IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
Archives
(PRELIMS & MAINS Focus)
Syllabus
- Prelims – Science and Technology
Context: The Indian government asked the smartphone makers to enable support for its NavIC navigation system in new devices sold in the country from next year.
Global standards body 3GPP has approved India’s regional NavIC:
- Earlier, Global standards body 3GPP, which develops protocols for mobile telephony, approved India’s regional navigation system NavIC, developed by Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO).
- The specification approval will boost commercial use of NaVIC (Navigation with Indian Constellation) by international and domestic mobile device makers, which means such manufacturers can now mass-produce navigation devices compatible with NaVIC so that users of these devices can easily access desi GPS or NaVIC signals.
- The implications of NavIC acceptance by 3GPP would bring NavIC technology to the commercial market for its use in 4G, 5G and Internet of Things (IoT).
- Indian companies and startups will have an opportunity to design integrated circuits (ICs) and products based on NavIC
What is 3GPP:
- It comprises seven telecommunications standard development organisations (ARIB, ATIS, CCSA, ETSI, TSDSI, TTA, TTC) from across the world and provides their members with a stable environment to produce specifications that define 3GPP technologies.
- 3GPP currently has global navigation satellite system support from BDS (Chinese), Galileo (European), GLONASS (Russian) & GPS (US) for cellular positioning system.
About NavIC:
- The Indian Regional Navigation Satellite System, with an operational name of NavIC, is an autonomous regional satellite navigation system that provides accurate real-time positioning and timing services. It covers India and a region extending 1,500 km around it, with plans for further extension
- NavIC, or Navigation with Indian Constellation, is an independent stand-alone navigation satellite system developed by the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO).
- It became operational in 2018.
- Three satellites in geostationary orbit and five satellites in geosynchronous orbit. Currently one at stand by.
- Currently, NavIC’s use is limited. It is being used in public vehicle tracking in India, for providing emergency warning alerts to fishermen venturing into the deep sea where there is no terrestrial network connectivity, and for tracking and providing information related to natural disasters.
- Enabling it in smartphones is the next step India is pushing for.
- At full functioning , IRNSS will provide two types of services, namely, Standard Positioning Service (SPS) which is provided to all the users and Restricted Service (RS), which is an encrypted service provided only to the authorised users.
- The IRNSS System is expected to provide a position accuracy of better than 20 m in the primary service area.
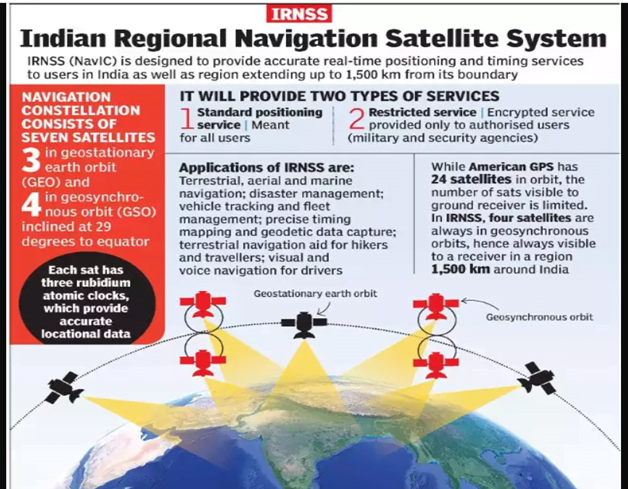
Applications of IRNSS:
- Terrestrial, Aerial and Marine Navigation
- Disaster Management
- Vehicle tracking and fleet management
- Integration with mobile phones
- Precise Timing
- Mapping and Geodetic data capture
- Terrestrial navigation aid for hikers and travellers
- Visual and voice navigation for drivers
Source: Indian Express
Previous Year Question
Q.1) With reference to the Indian Regional Navigation Satellite System (IRNSS), consider the following statements :
- IRNSS has three satellites in geostationary and four satellites in geosynchronous orbits.
- IRNSS covers entire India and about 5500 sq. km beyond its borders.
- India will have its own satellite navigation system with full global coverage by the middle of 2019.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct? (2018)
- 1 only
- 1 and 2 only
- 2 and 3 only
- None
Q.2) In which of the following areas can GPS technology be used? (2018)
- Mobile phone operations
- Banking operations
- Controlling the power grids
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
- 1 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
Syllabus
- Prelims – Economy
Context: Continuing its slide against the dollar, the rupee ended at a new low recently due to risk-off sentiment among investors following an aggressive rate hike announcement by the US Federal Reserve.
The weakness in the rupee also affected sentiment of equity market investors, as the benchmark Sensex at the BSE tanked 953 points, or 1.6 per cent, to close at 57,145.22. The broader Nifty at NSE lost 311 points, or 1.8 per cent, to end at 17,016.
About National Stock Exchange (NSE):
- It was incorporated in 1992, become recognized as a stock exchange in 1993, and trading began on it in 1994.
- It was the first stock exchange on which trading took place electronically.
- In the year 1995-96, NSE launched NIFTY 50 Index and commenced trading and settlement in dematerialised securities.
