IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
Archives
(PRELIMS & MAINS Focus)
Syllabus
- Prelims – Environment and Ecology
Context: A new cricket species was discovered by researchers on the Ashoka University campus.
About the Species:
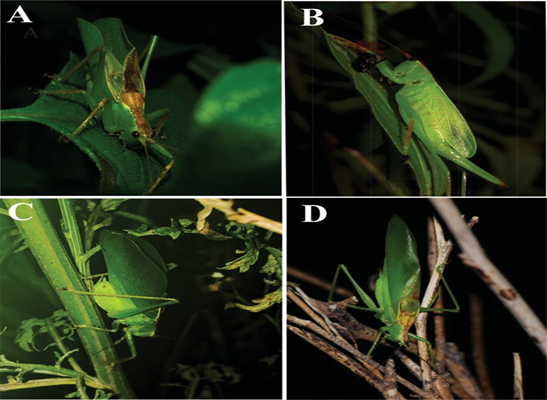
- Hexacentrus ashoka is a genus of predatory katydids.
- In India, the genus Hexacentrus is represented by 7 species of which 6 are morphologically characterized while one is only acoustically characterized.
- Hexacentrusis the type genus of bush-crickets in the subfamily Hexacentrinae.
- Most species of this genus occur in Southeast Asiaand in Africa.
About Crickets
- Crickets are divided into two groups-
- true crickets (ground and tree crickets)
- bush crickets/katydids.
- Crickets are nocturnal in nature.
- Bush crickets belong to an order called Orthoptera.
- This order includes species of grasshoppers and crickets.
SOURCE: THE HINDU
Previous Year Questions
Q.1) Consider the following kinds of organisms: (2021)
1. Copepods
2. Cyanobacteria
3. Diatoms
4. Foraminifera
Which of the above are primary producers in the food chains of oceans?
- 1 and 2
- 2 and 3
- 3 and 4
- 1 and 4
Q2. Which of the following is not a bird? (2022)
- Golden Mahseer
- Indian Nightjar
- Spoonbill
- White Ibis
Syllabus
- Prelims – International Relations
Context: A new round of negotiations on the much-awaited United Nations High Seas Treaty for conservation and sustainable use of marine biological diversity of areas beyond national jurisdiction (BBNJ) began in New York recently.
About BBNJ Treaty :
- The “BBNJ Treaty”, also known as the “Treaty of the High Seas”.
- It is an international agreement on the conservation and sustainable use of marine biological diversity in areas beyond national jurisdiction.
- It encompasses the high seas, beyond the exclusive economic zones or national waters of countries.
- This new instrument is being developedwithin the framework of the UNCLOS.
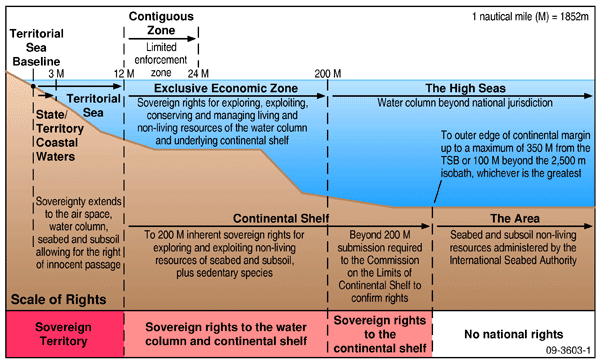
About UNCLOS( United Nations Convention for the Law of the Sea):
- UNCLOS is an international agreement that establishes the legal framework for marine and maritime activities.
- The Convention which concluded in the year 1982 replaced the quad-treaty of 1958.
- It came into effect in the year 1994.
- It divides marine areas into 5 zones :
-
- Internal-waters
- Territorial seas
- Contiguous Zone
- Exclusive Economic Zone (EEZ)
- Continental shelf or High seas
- India has been a party to the convention since 1995.
Source: DOWN TO EARTH
Previous Year Questions
Q.1) Which one of the following statements best describes the ‘Polar Code’? (2022)
- It is the international code of safety for ships operating in polar waters.
- It is the agreement of the countries around the North Pole regarding the demarcation of their territories in the polar region.
- It is a set of norms to be followed by the countries whose scientists undertake research studies at the North Pole and the South Pole.
