IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
Archives
(PRELIMS & MAINS Focus)
Syllabus
- Prelims – International Relations
Context : A recent report highlighted that India, Brazil, South Africa can play vital role in reforming digital governance.
About IBSA :-
CREDITS : ibsa-trilateral.org
- IBSA brings together India, Brazil, and South Africa, three large democracies and major economies from three different continents, facing similar challenges.
- Background : Its genesis can be traced back to the decades of efforts by countries and groupings working together to ensure South-South solidarity such as the Bandung conference in 1955, the Non-Aligned Movement in 1961, the G77 grouping, UNCTAD, the Buenos Aires Plan of Action 1978, and the 2009 Nairobi declaration.
- Formation : The grouping was formalized and named the IBSA Dialogue Forum when the Foreign Ministers of the three countries met in Brasilia in June 2003 and issued the Brasilia Declaration.
- Five IBSA Leadership Summits have been held so far.
- The 5th IBSA Summit was held in Pretoria in October 2011.
- India convened the 6th IBSA summit under the theme “Democracy for Demography and Development” in 2021.
- IBSA does not have a headquarters or a permanent executive secretariat.
- IBSAMAR (IBSA Maritime Exercise)
- Cooperation in IBSA is on three fronts: first, as a forum for consultation and coordination on global and regional political issues second, trilateral collaboration on concrete areas/projects and third, assisting other developing countries by taking up projects in the latter through IBSA Fund.
- The IBSA facility for poverty and hunger alleviation (IBSA Fund) was established jointly by India, Brazil, and South Africa in March 2004.
- The IBSA Visiting Fellowships Program was instituted, with the financial support of the Ministry of External Affairs, Government of India in 2016
MUST READ : BRICS
Source: THE HINDU
Previous Year Questions
Q.1)The ‘Fortaleza Declaration’ recently in the news, is related to the affairs of: (2015)
- ASEAN
- (b)BRICS
- OECD
- WTO
Q.2) With reference to a grouping of countries known as BRICS, consider the following statements:
- The First Summit of BRICS was held in Rio de Janeiro in 2009.
- South Africa was the last to join the BRICS grouping.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Syllabus
- Prelims – Economy and Government schemes
Context: Recently, the Prime Minister addressed a Post Budget Webinar on ‘PM Vishwakarma Kaushal Samman.
About Pradhan Mantri Vishwakarma Kaushal Samman (PM VIKAS) scheme :-
- The launch of PM Vishwakarma Kaushal Samman scheme was announced in the Union Budget 2023.
- PM Vishwakarma Kaushal Samman scheme is a new scheme for artisans and craftsmen.
Objectives: –
- improving skills of artisans
- ensuring easy credit
- help them in brand promotion so that their products reach the market quickly.
- seeks to handhold artisans and people associated with small businesses.
- to develop traditional artisans and craftsmen while preserving their rich traditions.
MUST READ : SAMARTH scheme and PM SVANidhi scheme
Source: PIB
Previous Year Questions
Q.1) With reference to Pradhan Mantri Kaushal Vikas Yojana, consider the following statements : (2018)
- It is the flagship scheme of the Ministry of Labour and Employment.
- It, among other things, will also impart training in soft skills, entrepreneurship, financial and digital literacy.
- It aims to align the competencies of the unregulated workforce of the country to the National Skill Qualification Framework.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 and 3 only
- 2 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
Q.2) What is the aim of the programme ‘Unnat Bharat Abhiyan’? (2017)
- Achieving 100% literacy by promoting collaboration between voluntary organizations and the government’s education system and local communities.
- Connecting institutions of higher education with local communities to address development challenges through appropriate technologies.
- Strengthening India’s scientific research institutions in order to make India a scientific and technological power.
- Developing human capital by allocating special funds for health care and education of rural and urban poor, and organizing skill development programmes and vocational training for them.
Syllabus
- Prelims – Geography and Science and Technology
Context: Recently, ISRO released the Landslide Atlas of India.