About Bombay Stock Exchange (BSE):
- BSE is the oldest stock exchange in Asia established in 1875.
- In 1986, Sensex was introduced, as the first equity index to provide a base for identifying the top 30 trading companies of the exchange.
- It ranks amongst the top 10 most valued exchanges globally.
- It offers trading in equities, derivatives, and Commodities.
Current Stock Exchanges in India:
- After the country gained independence, 23 stock exchanges were added apart from the BSE
- However, at present, there are only seven recognized stock exchanges, along with BSE & NSE as follows:
- Calcutta Stock Exchange Ltd.
- The Calcutta Stock Exchange began operations in 1908 and began trading shares of plantations and jute mills
- Magadh Stock Exchange Ltd
- Metropolitan Stock Exchange of India Ltd
- Opened in January 2017, India INX is India’s first international stock exchange
- It is also a subsidiary of BSE and is located at the International Financial Services Centre (IFSC), GIFT City in Gujarat
- Currently, INX offers only derivative products including equity, currency and commodities derivatives and debt instruments including masala bond and foreign currency bond
- India International Exchange (India INX)
- Opened in January 2017, India INX is India’s first international stock exchange
- It is also a subsidiary of BSE and is located at the International Financial Services Centre (IFSC), GIFT City in Gujarat
- Currently, INX offers only derivative products including equity, currency and commodities derivatives and debt instruments including masala bond and foreign currency bond
- NSE IFSC Ltd
- NSE IFSC Limited (NSE International Exchange) incorporated on 29th November 2016, is a wholly owned subsidiary of the National Stock Exchange (NSE) and is located at the International Financial Services Centre (IFSC), GIFT City in Gujarat.
- Products offerings are similar to India INX.
- Calcutta Stock Exchange Ltd.
Importance of Stock Exchanges:
Determining the fair price:
- The stock exchanges facilitate in discovering fair prices of the publicly listed securities. Relentless trading of securities helps in determining the price of the listed securities.
Facilitating industrial advancement:
- The industrialisation of a nation is reliant on capital availability. This is ensured by the stock exchanges as the public can invest directly in the companies through stock exchanges.
Protecting investors’ interest:
- The stock exchanges lay down guidelines for the operation of the listed entities. These norms have to be strictly followed by the companies, thereby protecting investors’ interest as they would have financed the operations.
Act as secondary markets:
- Stock exchanges will help investors of certain bonds, such as sovereign gold bonds (SGBs), to sell their holdings within the lock-in period or maturity.
Reduce the dependency on loan for corporates:
- The existence of stock exchanges has helped listed companies avoid availing a loan as they could raise capital by issuing securities. This has helped them save a significant amount in the form of regular interest outgo.
Source: Indian Express
Q.1) Convertible Bonds, consider the following statements:
- As there is an option to exchange the bond for equity, Convertible Bonds pay a lower rate of interest.
- The option to convert to equity affords the bondholder a degree of indexation to rising consumer prices.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct? (2022)
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Syllabus
- Prelims – Social Issues
Context: The Central Bureau of Investigation (CBI) conducted searches as part of a pan-India drive against the circulation and sharing of child sexual abuse material. The operation was code-named “Megh Chakra”.
About Operation Megh Chakra:
- Operation Megh Chakra is one of the CBI-led global operations in recent times for rapid response to online child sexual exploitation cases with international linkages and organized cyber enabled financial crimes.
- It is aimed at identifying and acting against the individuals and gangs involved in circulating child sexual abuse material and blackmailing minors.
- The operation is targeted at cloud storage — therefore the codename ‘Megha Chakra’ — used by peddlers to circulate audio-visual material on illicit sexual activities with minors.
- It sought to collate information from various law enforcement agencies within India, engage with relevant law enforcement agencies globally and coordinate closely through INTERPOL (International Criminal Police Organization) channels to combat online child sexual exploitation and such organized cyber-criminal activities.
- Coordination meetings were organised with INTERPOL and foreign law enforcement agencies for sharing critical information to dismantle such cybercrime networks.
Source: The Hindu
Syllabus
- Prelims – Environment
In News:
The first annual Breakthrough Agenda Report, delivers a progress report on the actions needed to deliver on the historic clean technology commitment by governments.
- The report puts forward 25 recommendations for leaders to discuss at the Global Clean Energy Action Forum and the 13th Clean Energy Ministerial to be held in Pittsburgh, the US.
About the report:
- The Breakthrough Agenda Report 2022 is a new report by the International Energy Agency (IEA), the International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA) and the UN Climate Change High-Level Champions.
- The report represents two-thirds of the global economy.
- Objective: It aims at supporting stronger international collaboration to amplify ambition, accelerate progress and drive faster reductions in global greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions. To align countries’ actions and coordinate investment to scale up deployment and drive do down costs across five key sectors — power, road transport, steel, hydrogen and agriculture
- Together, these sectors account for nearly 60% of global greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions and could deliver the bulk of emissions reductions needed by 2030 in a pathway that would make a significant contribution to limiting global warming to a maximum of 1.5 degrees Celsius, in line with the Paris Agreement goals.