- It is a trade and security agreement of the member countries of the Arctic Council.
Q.2) Consider the following statements. (2022)
- The Climate Group is an international non-profit organization that drives climate action by building large networks and running them.
- The International Energy Agency in partnership with the Climate Group launched a global initiative “EP100”.
- EP100 brings together leading companies committed to driving innovation in energy efficiency and increasing competitiveness while delivering on emission reduction goals.
- Some Indian companies are members of EP100.
- The International Energy Agency is the Secretariat to the “Under2 Coalition”.
Which of the statements given above is correct?
- 1,2, 4 and 5
- 1,3 and 4 only
- 2,3 and 5 only
- 1,2, 3, 4 and 5
Syllabus
- Prelims – Defense
Context – The 4th INDO-UZBEKISTAN joint military exercise ‘DUSTLIK’ commenced in Pithoragarh (Uttarakhand) recently.
About DUSTLIK :
- It is a biennial training exercise held between the armies of India and Uzbekistan.
- The first edition of the joint military exercise took place in Tashkent, Uzbekistan in 2019.
- The exercise focuses on Counter Terrorism operations in semi-urban terrain under a United Nations Mandate.
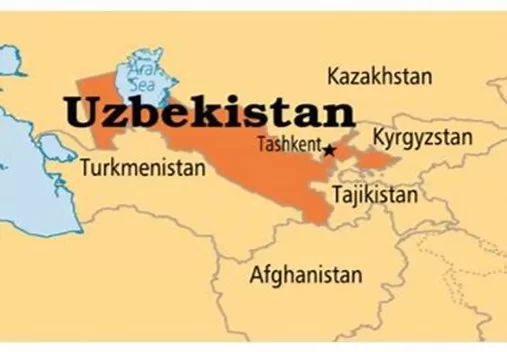
About Uzbekistan:
- Uzbekistan is a landlocked country in Central Asia.
- The capital of Uzbekistan is Tashkent.
- Uzbekistan lies mainly between two major rivers, the Syr Darya to the northeast and the Amu Darya to the southwest.
- Uzbekistan is bordered by 5 Asian nations namely: Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstanand Tajikistan, Afghanistan, and Turkmenistan.
Source: PIB
Previous Year Questions
Q.1) Consider the following countries: (2022)
- Azerbaijan
- Kyrgyzstan
- Tajikistan
- Uzbekistan
- Turkmenistan
Which of the above has borders with Afghanistan?
- 1, 2, and 5 only
- 1, 2, 3, and 4 only
- 3, 4, and 5 only
- 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5
Q.2) Consider the following pairs: (2022)
The region often mentioned in the news: Country
- Anatolia Turkey
- Amhara Ethiopia
- Cabo Delgado Spain
- Catalonia Italy
How many pairs given above are correctly matched?
- Only one pair
- Only two pairs
- Only three pairs
- All four pairs
Syllabus
- Prelims – Science, and Technology
Context: Recent studies probed the link between the gut microbiome and autism spectrum disorders.
Key Findings:
- Investigations of the dynamic cross-talk between the gut microbiome and the host environment have revealed potential connections to ASD symptoms.
- Biological crosstalk :refers to instances in which one or more components of one signal transduction pathway affects another.
- The gut microbiome is believed to have a big impact on immune modulation and metabolic activities in the human body.
- Immune modulation: refers to the efforts of the immune system to ensure its response is proportionate to a threat.
About Autism Spectrum Disease:
- Autism spectrum disorder (ASD) is the term for a group of neurodevelopmental disorders.
- It is characterized by difficulties in social interaction, verbal and nonverbal communication, and the presence of repetitive behavior and restricted interests.
- Signs of autism usually appear by age 2 or 3. Some associated development delays can appear as early as 18 months.
- There is no cure for autism.
- In 2008, the United Nations General Assembly unanimously declared 2ndApril as World Autism Awareness Day.
