IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
Archives
(PRELIMS & MAINS Focus)
Syllabus
- Prelims – History
Context: The Treaty of Alinagar, signed in 1757, was a reluctant agreement signed by Bengal’s Nawab Siraj ud Daula with the English East India Company.
About Treaty of Alinagar:

- The treaty of Alinagar (changed name of Calcutta) was signed between Robert Clive of the British East India Company and the Nawab of Bengal, Mirza Muhammad Siraj Ud Daula.
Terms of the treaty:
- The Nawab would recognize all the provisions of Mughal Emperor Farrukhsiyar’s farman of 1717.
- All British goods that passed through Bengal would be exempt from duties.
- The British would not be hindered from fortifying Calcutta, as well as mint coins in Calcutta.
- The signing of the treaty was one of the events leading up to the famous Battle of Plassey.
- The Nawab was defeated and killed by Clive and his allies.
Significance of the treaty:
- The Treaty strengthened the position of the British in Bengal.
- It laid foundations for the Battle of Plassey.
- It set the stage for British colonial expansion in India, turning what was an economic enterprise into an imperial one.
Source: Indian Express
Previous Year Questions
Q.1) With reference to Indian history, consider the following statements:
- The Dutch established their factories/warehouses on the east coast on lands granted to them by Gajapati rulers.
- Alfonso de Albuquerque captured Goa from the Bijapur Sultanate.
- The English East India. Company established a factory at Madras on a plot of land leased from a representative of the Vijayanagara empire.
Which of the statements given above are correct? (2022)
- 1 and 2 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
Q.2) In the first quarter of the seventeenth century, in which of the following was/were the factory/factories of the English East India Company located? (2021)
- Broach
- Chicacole
- Trichinopoly
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
- 1 only
- 1 and 2
- 3 only
- 2 and 3
Syllabus
- Prelims – Governance
Context: Recently, India’s national accreditation system under the Quality Council of India (QCI) has been ranked 5th in the world in the recent Global Quality Infrastructure Index (GQII) 2021.
- India’s overall QI system ranking continues to be in the Top 10 at the 10th position, with
- the standardization system (under BIS) at 9th and
- The metrology system (under NPL-CSIR) at 21st position in the world.
About Global Quality Infrastructure Index (GQII):
- The GQII ranks the 184 economies in the world on the basis of quality infrastructure (QI).
- The GQII is a database and ranking that allows interested persons to compare the quality infrastructure of different countries worldwide.
- The GQII program is an initiative of the independent consulting firms Mesopartner and Analytics to research and disseminate data on Quality Infrastructure.
- Quality Infrastructure means the international system of metrology, standardization, accreditation and quality-related services (testing, calibration, inspection, verification, training and awareness building).
- GQII rankings are published and presented post-facto for each year based on the data collected till the end of that year.
About Quality Council of India:
- It was established as a National body for Accreditation on recommendations of Expert Mission of EU after consultations in Inter-ministerial Task Force, Committee of Secretaries and Group of Ministers through a Cabinet decision in 1996.
- QCI was set up through a PPP model as an independent autonomous organization with the support of Government of India and the Indian Industry represented by the three premier industry associations, (i) Associated Chambers of Commerce and Industry of India (ASSOCHAM), (ii) Confederation of Indian Industry (CII) and (iii) Federation of Indian Chambers of Commerce and Industry (FICCI).
- QCI is a non-profit organization registered under the Societies Registration Act XXI of 1860.
- The Department of Industrial Policy and Promotion, Ministry of Commerce and Industry was designated as the nodal point for all matters connected with quality and QCI to structure and help implementation of the Cabinet decision.
- It is operated through the constituent Boards of QCI, primarily the National Accreditation Board for Certification Bodies (NABCB), which provides accreditation to the certification, inspection, and validation / verification bodies.
- The National Accreditation Board for Testing & Calibration Laboratories (NABL), which provides accreditation to the testing, calibration and medical laboratories.
Source: The Hindu
Previous Year Questions
Q.1) With reference to the ‘Banks Board Bureau (BBB)’, which of the following statements are correct? (2022)
- The Governor of RBI is the Chairman of BBB.
- BBB recommends for the selection of heads for Public Sector Banks.