About Landslide:-
- Landslide is a rapid movement of rock, soil, and vegetation down the slope under the influence of gravity.
- Landslides are caused due to three major factors: geology, morphology, and human activity.
Causes of landslide:-
- Rainfall and Snowfall- The occurrence of heavy or continuous rainfall may lead to heavy landslides in the areas of steep slopes where National Highways and roads have been constructed.
- Earthquakes and Volcanic Eruptions-Earthquakes are the most important cause of landslides in the folded mountainous areas. In India, Landslides are more frequent in the folded mountains of the Tertiary Period, like the Himalayas.
- Mining, Quarrying and Road cutting- The continuous extraction of coal, minerals, and stones from the mines and quarries and the development of roads by cutting the steep slopes in the folded mountains create conducive conditions for the occurrence of landslides.
- Loading by construction of houses- The unplanned growth of towns and cities in the hilly areas without testing soil and rocks in also an important cause of landslides.
- Deforestation- Deforestation and other human activities also induce landslides.
Landslide-Prone Areas in India:-
- Himalayan tract, hills/mountains in sub-Himalayan terrains of North-east India, Western Ghats, the Nilgiris in Tamil Nadu Konkan .
About Landslide Atlas of India:-
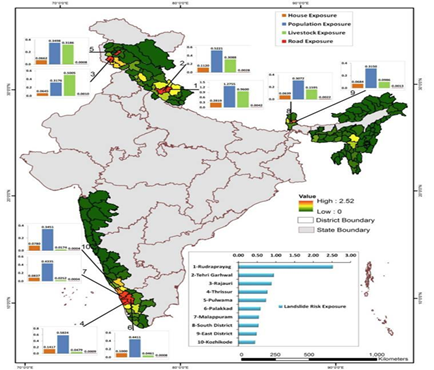
CREDITS : researchgate.net
- It is a database of landslide-prone regions of India based on events during 1998 – 2022.
- It is created by the National Remote Sensing Centre, ISRO Department of Space, Government of India
- In addition to aerial images, high-resolution satellite images captured using ResourceSat-1 and 2, etc., were used to study the landslides.
- This Atlas provides the details of landslides present in Landslide provinces of India
- The database covers landslide-vulnerable regions in 17 states and 2 UTs of India in the Himalayas and Western Ghats.
- The database includes three types of landslide inventory – seasonal, event-based, and route-wise for the 1998-2022 period.
- The technology used: Satellite data of high to very high resolution such as IRS-1D PAN+LISS-III, Resourcesat-1, 2 and 2A LISS-IV Mx, Cartosat-1 and 2S, data from International satellites (Sentinel-1&2, Pleiades and WorldView) and Aerial images were used in the mapping of landslides.
- Vulnerability Ranking: The database was used to rank 147 districts in 17 states and 2 UTs of India for their exposure to landslides in terms of key socio-economic parameters.
Steps taken by the government:-
- The Geological Survey of India (GSI) has done a national landslide susceptibility mapping for 85% of the entire 4,20,000 square km landslide-prone area in the country.
- The areas have been divided into different zones according to the propensity of the disaster.
NDMA Guidelines for Landslides –
- Landslide Hazard, vulnerability and Risk Assessment
- Multi – Hazard Conceptualization
- Landslide Remediation practice
- Research and Development, monitoring, and early warning
- Knowledge network and management
- Capacity building and Training
- Public awareness and Education
- Emergency preparedness and response
- Regulation and Enforcement
MUST READ : National Landslide Susceptibility Mapping (NLSM) programme and Joshimath Crisis
Source: THE INDIAN EXPRESS
Previous Year Questions
Q.1) If a major solar storm (solar flare) reaches the Earth, which of the following are the possible effects on the Earth? (2022)
- GPS and navigation systems could fail.
- Tsunamis could occur in equatorial regions.
- Power grids could be damaged.
- Intense auroras could occur over much of the Earth.
- Forest fires could take place over much of the planet.
- Orbits of the satellites could be disturbed.