About the Human microbiome:
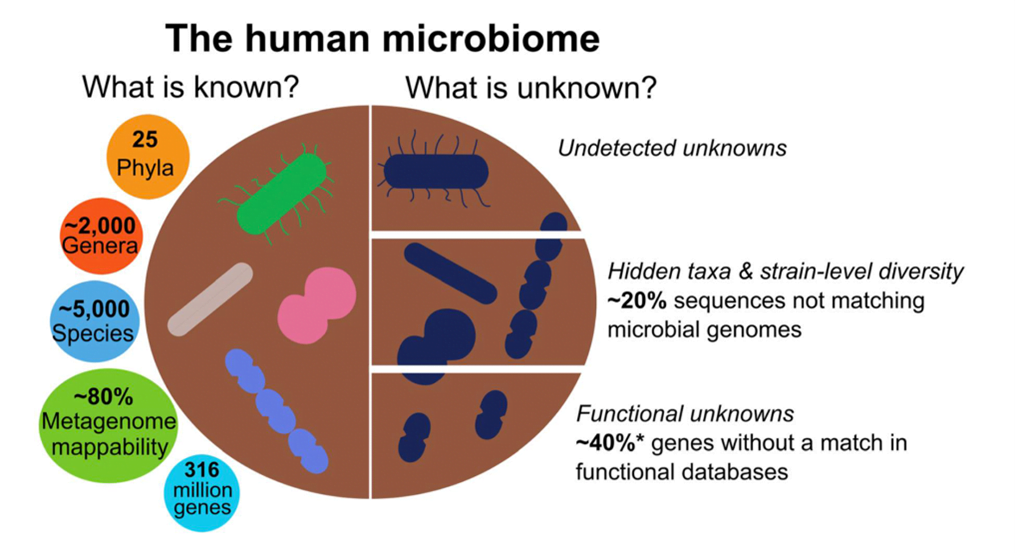
- The collective genome of all micro-organisms contained within the human body, residing inside tissues and bio-fluids is called Human Microbiome.
- Most of them have either commensal (co-existing without harming humans) or mutualistic (each benefit from the other).
- These organisms play a key role in many aspects of host physiology such as :
- The metabolism of complex indigestible carbohydrates and fats to produce essential vitamins
- Maintaining immune systems and
- Acting as the first line of defense against pathogens.
Source: THE HINDU
Previous Year Questions
Q.1) Consider the following statements in respect of probiotics : (2022)
- Probiotics are made of both bacteria and yeast.
- The organisms in probiotics are found in foods we ingest but they do not naturally occur in our gut.
- Probiotics help in the digestion of milk sugars.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- 1 and 3
- 2 and 3
Q.2) Which one of the following statements best describes the role of B cells and T cells in the human body?(2022)
- They protect the environmental allergens. body
- They alleviate the body’s pain and inflammation.
- They act as immunosuppressants in the body.
- They protect the body from diseases caused by pathogens.
Syllabus
- Prelims – Economy
Context: Recently, the approval of the GST Appellate Tribunal was announced by the Goods and Services Tax (GST) Council.
About GST Council:
- The 101st Amendment Act of 2016 (122nd Amendment Bill), paved the way for the implementation of GST.
- The GST Council is a joint forum of the Centre and the states under Article 279-A of the constitution.
- Article 279-A. gives the President the authority to appoint a GST Council by executive order.
- The members of the Council include the Union Finance Minister (chairperson), and the Union Minister of State (Finance) from various states.
- As per Article 279, it is meant to “make recommendations to the Union and the states on important issues related to GST, like the goods and services that may be subjected or exempted from GST, model GST Laws”.
- It also decides on various rate slabs of GST.
About GST Appellate Tribunal:
- The GST Appellate Tribunal (GSTAT) or simply the Appellate Tribunal is the second appeal forum under GST for any dissatisfactory order passed by the First Appellate Authorities, an application for revision of the same can be raised to the National Appellate Tribunal.
- The National Appellate Tribunal is also the first common forum to resolve disputes between the center and the states.
- Being a common forum, it is the duty of the GST Appellate Tribunal to ensure uniformity in the redressal of disputes arising under GST.
Powers of the Appellate Tribunal under GST:
- As per the Code of Civil Procedure, 1908, the GST Appellate Tribunal holds the same powers as the court and is deemed Civil Court for trying a case.
- The Appellate Tribunal has been granted the powers to hear appeals and to pass orders and directions, including those for the recovery of amounts due, for the enforcement of its orders, and for the rectification of mistakes.
