IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
Archives
(PRELIMS & MAINS Focus)
Syllabus
- Prelims – Environment
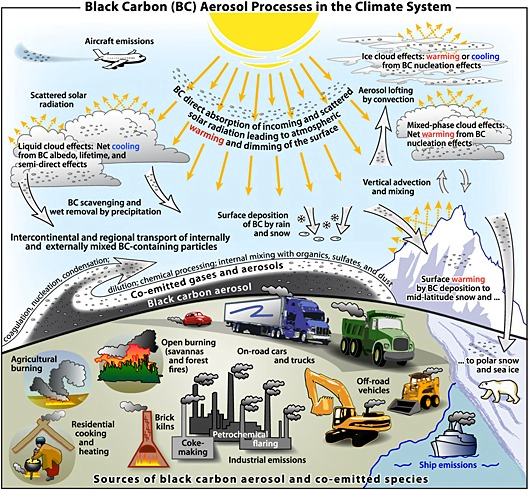
Context: A recent study conducted on Tibetan plateau showed that increase in South Asian black Carbon aerosols is increasing loss of glaciers from Tibetan Plateau.
Key highlights of the study:
- Black carbon deposition in snow reduces the albedo of surfaces which accelerate melting of glaciers and snow cover and changes hydrological process and water resources in the region.
- Albedo is ability to reflect back Sun’s radiations.
- Black carbon aerosols in South Asia heat up the middle and upper atmosphere and increases North South temperature gradient.
- This increases convective activity in South Asia which causes convergence of water vapour in South Asia.
- Black carbon also increases the number of cloud condensation nuclei in the atmosphere.
About Black Carbon:

- Black carbon is the sooty black material emitted from gas and diesel engines, coal-fired power plants, and other sources that burn fossil fuel.
- It comprises a significant portion of particulate matter or PM, which is an air pollutant.
Impact of black carbon:
- Climate impacts: It has a warming impact that is 460-1,500 times stronger than CO2 on climate.
- It converts incoming solar radiation to heat.
- It influences cloud formation and impacts regional circulation and rainfall patterns.
- Health impacts- With size of 2.5 micrometres (PM2.5) or smaller, it can penetrate into lungs and facilitate transport of toxic compounds into the bloodstream.
- 5 can cause premature death and cause heart and lung disease, strokes, heart attacks, chronic respiratory disease like bronchitis, asthma and pneumonia.
- Impacts on ecosystem and vegetation- if deposited on plant leaves it will decrease its capability of photosynthesis and thus reduce food production.
- It can reduce sunlight that reaches the earth and modify rainfall patterns.
About Black Carbon aerosols:
- It is produced by the incomplete combustion of fossil fuels and biomass.
- It has strong absorption of solar radiation like- visible and infrared radiation.
- It is also called soot and is part of particulate matter above PM2.5.
- Thus, it contributes to pollution and Global warming.
- It can increase the temperature of atmosphere and darken surfaces, specifically snow and ice.
- It has short lifetime in atmosphere and gets removed in 1-2 weeks, so its impacts tend to be more regional rather than global.
Source: The Hindu
Previous Year Questions
Q.1) Among the following crops, which one is the most important anthropogenic source of both methane and nitrous oxide ? (2022)
- Cotton
- Rice
- Sugarcane
- Wheat
Q.2) In the Guidelines, statements: context of WHO consider the Air Quality following
- The 24-hour mean of PM2.5 should not exceed 15 ug/m³ and annual mean of PM 2.5 should not exceed 5 µg/m³.
- In a year, the highest levels of ozone pollution occur during the periods of inclement weather.
- PM10 can penetrate the lung barrier and enter the bloodstream.
- Excessive ozone in the air can trigger asthma.
Which of the statements given above are correct? (2022)
- 1, 3 and 4
- 1 and 4 only
- 2, 3 and 4
- 1 and 2 only
Syllabus
- Prelims – Environment
Context: Recently, Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO) launched report on Urban forestry and urban greening in drylands.
Key findings of the report:
- 35% of the world’s largest cities are built in the world’s drylands.
- It includes Cairo, Mexico City and New Delhi.
- They are home to 2 billion people, 90% of them in developing countries.