Findings:
- The report notes an increase in practical international cooperation in recent years such as doubling of EV sales, increase in global renewable capacity of eight per cent in 2022 — pushing through the 300GW mark for the first time.
- The report also warns that far greater international cooperation is needed to get the world on track to meet its climate commitment.
About IEA:
- It was established in the framework of the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) in 1974 in the wake of the 1973 oil crisis.
- IEA is an autonomous intergovernmental organisation.
- Its mission is guided by four main areas of focus: energy security, economic development, environmental awareness, and engagement worldwide.
- Headquarters: Paris, France.
- Roles and functions:
- to help its members respond to major oil supply disruptions, a role it continues to fulfil today
- tracking and analysing global key energy trends,
- promoting sound energy policy,
- fostering multinational energy technology cooperation.
- Composition: It has 30 members at present. IEA family also includes eight association countries. A candidate country must be a member country of the OECD. But all OECD members are not IEA members.
- Three countries are seeking accession to full membership: Chile, Israel, and Lithuania.
Reports by IEA:
- Global Energy & CO2 Status Report.
- World Energy Outlook.
- World Energy Statistics.
- World Energy Balances.
- Energy Technology Perspectives.
Source: Economic Times
Previous Year Question
Q.1) In the Indian context, what is the implication of ratifying the ‘Additional Protocol’ with the ‘International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA)’? (2018)
- The civil nuclear reactors come under IAEA safeguards
- The military nuclear installations come under inspection of IAEA
- The country will have the privileged to buy uranium from the Nuclear Suppliers Group (NSG)
- The country automatically becomes a member of the NSG.
Syllabus
- Prelims – Current Affairs
In news: APOA held its first general body meeting on the side-lines of the 25th Globoil Summit being held in India.
- The next meeting of APOA is expected to be held in Indonesia early next year.
About:
- It is an edible oil trade association formed of five palm oil importing countries in South Asia – India, Pakistan, Sri Lanka, Bangladesh, and Nepal
- Objective: To gain collective bargaining power, to make imports sustainable and to safeguard the economic and business interests of the palm oil consuming countries
- The alliance would work towards ensuring that palm oil is recognised as a high-quality, economical, and healthy vegetable oil and to change the negative image of palm oil.
- The association is not involved in shaping the global discourse on sustainable palm oil in a collective way.
- The membership of APOA would be further expanded to include companies or industry bodies associated with production or refining of palm oil across the continent
About Palm Oil imports:
- India’s annual imports of edible oil is around 13-14 million tonnes (MT). Around 8 MT of palm oil is imported from Indonesia and Malaysia, while other oils, such as soya and sunflower, come from Argentina, Brazil, Ukraine, and Russia.
- Asia accounts for around 40% of the global palm oil consumption while Europe accounts for 12% of palm oil trade.
- Indonesia and Malaysia are the biggest palm oil exporters in the world.
- India is the largest importer of palm oil in Asia (15% of global imports), followed by China (9%), Pakistan (4%) and Bangladesh (2%).
About Oil Palm:
- It is a humid tropical crop and thrives best in temperature ranging from 22 °C to 24 °C. They require at least 5-6 hours of bright sunshine per day and 80% of humidity for optimum growth.
- Palm oil is a very productive crop. It offers a far greater yield at a lower cost of production than other vegetable oils. It produces high-quality oil used primarily for cooking in developing countries.
- It is also used in food products, detergents, cosmetics and, to a small extent, biofuel. Many packaged products contain palm oil—such as in lipstick, soaps, detergents and even ice cream.
Source: Financial Express
Syllabus
- Prelims – Science & Technology
In News: The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) hopes to achieve a remarkable feat — the 200th successful launch of the Rohini RH-200 sounding rocket in a row.
- It has completed 198 consecutive successful flights and the 199th and 200th launch are planned to take place during 2022.
- ISRO has launched more than 1,600 RH-200 rockets so far. The 100th consecutive successful mission happened in 2015.