- The Tribunal also has the power to impose penalties, revoke or cancel registrations, and take such other measures as may be necessary to ensure compliance with the GST laws.
Jurisdiction of the Appellate Tribunal under GST:
- The jurisdiction of the Appellate Tribunal extends to all cases where an appeal has been filed against an order, decision, or direction of a lower authority under the GST laws.
- The Tribunal has the power to hear and resolve disputes related to the assessment of taxes, determination of liability, imposition of penalties, and other matters related to the implementation and interpretation of the GST laws.
Constitution of the GST Appellate Tribunal
The GSTAT has the following structure:
- National Bench: The National Appellate Tribunal is situated in New Delhi, and constitutes a National President (Head) along with 2 Technical Members (1 from the Centre and one State each).
- Regional Benches: On the recommendations of the GST Council, the government can constitute (by notification) an ‘N’ number of Regional Benches, as required. As of now, there are 3 Regional Benches (situated in Mumbai, Kolkata, and Hyderabad) in India, wherein each bench constitutes a Judicial Member and 2 Technical Members(for Centre and State each).
- State Bench and Area Bench: The Government, on the recommendations of the GST council, has notified a number of State Benches.
Source: News on Air
Previous Year Questions
Q.1) Which of the following situations best reflects “Indirect Transfers” often talked about in media recently with reference to India? (2022)
- An Indian company investing in a foreign enterprise and paying taxes to the foreign country on the profits arising out of its investment
- A foreign company investing in India and paying taxes to the country of its base on the profits arising out of its investment
- An Indian company purchases tangible assets in a foreign country and sells such assets after their value increases and transfers the proceeds to India
- A foreign company transfers shares and such shares derive their substantial value from assets located in India
Q.2) What is/are the most likely advantages of implementing ‘Goods and Services Tax (GST)’? (2017)
- It will replace multiple taxes collected by multiple authorities and will thus create a single market in India.
- It will drastically reduce the ‘Current Account Deficit’ of India and will enable it to increase its foreign exchange reserves.
- It will enormously increase the growth and size of the economy of India and will enable it to overtake China in the near future.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
- 1 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
Syllabus
- Prelims – Governance
Context: The Supreme Court asked the Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) and the government to produce the existing regulatory framework in place to protect investors from share market volatility.
About SEBI (The Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) :
- The Securities and Exchange Board of India was established as a statutory body in the year 1992.
- Headquarters: Mumbai, Maharashtra
- Ministry: Ministry of Finance
- Chairperson: Ms. Madhabi Puri Buch
- The chairman is nominated by the Union Government of India. Two members, i.e., Officers from the Union Finance Ministry. One member from the Reserve Bank of India. The remaining five members are nominated by the Union Government of India, out of them at least three shall be whole-time members.
About National Stock Exchange
- The National Stock Exchange is an Indian stock exchange headquartered in Mumbai, Maharashtra.
- The NSE was designated as a stock exchange in 1993.
- More than 2000 companies are listed on the NSE.
- The NSE’s Stock Index – NIFTY – represents the top 50 stocks on the stock exchange.
About Bombay Stock Exchange (BSE)
- The BSE is one of Asia’s oldest stock exchanges, with a long history of fast trading
- The BSE was registered as a stock exchange in 1957 .
- The Stock Index of the Bombay Stock Exchange (BSE) – SENSEX – provides the top 30 stock indexes.
- More than 5000 companies are listed on the BSE.
- Functions:
- Quasi-legislative – drafts regulations
- Quasi-judicial – passes rulings and orders
- Quasi-executive – conducts investigation and enforcement action
- SEBI is responsible for the needs of three groups:
- Issuers of securities
- Investors
- Market intermediaries
- Powers:
- To approve by−laws of Securities exchanges.
- To require the Securities exchange to amend their by−laws.
- Inspect the books of accounts and call for periodical returns from recognized Securities exchanges.
- Inspect the books of accounts of financial intermediaries.
- Compel certain companies to list their shares in one or more Securities exchanges.
- Registration of Brokers and sub-brokers
Source: THE HINDU
Previous Year Questions
Q.1) With reference to the Indian economy, consider the following statements. (2022)
- An increase in Nominal Effective Exchange Rate (NEER) indicates the appreciation of rupee.