- Urban forestry and urban greening in drylands, these sprawling and crowded dryland cities face a high risk of social, environmental and economic crisis as they grow.
- They are becoming hotter and more polluted and face mounting pressure on their scarce natural resources.
- Weak infrastructure, making them among the most vulnerable places in the world to external shocks from the extreme weather events that climate change brings.
- More than half of the global population lives in cities and 95% of urban growth between now and 2050 is expected to take place in the global South.
- Thus, preserving and planting trees has been shown beneficial effect on the lives and health of the people.
About Green Urban Oases Programme:

- It was Launched in 2021 by FAO.
- It contributes to the FAO Green Cities initiative, which was launched in 2020.
- It aims to improve the resilience of dryland cities by tackling climate, health, food and economic challenges.
- To transform dryland cities into ‘green urban oases’ by strengthening their overall resilience to climatic, health, food and economic crises for the improved health and well-being of urban communities.
- It focuses on developing policy, technical capacity and outlines several pathways for transforming urban spaces by planting trees.
Key Recommendation from report:
- Community Level: Boosting participation and a sense of ownership, providing incentives to encourage tree planting and building capacity through environmental education, awareness raising campaigns towards public engagement.
- Government Level: Implementing robust policies for protection of urban greenery.
- Several initiatives including the Great Green Wall in Africa and the Three-North Shelter Forest Programme in China have been put in place to support the implementation of climate adaptation and mitigation strategies in dryland rural areas.
Source: FAO
Previous Year Question
Q.1) The “Miyawaki method” is well known for the: (2022)
- Promotion of commercial farming in arid and semi-arid areas
- Harvesting wind energy on coastal areas and on sea surfaces
- Development of gardens genetically modified flora using
- Creation of mini forests in urban areas
Q.2) Consider the following statements:
- The Climate Group is an international non-profit organisation that drives climate action by building large networks and runs them.
- The International Energy Agency in partnership with the Climate Group launched a global initiative “EP100”.
- EP100 brings together leading companies committed to driving innovation in energy efficiency and increasing competitiveness while delivering on emission reduction goals.
- Some Indian companies are members of EP100.
- The International Energy Agency is the Secretariat to the “Under2 Coalition”.
Which of the statements given above are correct? (2022)
- 1,2, 4 and 5
- 1,3 and 4 only
- 2,3 and 5 only
- 1,2, 3, 4 and 5
Syllabus
- Prelims – Polity and Governance
Context: By ruling that a citizen can seek enforcement of the fundamental rights to freedom of speech not just against the state, the Supreme Court has, effectively, extended the ground for seeking these rights against other citizens.
About Article 19:
Article 19(1) of the Constitution of India guarantees six fundamental freedoms to every citizen of India, namely:
- Freedom of speech and expression;
- Freedom to assemble peacefully and without arms;
- Freedom to form associations, unions or co-operative societies;
- Freedom to move freely throughout the territory of India;
- Freedom to reside and settle in any part of the territory of India, and
- Freedom to practice any profession, or to carry on any occupation, trade or business.
Importance of Article 19
- This freedom is essential because the censorial power lies in the people over and against the Government and not in the Government over and against the people.
- The freedom of speech and expression is required to fulfil the following objectives :
- To discover truth
- Non self-fulfilment
- Democratic value
- To ensure pluralism
Reasonable Restrictions under Article 19: The State can impose restrictions on the freedom of speech and expression in the interests of
- Sovereignty And Integrity Of India,
- The Security Of The State,
- Friendly Relations With Foreign States,
- Public Order, Decency Or Morality, Or
- In Relation To Contempt Of Court,
- Defamation, Or
- Incitement To An Offence.
Key details of the Supreme Court ruling:
- The court took this view while ruling that the right of free speech and expression guaranteed under the Article 19(1)(a) cannot be curbed by any additional grounds other than those already laid down in Article 19(2).
- Article 19 which guarantees freedom of speech and expression is a right invoked against the state.
- The court, extending free speech against private citizens, opens up a range of possibilities in Constitutional law.
- This interpretation could also bring an obligation on the state to ensure private entities also abide by Constitutional norms.
- K S Puttaswamy case: The Court relied on the 2017 verdict in Puttaswamy where a nine-judge bench unanimously upheld privacy as a fundamental right.
