activated when a reader is in the proximity.
- Passive RFIDs are activated through the reader using the electromagnetic energy it transmits. This is enough power for the tag to transmit information back to the reader. Active tags have a longer read range, around 300 ft, compared to passive tags.
How do RFIDs work?
- RFID tags use an integrated circuit and an antenna to communicate with a reader using radio waves at several different frequencies – low frequency (LF), high frequency (HF), and ultra-high frequency (UHF).
- The message sent back by the tag in form or radio waves is translated into data and analysed by the host computer system. Unlike Barcodes, RFIDs do not require direct line of sight to identify objects. They also have a bigger range.
Usage: Retail giants use them for inventory tracking. RFID chips are used as access keys in labs. They are also built into credit cards and library books. FastTags being used for toll payments across the country are also RFID tags.
Is it possible to hack RFID tags?
- Depending on data to be shared, grades of encryption can be introduced between the tag and the reader to verify credentials.
- Memory segments of the card can hold data encrypted with cryptographic keys.
- While a casual data theft is not possible, hackers can use ‘side-channel attacks’ to extract the cryptographic information.
- But that hack is not easy to pull off given that tag manufacturers continue to improve security features.
Source: Indian Express
Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Q.1) With reference to visible light communication (VLC) technology, which of the following statements are correct? (2020)
- VLC uses electromagnetic spectrum wavelengths 375 to 780nm