- BBB helps the Public Sector Banks in developing strategies and capital raising plans.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
- 1 and 2 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
Q.2) Consider the following statements :
- The weightage of food in Consumer Price Index (CPI) is higher than that in Wholesale Price Index (WPI).
- The WPI does not capture changes in the prices of services, which CPI does.
- The Reserve Bank of India has now adopted WPI as its key measure of inflation and to decide on changing the key policy rates.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct? (2020)
- 1 and 2 only
- 2 only
- 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
Syllabus
- Prelims – Governance
Context: The government informed that there is no proposal to convert National Commission for Safai Karmacharis into a statutory body.
About the National Commission for Safai Karmacharis:
- The National Commission for Safai Karamcharis (NCSK) is currently a non-statutory body.
- It investigates the conditions of Safai Karamcharis in India and makes recommendations to the Government of India.
- It was constituted in 1994 as a statutory body for a three-year period under the NCSK ACT, 1993.
- It continued till February 2004, when the relevant Act expired.
Functions of the commission:
- recommending programmes to the Central Government to eliminate inequalities in status and facilities, and to promote opportunities for Safai Karamcharis.
- studying and evaluating the implementation of the programmes and schemes for the social and economic rehabilitation of Safai Karamcharis.
- Investigating specific grievances and take suo moto notice non-implementation of:
- programmes or schemes in respect of any group of Safai Karamcharis;
- decisions, guidelines or instructions, aimed at mitigating the hardship of Safai Karamcharis with measures for the social and economic upliftment of Safai Karamcharis;
- the provisions of any law in its application to Safai Karamcharis,
- take up such matters with the concerned authorities or with the Central or State Governments;
- make periodical reports to the Central and State Governments
- In the discharge of its functions, NCSK can demand information from any Government or local or other authority.
- As per mandate of National Commission for Safai Karamcharis identification of safai karamcharis has not to be done by them.
- Sanitation is a state subject and no central data is maintained in this regard.
National Safai Karamcharis Finance and Development Corporation:
- NSKFDC is a not-for-profit company under the Ministry of Social Justice and Empowerment.
- It aims to uplift the Safai Karamcharis, Scavengers and their dependents socially and economically.
- The Prohibition of Employment as Manual Scavengers and their Rehabilitation Act, 2013
- The Act aims to eliminate insanitary latrines (those not connected to pits/septic tanks/sewage lines) alongside tracking the rehabilitation of manual scavengers in other occupations and conducting periodic surveys.
- To eliminate this practice, the act has provisions for stringent penalties, for direct or indirect employment of any person in hazardous cleaning of sewers or septic tanks by any person, local authority or agency.
- For example, even the first instance of its contravention is punishable with imprisonment up to two years or fine up to Rs 2 lakh or both.
- If a worker dies while performing such work, even with safety gear and other precautions, the employer is required to pay compensation of Rs 10 lakh to the family.
Source: PIB
Previous Year Questions
Q.1) In India under cyber insurance for individuals, which of the following benefits are generally covered, in addition to payment for the loss of funds and other benefits? (2020)
- Cost of restoration of the computer system in case of malware disrupting access to one’s computer
- Cost of a new computer if some miscreant wilfully damages it, if proved so
- Cost of hiring a specialized consultant to minimize the loss in case of cyber extortion
- Cost of defence in the Court of Law if any third party files a suit
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
- 1, 2 and 4 only
- 1, 3 and 4 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1, 2, 3 and 4
Q.2) Which of the following statements is/are correct regarding the Maternity Benefit Amendment Act, 2017? (2019)
- Pregnant women are entitled for three months pre-delivery and three months post-delivery paid leave.
- Enterprises with creches must allow the mother minimum six creche visits daily.
- Women with two children get reduced entitlements.
Select the correct answer using the code given below.
- 1 and 2 only
- 2 only
- 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
Syllabus
- Prelims – Science and Technology
Context: Sixth edition of joint exercise TARKASH recently concluded by The National Security Guard (NSG) and US Special Operations Forces (SOF).
About Exercise TARKASH:
- The exercise for the first time included “Chemical, Biological, Radiological and Nuclear (CBRN) terror response” in its drill.
- The objective was to rapidly neutralise the terrorists, rescue the hostages safely and deactivate the chemical weapons being carried by the terrorists.
Chemical, Biological, Radiological and Nuclear (CBRN) Weapons:
- CBRN weapons are also classified as weapons of mass destruction.