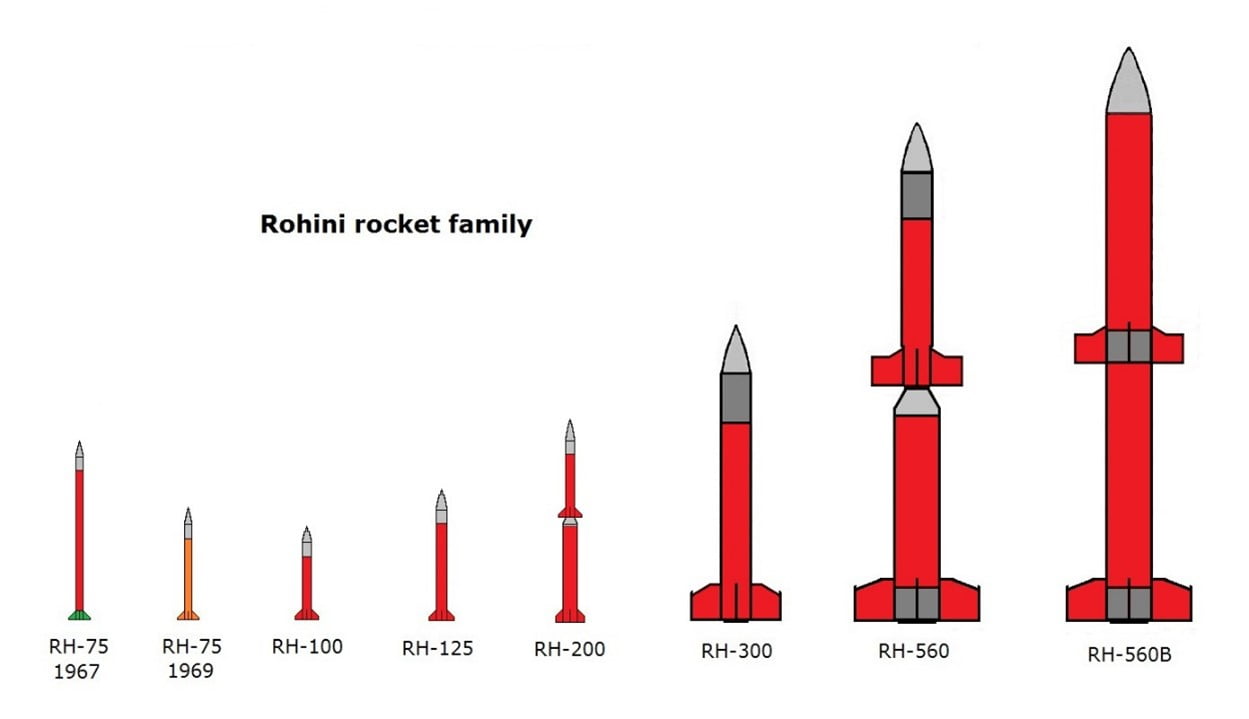
About the rocket:
- Sounding rockets are one or two stage solid propellant rockets used for probing the upper atmospheric regions and for space research developed the ISRO.
- RH-200 is a 3.5-metre-tall two-stage rocket capable of climbing to a height of 70 km bearing scientific payloads.
- The first and second stages of RH-200 are powered by solid motors.
- The ‘200’ in the name denotes the diameter of the rocket in mm.
- Other operational Rohini variants are RH-300 Mk-II and RH-560 Mk-III.
- The first RH-200 to use a new propellant based on hydroxyl-terminated Polybutadiene (HTPB) was successfully flown in 2020, while the previous versions had used a polyvinyl chloride (PVC)-based propellant.
About sounding rockets:
- Sounding rockets have been used for a variety of experiments, including those on phenomena related to eclipses.
- The first sounding rocket was the American Nike-Apache – launched in 1963.
- The ISRO launched its own version – Rohini RH-75 – in 1967.
- The sounding rocket programme was the bedrock on which the edifice of launch vehicle technology was built.
- Today, these small rockets are launched both from the Thumba Equatorial Rocket Launching Station (TERLS) and the Satish Dhawan Space Centre, Sriharikota.
Source: The Hindu
Previous Year Question
Q.1) What is ‘Greased Lightning-10 (GL-10)’, recently in the news? (2016)
- Electric plane tested by NASA
- Solar-powered two-seater aircraft designed by Japan
- Space observatory launched by China
- Reusable rocket designed by ISRO
Syllabus
- Prelims – Art & Architecture
In News: With three-fourth of the art in the Sittanavasal rock cave temple in Pudukottai district of Tamil Nadu either damaged or vandalised, Archaeological Survey of India has undertaken conservation measures and also introduced digital checks to track public access.
- Periodic maintenance in the form of conservation (for structural repairs) and chemical preservation (for the restoration of paintings) of the monument is being undertaken.
About the caves:
- Sittanavasal Cave (also, Arivar Koil) is a 2nd-century Tamil Śramaṇa complex of caves in Sittanavasal village in Pudukottai district of Tamil Nadu.
- Sittanavasal is the name used synonymously for the hamlet and the hillock that houses the Arivar Kovil i.e., temple of Arihats – Jains who conquered their senses, ‘Ezhadipattam’ (a cavern with 17 polished rock beds), megalithic burial sites and the Navachunai tarn (small mountain lake) with a submerged shrine.
- This is the only place in Tamil Nadu where one can see Pandya paintings.
- The site and art were first mentioned by local historian S. Radhakrishnan Iyer in his 1916 book General History of Pudukottai State.