- Shortwave radio communication of the aircraft flying over polar regions could be interrupted.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
- 1, 2, 4, and 5 only
- 2, 3, 5, 6, and 7 only
- 1, 3, 4, 6, and 7 only
- 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 and 7
Q.2) In which of the following activities are Indian Remote Sensing (IRS) satellites used? (2015)
- Assessment of crop productivity
- Locating groundwater resources
- Mineral exploration
- Telecommunications
- Traffic studies
Select the correct answer using the code given below :
- 1, 2, and 3 only
- 4 and 5 only
- 1 and 2 only
- 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5
Syllabus
- Prelims – Government schemes
Context: Union Minister for MSME launched the MSME Competitive (LEAN) Scheme recently.
About MSME Competitive (LEAN) Scheme:-
- It is implemented by the Ministry of Micro, Small & Medium Enterprises, Government of India.
- E- Certificate towards participation under the scheme will be issued by MoMSME after completion of Basic Level, Intermediate Level, and Advanced Level.
Aim: It aims to enhance their productivity, efficiency, and competitiveness by reduction of wastage in processes, inventory management, space management, energy consumption, etc.
OBJECTIVES: –
- Reduction in: rejected rates, product and raw material movements and the Product Cost
- Optimization of: space utilization, resources like Water, Energy, Natural Resources etc.
- Enhancement of: quality in process and product, production & export capabilities, workplace safety, knowledge & skills sets, innovative work culture, Social & environmental accountability, profitability, introduction & awareness to industry 4.0 and Digital Empowerment
Components of Schemes: –
- Industry Awareness Programmes/Workshop: MSMEs will be made aware of the Scheme through Nationwide awareness programmes.
- Training Programmes: Stakeholders like the MSME Officers, Assessors and Consultants will be trained
- Handholding: MSMEs will be provided handholding towards the implementation of Lean Tools and Techniques at three different levels – Basic, Intermediate, and Advanced.
- Benefits/Incentives: Graded incentives will be announced by the Ministry of MSME for MSMEs for encouraging MSME units’ participation under the scheme.
- The PR campaign, Advertising & Brand Promotion: For popularizing the Lean Scheme, nationwide publicity will be done.
- Digital Platform: Lean Scheme process will be e-enabled through a single window digital platform.
- Under the scheme, MSMEs will implement LEAN manufacturing tools like 5S, Kaizen, KANBAN, Visual workplace, Poka Yoka etc under the able guidance of trained and competent LEAN Consultants
Eligibility:-
- All MSMEs registered with the UDYAM registration portal.
- Common Facilities Centres (CFCs) under SFURTI (Scheme of Fund for Regeneration of Traditional Industries)
- Micro & Small Enterprises under the Cluster Development Program (MSE-CDP) Schemes.
MUST READ: MSME Sustainable (ZED) Certification Scheme and Finance-Related Problems of MSME Sector
Source: PIB
Previous Year Questions
Q.1) Recognition of the Prior Learning Scheme’ is sometimes mentioned in the news with reference to (2017)
- Certifying the skills acquired by construction workers through traditional channels.
- (b)Enrolling the persons in Universities for distance learning programmes.
- (c)Reserving some skilled jobs to rural and urban poor in some public sector undertakings.
- (d)Certifying the skills acquired by trainees under the National Skill Development Programme.
Q.2) Pradhan Mantri MUDRA Yojana is aimed at (2016)
- bringing small entrepreneurs into the formal financial system
- providing loans to poor farmers for cultivating particular crops
- providing pensions to old and destitute persons
- funding the voluntary organizations involved in the promotion of skill development and employment generation
Syllabus
- Prelims – Government initiatives
Context: Recently, the Prime Minister inaugurated the 3rd Session of the National Platform for Disaster Risk Reduction.
About the National Platform for Disaster Risk Reduction (NPDRR):-
- It was constituted by the Government of India through a resolution in 2013.
- It is chaired by the Union Home Minister and the Minister of State in charge of Disaster Management in the Ministry of Home Affairs.