- One of the key arguments by the government was that privacy is a right enforceable against other citizens and, therefore, cannot be elevated to the status of a fundamental right against the state.
- Under Indian Constitution, all the Fundamental Rights are available against the State but only 4 fundamental Rights are available against both State and individuals.
- Article 15(2) – no citizen shall be subjected to any form of discrimination based on caste, religion, place of birth, or caste.
- Article 17 – abolition of Untouchability.
- Article 23 – Prohibits trafficking of humans and forced labour.
- Article 24 – Prohibits employment of children in factories and hazardous place.
Source: Indian Express
Previous Year Questions
Q.1) What is the position of the Right to Property in India? (2021)
- Legal right available to citizens only
- Legal right available to any person
- Fundamental Right available to citizens only
- Neither fundamental Right nor legal right
Q.2) A legislation which confers on the executive or administrative authority an unguided and uncontrolled discretionary power in the matter of the application of law violates which one of the following Articles of the Constitution of India? (2021)
- Article 14
- Article 28
- Article 32
- Article 44
Syllabus
- Prelims – Governance
Context: Union Education and Skill Development & Entrepreneurship Minister chaired the 3rd meeting of the steering committee of National Skill Development Mission.
About National Skill Development Mission:
- The National Skill Development Mission was approved by the Union Cabinet on 01.07.2015, and officially launched by the Hon’ble Prime Minister on 15.07.2015 on the occasion of World Youth Skills Day.
- The Mission has been developed to create convergence across sectors and States in terms of skill training activities.
- Further, to achieve the vision of ‘Skilled India’, the National Skill Development Mission would not only consolidate and coordinate skilling efforts, but also expedite decision making across sectors to achieve skilling at scale with speed and standards.
- It will be implemented through a streamlined institutional mechanism driven by Ministry of Skill Development and Entrepreneurship (MSDE).
- Key institutional mechanisms for achieving the objectives of the Mission have been divided into three tiers, which will consist of a Governing Council for policy guidance at apex level, a Steering Committee and a Mission Directorate (along with an Executive Committee) as the executive arm of the Mission.
- Mission Directorate will be supported by three other institutions:
- National Skill Development Agency (NSDA),
- The NSDA focuses on policy research via National Skills Research Division, quality assurance and implementation of quality standards across all skilling agencies.
- It develops protocols for training and accreditations for private trainers, etc.
- National Skill Development Corporation (NSDC)
- NSDC overlooks training, capacity building aspects of trainers, both public and private, lead the engagement with industries, drive the sectors skills councils., and
- Directorate General of Training (DGT)
- The DGT maintains the skill training structures of Advanced Training Institutes (ATIs), Regional Vocational Training Institute (RVTIs) and other such institutes, advises on training policies, trains instructors, provides technical support, runs women-centric training institutes, etc.
- all of which will have horizontal linkages with Mission Directorate to facilitate smooth functioning of the national institutional mechanism. Seven sub-missions have been proposed initially to act as building blocks for achieving overall objectives of the Mission.
- National Skill Development Agency (NSDA),
- They are: (i) Institutional Training, (ii) Infrastructure, (iii) Convergence, (iv) Trainers, (v) Overseas Employment, (vi) Sustainable Livelihoods, (vii) Leveraging Public Infrastructure.
Source: NewsOnAir
Previous Year Questions
Q.1) In India under cyber insurance for individuals, which of the following benefits are generally covered, in addition to payment for the loss of funds and other benefits? (2020)
- Cost of restoration of the computer system in case of malware disrupting access to one’s computer
- Cost of a new computer if some miscreant wilfully damages it, if proved so
- Cost of hiring a specialized consultant to minimize the loss in case of cyber extortion
- Cost of defence in the Court of Law if any third party files a suit
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
- 1, 2 and 4 only
- 1, 3 and 4 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1, 2, 3 and 4
Syllabus
- Prelims – Science and Technology
Context: Scientists made a monumental breakthrough by identifying an organism, Halteria that dines entirely on viruses.
About Halteria:
- Halteria is a microscopic ciliates (a single-celled organism with minuscule hairs) that populate freshwater worldwide which can thrive wholly on a virus-only diet or ‘virovory’.
- Virovory is sufficient to support an organism’s physiological development and even population increase.
