IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
Archives
(PRELIMS & MAINS Focus)
Syllabus
- Prelims – Current Affairs
In News: PM unveils National Emblem cast on the roof of the new Parliament Building.
- The National Emblem is made of bronze with a total weight of 9500 Kg and is 6.5 m in height.
State Emblem
- The State Emblem of India is the national emblem of the Republic of India and is used by the union government, state governments, and other government agencies.
- The State Emblem is an adaptation of the Lion Capital of Asoka at Sarnath.
- In the original, there are four lions, mounted back to back, on a circular abacus, which itself rests on a bell-shaped lotus.
- The frieze of the abacus has sculptures in high relief of an elephant, a galloping horse, a bull and a lion separated by intervening Dharma Chakras.
- The profile of the Lion Capital showing three lions mounted on the abacus with a Dharma Chakra in the centre, a bull on the right and a galloping horse on the left, and outlines of Dharma Chakras on the extreme right and left was adopted as the State Emblem of India on January 26, 1950.
- The bell-shaped lotus was omitted.
- The motto Satyameva Jayate, which means ‘Truth Alone Triumphs’, written in Devanagari script below the profile of the Lion Capital is part of the State Emblem of India.

Source: Pib.Gov
Syllabus
- Prelims – Polity
In News: The Supreme Court held that Centre was bound to advise the President of India for the exercise of his powers under Article 72 of the Constitution and to release the appellant (Abu Salem).
Background
- The then Deputy Prime Minister and Home Minister L. K. Advani had given a ‘solemn sovereign assurance’ to a Portugal court that Abu Salem would neither be sentenced to death nor serve more than 25 years in prison.
- The case had triggered concern in the Supreme Court about the “international ramifications” India may face if seen to take back on solemn promises made to foreign powers and their courts while securing an extradition.
- However, the Central Bureau of Investigation, in a recent affidavit, had maintained that Mr. Advani’s assurance was no guarantee.
Article 72
Pardoning Power of the President in India:
- Under Article 72 of the Constitution, the President shall have the power to grant pardons, reprieves, respites or remissions of punishment or to suspend, remit or commute the sentence
- Although the President is bound by the Cabinet’s advice, Article74 (1) empowers him to return it for reconsideration once. If the Council of Ministers decides against any change, the President has no option but to accept it.
President to grant pardons to persons who have been tried and convicted of any offence in all cases where the:
- Punishment or sentence is for an offence against a Union Law;
- Punishment or sentence is by a court martial (military court); and
- Sentence is a sentence of death.
- The pardoning power of the President is independent of the Judiciary; it is an executive power.
- But, the President while exercising this power, does not sit as a court of appeal.
- The object of conferring this power on the President is two-fold:
(a) to keep the door open for correcting any judicial errors in the operation of law; and, (b) to afford relief from a sentence, which the President regards as unduly harsh.
- Under Article 161, the Governor in India too has pardoning powers.
Difference Between Pardoning Powers of President and Governor:
- The scope of the pardoning power of the President under Article 72 is wider than the pardoning power of the Governor under Article 161 which differs in the following two ways:
- Court Martial: The power of the President to grant pardon extends in cases where the punishment or sentence is by a Court Martial but Article 161 does not provide any such power to the Governor.
- Death sentence: The President can grant pardon in all cases where the sentence given is the sentence of death but the pardoning power of the Governor does not extend to death sentence cases.
The pardoning power of the President includes the following:
- Pardon: It removes both the sentence and the conviction and completely absolves the convict from all sentences, punishments and disqualifications.
- Commutation: It denotes the substitution of one form of punishment for a lighter form.
- Remission: It implies reducing the period of sentence without changing its character..
- Respite: It denotes awarding a lesser sentence in place of one originally awarded due to some special fact, such as the physical disability of a convict or the pregnancy of a woman offender.
- Reprieve: It implies a stay of the execution of a sentence for a temporary period.
Its purpose is to enable the convict to have time to seek pardon or commutation from the President.
Source: The Hindu
Previous Year Question
Q.1) If the President of India exercises his power as provided under Article 356 of the Constitution in respect of a particular State, then (2018)
- the Assembly of the State is automatically dissolved.
- the powers of the Legislature of that State shall be exercisable by or under the authority of the Parliament.
- Article 19 is suspended in that State.
- the President can make laws relating to that State.