- The Vice-Chairman of, the National Disaster Management Authority is the Vice-Chairperson of the NPDRR.
- The First Session of NPDRR was organized on the theme of “Mainstreaming DRR in Development: From Risk to Resilience” in New Delhi in 2013.
OBJECTIVES:-
- The National Platform aims to bring together the whole range of India’s disaster risk community from Government, Parliamentarians, Mayors, Media, International Organizations, NGOs, local community representatives, scientific and academic institutions and corporate businesses, etc.
Functions:-
- To review the progress made in the field of disaster management from time to time.
- To appreciate the extent and manner in which the Disaster Management Policy has been implemented by the Central and State Governments, and other concerned agencies.
- To advise on coordination between the Central and State Governments/UT Administrations, local self-governments, and civil society organizations for Disaster Risk Reduction.
- To advise suo-moto or on a reference made by the Central Government or any other State Government or a Union territory Administration on any question pertaining to disaster management.
- To review the National Disaster Management Policy.
About Subhash Chandra Bose Aapda Prabandhan Puraskar:-
- It is an award to recognize and honor the invaluable contribution and selfless service rendered by individuals and organizations in India in the field of disaster management.
- Administered By: National Disaster Management Authority under the Ministry of Home Affairs.
- The award is announced every year on 23rd January, the birth anniversary of Netaji Subhash Chandra Bose.
- The award carries a cash prize of Rs. 51 lakhs and a certificate in the case of an institution and Rs. 5 lakhs and a certificate in the case of an individual.
Eligibility:-
- Only Indian nationals and Indian institutions can apply for the award.
- The nominated individual or institution should have worked in any area of disaster management like Prevention, Mitigation, Preparedness, Rescue, Response, Relief, Rehabilitation, Research, Innovation, or early warning in India.
Winners of 2022 Award in the field of Disaster Management:-
- Gujarat Institute of Disaster Management (GIDM): established in 2012, the Gujarat Institute of Disaster Management (GIDM) has been working to enhance the disaster risk reduction (DRR) capacity of Gujarat.
- Professor Vinod Sharma: a senior professor at the Indian Institute of Public Administration and Vice-Chairman of the Sikkim State Disaster Management Authority, was the founder co-ordinator of the National Centre of Disaster Management, now known as the National Institute of Disaster Management.
Source: PIB
Previous Year Questions
Q.1) Consider the following freedom fighters: (2022)
- Barindra Kumar Ghosh
- Jogesh Chandra Chatterjee
- Rash Behari Bose
Who of the above was/were actively associated with the Ghadar Party?
- 1 and 2
- 2 only
- 1 and 3
- 3 only
Q.2)One common agreement between Gandhism and Marxism is (2020)
- The final goal of a stateless society
- Class struggle
- Abolition of private property
- Economic determinism
Syllabus
- Prelims – Environment and Ecology and Geography
Context: Sea ice levels on both poles marked a record low, according to the recent reports of the United Nations meteorological agency.
About the North Pole:-

- The geographic North Pole is the northern point of Earth’s axis of rotation.
- The North Pole is the northernmost point on Earth.
- Its latitude is 90 degrees north, and all lines of longitude meet there.
- The North Pole is found in the Arctic Ocean.
- It is constantly shifting pieces of sea ice.
- The North Pole is much warmer than the South Pole.
- This is because sits at a lower elevation (sea level) and is located in the middle of an ocean, which is warmer than the ice-covered continent of Antarctica.
- In fact, the North Pole experiences only one sunrise (at the March equinox) and one sunset (at the September equinox) every year.
- The North Pole is not part of any nation.
- Ecosystem: Polar bears (Ursus maritimus), Arctic foxes (Vulpes lagopus), and other terrestrial animals rarely migrate to the North Pole.
