IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
Archives
(PRELIMS & MAINS Focus)
Syllabus
- Prelims – Polity
- Mains – GS 2 (Polity)
In News: Tamil Nadu Chief Minister wrote to Prime Minister of India asking that at least three meetings of the Inter-State Council should be held every year to strengthen the spirit of cooperative federalism
Inter-State Council
Constitutional Provisions
- According to Article 263 of the Indian Constitution, an Inter-State Council (ISC) may be constituted “if it seems to the President at any time that the public interests would be served by the creation of a Council”.
- It was set up in 1990 through a presidential ordinance for the first time as per the recommendations of the Sarkaria Commission under the Ministry of Home affairs.
Inter-State Council Composition
- Prime Minister acts as the chairman of the council.
- Union Ministers of Cabinet rank in the Union
- Council of Ministers nominated by the Prime Minister.
- Chief Ministers of all states
- Chief Ministers of Union Territories having a Legislative Assembly
- Administrators of UTs not having a Legislative Assembly
- Governors of the states being administered under President’s rule
Functions of Inter-State Council
- Inter-State Council is a recommendatory body with duties to investigate and discuss the subjects of common interest between the Union and State(s) or among the States, making recommendations particularly for better coordination of policy and action on these subjects and deliberating upon such other matters of general interest to the States which may be referred to it by its Chairman
- Making suggestions on any such subject, for the better coordination of policy and action with respect to that subject
Issues
- The Council has met only once in the last six years and there has been no meeting since July 2016.
- Since its constitution in 1990, the body has met only 11 times, although its procedure states it should meet at least three times every year.
- In 2016, the meeting included consideration of the Punchhi Commission’s recommendations on Centre-State Relations that were published in 2010
Current Stats:
- The Council was reconstituted recently by the Government of India
- Headed by the PM, the Council will comprise six Union ministers, besides the Chief Ministers of the 28 states and UTs with a legislature, and administrators of UTs without a legislature.
- It will also have 10 Union ministers as permanent invitees.
- The government has also reconstituted the standing committee of the Council, with Union Home Minister as it chairman.
Source: Indian Express
Previous Year Questions
Q.1) Who among the following constitutes the National Development Council? (2013)
- The Prime Minister
- The Chairman, Finance Commission
- Ministers of the Union Cabinet
- Chief Ministers of the States
Select the correct answer using the codes given below:
- 1, 2 and 3 only
- 1, 3 and 4 only
- 2 and 4 only
- 1, 2, 3 and 4
Syllabus
- Prelims – International Organization (Current Affairs)
In News: The global money laundering and terrorist financing watchdog FATF has retained Pakistan on its terrorism financing “grey list” and asked Islamabad to address at the earliest the remaining deficiencies in its financial system
- Pakistan has been on the grey list of the Financial Action Task Force (FATF) since June 2018 for failing to check money laundering, leading to terror financing, and was given a plan of action to complete it by October 2019.
- The plenary recently decided against existing Pakistan from the category despite the country meeting 32 out of 34 action points
- Pakistan’s robust progress on its global commitments to fight financial crimes was appreciated at the concluding session
Financial Action Task Force
- An inter-governmental body established in 1989 during the G7 Summit in Paris.
- Assesses the strength of a country’s anti-money laundering and anti-terror financing frameworks.
Objectives:
- To set standards and promote effective implementation of legal, regulatory and operational measures for combating money laundering, terrorist financing and other related threats to the integrity of the international financial system.
Headquarters:
- Its Secretariat is located at the Organisation for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD) headquarters in Paris.
Member Countries:
- The FATF currently has 39 members including two regional organisations – the European Commission and Gulf Cooperation Council. India is a member of the FATF.
Lists under FATF:
Grey List:
- Countries that are considered safe haven for supporting terror funding and money laundering are put in the FATF grey list.
- This inclusion serves as a warning to the country that it may enter the blacklist.
Black List:
- Countries known as Non-Cooperative Countries or Territories (NCCTs) are put in the blacklist. These countries support terror funding and money laundering activities.
- The FATF revises the blacklist regularly, adding or deleting entries.
- Currently, Iran and Democratic People’s Republic of Korea (DPRK) are under High-risk Jurisdiction or black list.
Sessions:
- The FATF Plenary is the decision making body of the FATF. It meets three times per year.