About the artwork:
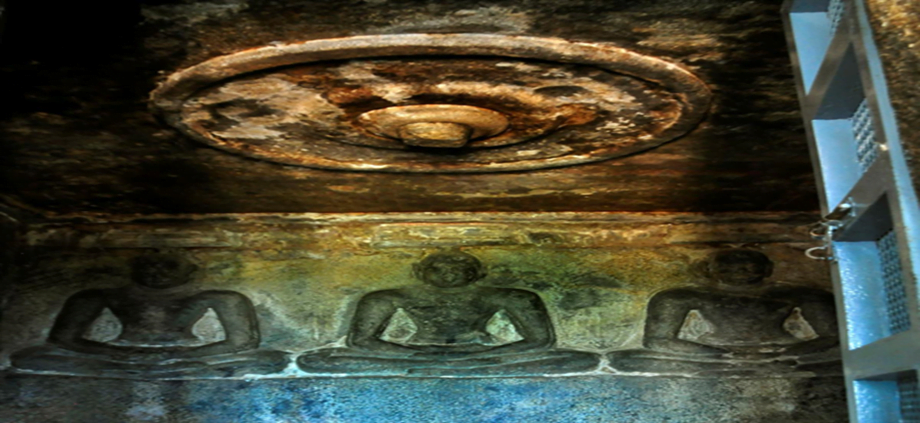

- The artwork on the ceiling of the sanctum and the ardha mandapam of Arivar Kovil is an early example of post-Ajanta cave paintings of the fourth to sixth centuries, done using the fresco-secco technique (a process that dispenses with preparation of the wall with wet plaster).
- The ceiling paintings show ‘bhavyas’ (exalted souls who work to achieve moksha or spiritual liberation) enjoying themselves in a pool, full of blooming lotuses.
- Faint outlines linger of dancing girls on the ‘ardha mandapam’ pillars.
- The pillars of the verandah (added by the Maharaja of Pudukottai at the instance of then Diwan Alexander Tottenham in the 1900s), were brought from Kudumiyanmalai.
- The colours are a mixture of plant dyes and mineral elements such as lime, lamp black, and clay pigments such as ochre for yellow and terre verte for the greyish-green tints.
- The design elements hint at its possible earlier existence as a Saivite shrine.
- Inscriptions in Brahmi and ‘vattaezhuthu’, from the third century AD are present here. Early Tamil inscriptions from the ninth century AD of the Jain monk Ilan-Gautaman, are inside the complex.
- Of the 20 cave temples in Pudukottai district, 19 belong to Saivite and Vaishnavite streams of Hinduism; Sittanavasal is the only Jain temple with sculptures.
Concerns:
- Unrestricted public access and general exposure to the elements have led to a gradual fading away of these paintings.
- Some inscriptions have been vandalised beyond recognition
- Small heaps of litter can be seen throughout the compound.
- Groups of monkeys run free amid visitors, looking for scraps of food.
Measures:
- ASI has put in digital checks by introducing electronic ticketing to track visitor numbers.
- To increase the number of security guards
- Installation of closed-circuit TV cameras
- Programmes to create awareness about Sittanavasal among young people.
- Building of a centre to study Jainism’s influence in the region.
Source: The Hindu
Previous Year Question
Q.1) Which one of the following statements is correct? (2021):
- Ajanta Caves lie in the gorge of Waghora river
- Sanchi Stupa lies in the gorge of Chambal River.
- Pandu-Leni Cave shrines lie in the gorge of Narmada River.
- Amaravati Stupa lies in the gorge of Godavari River.
Syllabus
- Mains: GS 2 (International Relations)
In News: Indian External Affairs Minister S. Jaishankar’s visit to the United States (September 18-28) has set the stage for an expansive range of bilateral and multilateral diplomacy by India. It is a unique visit as it seeks to achieve a vast list of objectives led by the Indian delegation’s participation in the High-Level Week at the 77th Session of the United Nations General Assembly.
- The theme of the 77th General Assembly, which seeks “A watershed moment: Transformative Solutions to Interlocking Challenges”, places India right in the midst as a strong partner of the U.N.
Context:
- India calls for a structural overhaul of UN-led multilateralism to incorporate institutional accountability and a wider representation of the developing countries.
- India searches for a new framework of global governance, amidst growing frustration with the extant multilateral order.
- It highlights needs of reforms in UNSC and the limitations of UN institutions and expresses concerns over Chinese dominance.
Need for reforms in UNSC:
- United Nations Security Council should reform itself to become a more inclusive organisation representing the contemporary realities of today.
- Countries of the global South, including India, stepped up through relief efforts, drug distribution and vaccine manufacturing, thus creating a space for a more inclusive UN.
- The growing stakes of developing countries in the Security Council could foster trust and leadership across the world.
- Recent global developments like the COVID-19 pandemic highlighted the UN’s institutional limitations; when countries closed their borders, supply chains were interrupted and almost every country needed vaccines.
The U.N.’s fault lines in preventing wars:
- U.N.-led multilateralism has been unable to provide strong mechanisms to prevent wars.
- The ongoing Russia-Ukraine war has loomed large over several deadlocks in U.N.S.C. resolutions – With the West boycotting Russia, the veto provision of the U.N.S.C. is expected to reach an even more redundant level than in the past.
- As such, a reformed multilateralism with greater representation could generate deeper regional stakes to prevent wars.
Concern over China’s dominance:
- China’s rise, belligerence, and aggression has been on display through its actions
- China has been stonewalling India’s bid for Permanent Seat In UNSC for years, pointing to the lack of consensus even though the other four permanent members, the US, the UK, France and Russia have expressed backing for New Delhi’s membership.
- China blocked a joint India-U.S. proposal at the U.N. to enlist Sajid Mir, a top Lashkar-e-Taiba (LeT) operative involved in directing the 2008 Mumbai attacks, as a ‘global terrorist’.
