IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
Archives
(PRELIMS & MAINS Focus)
Syllabus
- Prelims – Geography
Context: Recently export demand for Teja variety of red chilli has gone up due to its culinary, medicinal and other wide-ranging uses.
About Teja Chillies:

- Chilli was originally cultivated in North Mexico but is believed to be brought to India by the Portuguese.
- It is a fine variety of Guntur chilli.
- It is a fruit that belongs to genus Capsicum.
Health benefits of Teja Chilli:
- Rich in Vitamins and Minerals like Copper, Potassium, Vitamin C, Vitamin B, Vitamin A.
- It is a powerful anti-oxidant.
- Studies suggest that it aids in weight loss.
- Clears congestion.
- Boosts mood and reduces pain.
- It has antibacterial properties that helps in curing skin infection.
- Decreases the risk of osteoporosis.
- Protects the body against prostate problems.
Source:The Hindu
Previous Year Questions
Q.1) With reference to the “Tea Board” in India, consider the following statements:
- The Tea Board is a statutory body.
- It is a regulatory body attached to the Ministry of Agriculture and Farmers Welfare.
- The Tea Board’s Head Office is situated in Bengaluru.
- The Board has overseas office at Dubai and Moscow.
Which of the statements given above are correct? (2022)
- 1 and 3
- 2 and 4
- 3 and 4
- 1 and 4
Q.2) Consider the following statements:
- Moringa (drumstick tree) is a leguminous evergreen tree.
- Tamarind tree is endemic to south Asia.
- In India, most of the tamarind is collected as minor forest produce.
- India exports tamarind and seeds of moringa.
- Seeds of moringa and tamarind can be used in the production of biofuels.
Which of the statements given above are correct? (2021)
- 1, 2, 4 and 5
- 3, 4 and 5
- 1, 3 and 4
- 1,2, 3 and 5
Syllabus
- Prelims – Science and Technology
Context: Recently, Italian researchers have discovered a Dark Galaxy or Invisible Galaxy using Atacama Large Millimeter Array (ALMA).
About Dark Galaxy:
- It is termed invisible because the light emitted couldn’t be seen from the earth.
- The presence of the galaxy has been discovered using the gravitational lensing technique.
Gravitational lensing technique:
- It is an effect of Einstein’s theory of general relativity – simply put, mass bends light.
- The gravitational field of a massive object will extend far into space, and cause light rays passing close to that object to be bent and refocused somewhere else.
- It is discovered as compact.
- It is young and has interstellar dust.
- It is forming new stars at the rate of 1000 times the Milky Way.
Atacama Large Millimeter Array (ALMA):
- It is an international partnership of the European Southern Observatory (ESO), with U.S., Japan, Canada, Taiwan, Korea and Chile.
- It is the world’s largest ground-based facility for observations in the millimeter/submillimetre regime.
- It is a single telescope composed of 66 high precision antennas.
- It is located on the Chajnantor plateau, 5000 meters altitude in northern Chile.
- It allows scientists to unravel longstanding and important astronomical mysteries, in search of our Cosmic Origins.
Source: Livescience
Previous Year Questions
Q.1) Which one of the following statements best reflects the idea behind the “Fractional Orbital Bombardment System” often talked about in media? (2022)
- A hypersonic missile is launched into space to counter the asteroid approaching the Earth and explode it in space.
- A spacecraft lands on another planet after making several orbital motions.
- A missile is put into a stable orbit around the Earth and deorbits over a target on the Earth.
- A spacecraft moves along a comet with the same speed and places a probe on its surface.
Q.2) If a major solar storm (solar flare) reaches the Earth, which of the following are the possible effects on the Earth? (2022)
- GPS and navigation systems could fail.
- Tsunamis could occur at equatorial regions.
- Power grids could be damaged.
- Intense auroras could occur over much of the Earth.
- Forest fires could take place over much of the planet.
- Orbits of the satellites could be disturbed.
- Shortwave radio communication of the aircraft flying over polar regions could be interrupted.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
- 1, 2, 4 and 5 only
- 2, 3, 5, 6 and 7 only
- 1, 3, 4, 6 and 7 only
- 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 and 7
Syllabus
- Prelims – Environment
Context: India’s Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR) framework for used tyres, batteries, and revised rules for e-waste and plastics kindled interest among the G20 countries.