- They’re made up of nucleic acids, a lot of nitrogen and phosphorous.
Source: ScienceAlert
Previous Year Question
Q.1) With reference to recent developments regarding ‘Recombinant vector Vaccines’, consider the following statements:
- Genetic engineering is applied in the development of these vaccines.
- Bacteria and viruses are used as vectors.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct? (2021)
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Syllabus
- Prelims – Governance
In News: The Cabinet Committee on Economic Affairs approved regarding “Broadcasting Infrastructure and Network Development” (BIND) scheme at a cost of ₹2,539.61 crore.
Broadcasting Infrastructure and Network Development (BIND):
Aim:
- For infrastructure development and for providing financial support to Prasar Bharati for expenses related to expansion and upgradation of its broadcasting infrastructure, content development and civil work related to the organization.
- The BIND scheme will enable the public broadcaster to undertake a major upgradation of its facilities with better infrastructure which will widen its reach, including in the LWE, border and strategic areas
- Development of high-quality content for both domestic and international audience and ensuring availability of diverse content to the viewers by upgradation of capacity of DTH platform to accommodate more channels.
About the scheme:
- Central Sector Scheme
- Under the Ministry of Information and Broadcasting
- Purchase of OB vans and digital upgradation of DD and AIR Studios to make them HD ready will be also be done as part of the project.
- The Scheme will increase coverage of AIR FM transmitters in the country to 66% by geographical area and 80% by population up from 59% and 68% respectively.
- The Scheme also envisages free distribution of over 8 lakh DD Free Dish STBs to people living in remote, tribal, LWE and border areas.
- The Project for modernization and augmentation of broadcast infrastructure also has the potential to generate indirect employment by way of manufacturing and services related to supply and installation of broadcast equipment.
- Content generation and content innovation for AIR & DD has the potential of indirect employment of persons with varied experience of different media fields in the content production sector including TV/Radio production, transmission and associated media related services.
- Government of India reiterates its commitment to the development, modernization and strengthening of Doordarshan and Akashvani (Prasar Bharati) infrastructure and services, which is a continuous process.
Prasar Bharti:
- Prasar Bharati is the public broadcaster of the country and consists of All India Radio (AIR) and Doordarshan (DD)
- It is the most important vehicle of information, education, entertainment and engagement for the people especially in the remote areas of the country through Doordarshan and All India Radio.
- Prasar Bharati played a stellar role in communicating public health messages and awareness to the public during the covid pandemic.
- At present, Doordarshan operates 36 TV channels including 28 regional channels and All India Radio operates more than 500 broadcasting centres.
Source: PIB
Syllabus
- Prelims – Environment
In News: A bird survey conducted at the Silent Valley National Park identified 141 species, of which 17 were new. So far, 175 species of birds have been spotted in Silent Valley.
About the survey
- The survey was held in association with the Kerala Natural History Society.
- Brown wood owl, Banded bay cuckoo, Malabar wood shrike, White-throated kingfisher, Indian nightjar, Jungle nightjar, and Large cuckoo shrike were among the 17 species newly identified in the Silent Valley.
Silent valley national park
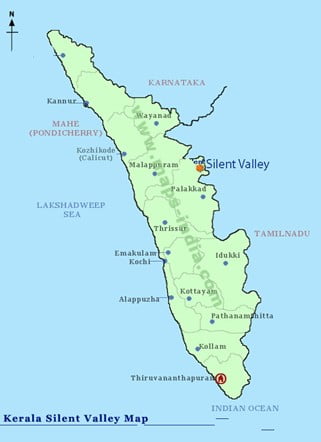
- Silent Valley National Park is a national park in Kerala, India.
- It is located in the Nilgiri hills, has a core area of 89.52 km2 which is surrounded by a buffer zone of 148 km2
- Declared national park in 1984, inaugurated in 1985
- In 1914, Silent Valley forests were declared as Reserved Forest.
- During 1921, it came under control of Palakkad Forest Division
- This national park has some rare species of flora and fauna.
- This area was explored in 1847 by the botanist Robert Wight.
- It is located in the rich biodiversity of Nilgiri Biosphere Reserve.
- Mukurthi peak, the fifth-highest peak in South India, and Anginda peak are also located in its vicinity.