- Control over multilateral organisations—unofficial pressure China exerted on the former U.N.’s human rights chief to stop the release of a report by the N. Human Rights Council on the condition of Uyghurs in China.
- Conflicts in South China Sea and the Indo-Pacific region
- China’s growing dominance could lead it to carve its own multilateral matrix circumventing the West, economically and strategically.
- The international isolation of Russia and Iran as well as increasing the United States’ Taiwan-related steps could usher in these changes more rapidly than expected.
India’s multilateral diplomacy:
- Mr. Jaishankar’s hosting of a ministerial meeting of the G4 (Brazil, India, Germany, and Japan)
- A high-level meeting of the Indian delegation with the L.69 Group, on “Reinvigorating Multilateralism and Achieving Comprehensive Reform of the U.N. Security Council”.
- India-CARICOM (Caribbean Community) and other trilateral formats, such as India-France-Australia, India-France-the United Arab Emirates and India-Indonesia-Australia.
- Participation in plurilateral meetings of the Quad (Australia, India, Japan, the U.S.), IBSA (India, Brazil, and South Africa), BRICS (Brazil, Russia, India, China, and South Africa) and Presidency Pro Tempore CELAC (Community of Latin American and the Caribbean States)
About The United Nations Security Council (UNSC):
- It is one of the six principal organs of the United Nations
- It is charged with ensuring international peace and security, recommending the admission of new UN members to the General Assembly, and approving any changes to the UN Charter. Its powers include establishing peacekeeping operations, enacting international sanctions, and authorizing military action.
- The UNSC is the only UN body with the authority to issue binding resolutions on member states.
- It was created after World War II in 1946 to address the failings of the League of Nations in maintaining world peace.
- The Security Council consists of fifteen members including India, of which five are permanent: China, France, Russia, the United Kingdom, and the United States. Permanent members can veto (block) any substantive Security Council resolution
Criticism of UNSC
- Unlike the General Assembly which truly represents the interests of all the member states, the Security Council represents the interest and domination of only the five permanent members which includes China, France, Russia, the United Kingdom, and the United States of America.
- The veto power has been misused by the five permanent members – For passing any resolution, the approval of all the five permanent members is necessary and even if one of the members says no the resolution cannot be passed.
India and UN Security Council
- India was offered seat at UNSC in 1950. The 1955 offer was made by USSR to India for a permanent seat in the UN (at a time when the USSR and China’s alliance had reached a certain height).
- India has basically followed two strategies for the expansion of the Security Council. “The first focuses on a narrow major-power claim, which emphasizes India’s capabilities and contributions to the UNSC as the basis for permanent membership”.
- The second approach basically focuses on the “problem of representation in the UNSC” and makes the case for expanding both permanent and non-permanent categories of membership.
- India is also seen as a proliferating nuclear power. Analysts believe that this is the single most factor that is being a roadblock for India’s UNSC dreams
Way forward:
- UN could integrate burden-sharing practices within its institutional ambit.
- At a challenging time for the world order, New Delhi continues to affirm its commitment to “diplomacy and the need for international cooperation”
Source: Indian Express
Syllabus
- Prelims – International relations
- Mains – GS 2 (International Relations)
Context: On the side-lines of Shanghai Cooperation Organization summit, the Prime Minister of India and the President of Russia discussed about defence cooperation amid the ongoing Russia – Ukraine war.
Let us discuss the Bilateral Relations between the two countries

Historical relationship:
- During that, Russia has mentioned the support of the Soviet Union for India’s sovereignty over the disputed territories of Kashmir and Portuguese coastal enclaves such as Goa. Even after the abrogation of Article 370 Russia still supports India’s claim over Kashmir.
- The USSR agreed to transfer technology to co-produce the Mikoyan-Gurevich MiG-21 jet fighter in India in 1962. But the USSR rejected a similar move to China.
- India signed the Indo-Soviet Treaty of Friendship and Cooperation in 1971 during the Bangladesh liberation war.
Political Relations:
- The Annual Summit meeting between the Prime Minister of India and the President of the Russian Federation is the highest institutionalised dialogue mechanism in the strategic partnership between India and Russia. As of 2020, 20 Annual Summit meetings have taken place alternatively in India and Russia.
- In 2019, President Putin signed the Executive Order on awarding PM of India with Russia’s highest state decoration – The order of St Andrew the Apostle.
- Two Inter-Governmental Commissions – one on Trade, Economic, Scientific, Technological and Cultural Cooperation (IRIGC-TEC), and another on Military-Technical Cooperation (IRIGC- MTC), meet annually.
Defence and Security Relations
- India-Russia military-technical cooperation has evolved from a buyer-seller framework to one involving joint research, development and production of advanced defence technologies and systems
- Joint Tri-Services Exercise ‘INDRA 2019’ between India and Russia was carried out simultaneously in Babina, Pune, and Goa in 2019.