About Extended Producer Responsibility:
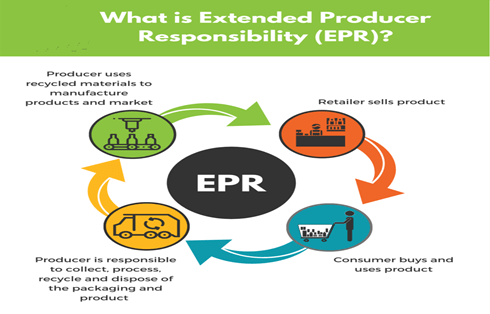
- Extended producers’ Responsibilities is a globally recognized policy used as an effective tool to put the onus on the producers for efficient end of life waste management of the plastic, electronic and electrical equipment.
- The concept of EPR responsibility is based on three foundation principles:
- Pollution prevention approach
- Life cycle thinking,
- Polluter pay principle
- EPR responsibility makes it the responsibility of the producers not only to take back products for recycling but also to design better and longer life products to minimize the amount of waste generated.
EPR in India:
EPR responsibility Certificate:
- EPR responsibility Certificate is authorized by Central Pollution Control Board which is mandatory for Producers/Importers of the Electronic products.
- Under these rules, the producers have a responsibility to delegate this responsibility to the third party or specialized organizations which manufacturers can financially aid for proper waste management.
EPR Responsibility Policies under E-Waste Management Rules:
- E-Waste (management and handling) Rules, 2016 adopted Extended Producers Responsibility for the first time in India.
- EPR responsibility under E-Waste (management) Rules, 2016 stipulates collection targets of E–Waste for producers.
- The producers are responsible for setting up collection centres for e-waste and financing and organizing a system for environmentally sound management of e-waste.
- The producers are required to have an arrangement with dismantlers and recyclers through either the Producers responsibility organization or the E-Waste exchange system.
- Marketing or selling any electronic equipment without EPR responsibility Authorization is considered a violation of the rules.
EPR responsibility Policy under Plastic Waste Management Rules:
- The Plastic Waste Management (Amendment) Rules, 2022 provide guidelines for strengthening the circular economy of plastic packaging waste as well as promoting alternatives to plastic.
- Producers of waste are mandated to ensure that generation of plastic waste is minimized, and plastic waste is not littered and stored at the source, which is then handed over to local bodies or authorized agencies.
Source: Indian Express
Previous Year Questions
Q.1) “Climate Action Tracker” which monitors the emission reduction pledges of different countries is a : (2022)
- Database created by coalition of research organisations
- Wing of “International Panel of Climate Change”
- Committee under “United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change”
- Agency promoted and financed by United Nations Environment Programme and World Bank
Q.2) Consider the following statements:
- The Climate Group is an international non-profit organisation that drives climate action by building large networks and runs them.
- The International Energy Agency in partnership with the Climate Group launched a global initiative “EP100”.
- EP100 brings together leading companies committed to driving innovation in energy efficiency and increasing competitiveness while delivering on emission reduction goals.
- Some Indian companies are members of EP100.
- The International Energy Agency is the Secretariat to the “Under2 Coalition”.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
- 1,2, 4 and 5
- 1,3 and 4 only
- 2,3 and 5 only
- 1,2, 3, 4 and 5
Syllabus
- Prelims – Science and Technology
Context: Recently, World’s first global summit on Responsible AI in the Military was organized in Netherlands.
About REAIM:
- It brings together governments, corporations, academia, startups, and civil societies to raise awareness, discuss issues, and possibly, agree on common principles for deploying and using AI in armed conflicts.
- India wasn’t part of this summit.
- It was co-hosted by the Republic of Korea.
Themes of REAIM: “ Myth busting AI: breaking down the characteristics of AI “.
Aim:
- To put the topic of responsible AI in the military domain higher on the political agenda.
- To mobilise and activate a wide group of stakeholders to contribute to concrete next steps.
- To foster and increase knowledge by sharing experiences, best practices and solutions.
Source: The Hindu
Syllabus
- Prelims – Science and Technology
Context: Recently Vinyl chloride – the chemical in several of the train cars that derailed and burned in East Palestine, Ohio– can wreak havoc on the human liver.
About Vinyl Chloride:

- It is a colourless gas that burns easily.
- It is produced industrially for its commercial uses.
- It can’t occur naturally.
- Used primarily to make polyvinyl chloride (PVC).
- PVC is a hard plastic resin used to make a variety of plastic products, including pipes, wire and cable coatings, and packaging materials.