- Bhavani River, a tributary of Kaveri River, and Kunthipuzha River, a tributary of Bharathappuzha river, originate in the vicinity of Silent Valley.
- The Kadalundi River has also its origin in Silent Valley.
- 41 mammals, 211 birds, 49 reptiles, 47 amphibians, 12 fishes, 164 butterflies and 400 species of moths are found here.
- Lion tailed macaques is the flagship species of the Park.
- The indigenous tribal groups that live within park boundaries include Irulas, Kurumbas, Mudugas and Kattunaikkars, the ethnic heritage of these communities is well protected.
- Karimpuzha Wildlife Sanctuary, New Amarambalam Reserved Forest, and Nedumkayam Rainforest in Nilambur Taluk of Malappuram district, Attappadi Reserved Forest in Mannarkkad Taluk of Palakkad district, and Mukurthi National Park of Nilgiris district, are located around Silent Valley National Park.
Source: The hindu
Previous Year Question
Q.1) With reference to India’s Desert National Park, which of the following statements are correct? (2020)
- It is spread over two districts.
- There is no human habitation inside the Park.
- It is one of the natural habitats of Great Indian Bustard.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
- 1 and 2 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
Syllabus
- Prelims – Environment
In News: A new initiative of sustainable shrimp cultivation provides hope for mangrove restoration in Sundarbans.
SAIME:
- The community-based initiative of sustainable shrimp cultivation is being conceived by NEWS and Global Nature Fund (GNF), Naturland Bangladesh Environment and Development Society (BEDS).
- The initiative started in 2019, has established a collaborative ecosystem integrating several key stakeholders from government departments, academia, and research institutes for co-creation and comprehensive advancement of this project.
- Farmers have taken up cultivation of shrimp in West Bengal including indigenous varieties of shrimps such as black tiger shrimp (P. monodon) and giant freshwater prawn (M. rosenbergii ).
- A research program on the contribution of mangrove leaf litter in the nutritional dynamics in SAIME ponds has been initiated in collaboration with the Centre for Excellence in Blue Economy (CoE-BE) of the Indian Institute of Science Education and Research (IISER), Kolkata
- Fishing, particularly shrimp cultivation, is one of the key occupations of the people of Sundarbans, which is a complex network of rivers and low-lying islands that face a tide surge twice a day.
- Shrimp cultivation is practised in about 15,000 to 20,000 hectares of the unique ecosystem in India. T
- The Sundarbans forest is about 10,000 sq. km across India and Bangladesh, of which 40% lies in India.
MUST READ: Sunderbans
Source: The hindu
Previous Year Question
Q.1) Consider the following protected areas
- Bandipur
- Bhitarkanika
- Manas
- Sunderbans
Which of the above are declared Tiger Reserves?
- 1 and 2 only
- 1, 3 and 4 only
- 2, 3 and 4 only
- 1, 2, 3 and 4
Syllabus
- Prelims – Science and Technology
In News: The United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) has granted a conditional license for world’s first vaccine for honeybees to curb American foulbrood (AFB), a fatal bacterial disease for the insect, reported The Guardian.
- Honeybee populations are declining sharply, spurred by habitat loss, pesticide use and the climate crisis.
- Fewer honeybees mean not just less honey but also less food — honeybees are critical to pollinating up to 95 crops in the US.
AFB
- AFB is caused by the spore-forming bacterium Paenibacillus larvae.
- Infected broods usually die at the pre-pupal or pupal stage.
- It is not a stress-related disease and can infect the strongest to the weakest colony in an apiary.
- Heavy infections can affect most of the brood, severely weakening the colony and eventually killing it.
- The disease cannot be cured, meaning that the destruction of infected colonies and hives or irradiation of infected material is the only way to manage AFB.
- The bacteria Melissococcus plutonius causes another similar disease, European foulbrood. However, the incidence of EFB is generally higher when the colony is under stress.
Vaccine:
- The first such vaccine, developed by biotechnology company Dalan Animal Health, gives hope of a new weapon against diseases that routinely ravage colonies relied upon for food pollination.
- The vaccine technology exposes queen bees to inactive (ie, “dead”) bacteria, which enables the larvae hatched in the hive to resist infection.