- They have been used by States and terror elements in the past.
- The most recent use of CBRN in the form of a sarin gas attack was witnessed in Syria in 2017 when more than 100 people died.
International Treaties related to WMD:
- The use of chemical, biological, and nuclear weapons is regulated by a number of international treaties and agreements.
Among them are the:
- Geneva Protocol, 1925, that banned the use of chemical and biological weapons
- Biological Weapons Convention, 1972, and Chemical Weapons Convention, 1992, which put comprehensive bans on the biological and chemical weapons respectively.
- India has signed and ratified both the 1972 and 1992 treaties.
- There are very few non-signatory countries to these treaties, even though several countries have been accused of non-compliance.
- The use and proliferation of nuclear weapons is regulated by treaties such as Nuclear Non-Proliferation Treaty (NPT) and the Comprehensive Test Ban Treaty (CTBT).
Source: Indian Express
Syllabus
- Prelims – Polity and Governance
Context: Recently, the Congress President cited Article 105 of the Constitution that deals with the privileges and powers of parliamentarians, to protest against the expunction of parts of his speech.
About Article 105 of the Constitution:
- Article 105 pertains to the powers, privileges, etc, of Parliament, its members and committees.
- Article 194, protects the privileges and powers of the houses of legislature, their members and committees in the states.
- Simply put, Members of Parliament are exempted from any legal action for any statement made or act done in the course of their duties.
- For example, a defamation suit cannot be filed for a statement made in the House.
- This immunity extends to certain non-members as well, such as the Attorney General for India or a Minister who may not be a member but speaks in the House.
- In cases where a Member oversteps or exceeds the contours of admissible free speech, the Speaker or the House itself will deal with it, as opposed to the court.
- The speech of MPs is subject to the discipline of the Rules of Parliament, “good sense” of its Members, and the control of proceedings by the Speaker.
- These checks ensure that MPs cannot use “defamatory or indecent or undignified or unparliamentary words” inside the House.
Source: Indian Express
Previous Year Questions
Q.1) Consider the following statements:
- The Constitution of India classifies the ministers into four ranks viz. Cabinet Minister, Minister of State with Independent Charge, Minister of State and Deputy Minister.
- The total number of ministers in the Union Government, including the Prime Minister, shall not exceed 15 percent of the total number of members in the Lok Sabha.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct? (2022)
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Q.2) Consider the following statements:
- The President of India can summon a session of the Parliament at such a place as he/she thinks fit.
- The Constitution of India provides for three sessions of the Parliament in a year, but it is not mandatory to conduct all three sessions.
- There is no minimum number of days that the Parliament is required to meet in a year.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 2 and 3 only
Syllabus
- Prelims – Geography
Context: Geological Survey of India for the first time established Lithium inferred resources in the Salal-Haimana area of the Reasi district of Jammu and Kashmir.
About Lithium:
- Lithium is a non-ferrous metal and is one of the key components in EV batteries.
- It has the symbol Li and is a chemical element.
- It’s a silvery-white metal with a delicate texture.
- It is the lightest metal and the lightest solid element under normal circumstances.
- It must be kept in mineral oil since it is very reactive and combustible.
- It is both an alkali and a rare metal.
India’s lithium reserves:
- According to the Indian Mines Ministry, the government agencies made the small discovery of lithium resources at a site in Mandya, Karnataka.
- It is the country’s first lithium reserve.
Lithium Production in the world:
- Australia, Chile, China and Argentina are the world’s top four lithium-producing countries.
- Australia is by far the world’s top producer of lithium, with an output of 42,000 tonnes in 2019.
- The Lithium Triangle is a region of the Andes rich in lithium reserves around the borders of Argentina, Bolivia and Chile.
- The lithium in the triangle is concentrated in various salt pans that exist along the Atacama Desert and neighbouring arid areas.
- The area is thought to hold around 54% of the world’s lithium reserves.
- The Indian Navy has shown interest in the Lithium Triangle as lithium will be required on Li-ION batteries that are planned to be fitted in future submarines.
MUST READ: Geological Survey of India
Source: Indian Express
Syllabus
- Prelims – Governance
Context: Union Finance Minister has announced 500 new ‘waste to wealth’ plants for promoting a circular economy with a total investment of Rs 10,000 crore under the GOBAR-Dhan scheme.