- It spread through inhaling contaminated air, tobacco smoke, drinking contaminated water, etc.
- Disease burden: rare forms of liver cancer, as well as primary liver cancer brain and lung cancers, lymphoma, and leukemia.
Source: The Hindu
Previous Year Questions
Q.1) Bisphenol A (BPA), a cause of concern, is a structural/key component in the manufacture of which of the following kinds of plastics? (2021)
- Low-density polyethylene
- Polycarbonate
- Polyethylene terephthalate
- Polyvinyl Chloride
Q.2) “Triclosan” considered harmful when exposed to high levels for a long time, is most likely present in which of the following? (2021)
- Food preservatives
- Fruit ripening substances
- reused plastic containers
- Toiletries
Syllabus
- Prelims – Miscellaneous
Context: Recently, the All-India Council for Technical Education and the Bureau of Police Research and Development Jointly Launched KAVACH-2023.
About KAVACH-2023:

- It is a National Level Hackathon to tackle cyber threats and provide effective solutions.
- Hackathon: It is a competition in which participants use technology to achieve an objective.
- Aims: To identify innovative ideas and technological solutions for addressing the cyber security and cybercrime challenges of the 21st century.
- Conducted by: Ministry of Education’s Innovation Cell, All India Council for Technical Education (AICTE), Bureau of Police Research and Development (BPR&D) and Indian Cyber Crime Coordination Centre (I4C).
- Objective: To challenge the country’s innovative minds to conceptualize frameworks focusing on cybersecurity issues while using artificial intelligence, machine learning, automation, big data and cloud computing.
- It includes 20 unique and important matters such as women’s safety apps, obscenity blocker solutions, phishing detection solutions, dark web crawlers, citizen safety apps and malware analysis tools.
Source: Indian Express
Syllabus
- Prelims – Science and Technology
Context: Recently, Defense Minister of India has inaugurated e-MMS and SAMAR portal.
About SAMAR and e-MMS:
- SAMAR serves as the standard by which defense manufacturing companies are evaluated for their competence.
- It is an outcome of the collaboration between DRDO and Quality Council of India (QCI).
- e-MMS was launched by Indian Air Force (IAF).
- It is one of the largest Maintenance Repair Overhaul (MRO) IT implementation in the world.
- It has been designed and developed by the Indian IT giant Wipro.
- It seeks to seamlessly connect squadrons, wings, commands, and Air headquarters after its implementation.
- It will transform IAF’s paper-based legacy maintenance system to an online system as it will be implemented in IAF’s hierarchy and functioning.
- It will help to monitor the operational availability of all fleets and systems in real time at various hierarchical levels.
Source: NewsOnAir
Syllabus
- Mains – GS 3 (Disaster Management)
Context: The National Disaster Management Authority (NDMA) received the final inputs on the draft of India’s first national policy for the mitigation and rehabilitation of the people affected by river and coastal erosion.
- The Union Ministry of Home Affairs has directed NDMA to draft a policy based on the 15th Finance Commission’s report.
About Disaster and its classification:
- Disaster is an undesirable catastrophe resulting from the forces that are largely beyond human control, strikes quickly with little or no warning, and causes or threatens serious disruption of life and property. For example, earthquake, tsunami, cyclone, flood, etc.
Categories of Natural Disaster:
- Natural Disasters are broadly categorized as − Atmospheric Disasters, Terrestrial Disasters, Aquatic Disasters and Biological Disasters.
- Atmospheric disasters include blizzard, thunderstorm, lightning, tropical cyclone, tornado, drought, hailstorm, frost, heat wave, cold waves, etc.
- Terrestrial disasters include earthquake, volcanic eruption, landslide, avalanches, subsidence, etc.
- Aquatic disasters include flood, tidal waves, storm surge, tsunami, etc.
- Biological disasters include fungal, bacterial, and viral diseases (e.g. bird flu, dengue, etc.).
About NDMA:
- National Disaster Management Authority is an apex body for disaster management in India.
- It is headed by the Prime Minister of India and has a Vice-Chairman, nine members, and a CEO.
- It was established under the Disaster Management Act, 2005 and provides guidelines for disaster management to various agencies.
- It is responsible for preparing and implementing disaster management plans at national, state, and district levels.
Major highlights of the policy:
Allocations:
- 15th Finance Commission’s report allocates Rs 1,500 crore for 2021-26 for mitigation measures to prevent erosion under NDMF.
- Rs 1,000 crore allocated for resettlement of displaced people affected by erosion under NDRF for the same period.