Source: The Hindu, Indian Express
Previous Year Questions
Q.1) With Reference to the “United Nations Credentials Committee”, consider the following statements: (2022)
- It is a committee set up by the UN Security Council and works under its supervision.
- It traditionally meets in March, June and September every year.
- It assesses the credentials of all UN members before submitting a report to the General Assembly for approval.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 3 only
- 1 and 3
- 2 and 3
- 1 and 2
Syllabus
- Prelims – Ancient History
In News: Volunteers have spotted rock paintings in the Bargur Hills, Erode district, Tamil Nadu
- The place, called Rukkal Muniyappan, is where a deity of Muneeswarar is located.
- It is worshipped by tribal people, including the Sholagar, the Kurumbar and the Bedagampana Lingayat.
- A rock, 30 feet high and 250 feet in length, has paintings in red ochre and white.
- A hunting scene in red displays human figures and a herd of deer standing opposite each other, while in some images, deer of various sizes are presented.
- An anthropomorphic painting, four feet high, was seen. It looks similar to the Mother Goddess megalithic structures – Two deer and a few animals can be seen beneath the leg of the painting, which depicts the deity blessing humans with resources for hunting.
- The elephant, tiger, and deer paintings are seen separately, while the middle row has the painting of a human.
- It comprises a man standing on a crescent-shaped object and some other symbols, and is considered to be a picture of a boat ride.
- The bottom layer depicts the racial conflict between people, with three warriors opposing 10.
- The conflict between the racial groups is depicted at three more places as ethnic groups fight to dominate or rule the region.
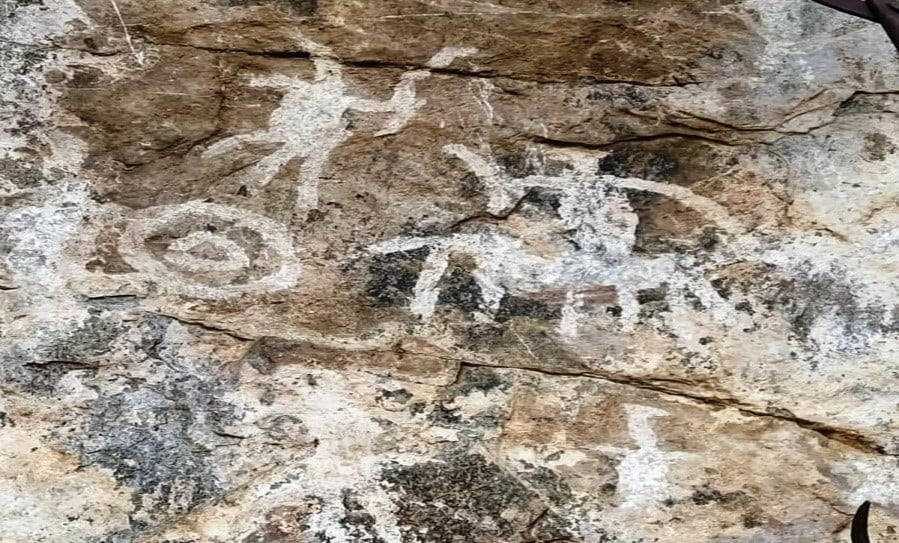
Source: The Hindu
Previous Year Question
Q.1) With reference to the history of Indian rock-cut architecture, consider the following statements: (2013)
- The caves at Badami are the oldest surviving rock-cut caves in India
- The Barabar rock-cut caves were originally made for Ajivikas by Emperor Chandragupta Maurya
- At Ellora, caves were made for different faiths.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
Syllabus
- Prelims – International Relations – Current Affairs
In News: India backs China’s plan for joint border activity
- India has supported an initiative by China to conduct a “joint border operation” in 2023 of all member countries of SCO
- The border operation called “Solidarity-2023” will be organised by China
- The Border Security Force (BSF) hosted the 21st meeting of Experts’ Group and Border Security Conference of SCO countries
- At the meeting participants exchanged information reflecting assessments of the situation on the State borders of the SCO member states, trends and forecasts of its development.
- The results of the Joint Border Operation “Solidarity-2019-2021” carried out in 2021 by the border services of the competent authorities of the SCO member states were discussed and highly appreciated.