Syllabus
- Prelims – Current Affairs
In News: Union Defence Minister unveils 75 AI-based products and technologies at defence symposium.
- Indian soldiers patrolling on the Line of Actual Control (LAC) will soon be able to understand Mandarin and reply back instantly
- It is a 600gm Artificial Intelligence-based device developed by an Indian start-up, Cogknit.
- It was one of the 75 AI-enabled products and applications unveiled by Defence Minister at the ‘AI in Defence’ symposium.
- It is an offline handheld language translation system which works based on AI.
- It is bidirectional with a range of 5-10 feet and converts Mandarin to English.
- Troops of India and China come face to face on various occasions during patrols and local commanders too interact at various levels as part of efforts to maintain peace on the ground.
- Language is a major hindrance and interpreters need to be present during occasions like flag meetings.
- The exhibition also had several other AI-enabled products like robotic mine detector, intrusion detection system and integrated command fusion, remote weapon station, rail mounted robo, sensors for underwater domain awareness, and swarm drones, among others.
Source: The Hindu
Previous Year Question
Q.1) With reference to “Blockchain Technology”, consider the following statements: (2020)
- It is a public ledger that everyone can inspect, but which no single user controls.
- The structure and design of blockchain is such that all the data in it are about cryptocurrency only.
- Applications that depend on basic features of blockchain can be developed without anybody’s permission.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 1 and 2 only
- 2 only
- 1 and 3 only
Syllabus
- Prelims – Current Affairs
- Mains – GS 3 (Economy)
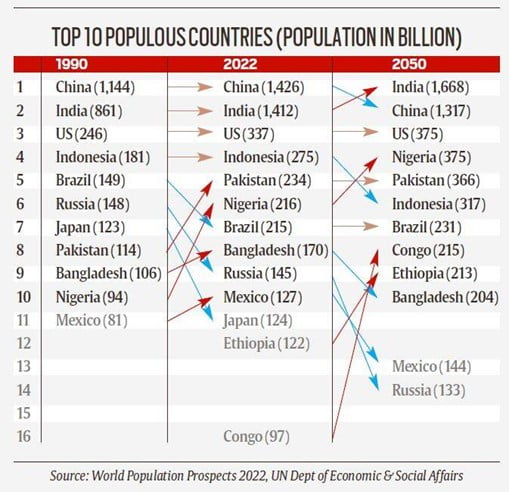
In News: World Population Prospects 2022 was released UN Dept of Economic & Social Affairs
World Population Prospects
- The Population Division of the UN has been publishing the WPP in a biennial cycle since 1951.
- Each revision of the WPP provides a historical time series of population indicators starting in 1950.
- It does so by taking into account newly released national data to revise estimates of past trends in fertility, mortality or international migration.
Takeaways for the global population
- Currently, with 7 billion Asia is the most populous continent and has 61 per cent of the global population, 17 per cent reside in Africa (1.3 billion), 10 per cent in Europe (750 million), 8 per cent in Latin America and the Caribbean (650 million), and the remaining 5 per cent in Northern America (370 million) and Oceania (43 million).
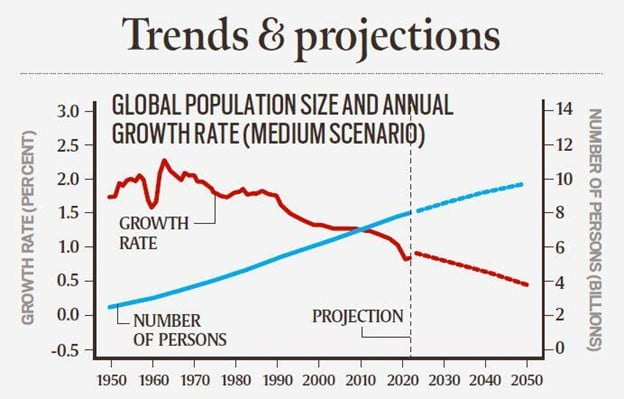
- The world’s population continues to grow, but the pace of growth is slowing down: The global population is expected to grow to around 8.5 billion in 2030, 7 billion in 2050 and 10.4 billion in 2100.
- In 2020, the global growth rate fell under 1% per year for the first time since 1950.