- An increase in the Real Effective Exchange Rate (REER) indicates an improvement in trade competitiveness.
- An increasing trend in domestic inflation relative to inflation in other countries is likely to cause an increasing divergence between NEER and REER.
Which of the above statements are correct?
- 1 and 2 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
Q.2) Consider the following statements: (2022)
- In India, credit rating agencies are regulated by Reserve Bank of India.
- The rating agency popularly known as ICRA is a public limited company.
- Brickwork Ratings is an Indian credit rating agency.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
- 1 and 2 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
Syllabus
- Prelims – Environment and Ecology
Context: IIT-Madras recently uncovered a low-cost, eco-friendly emulsifier in the latex sap of a commonly found plant called the Apple of Sodom.
About Apple of Sodom :

- Calotropis procera is commonly known as the Apple of Sodom.
- It is a species of flowering plant in the Milkweed family, Asclepiadaceae.
- It is native to West Africa as far south as Angola, North and East Africa, Madagascar, the Arabian Peninsula, Southern Asia, Indo-China region and Malaysia.
- The green fruits contain a toxic milky sap that is extremely bitter and hardens into a soap-resistant gluey coating.
Ayurvedic Health benefits of Apple of Sodom:-
- Ascites: Apply the latex of Sodom locally on the affected areas.
- Leprosy: Use the latex of Sodom plant on the affected skin.
- Ringworms: Apply the milky fluid of Sodom plant over infected skin.
- Stings: Locally apply the milk fluid of Sodom plant on the damaged skin.
- Deafness: Take a ripe yellow leaf of Sodom. Warm it. Squeeze the leaf juice drops in ears.
- Use it for 2 weeks.
- Caries: Apply the latex of Sodom on the affected teeth.
- Gastroenteritis: Roast the leaves of Sodom and apply locally.
Health Benefits of Apple:
- Juice of the plant is poisonous it has been used as an infanticide in Africa.
- Both the bark and the latex are widely used as arrow and spear poisons.
- Latex is cardio toxic with the active ingredient being calotropin.
- All parts of plant are poisonous if ingested.
- Handling plant may cause skin irritation or allergic reaction
Source: THE HINDU
Previous Year Questions
Q.1) With reference to “Gucchi” sometimes mentioned in the news, consider the following statements: (2022)
- It is a fungus.
- It grows in some Himalayan forest areas.
- It is commercially cultivated in the Himalayan foothills of north-eastern India.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 3 only
- 1 and 2
- 2 and 3
Q.2) Which of the following statements is correct regarding the general difference between plant and animal cells? (2020)
- Plant cells have cellulose cell walls whilst animal cells do not
- Plant cells do not have plasma membranes unlike animal cells which do
- A mature plant cell has one large vacuole vacuoles
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
- 1 and 2 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
Syllabus
- Prelims – Governance
Context: At the 190th Meeting of ESI Corporation, the Ministry for Labour & Employment announced several decisions on strengthening social security for Shram Jeevis.
About ESIC:
- It is a state-run organization set up under the Employee State Insurance Act of 1948.
- It is responsible for overseeing the ESI plan.
- Ministry: The Ministry of Labour & Employment
- It provides socio-economic protectionto the worker population and immediate dependent or family covered under the ESI scheme.
About ESI Scheme:
- The Employees’ State Insurance Scheme (ESI)is an integrated measure of social Insurance embodied in the Employees’ State Insurance Act, of 1948.
- It applies to factories and other establishments Road Transport, Hotels, Restaurants, Cinemas, Newspaper, Shops, and Educational/Medical Institutions wherein 10 or more persons are employed.
- The benefits of the ESI system are described below.
- Physical Disability Benefits
- Medical Benefits
- Maternity Benefits
- Dependent Benefit
- Unemployment Allowance.
- Sickness Benefit
About Atal Beemit Vyakti Kalyan Yojana(ABVKY):
- It is a welfare measure being implemented by the Employee’s State Insurance (ESI) Corporation.
- It was introduced in
- This scheme aims to financially aid people who lost their jobs due to changing employment patterns and due to the Covid-19 pandemic.
- It offerscash compensation to insured persons when they are rendered unemployed.