- The vaccine is mixed in queen candy — the primary food source for both the queen bees and the attendant bees living in cages.
- Worker bees consume the vaccine with the queen candy, which is then digested and transferred to the glands that produce the royal jelly. Worker bees then feed the royal jelly containing the vaccine to the queen bee.
- The queen digests the royal jelly and the vaccine is transferred to her ovaries. She is then released into the hive. The vaccine gets transferred to the developing eggs. The developing larvae get vaccinated and are more immune to infection as they hatch.
- Tests also showed no negative impact on honey.
Source DTE
Previous Year Question
Q.1) The term ‘ACE2’ is talked about in the context of (2021)
- genes introduced in the genetically modified plants
- development of India’s own satellite navigation system
- radio collar for wildlife tracking
- spread of viral diseases
Syllabus
- Prelims – GS 2 (Governance) and GS 3 (Environment)
Context: The Union Cabinet, chaired by the Prime Minister has approved India’s Rs 20,000 cr National Green Hydrogen Mission (NGHM).
About Hydrogen:
- Hydrogen is the chemical element with the symbol H and atomic number 1.
- Hydrogen is the lightest element and the most abundant chemical substance in the universe, constituting roughly 75% of all normal matter.
- It is colourless, odourless, tasteless, non-toxic, and highly combustible.
- Hydrogen fuel is a zero-emission fuel burned with oxygen. It can be used in fuel cells or internal combustion engines and as a fuel for spacecraft propulsion.

Extraction of Hydrogen:
- Hydrogen exists in combination with other elements.
- Hence, for using it as a source of energy, it has to be extracted from naturally occurring compounds like water (which is a combination of two hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom).
- The sources and processes by which hydrogen is derived are categorised by different colours.
Benefits of Green Hydrogen
- Creation of export opportunities for Green Hydrogen and its derivatives
- Decarbonisation of industrial, mobility and energy sectors
- Self-Reliance: Reduction in dependence on imported fossil fuels and feedstock
- Make in India, for India: Development of indigenous manufacturing capabilities
- Creation of employment opportunities
- Development of cutting-edge technologies
Major Challenges in harnessing Green Hydrogen:
- Lack of fuel station infrastructure: India will need to compete with around 500 operational hydrogen stations in the world today which are mostly in Europe, followed by Japan and South Korea.
- Energy-intensive nature of Hydrogen generation process:
- The technology is in an infant stage and the energy requirement for splitting water or Methane is high. Besides, the whole process is costly at present.
- High R and D requirement for the newer technology for making the process cheap and operational and scalable.
- Multiplicity of regulatory authorities: Involvement of multiple Ministries and Departments causes red tape in government functioning.
- Risks associated with the transportation of hydrogen: Hydrogen in gaseous form is highly inflammable and difficult to transport, thereby making safety a primary concern.
About National Green Hydrogen Mission (NHM):
- NGHM is a part of National Hydrogen Mission (NHM) which was announced by the finance minister in the Union Budget 2021-22.
- The Prime Minister of India also announced the National Hydrogen Mission on India’s 75th Independence Day.
- The Ministry of New and Renewable Energy (MNRE) will formulate the scheme guidelines for implementation of the respective components.
Objectives of the mission:
- To make India a global hub for the production and export of green hydrogen.
- To harness green hydrogen energy to fulfill India’s Nationally Determined Contributions (NDCs).
Key Components of the mission:
- The NGHM will facilitate demand creation, production, utilization and export of Green Hydrogen.
- The Mission will also support pilot projects in emerging end-use sectors and production pathways.
- An enabling policy framework will be developed to support establishment of the Green Hydrogen ecosystem.
- A public-private partnership framework for R&D will be facilitated under the Mission. R&D projects will be goal-oriented, time bound, and suitably scaled up to develop globally competitive technologies.
Significance of the NGHM:
- Renewable Energy Capacity Enhancement: Development of green hydrogen production capacity of at least 5 MMT (Million Metric Tonne) per annum.
- An associated renewable energy capacity addition of about 125 GW in the country
- It will boost Investment opportunities for India and create sustainable employment.
- Cumulative reduction in fossil fuel imports.
- Green House Gas Emission Reduction: Abatement of nearly 50 MMT of annual greenhouse gas emissions and help government in achievement the commitments made at COP 26.