- Rates of population growth vary significantly across countries and regions: More than half of the projected increase in global population up to 2050 will be concentrated in just eight countries: the Democratic Republic of the Congo, Egypt, Ethiopia, India, Nigeria, Pakistan, the Philippines and the United Republic of Tanzania.
- The 46 least developed countries (LDCs) are among the world’s fastest-growing.
- Many are projected to double in population between 2022 and 2050, putting additional pressure on resources and posing challenges to the achievement of the UN’s Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs).
- A sustained drop in fertility has led to an increased concentration of the population at working ages (between 25 and 64 years), creating an opportunity for accelerated economic growth per capita.
- International migration is having important impacts on population trends for some countries:
- For high-income countries between 2000 and 2020, the contribution of international migration to population growth (net inflow of 80.5 million) exceeded the balance of births over deaths (66.2 million).
- Over the next few decades, migration will be the sole driver of population growth in high-income country
India specific findings
- India is expected to surpass China as the world’s most populous country in 2023.
- Presently 417 billion, India’s population is expected to rise to 1.429 billion to surpass China.
- The concern now is not about the absolute numbers — India’s population is already 1.4 billion and may go up to 1.6 billion before declining — but the quality of life for the people alive.
- The focus now has shifted to whether we can reduce poverty, provide healthcare facilities, education
- From data it is clear that cohorts of 0-14 years and 15-24 years will continue to decline while those of 25-64 and 65+ will continue to rise for the coming decades.
Policy implications arising out of these two trends
For those already in the 25-64 age bracket
- Skilling is the only way to ensure they are more productive and have better incomes.
The 65+ category
- Provisioning of social security is obviously a big challenge. This will stretch the resources of the future governments.
- In this context, aged stay within the family set-up, reduces the burden on the government.
Source: Indian Express
Previous Year Question
Q.1) The Global Competitiveness Report is published by the (2019)
- International Monetary Fund
- United Nations Conference on Trade and Development
- World Economic Forum
- World Bank
Syllabus
- Prelims – Science and Technology
In News: Dark matter detector experiment named LUX-ZEPLIN (LZ) in South Dakota in the U.S. was recently in news
- As of today, this is the most sensitive dark matter detector in the world.
What is dark matter and why is it so elusive?
- All interactions in the universe are a result of four fundamental forces acting on particles — strong nuclear force, weak nuclear force, electromagnetic force and gravitation.
- Dark matter is made up of particles that do not have a charge — which means they do not interact through electromagnetic interactions.
- So, these are particles that are “dark”, namely because they do not emit light, which is an electromagnetic phenomenon, and “matter” because they possess mass like normal matter and hence interact through gravity.
- Gravitational force, besides not being fully integrated and understood by particle physicists, is extremely weak.
- For one thing, a particle that interacts so weakly becomes rather elusive to detect.
- This is because interactions from other known particles could drown out signals of dark matter particles.
Why do physicists believe strongly that dark matter exists?
- There is strong indirect evidence for dark matter, and this evidence is reflected at various levels (or distance scales).
- The discrepancy between the calculated and observed value of velocities in rotating galaxies proves that there is a certain fraction of matter which exerts a gravitational pull on the rest of the stars in the galaxy.
- This means that there is a definite amount of dark matter in the galaxy.
What are the evidences from other distance scales?
- The second evidence came from observations of the so-called Bullet cluster of galaxies.
- The Bullet cluster is formed through the merging of two galaxy clusters.
- Physicists found from their calculations that the way these mergers took place could not be fully explained if we believed that the visible universe were all that existed.
- Therefore, there should be something like dark matter as well as an estimate of how much dark matter there should be in the universe.
What are the candidates for dark matter particles?
- Postulated entities include the supersymmetric partner of the Z boson, a particle that mediates the electro-weak interaction.
- Yet other explanations talk about “hidden sector particles” and Axions, a boson and a condensate of dark matter.
- There are many other theories.
The search is on to find one of these candidates, for the story is one that spins together gravity.
Source: The Hindu
Syllabus
- Mains – GS 2 (Polity & Governance)
Context: A suitable intermediary
Role
- Since its inception in 2015, NITI Aayog has been instrumental in promoting competitive and cooperative federalism.
- NITI Aayog organises the annual meeting of the Governing Council (GC) under the leadership of the PM, which brings together chief ministers/Lieutenant-governors of the states/UTs to discuss inter-sectoral, inter-departmental and federal issues to accelerate the implementation of the National Development Agenda.