Source: PIB
Previous Year Questions
Q.1) In India, which one of the following compiles information on industrial disputes, closures, retrenchments, and lay-offs in factories employing workers? (2022)
- Central Statistics Office
- Department for Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade
- Labour Bureau
- National Technical Manpower Information System
Q.2) With reference to the casual workers employed in India, consider the following statements: (2021)
- All casual workers are entitled to employees Provident Fund Coverage
- All casual workers are entitled to regular working hours and overtime payment
- The government can by notification specify that an establishment or industry shall pay wages only through its bank account.
Which of the above statements is correct?
- 1 and 2 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 1,2 and 3
Syllabus
- Mains – GS 3 (Economy) and Environment
Context: The Union budget increased allocation for the Production-linked incentive (PLI) scheme for high-efficiency solar modules.
About Solar Panel and its working:
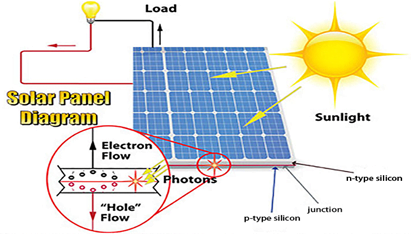
- A solar panel is a collection of photovoltaic (PV) cells that collect sunlight and convert it into electric current.
- When sunlight hits the semiconductor in the solar PV cell the energy from the light in the form of photons is absorbed.
- This energy absorption results in exciting a number of electrons, which then drift freely in the cell.
- The solar cell is specifically designed to create an electric field.
- This electric field forces the electrons to flow in a certain direction- towards the electrical terminals that line the cell.
- This flow is known as an energy current, and the strength of the current is determined by how much electricity each cell can produce.
- Once the electrons reach terminals the current is then directed into wires making the panel a source of electrical energy.
Solar Energy potential in India:
- From less than 10 MW in 2010, India has added significant PV capacity over the past decade, achieving over 50 GW by 2022 .
- By 2030, India is targeting about 500 GW of renewable energy deployment, out of which ~280 GW is expected from solar PV.
- This calls for 30 GW of solar capacity every year until 2030.
- India’s current solar module manufacturing capacity is limited to around 15 GW per year rest is met through imports.
- An estimated 85 per cent of this import need is met by three countries China, alongside Vietnam and Malaysia.
- The value of solar imported since 2014 adds up to $12.93 billion, or Rs 90,000 crore.
Advantages of Solar Energy in India:
- This is an inexhaustible source of energy and the best replacement to other non-renewable energies in India.
- Solar energy is environment friendly, hence it is very suitable for India as it is being one of the most polluted countries of the world.
- Solar energy can be used for variety of purposes like as heating, drying, cooking or electricity, which is suitable for the rural areas in India replacing other energy resources.
- It can also be used in cars, planes, large power boats, satellites, calculators and many more such items, just apt for the urban population.
- In an energy deficient country like India, where power generation is costly, solar energy is the best alternate means of power generation.
- Solar panels can be easily installed; hence it is quite inexpensive compared to other sources of energy.
- By 2012, a total of 4,600,000 solar lanterns and 861,654 solar-powered home lights were installed.
- Typically replacing kerosene lamps, they can be purchased for the cost of a few months’ worth of kerosene with a small loan.
- The Ministry of New and Renewable Energy is offering a 30- to 40-percent subsidy of the cost of lanterns, home lights and small systems.
- Solar photovoltaic water-pumping systems are used for irrigation and drinking water.
Challenges of solar energy manufacturing in India:
- Solar cell manufacturing needs a huge amount of capital.
- The cost of debt in India (11%) is highest in the Asia-Pacific region, while in China it is about 5%.
- Solar cell manufacturing is a complicated process that is technology intensive.
- Establishing state-of-the-art manufacturing facilities needs access to technology.
- It is unlikely that companies that have spent millions of dollars on R&D would make it easy for India to access the latest technologies easily or at a lower cost.
- Lack of an integrated set-up and the economies of scale (despite 100 per cent FDI in the renewable energy sector) translates into higher cost of domestic production
- Solar panel Manufacturing suffers from a huge raw material supply crunch.
- Silicon wafer, the most expensive raw material in the panel, is not manufactured in India.