The joint military programmes between India and Russia include:
- BrahMos cruise missile programme
- 5th generation fighter jet programme
- Sukhoi Su-30MKI programme
- Ilyushin/HAL Tactical Transport Aircraft
- KA-226T twin-engine utility helicopters
The military hardware purchased/leased by India from Russia includes:
- S-400 TRIUMF
- Kamov Ka-226 200 to be made in India under the Make in India initiative
- T-90S Bhishma
- INS Vikramaditya aircraft carrier programme
- S-400 air defence system
Russia also plays a very important role in assisting the Indian Navy with its submarine programmes:
- Indian Navy’s first submarine, ‘Foxtrot Class’ came from Russia
- India is dependent on Russia for its nuclear submarine programme
- INS Vikramaditya, the sole aircraft carrier operated by India, is also Russian in origin
- Nine of the fourteen conventional submarines operated by India are Russian
India Russia Trade Relations:
- The two countries intend to increase bilateral investment to US$50 billion and bilateral trade to US$30 billion by 2025
- In 2019, total bilateral trade between the two countries from January-September, 2019 stood at USD 7.55 billion
- From 2013 to 2016 there was a major decline in the trade percentage between the two countries. However, it increased from 2017 onwards and a constant increase was noticed in 2018 and 2019 as well
Cultural Relations:
- About 20 Russian Institutions, including leading universities and schools, regularly teach Hindi to about 1500 Russian students.
- Apart from Hindi, languages such as Tamil, Marathi, Gujarati, Bengali, Urdu, Sanskrit and Pali are taught in Russian Institutions.
- Indian dance, music, yoga, and Ayurveda are among few other interests that people of Russia enjoy.
Why is Russia Important for India?
- Russia’s status in international sphere: Russia remains, and will remain a pre-eminent nuclear and energy power and a permanent member of the United Nations Security Council
- Multipolar World Politics: Since the world is becoming increasingly multipolar, maintaining close and strategic relations with Russia and the US at the same time is indispensable for India. Strong partnership with Russia provides India leverages to deal with other countries.
- Support for UNSC seat: Russia has stated publicly that it supports India receiving a permanent seat on the United Nations Security Council.
- Counterbalance to China Aggression: India has no option but to have a close relationship both with the US and Russia and to manage its difficult relationship with China. So long as Russia’s relationship with the West remains strained, Russia will look towards China. So long as Sino-Indian relations remain troubled, Russia’s going into the Chinese sphere of influence will not suit India.
- India’s energy security: Russia has huge reserves of oil. India to look towards Russia as an alternative source of energy supplies as the situation in the Middle East is escalating with threats to essential oil trade routes
Challenges in India Russia Relationships:
- The rapid expansion of India-US relations: This is one of the most cited reasons for strain in India-Russia relations. The development of India US defence cooperation is rapid since 2008.
- In 2014 US emerged as the top arms supplier to India by overtaking Russia.
- Further, India also signed all the Foundational agreements with the US. Such as LEMOA, COMCASA, BECA.
- Due to these developments, Russia changed their decades-old policy and start supplying China with weapon systems like Sukhoi 35 and the S-400 missile defence system.
- Closer proximity of Russia towards China:
- Russia already proposed a Russia-India-China (RIC) forum of foreign ministers. But there is no major diplomatic success of RIC due to India’s unresolved issues with China.
- China-Russian ties are growing due to their shared interest in opposing the US. The intense geostrategic rivalry between China and the US in the region. Russia which opposes the US joined hands with China. This is evident as Russia joined the Chinese One Belt One Road initiative.
Conclusion: India and Russia continue to share a common strategic rationale for their relationship: apart from bilateral synergies, the two are members of various multilateral organisations including BRICS, RIC, G20, East Asia Summit and SCO—where avenues for cooperation on issues of mutual importance exist.
On the whole, Both India and Russia will have to learn to navigate their relationship amidst challenges emerging not just from bilateral factors but also regional and global ones, as both countries seek to strengthen their position at a time of flux in the international order.
Source: Indian Express
Syllabus
- Prelims – Economy and Environment
- Mains – GS 3 (Economy and Environment)
Context: Recently a gathering of State Tourism Ministers to discuss on modes and mechanisms to develop tourism in India, came up with ‘The Dharamshala Declaration’ (2022).
It draws inspiration from central government’s ‘Whole of Government’ approach, which enables the breaking down of silos and encouraging synergies across various government corridors.
About Dharamshala Declaration:
- On the occasion of World Tourism Day (September 27), Dharamshala Declaration aims to recognise India’s role in contributing towards global tourism as well as focusing on recovery by also promoting domestic tourism — which has been overlooked for long.
- In the declaration, the Tourism Ministry has come up with a strategy and action plan to encourage more Indians to travel domestically and explore India’s natural, cultural, and spiritual beauty while simultaneously reaching the goal of an ‘Ek Bharat Shrestha Bharat’ (interaction and mutual understanding).
- The ‘Ek Bharat Shrestha Bharat’ scheme was launched to celebrate the cultural vibrancy of India while establishing a strong mechanism to inculcate nationalism and cultural awareness among the citizens of our nation.
- In parallel, the Ministry has also been working with the Ministry of External Affairs to identify 20 Indian missions abroad with the highest tourist footfalls to India and build country-specific strategies to attract foreign tourists.