What needs to be done?
Importance of States
- As custodians of regional policy and prime executors of development programmes, states are the Indian economy’s growth drivers.
- NITI Aayog must ensure productive engagement and dialogue with the states to develop a growth roadmap.
Socio-economic cohesion within the country
- To achieve greater socio-economic cohesion within the country, achieving income convergence across states must be a policy priority.
- Over the last two decades, half of India’s GDP has been contributed by just a handful of states.
- NITI Aayog needs to engender discourse to address this crucial issue through improved governance structures, adequate financial development and infrastructure.
Monitoring Social indicators
- NITI Aayog has developed several social sector indices and dashboards for effectively tracking and monitoring outcomes.
- Regular monitoring and performance evaluation will incentivise states to achieve better social outcomes.
Addressing inter-state and inter-district variations
- The Prime Minister launched the Aspirational Districts Programme (ADP) to address these challenges through data-driven, outcome-based governance.
- NITI Aayog must focus on guiding state governments in replicating the ADP template at the block level and for districts not categorised as aspirational.
Urbanization
- There is a need to tap into resources other than government budgets, such as monetising land assets and engaging private capital in service delivery.
- Efforts to empower and make large urban local bodies atmanirbhar are the needs of the hour.
Challenge of climate change
- India aspires to grow fast but is now subject to a carbon constraint.
- At the state level, it is crucial to frame the decarbonisation challenge in the context of the states’ urgent need to create millions of new jobs, increase incomes and improve public health.
- NITI Aayog is well-positioned to generate such a conversation and guide states to catalyse climate action.
Act as an intermediary
- NITI Aayog must act as an intermediary between the Centre and states to ensure cross-sharing of these best practices, insights and perspectives.
Thus establishing open borders within the country for an open labour market; facilitating effective implementation of national programmes that promote job creation, improve the quality of the labour force and enhance ease of doing business; ensuring high-quality public expenditure, particularly capital expenditure; and ensuring policy predictability at the state level, NITI Aayog along with boosting cooperative federalism can contribute enormously to India’s growth and development.
Source: Indian Express
Baba’s Explainer – Aarey Controversy
Syllabus
- GS-2: Conservation, environmental pollution and degradation, environmental impact assessment.
- GS-3: Government policies and interventions for development in various sectors and issues arising out of their design and implementation.
Context: The Aarey Milk Colony is back in the spotlight, as the fight to preserve this green space in the heart of Mumbai continues
- Following the recent political upheaval in the State, the Aarey issue has resurfaced and so have the protests.
- Recently, activists and political parties like the Shiv Sena and the AAP staged a protest at the Aarey Colony to oppose the Government’s decision to shift back the metro car project from Kanjurmarg to Aarey.
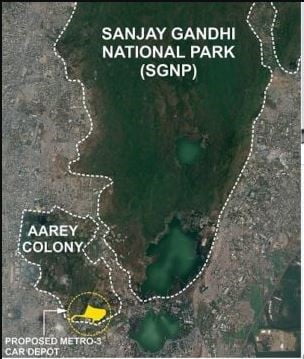
Read Complete Details on Aarey Controversy
Daily Practice MCQs
Q.1) Article 72 of the Indian Constitution recently seen in news is related to?
- It provides for a Council of Ministers which shall aid the President in the exercise of the President’s functions.
- Ordinance making power of the President of India
- Procedure related to election of President of India
- Pardoning power of President of India
Q.2) Consider the following statements
- All interactions in the universe are a result of four fundamental forces acting on particles.
- Dark matter is made up of particles that do not have a charge
- Dark matter possess mass like normal matter
Choose the correct statements
- 1 and 2
- 2 and 3
- 1, 2 and 3
- 1 and 3
Q.3) Which of the following bodies are constitutional bodies?
- NITI Aayog
- National Commission for Women
- Zonal Council
Choose the correct code:
- 1 only
- 1 and 3
- 1, 2 and 3
- None
Comment the answers to the above questions in the comment section below!!
ANSWERS FOR ’12th JULY 2022 – Daily Practice MCQs’ will be updated along with tomorrow’s Daily Current Affairs.
ANSWERS FOR 11th JULY 2022 – Daily Practice MCQs
Q.1) – b
Q.2) – c
Q.3) – a