- The plan for the preparation and conduct of the Joint Border Operation “Friendship Border – 2022, this year was reviewed and approved.
Shanghai Cooperation Organization (SCO)
- SCO is a permanent intergovernmental international organization.
- It’s a Eurasian political, economic and military organization aiming to maintain peace, security and stability in the region.
- It was created in 2001.
- The SCO Charter was signed in 2002, and entered into force in 2003.
- Founding members: Kazakhstan, China, Kyrgyzstan, Russia and Tajikistan were members of the Shanghai Five.
- Following the accession of Uzbekistan to the organization in 2001, the Shanghai five was renamed the SCO.
- India and Pakistan became members in 2017.
Structure:
- Heads of State Council – The supreme SCO body which decides its internal functioning and its interaction with other States & international organizations
- Heads of Government Council – Approves the budget, considers and decides upon issues related to economic spheres of interaction within SCO.
- Council of Ministers of Foreign Affairs – Considers issues related to day-to-day activities.
- Regional Anti-Terrorist Structure (RATS) – Established to combat terrorism, separatism and extremism.
- SCO Secretariat – Based in Beijing to provide informational, analytical & organizational support.
Official language:
- The official working language of the SCO Secretariat is Russian and Chinese.
Source: The Hindu
Previous Year Questions
Q.1) Consider the following: (2022)
- Asian Infrastructure Investment Bank
- Missile Technology Control Regime
- Shanghai Cooperation Organisation
India is a member of which of the above?
- 1 and 2 only
- 3 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
Syllabus
- Prelims – International Relations – Current Affairs
In News: The European Union has recommended that Ukraine and Moldova become candidates for membership in EU.
- If the European Commission’s decision is ratified as expected next week at a summit, it will be a morale boost for Kyiv
- This will pave a way to remove the grey zone in Eastern Europe between the EU and Russia
- And Russia has not opposed the move
European Union
- The European Union is a group of 28 countries that operate as a political and economic block.
- The EU grew out of a desire to form a single European political entity to end centuries of warfare among European countries that culminated with World War II
Governance
European Council:
- It is a collective body that defines the European Union’s overall political direction and priorities.
- It comprises of the heads of state or government of the EU member states, along with the President of the European Council and the President of the European Commission.
- The High Representative of the Union for Foreign Affairs and Security Policy also takes part in its meetings
European Parliament:
- It is the only parliamentary institution of the European Union (EU) that is directly elected by EU citizens aged 18 years or older.
- Together with the Council of the European Union (also known as the ‘Council’), it exercises the legislative function of the EU
Council of the European Union:
- It is part of the essentially bicameral EU legislature and represents the executive governments of the EU’s member states.
European Commission (EC):
- It is an executive body of the European Union, responsible for proposing legislation, implementing decisions, upholding the EU treaties and managing the day-to-day business of the EU.
- The Commission operates as a cabinet government, with 28 members of the Commission.
- One of the 28 members is the Commission President proposed by the European Council and elected by the European Parliament.
The Court of Justice of the European Union (CJEU):
- It interprets EU law to make sure it is applied in the same way in all EU countries, and settles legal disputes between national governments and EU institutions.
The European Central Bank (ECB):
- It is the central bank for the euro and administers monetary policy within the Euro zone, which comprises 19 member states of the European Union
Membership of EU
- In order for a country to become part of the EU the country must meet Copenhagen Criteria
- The main criteria are the free-market economy, a stable democracy and the rule of law, and the acceptance of all EU legislation, including the euro.
- The regular procedure for EU membership consists of three stages.
- The first stage is when a country is granted the status of an official candidate for membership.
- The second stage is when membership negotiations between the EU and the candidate country start, which is a process that includes the adoption of EU law into national law, and the preparation for the implementation of this law in judicial as well as other reforms.
- The third stage is when the candidate country has met all accession criteria and is ready to become part of the EU.
Source: The Hindu
Syllabus
- Mains – GS 1 (Social Issues)
Context: In 1952, in the first parliamentary session Indian Republic had 39 strong, intelligent, and passionate women leaders in its parliament
- India was leading the way in the fight towards more inclusive world democracies with 5.5% women representation.
- But 70 years post-independence, it seems we have strayed from that path.
Current stats: As per the latest Election Commission of India (ECI) data
- Women represent 5% of the total members of the Parliament.