About GOBAR-Dhan Scheme:
- Galvanizing Organic Bio-Agro Resources (GOBAR)-Dhan was launched by the Government of India in April 2018 as a part of the biodegradable waste management component under the Swachh Bharat Mission-Gramin.
- The scheme intends to positively impact village cleanliness and generate wealth and energy from cattle and organic waste.
- The main focus areas of GOBAR-Dhan are to keep villages clean, increase the income of rural households and generate energy and organic manure from cattle waste.
- The Sustainable Alternatives towards Affordable Transporation (SATAT) scheme by the Ministry of Petroleum and Natural Gas (MoPNG) encourages entrepreneurs to set up CBG plants produce and supply CBG to oil and gas marketing companies (OGC/OMC) for selling it as automotive and industrial fuels.
About Sustainable Alternative Towards Affordable Transportation (SATAT):
- It is an initiative aimed at setting up of Compressed Bio-Gas production plants and make it available in the market for use in automotive fuels by inviting Expression of Interest from potential entrepreneurs.
- The initiative was launched in October 2018 by the Ministry of Petroleum & Natural Gas in association with Public Sector Undertaking (PSU) Oil Marketing Companies (OMC) viz. Indian Oil Corporation Ltd., Bharat Petroleum Corporation Ltd. and Hindustan Petroleum Corporation Ltd.
- It aims to produce compressed biogas (CBG) from Waste and Biomass sources like
- agricultural residue, cattle dung, sugarcane press mud, Municipal Solid Waste(MSW) and sewage treatment plant waste and make CBG available in the market for use as a green fuel.
- Compressed Bio-Gas (CBG) plants are proposed to be set up mainly through independent entrepreneurs.
- CBG produced at these plants will be transported through cascades of cylinders to the fuel station networks of OMCs for marketing as a green transport fuel alternative.
Source: The Economic Times
Syllabus
- Prelims – International Relations
Context: The United Kingdom Supreme Court recently ruled that the Northern Ireland Protocol, which is a post-Brexit agreement that created a trade border between Northern Ireland and the rest of the UK, is lawful.
About the Protocol:
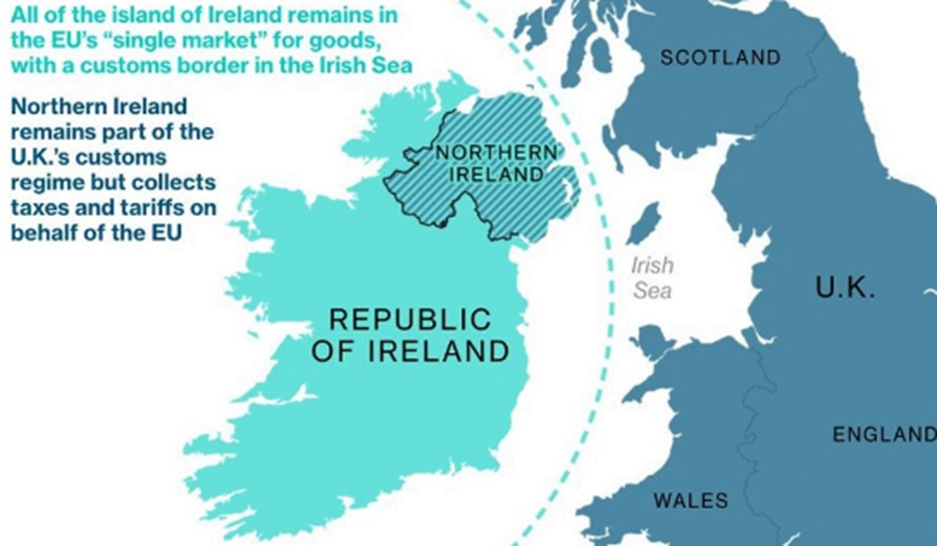
- Northern Ireland (part of the UK) shared a land border with the Republic of Ireland (an EU member).
- EU and UK have different product standards, checks are necessary for goods to move from Northern Ireland to Ireland.
- The Northern Ireland Protocol is a post-BREXIT agreement that created a trade border between Northern Ireland and the rest of the UK.
- The protocol was an integral part of the 2019 BREXIT agreement signed between the UK and the EU.