- Solar cell technology sees upgrades every 8-10 months making manufacturing inefficient for new entrants.
Govt. of India Initiatives:
- The govt. of India established a 19,500-crore production linked incentive (PLI) scheme on ‘national programme on high efficiency solar PV modules’, seeking to attract Rs 94,000-crore investment in the sector.
- Modified Special Incentive Package Scheme (M-SIPS) of Ministry of Electronics & Information Technology offers a 20-25 per cent subsidy for investments in capital expenditure for setting up a manufacturing facility.
- Atal Jyoti Yojana (AJAY): The AJAY scheme was launched in September 2016 for the installation of solar street lighting (SSL) systems in states with less than 50% of households covered with grid power (as per Census 2011).
- PM KUSUM: The scheme aims to add solar and other renewable capacity of 30,800 MW by 2022 with total central financial support of Rs. 34,422 Crores.
- Solar Park Scheme: The Solar Park Scheme plans to build a number of solar parks, each with a capacity of nearly 500 MW, across several states.
- SRISTI Scheme: Sustainable rooftop implementation of Solar transfiguration of India (SRISTI) scheme to promote rooftop solar power projects in India.
- National Solar Mission: It is a major initiative of the Government of India and State Governments to promote ecologically sustainable growth while addressing India’s energy security challenge.
Source: The Hindu
Previous Year Questions
Q.1) Consider the following statements:
- The Climate Group is an international non-profit organisation that drives climate action by building large networks and runs them.
- The International Energy Agency in partnership with the Climate Group launched a global initiative “EP100”.
- EP100 brings together leading companies committed to driving innovation in energy efficiency and increasing competitiveness while delivering on emission reduction goals.
- Some Indian companies are members of EP100.
- The International Energy Agency is the Secretariat to the “Under2 Coalition”.
Which of the statements given above are correct? (2022)
- 1,2, 4 and 5
- 1,3 and 4 only
- 2,3 and 5 only
- 1,2, 3, 4 and 5
Q.2) The Partnership for Action on Green Economy (PAGE) a UN mechanism to assist countries transition towards greener and more inclusive economies, emerged at (2018)
- The Earth Summit on Sustainable Development 2002, Johannesburg
- The United Nations Conference on Sustainable Development 2012, Rio de Janeiro
- The United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change 2015, Paris
- The World Sustainable Development Summit 2016, New Delhi
Syllabus
- Mains – GS 3 (Science and Technology)
Context: A data protection law must safeguard and balance peoples’ right to privacy and their right to information, which are fundamental rights flowing from the Constitution.
Key features of the Digital Personal Data Protection Bill:
- The Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology has drafted a Digital Personal Data Protection (DPDP) Bill.
Significance of the bill:
- The purpose of the bill is to provide for the processing of digital personal data in a manner that recognises both the right of individuals to protect their personal data and the need to process personal data for lawful purposes.
- It is India’s first attempt to domestically legislate on the issue of data protection.
The categories of Data created by the Bill are as follows:
Personal data:
- Data from which an individual can be identified like name, address etc.
- No Data Mirroring is required.
- Individual consent will suffice.
Sensitive personal data (SPD):
- Some types of personal data like as financial, health, sexual orientation, biometric, genetic, transgender status, caste, religious belief, and more.
- To be stored only in India.
- It can be processed abroad only under certain conditions including approval of a Data Protection Agency (DPA).
Critical personal data:
- Anything that the government at any time can deem critical, such as military or national security data.
- Critical personal data must be stored and processed in India.
Non-Personal Data:
- The Bill mandates fiduciaries to provide the government any non-personal data when demanded.
- The ‘data fiduciary’ may be a service provider who collects, stores and uses data in the course of providing such goods and services.
- Non-personal data refers to anonymised data, such as traffic patterns or demographic data.
- The previous draft did not apply to this type of data, which many companies use to fund their business model.
Impact on Social Media Companies:
- Significant Data Fiduciaries (the fiduciaries with huge volume and processing sensitive data) have to develop their own user verification mechanism.
- It will reduce the anonymity of users and decrease trolling, fake news and cyberbullying.
- Exemptions for Data Processing without consent:
- They have been provided for reasonable purposes like
- Security of the state.