- The scenario for women Members of Legislative Assemblies (MLAs) across all state assemblies in India is even worse, with the national average being a pitiable 9%.
- In the last 75 years of independence, women’s representation in Lok Sabha has not even increased by 10%.
Reasons
Lack of Political Education:
- Education influences the social mobility of women. Formal education such as provided at educational institutions creates opportunities for leadership, and impart leadership essential skills.
- Because of a lack of understanding of politics, they do not know about their basic and political rights.
Stereotypes:
- The role of managing household activities has been traditionally assigned to women
Work and Family:
- Uneven distribution of family care responsibilities means that women spend far more time than men in home and child-care.
Lack of Resources:
- Because of their low proportion in the inner political party structure of India, women fail to gather resources and support for nurturing their political constituencies.
Unfriendly Environment:
- Rise in criminalization, corruption, insecurity has driven women out of the political arena.
Absence of gender-neutral language
- For instance – in the Rajya Sabha, the Rules of Procedure continue to refer to the Vice-President of India as the ex-officio Chairman, stemming from the lack of gender-neutral language in the Constitution of India
- The alarming degree of usage of masculine pronouns assumes a power structure biased towards men.
Lack of gender-neutral Acts
- Acts have made references to women not as leaders or professionals (such as policemen), but usually as victims of crimes.
Government measures
Reservation for Women in Panchayati Raj Institutions:
- Article 243D of the Constitution ensures participation of women in Panchayati Raj Institutions by mandating not less than one-third reservation for women out of total number of seats to be filled by direct election and number of offices of chairpersons of Panchayats.
Parliamentary Committee On Empowerment Of Women:
- The Committee on Empowerment of Women was constituted for the first time in 1997 during the 11th Lok Sabha of the Parliament for improving the status of women.
Rules of Procedure of the Lok Sabha
- In 2014, under the leadership of the then Speaker of the Lok Sabha, Meira Kumar, and the Rules of Procedure of the Lok Sabha were made entirely gender neutral.
- Since then, each Lok Sabha Committee Head has been referred to as Chairperson in all documents.
The Women’s Reservation Bill 2008:
- It proposes to amend the Constitution of India to reserve 1/3rd of all seats in the Lower house of Parliament of India, the Lok Sabha, and in all state legislative assemblies for women.
Way forward
- Bring women quotas in political parties
- Promoting Inner party democracy
- Passage of Women’s Reservation Bill
- Fighting stereotypes
- Bringing gender neutral languages
The pre-requisite of inclusive society is inclusive parliament, the need of the hour is to have equal participation of all the sections of society in mainstream political activity and decision making.
Source: The Hindu
Baba’s Explainer – Agnipath Recruitment Scheme

Syllabus
- GS-2: Structure, organization and functioning of the Executive
- GS-2: Government policies and interventions for development in various sectors and issues arising out of their design and implementation.
- GS-3: Security & issues
Context:
Just before the Covid crisis at the end of 2019-20 financial year, India had around 403.5 million employed people and around 35 million (or 3.5 crore) openly unemployed people (those who are seeking work and not finding it) in the country.
- Amidst this, the government has launched Agnipath recruitment scheme for soldiers that is being projected as providing employment opportunities for burgeoning youth.
Read Complete Details on Agnipath Recruitment Scheme
Daily Practice MCQs
Q.1) The term ‘Solidarity-2023’ recently seen in news is related to?
- Quad
- BRICS
- SCO
- NATO
Q.2) Consider the following statements about Inter-State Council
- It was set up as per the recommendations of the Sarkaria Commission
- Union Home Minister acts as the chairman of the council
- The recommendations of the council are binding on the Union and the State Governments
Choose the incorrect statements:
- 1 and 3
- 1, 2 and 3
- 2 and 3
- 2 only
Q.3) Consider the following statements about Financial Action Task Force
- It is an inter-governmental body established in 1989
- The FATF Plenary is the decision making body of the FATF
- Currently Pakistan, Iran and North Korea are under the blacklist of FATF
Choose the correct statements:
- 1 and 2
- 2 and 3
- 1 only
- 1, 2 and 3
ANSWERS FOR 17th JUNE 2022 – Daily Practice MCQs
Q.1) – c
Q.2) – c
Q.3) – a