- VLC is known as long-range optical wireless communication
- VLC can transmit large amounts of data faster than Bluetooth
- VLC has no electromagnetic interference
Select the correct code:
- 1, 2 and 3 only
- 1, 2 and 4 only
- 1, 3 and 4 only
- 2, 3 and 4 only
Q.2) With reference to communication technologies, what is/are the difference/differences between LTE (Long-Term Evolution) and VoLTE (Voice over Long-Term Evolution)?(2019)
- LTE is commonly marketed as 3G and VoLTE is commonly marketed as advanced 3G.
- LTE is data-only technology and VoLTE is voice-only technology.
Select the correct code:
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Syllabus
- Prelims – Geography
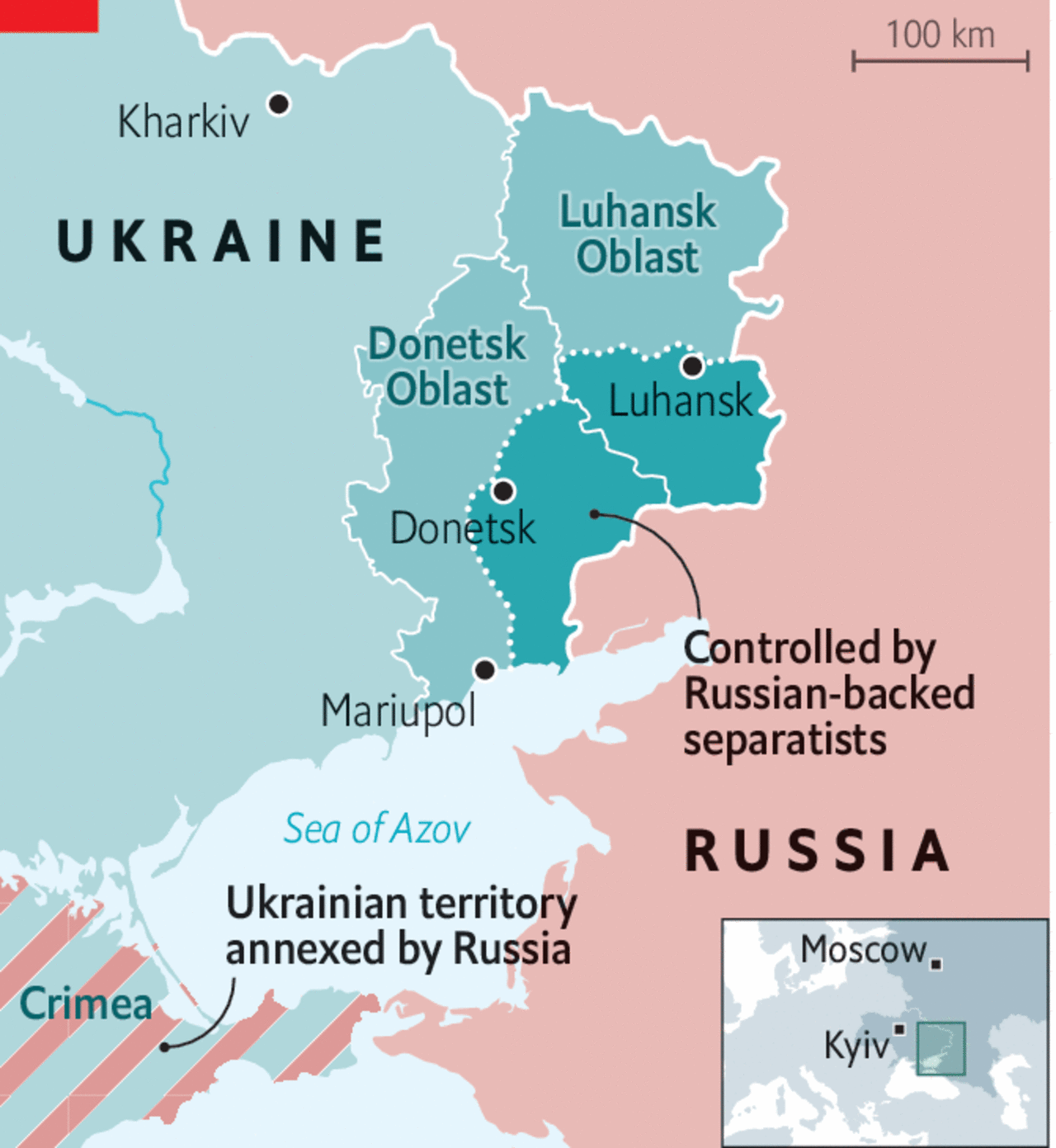
Why in News: It has become the most heavily bombed and damaged city in Ukraine’s war with Russia
About
- It is a city in Ukraine, on the north coast of the Sea of Azov at the mouth of the Kalmius river, in the Pryazovia region.
- While internationally recognized as in Ukraine, the city is under the de facto administration of the Donetsk People’s Republic.
Taking the port city would be a strategic win for Russia – and a major blow for Ukraine:
- If Mariupol was seized, Russia would also end up with full control of more than 80% of Ukraine’s Black Sea coastline – cutting off its maritime trade and further isolating it from the world.
- Mariupol is a key export hub for Ukraine’s steel, coal, and corn going to customers in the Middle East and beyond.
Syllabus
- Prelims – Geography
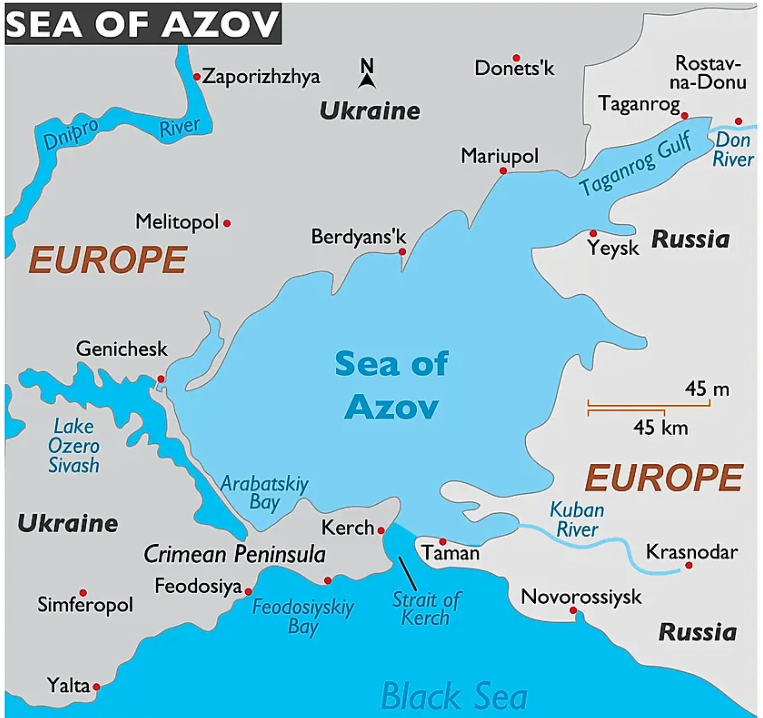
Sea of Azov
- A sea in Eastern Europe connected to the Black Sea by the narrow (about 4 km or 2.5 mi) Strait of Kerch
- Sometimes regarded as a northern extension of the Black Sea.