- Detection of any unlawful activity or fraud.
- Whistleblowing etc
Creation of Independent Regulator:
- The Bill calls for the creation of an independent regulator Data Protection Authority, which will oversee assessments and audits and definition-making.
- Each company will have a Data Protection Officer (DPO) who will liaison with the DPA for auditing, grievance redressal, recording maintenance and more.
- The Bill proposes “Purpose limitation” and “Collection limitation” clause, which limit the collection of data to what is needed for “clear, specific, and lawful” purposes.
Control Over Data:
- It also grants individuals the right to data portability and the ability to access and transfer one’s own data.
- The right to be forgotten is also given.
- With historical roots in European Union law, General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), this right allows an individual to remove consent for data collection and disclosure.
Penalty – The Bill stated the penalties as:
- Rs 5 crore or 2 percent of worldwide turnover for minor violations and Rs 15 crore or 4 percent of total worldwide turnover for more serious violations.
- Also, the company’s executive-in-charge can also face jail terms of up to three years.
Problems associated with the Bill:
In conflict with RTI Act:
- The Bill is criticised for seeking to dilute the provisions of the Right to Information (RTI) Act, which has empowered citizens to access information and hold governments accountable.
- The RTI Act includes a provision to protect privacy through Section 8(1)(j).
- In order to invoke this section to deny personal information, at least one of the following grounds has to be proven.
- The information sought has no relationship to any public activity or public interest or is such that it would cause unwarranted invasion of privacy and the Public Information Officer is satisfied that there is no larger public interest that justifies disclosure.
- The proposed bill seeks to amend this section to expand its purview and exempt all personal information from the ambit of the RTI Act.
In conflict with the Right to privacy:
- By empowering the executive to draft rules on a range of issues, the proposed Bill creates wide discretionary powers for the Central government and thus fails to safeguard people’s right to privacy.
No autonomy for the Data Protection Board:
- The bill does not ensure autonomy of the Data Protection Board, the institution responsible for enforcement of provisions of the law.
- Given that the government is the biggest data repository, it was imperative that the oversight body set up under the law be adequately independent to act on violations of the law by government entities.
Digital by design:
- The Bill stipulates that the Data Protection Board shall be ‘digital by design’, including receipt and disposal of complaints.
- As per the latest National Family Health Survey, only 33% of women in India have ever used the Internet.
- The Bill, therefore, effectively fails millions of people who do not have meaningful access to the Internet.
Way Forward:
Therefore the challenge lies in finding an adequate balance between the right to privacy of data principles and reasonable exceptions, especially where government processing of personal data is concerned. The DPDP Bill needs to be suitably amended and harmonised with the provisions and objectives of the RTI Act.
Given the rate at which technology evolves, an optimum data protection law design needs to be future proof — it should not be unduly detailed and centred on providing solutions to contemporary concerns while ignoring problems that may emerge going forward.
Source: The Hindu
Previous Year Question
Q.1) ‘Right to Privacy’ is protected under which Article of the constitution of India? (2021)
- Article 15
- Article 19
- Article 21
- Article 29
Practice MCQs
Q.1) Consider the following statements regarding Employees State Insurance Corporation (ESIC):
- It is a state-run organization set up under the Employee State Insurance Act of 1948.
- It works under the Ministry of Labour and Employment.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Q.2) Consider the following statements regarding stock market in India:
- The BSE is one of Asia’s oldest stock exchanges, with a long history of fast trading.
- Stock market in India is regulated by the Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI).
- The Chairman of SEBI is nominated by the Union Government of India.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
- 1 and 2 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 1 2 and 3
Q.3) Consider the following countries:
- Kazakhstan
- Kyrgyzstan
- Mongolia
- Tajikistan
Which of the above countries borders with Uzbekistan?
- 1 2 and 4 only
- 2 3 and 4 only
- 1 3 and 4 only
- All of the above
Comment the answers to the above questions in the comment section below!!
ANSWERS FOR ’ 22nd February 2023 – Daily Practice MCQs’ will be updated along with tomorrow’s Daily Current Affairs.st
ANSWERS FOR 21st February – Daily Practice MCQs
Q.1) – d
Q.2) – b
Q.3) – a