Rethinking and reimagining tourism:
- Tourism has been one of the sectors severely affected by COVID-19. The Government of India’s Emergency Credit Line Guarantee Scheme (ECLGS) was recently enhanced to ₹5 lakh crore to benefit enterprises in hospitality and related sectors such as hotels and restaurants, marriage halls, travel agents, tour operators, adventure, and heritage facilities.
- The pandemic has also given us the time to reset and rethink the way forward for tourism in India.
- The Ministry of Tourism, after wide-ranging consultations, has prepared a draft National Tourism Policy 2022, which aims at improving the framework conditions for tourism development in the country, supporting tourism industries, strengthening tourism support functions, and developing tourism sub-sectors.
- The guiding principles include promoting sustainable, responsible, and inclusive tourism in line with our civilisational ethos.
- From Gautama to Gandhi, India has always spoken about the inherent need to live harmoniously with nature and within our means. The National Green Tourism Mission aims at institutionalising this approach.
- The National Tourism policy also aims to give impetus to digitalisation, innovation and technology through the National Digital Tourism Mission and skilling through the Tourism and Hospitality Sector Skill Mission.
- The policy also gives a special impetus to private sector participation through public-private-partnerships (PPP).
- Various other schemes involving PPP mode development will also compliment tourism sector, like the National Investment Pipeline (NIP) and the National Monetisation Pipeline (NMP).
Important features of draft National Tourism Policy 2022:
- To promote investment in the tourism sector, industry status is proposed to be granted to the sector, along with formally granting infrastructure status to hotels.
- It identifies 5 key areas to be given significant focus in the next 10 years — green tourism, digital tourism, destination management, skilling the hospitality sector and supporting tourism-related to MSMEs.
- Relief Measures and Taxation Breaks for the contact-sensitive industry, which has been the worst sufferer over the last two years of the COVID-19 pandemic,
- Other framework conditions to help the sector, especially in the wake of the pandemic. The overall mission and vision are being laid out to improve the experience of tourists, foreign as well as local.
Potential during the G20 presidency:
- The country has an opportunity to position itself as a major tourism destination during India’s presidency of the G20 (2023).
- India welcomes delegates from the 20 countries/European Union, including personnel from the central banks and finance ministries ranging from anti-corruption and agriculture to health, culture and tourism and foreign ministers, and other ministerial meetings.
- Even as the final list of cities is being finalised based on a set of transparent criteria such as conference infrastructure, accommodation availability, rankings in Swachh Bharat and other parameters, close to 35 cities with this potential have already been identified.
- During this time, the plan is to ensure due rigour, dedication and showcase the country’s cultural richness while welcoming the world to India.
- The Ministry of Tourism also plans to work with other Ministries to bring in necessary interventions such as visa reforms, ease of travel, traveller-friendly and improved immigration facilities at airports.
Way forward:
- Over the past few months, all the major tourism indices such as domestic air passenger traffic, hotel occupancy and tourist footfalls have shown signs of recovery and are going back to pre-pandemic levels.
- By mid-2024, we would be at pre-pandemic levels, with India achieving $150 billion as GDP contribution from tourism and $30 billion in foreign exchange earnings with 15 million foreign tourist arrivals.
- By 2030, India is estimated to grow at 7%-9% compounded annual growth rate and we expect the enabling policy framework to bring in $250 billion in GDP contribution from tourism, 140 million jobs in the tourism sector.
- India’s age-old dictum of ‘Atithi Devo Bhava’ will come to the fore as it welcomes tourists across the world under a new age tourism policy.
Source: The Hindu
Baba’s Explainer -A Push for Semiconductor Industry
Syllabus
- GS-3: Indian Economy and issues relating to planning, mobilization, of resources, growth, development and employment.
Context: Semiconductors are the new battleground in the field of high technology as nations race to establish a foothold in the manufacture of these vital components that power everything from traffic lights to advanced weaponry
In a bid to make India’s $10 billion chip-making initiative more attractive to investors, the Centre on September 21, approved changes to the scheme for the development of a semiconductor and display manufacturing ecosystem.
Read Complete Details on A Push for Semiconductor Industry
Daily Practice MCQs
Q.1) Which one of the following issues the ‘The Breakthrough Agenda Report 2022’ report periodically?
- International Atomic Energy Agency
- The World Bank
- International Energy Agency
- International Union for Conservation of Nature
Q.2) Consider the following statements in respect of the Asian Palm Oil Alliance (APOA):
- It is an edible oil trade association formed of palm oil importing countries.
- It was formed in the year 2020.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 and 2
Q.3) In which of the following areas can GPS technology be used?
- Mobile phone operations
- Creating maps of the world
- Monitoring personal/Object movement
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
- 1 and 3 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1 and 2 only
- 1 2 and 3
Comment the answers to the above questions in the comment section below!!
ANSWERS FOR ’27th September 2022 – Daily Practice MCQs’ will be updated along with tomorrow’s Daily Current Affairs.
ANSWERS FOR 26th September – Daily Practice MCQs
Q.1) – c
Q.2) – a
Q.3) – b