- The sea is bounded by Russia on the southeast and by Ukraine on the northwest.
- It is the shallowest sea in the world.
Syllabus
- GS-2: Governance
- GS-3: Energy
Why in News: In a knee-jerk reaction to the ongoing power shortage crisis, the Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change has eased environmental norms for coal mining.
- Granted some coal mines an exemption from environmental clearance and public consultation for an expansion by a further 10% of their existing capacity. This is a further relaxation of an earlier exemption that granted expansion of up to 40%.
- The move: a special dispensation to counter the coal shortage to meet the ongoing steep rise in power demand.
Coal accounts for nearly 75 per cent of India’s power generation and power plants account for over three-fourths of the over one billion tonnes of annual coal consumption.
Current Situation
India’s electricity demand jumped 15% in April 2022 compared to the same month in 2021.
- A bounce-back in demand – With office spaces, and factories resuming in full force as Covid cases remain low, demand for electricity has spiked.
- The early onset of summer was exacerbated by record-breaking heatwaves across northern India
- Russia’s war in Ukraine disrupted trade flows and crippled supply amid additional demand from Europe.
- Record high prices of imported coal: Plants designed to operate on imported low-ash coal are suffering due to the record high prices of imported coal.
- Extremely low utilization of a total of 17GW of such plants has been another obstacle to meeting the high demand.
- The shortage of trains to transport coal is exacerbating a fuel supply crisis
- Railways face the challenge of hauling coal from mines to plants across the country over distances up to 1,500 km.
- Continues to face the pressure of managing passenger freights versus coal freights, both of which run on the same lines.
- Lack of coordination between the Ministries – Coal, Railways and Power
- Delayed payments and mounting debts in the power sector
The supply-demand mismatch has caused brownouts all across India. The current crisis has more to do with the shortage of coal stockpiles at coal-based power plants and coal transportation logistics than volumes of coal mined.
Power cuts are not the only concern at the moment.
- The rising mercury could lead to serious health complications, deaths, water shortage and more.
- Put blue-collar workers — including rickshaw drivers, street vendors, construction workers, delivery people — at greater risk since they are usually working out in the sun.
- Also leads to increased fire incidents in jungles, important buildings and hospitals
India’s Coal Production
- India’s domestic coal production grew by 8.5% to 777 million tonnes (mt) in FY22 from 716 mt in FY21.
- Coal production in April 2022 was 29% higher compared to the same month last year
- But the coal dispatch volumes only increased by 9%. Even then, plants have failed to maintain the necessary coal stockpiles.
Is it the correct move?
- Exempting coal-mine expansions from proper environmental and social impact assessment is not a long-term solution for power-supply security.
- Could have severe social and economic impacts on indigenous communities living near the coal mines as well as the flora and fauna surrounding the mines.
The Way Forward
The current crisis presents an opportunity to accelerate the commissioning of clean energy capacity.
- Policies to increase the uptake of distributed and rooftop solar PV, which could be built faster without putting pressure on transmission networks, will provide better outcomes.
- Small and medium industries (SMEs), educational institutes, banks, hospitals and residential communities will benefit from reducing their dependence on the grid and by producing their own electricity and selling some back to the grid.
- There is a strong case for the government to give a further push to distributed solar to protect India’s economic activities from frequent power outages.
- Ramping up of production capacity
- Hospitals across country should set up hospitals to set up special wards for heat stroke and other heat-related diseases.
Source: Financial Express
Syllabus
- GS-3: Indian Economy
In News: RBI has issued regulations to bridge the regulatory gaps between commercial banks and NBFCs/cooperatives.
Shadow Banks
- Traditionally, regulators have adopted a strict regulatory approach for commercial banks, but followed a light touch regulation for NBFCs. This is because banks receive deposits from general public whereas NBFCs draw their funds mainly from financial institutions primarily banks.
- As banks are much better-informed than the public, there is a belief that NBFCs need not be regulated as strictly as banks. Light regulation helps them innovate.