- Both funds require state governments to contribute 25% of costs on a cost-sharing basis, except Northeastern states which only need to contribute 10% of state funds.
- NDMA to coordinate allocations and expenses under NDRF and NDMF for mitigation and rehabilitation.
Implementation and institutional mechanisms:
- District disaster management authorities (DDMAs) to implement measures, aided by other district agencies and a specific panchayat-level committee.
- DDMA to prepare mitigation and rehabilitation plans and submit them to SDMAs for appraisal by NDMA and approval by home ministry’s high-level committee for disbursal of funds.
- DDMAs will be responsible for organizing, monitoring, and evaluating efforts under supervision of state and national counterparts.
- NDMA to consultant and emphasize the need for qualified disaster management professionals in all teams.
Challenges and recommendations
- Policy addresses erosion-linked displacement but not displacement caused by deposition of eroded materials and soil piping.
- Financial allocation under policy not yet clear; funds currently allocated on first-come, first-serve basis for states.
- Population density should be considered during allocation.
- Hazard assessments carried out by central agencies should be made available to SDMAs in GIS formats.
- Policy recommends mapping of fallow areas for rehabilitation with input from affected and vulnerable communities.
Significance of disaster management in India:
- Human lives are at stake: Disaster management can help reduce the loss of life and minimize the impact of disasters which leads to loss of life and property, and long-term health consequences.
- Climate change: Effective disaster management can help in mitigating the effects of climate change which has led to more frequent and severe natural disasters.
- Economic impact: Disaster management can help minimize the economic impact of disasters which have a significant impact on the economy, including loss of property and infrastructure, decreased productivity, and disrupted supply chains.
- Humanitarian assistance: Disaster management can help in coordinating relief efforts and ensuring that assistance reaches those who need it the most.
- Infrastructure: It can help in improving the resilience of infrastructure which are vulnerable to natural disasters such as roads, bridges, and buildings.
Challenges of disaster management:
- Lack of preparedness: Despite frequent disasters, there is still a lack of preparedness at all levels of governance and society leading to delays in response time and inadequate resources to deal with disasters effectively.
- Population density: India is one of the most densely populated countries in the world, which can make evacuations and relief efforts more difficult during disasters.
- Climate change: With the increasing threat of climate change, India is experiencing more frequent and intense disasters, such as floods, droughts, and cyclones putting pressure on the country’s disaster management systems to adapt and respond effectively.
- Funding: Despite the increasing frequency and severity of disasters, funding for disaster management is often inadequate which often limit the resources available for preparedness, response, and recovery efforts.
- Lack of coordination: There is often a lack of coordination between different agencies involved in disaster management, such as the government, NGOs, and international organizations leading to duplication of efforts and inefficiencies.
- Poor infrastructure: Many areas in India lack basic infrastructure such as roads, bridges, and communication networks, making it difficult to reach affected areas during disasters.
Way Forward:
Disaster management in India faces various challenges, such as inadequate resources, poor infrastructure, limited awareness and education, weak institutional capacity, inadequate coordination and communication, and inadequate research and innovation.
Therefore, steps such as continuous improvement and innovation in disaster management, based on the best available science, technology, and practices, and involving all stakeholders in a participatory and inclusive manner can go a long way in changing the scenario.
Source: DownToEarth
Practice MCQs
Q.1) Consider the following statements regarding National Disaster Management Authority (NDMA):
- It is a statutory body established under the Disaster Management Act, 2005.
- It is headed by the President of India.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Q.2) Vinyl Chloride, a cause of concern, is a structural/key component in the manufacture of which of the following kinds of plastics?
- Low-density polyethylene
- Polyvinyl Chloride
- Polycarbonate
- Polyethylene terephthalate
Q.3) Consider the following statements regarding Atacama Large Millimeter Array (ALMA):
- It is an international partnership of the European Southern Observatory (ESO), with U.S., Japan and other countries.
- It is located on the Chajnantor plateau.
- It is the world’s largest ground-based facility for observations in the millimeter/submillimetre regime.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 and 2 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 1 2 and 3
Comment the answers to the above questions in the comment section below!!
ANSWERS FOR ’ 18th February 2023 – Daily Practice MCQs’ will be updated along with tomorrow’s Daily Current Affairs.st
ANSWERS FOR 18th February – Daily Practice MCQs
Q.1) – a
Q.2) – b
Q.3) – d