Initiatives taken by the world countries and India:
- Japan: Basic Hydrogen Strategy 2017 and plan to develop the international hydrogen supply chain by 2030.
- South Korea: Hydrogen Economy Development and Safe Management of Hydrogen Act, 2020.
- The Ministry of Road Transport and Highways (MoRTH) issued a notification proposing amendments to the Central Motor Vehicles Rules, 1989 with safety evaluation standards for hydrogen fuel cell-based vehicles.
- Delhi State Government: Hydrogen Spiked Compressed Natural Gas Buses (H-CNG) i.e. 18% blend of hydrogen with CNG (Plan to have 80% H-CNG buses by 2025)
- NTPC Ltd is operating a pilot to run 10 hydrogen fuel cell-based electric buses and fuel cell electric cars in Leh and Delhi.
Way Forward:
The National Hydrogen Mission have the capability of ensuring integration of India’s clean energy supply chains with that of the world when Inter-Ministerial and various departments work together.
The National Hydrogen Mission will also will ensure realization of the goal of making India carbon neutral and global hub of clean hydrogen energy and will have multiplier effects on the $5 trillion economy.
Source: Indian Express
Syllabus
- Mains – GS 2 International Relations
Context:

- 36th India-France Strategic Dialogue between National Security Adviser Ajit Doval and Diplomatic Adviser to the President of France, Emmanuel Bonne was held in New Delhi.
- India and France reiterated their commitment to take forward their strategic partnership to ensure peace, stability and security in the Indo-Pacific based on common beliefs in the rules-based international order and strategic autonomy.
- Both sides reiterated that in view of the emerging uncertainties and volatile global security environment, there was a need for closer cooperation between India and France, including in the UNSC and other multilateral forums..
Bilateral relationship:
- The new French Indo-Pacific strategy advances three key threats to be met by Paris, beyond dealing with North Korean belligerence:
- Transnational terrorism
- Chinese challenges to the multilateral order in the region
- Climate change
- Indo Pacific: France is a preferred partner in the Indo-Pacific and there is now a blueprint for cooperation in this field in the form of a Joint Strategic Vision for cooperation in the Indian Ocean Region concluded by both countries in 2018.
Economic:
- France is the 7th largest foreign investor in India with a cumulative FDI stock of USD 9 billion from 2000 to 2020, which represents 2 % of the total FDI inflows into India.
- In FY 2020-21, bilateral trade stood at $ 9.12 Bn and has increased to $ 9.87 Bn during the period April 2021 – January 2022.
- Launch of Unified Payment Interface (UPI) in France
- “Co-localisation of production” with India as a priority indicates urgency to take steps for ensuring a more diversified and stable Indo-Pacific and global periphery.
Security:
- Bilateral defence ties are in fine fettle and France has largely stuck to the promised delivery of Rafale aircrafts to India.
- The challenge here is to move from a buyer-seller relationship to an investor-investee one by making defence equipment in India accompanied by a transfer of technology.
- Safran Group’s decision to set up their largest and first aircraft engine MRO (maintenance, repair, and overhaul) facility in Hyderabad.
- The facility will be set up with an investment of Rs 1200 cr and is expected to create about 1,000 high-skilled jobs in Telangana.
- India and France have conducted joint patrols from the Reunion Island for the first time.
- The patrol was conducted by a P-8I aircraft with French Navy personnel on board.
- Bilateral military exercises
- Exercise Shakti (Army)
- Exercise Varuna (Navy)
- Exercise Garuda (Air Force)
- IMEX 22
Technology:
- For the first time, the two countries concluded a Joint Vision for Space Cooperation in 2018.
- The vision document talks of bringing societal benefits of space technology, situational awareness in space domain and cooperation in satellite navigation and related technologies.
- As for nuclear energy, the two leaders must review progress in the joint construction of the world’s largest nuclear park in Jaitapur, Maharashtra.
- The French tech services multinational Atos, for instance, provides India with supercomputing hardware and quantum computing simulation software.
- A recent Track 1.5 Dialogue hosted jointly by think tanks — Gateway House in Mumbai and Ifri in Paris — revealed the importance of Bangalore for the French economy, noting the large number of tech engineers from France who are located in the southern city.