- Under the protocol,
- Northern Ireland remains in the EU single market, and
- Trade-and-customs inspections of goods coming from Great Britain take place at Northern Ireland ports along the Irish Sea.
Plan of UK:
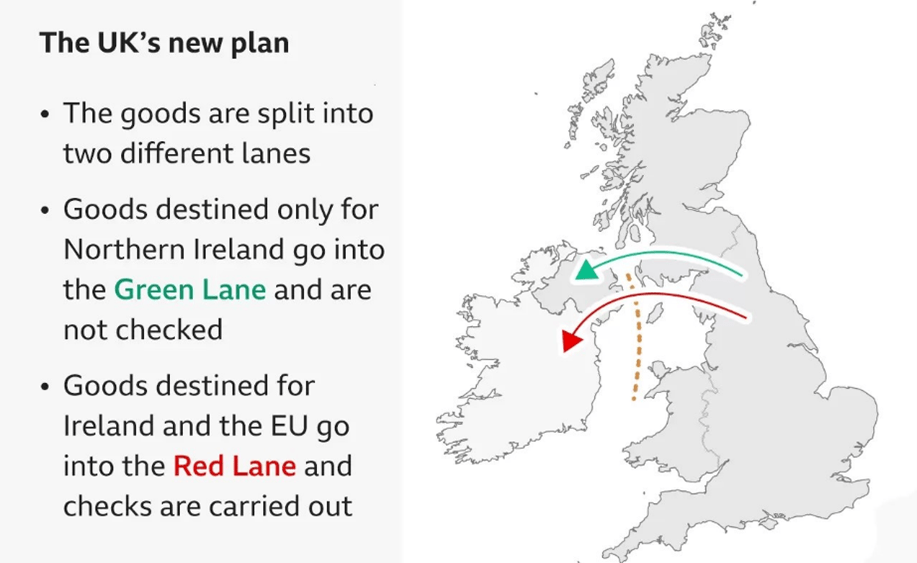
- The UK government has proposed the creation of a ‘green lane’ and a ‘red lane’ for checking.
- The ‘green lane’ would have fewer checks and customs controls only for goods going to Northern Ireland.
- The ‘red lane’ would have a more stringent checks and for goods going on to the Republic of Ireland and the rest of the EU.
- In January 2023, both EU and UK signing a deal on sharing data regarding trade between them.
- The Good Friday Agreement, also known as the Belfast Agreement, was a political deal designed to bring an end to the 30 years ‘Troubles’ in the Northern Ireland.
Source: Indian Express
Previous Year Questions
Q.1) In which one of the following groups are all the four countries members of G20? (2020)
- Argentina Mexico, South Africa and Turkey
- Australia Canada, Malaysia and New Zealand
- Brazil, Iran, Saudi Arabia and Vietnam
- Indonesia Japan Singapore and South Korea
Q.2) Consider the following pairs:
International agreement/ set-up Subject
- Alma-Ata Declaration – Healthcare of the people
- Hague Convention – Biological and Chemical Weapons
- Talanoa Dialogue – Global Climate Change
- Under2 Coalition – Child Rights
Which of the pairs given above is/are correctly matched? (2020)
- 1 and 2 only
- 4 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 2,3 and 4 only
Practice MCQs
Q.1) Consider the following statements regarding the Treaty of Alinagar:
- It was signed between Robert Clive of the British East India Company and the Nawab of Bengal, Mirza Muhammad Siraj Ud Daula.
- It laid foundations for the Battle of Buxar.
- All British goods that passed through Bengal would be exempt from duties under the treaty.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
- 1 and 2 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 1 2 and 3
Q.2) Consider the following statements regarding Quality Council of India:
- It was established as a National body for Accreditation on recommendations of Expert Mission of EU.
- QCI was set up through a PPP model as an independent autonomous organization with the support of Government of India and the Indian Industries.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Q.3) Consider the following statements regarding Lithium reserves:
- The first lithium reserve in India was discovered at a site in Mandya, Karnataka.
- China is by far the world’s top producer of lithium.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Comment the answers to the above questions in the comment section below!!
ANSWERS FOR ’ 11th February 2023 – Daily Practice MCQs’ will be updated along with tomorrow’s Daily Current Affairs.st
ANSWERS FOR 10th February – Daily Practice MCQs
Q.1) – d
Q.2) – a
Q.3) – b