- The belief of different regulatory structures was turned on its head in the wake of the 2008 crisis. The losses spread to the banking system as NBFCs are connected to the overall system via a complex maze of interlinkages. The global financial system was also connected to the US financial system bringing the entire global financial system and global economy to a halt.
The global financial crisis earned a new name for the NBFCs—shadow banks
- Called so as they worked like banks but without being regulated as strictly, thus under the shadow.
- The crisis also led to lot of discussion around shadow-banking, and what could be done to bridge the regulatory gaps between banks and non-banks.
- In 2017, the Financial Stability Board, an international body that monitors and makes recommendations on the global financial system, recommended changing the name from shadow banks to non-bank financial entities.
NBFC situation in India
India faced a crisis in 2018.
- The failure of the IL&FS group put other NBFCs under the spotlight.
- The other NBFCs struggled to get funds from banks, their major source of finance. RBI does not provide direct funds to NBFCs, and thus opened a special window via banks for supporting NBFCs. Even before 2018, there has been a long history of NBFC failure and RBI efforts to regulate them.
- Post-Independence, RBI did not pay much attention to NBFCs as their share in overall financial activity was negligible. As a result, the Banking Regulation Act (1949), did not have any clause for regulating NBFCs. RBI’s thinking began to change in 1960s with failures and frauds in certain NBFCs.
- There have been multiple committees to study the NBFC sector. The committees have suggested reforms which have been mainly around strengthening capital base of the NBFCs, higher prudential norms, and so on. RBI has acted on the suggestions, but gaps have remained given the nature of the NBFC sector, due to the multiple types of NBFCs that have mushroomed over the years and are regulated by multiple type of regulators.
Regulations passed in 2021 by RBI
- Classified all its regulated NBFCs into four layers, based on size: base layer, middle layer, upper layer and top layer. This scale-based regulation allows RBI to initiate regulations based on size rather than type of NBFCs (the case earlier).
- Passed multiple regulations attempting to strengthen regulatory and compliance requirements at Middle (NBFC-ML) and Upper Layers (NBFC-UL) of NBFCs.
- Asked NBFC-UL to maintain capital equity ratio at 9%, similar to that for banks.
- Applied the large exposure framework on NBFC-UL, which minimises loans to one or more interconnected counterparties.
- Issued guidelines restricting granting loans and advances to directors and their relatives. It has also advised NBFCs to follow loan appraisal policies carefully while lending to the real estate sector.
- The central bank has come up with legal entity identifiers (LEIs), where codes are given to individual borrowers of a certain large amount. The LEIs were first applied to commercial banks and have been now extended to NBFC-UL and cooperatives.
- RBI has asked the NBFCs to appoint a chief compliance officer, similar to that of commercial banks.
Conclusion
The above reforms are welcome as they bring NBFC regulation closer to that of commercial banks. RBI has also applied these regulations at middle and upper layers NBFCs, leaving the base layer to continue evolving and innovating.
Source: Financial Express
Baba’s Explainer – Pardoning Powers
Syllabus
- GS-2: Structure, organization, and functioning of the Executive and the Judiciary
- GS-2: Federal Challenges
Why In News: Symbols of Sikh separatism that appeared at the Himachal Pradesh Assembly complex in Dharamshala suggest that forces promoting it are active and capable of mischief.
Read Complete Details on Pardoning Powers – CLICK HERE
Daily Practice MCQs
Q.1) Consider the following statements regarding ‘Non-Banking Financial Companies (NBFC)’
- None of the NBFCs can accept Time deposits.
- NBFCs can invest the money in the Share Market, unlike banks which are not allowed to do so.
- CRR does not apply to any NBFC while SLR applies only to deposit-taking NBFC.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 and 2 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 2 and 3 only
- All of the above
Q.2) Infrastructure Leasing & Financial Services (IL&FS) was recently in the news. Consider the following statements regarding IL&FS
- It is a Systemically Important Non-Deposit Core Investment Company (CIC-ND-SI).
- It is entirely owned by the Government of India.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
ANSWERS FOR 19th MAY 2022 – Daily Practice MCQs
Q.1) – c Q.2) – a