- France also has a special tech visa for Indian engineers, enabling robust exchanges.
- Digital cooperation is being stepped up in cyber security and on building standards for public digital infrastructure.
Environment and Ecology:
- India will be the first “country of honour” at the Sea Tech . Week in Brest, France, a major international event bringing together Blue Economy stakeholders.
- France announced its support for Prime Minister Modi’s Lifestyle for the Environment (LIFE) initiative, and will seek to work with India on promoting sustainable lifestyles to fight climate change.
- Regarding solar alliance, India has started having annual summits with France and Germany from 2000.
- 2021: Year Of Indo-French Alliance Towards A Greener Planet
- To strengthen Indo-French cooperation in sustainable development, increase the effectiveness of actions in favour of global environment protection and give them greater visibility.
- Based on five main themes: (1) Environmental protection; (2) Climate change; (3) Biodiversity conservation; (4) Sustainable urban development; (5) Development of renewable energies and energy efficiency.
Suggestions for future:
- France holds the rotating presidency of the EU
- In this regard, discussion on FTA and the Investment Agreement that India is negotiating with the EU and persuade France to weigh in favourably with the Brussels bureaucracy and other stakeholders.
- More can be done in the area of digital sovereignty where India is a potential model for France with its use of open platforms and open-source public goods like India Stack and MOSIP; regulation, especially personal data empowerment and protection; health data and health tech.
- France and India must now invest in preventing digital platforms from being weaponised and avert threats to critical infrastructure.
- They must use their unique strengths — India in conceptualising and deploying large-scale open-source platforms, foundational IDs, IT services and fintech, and France in AI, cyber, quantum technologies, data empowerment and protection, to create the next-gen solutions for the world.
- Accelerate investment between two countries in low carbon alternatives like wind, solar PV, biomethane, heat pumps, nuclear and clean hydrogen.
- India has the market, France has the technology and capital, and the EU has the political will and incentives to drive the transition to green hydrogen.
- Major French multinationals such as Air Liquide, Engie and TotalEnergies are already pursuing hydrogen energy, and pilot projects with Indian partners can be planned
- They discussed expanding the scope of defence cooperation to include the co-development of futuristic technologies in line with India’s priorities of Make in India and Atmanirbhar Bharat.
Way forward:
- Newer areas of cooperation such as connectivity, climate change, cyber-security and science and technology.
- In these important areas, the two leaders will be briefed by officials about progress made so that roadblocks, if any, can be tackled.
- France has supported India’s G20 presidency and it goes a long way in strengthening ties between the two countries.
Source: The hindu
Baba’s Explainer – Jallikattu & the controversy
Syllabus
- GS-1: Indian Society and History
- GS-2: Federalism; Judiciary
- GS-3: Animal Conservation and Rural Economy
Context: With the Supreme Court recommencing its work after the winter vacation, all eyes in Tamil Nadu are on the verdict of a five-member Constitution Bench of the Court on a batch of petitions seeking to strike down a 2017 Tamil Nadu law that protects jallikattu, a traditional event involving bulls.
- As the conduct of the event will coincide with the Pongal festival, the Supreme Court’s verdict is keenly watched.
Read Complete Details on Jallikattu & the controversy
Practice MCQs
Q.1) With reference to ‘Silent Valley National Park’, consider the following statements?
- Lion tailed macaque is its flagship species
- It comes under Annamalai Biosphere reserve
Which of the following statements are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Q.2) With reference to ‘American foulbrood (AFB) disease’, consider the following statements?
- The disease affects pollination in maize plants.
- It is caused by spore-forming bacteria
Which of the following statements are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Q.3) Consider the following:
- Households
- Agriculture
- Fossil fuels
- Transportation
Which of the are sources of Black carbon which has serious consequences on climate change?
- 1 2 and 3 only
- 2 3 and 4 only
- 1 3 and 4 only
- 1 2 3 and 4
Comment the answers to the above questions in the comment section below!!
ANSWERS FOR ’ 6th January 2023 – Daily Practice MCQs’ will be updated along with tomorrow’s Daily Current Affairs.st
ANSWERS FOR 5th January – Daily Practice MCQs
Q.1) – d
Q.2) – d
Q.3) – c