About the South pole:-
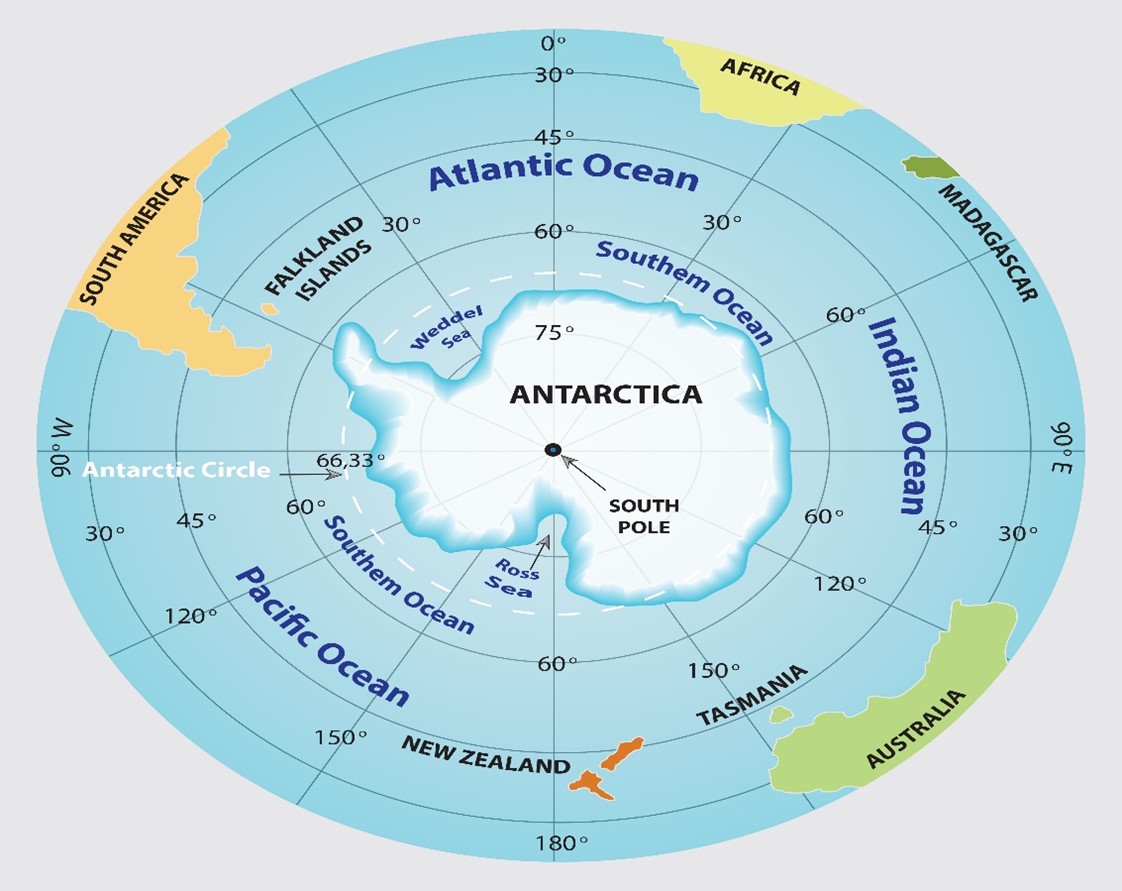
- The South Pole is the southernmost point on Earth.
- Its latitude is 90 degrees south, and all lines of longitude meet there (as well as at the North Pole).
- The South Pole is located in Antarctica.
- It experiences only one sunrise (at the September equinox) and one sunset (at the March equinox) every year.
- From the South Pole, the sun is always above the horizon in the summer and below the horizon in the winter. This means the region experiences up to 24 hours of sunlight in the summer and 24 hours of darkness in the winter.
- Due to plate tectonics, the exact location of the South Pole is constantly moving.
- The habitat is far too harsh for most organisms to survive.
MUST READ: India’s operational research stations at the South Pole
Source: DOWN TO EARTH
Previous Year Questions
Q.1) Which one of the following statements best describes the ‘Polar Code’? (2022)
- It is the international code of safety for ships operating in polar waters.
- It is the agreement of the countries around the North Pole regarding the demarcation of their territories in the polar region.
- It is a set of norms to be followed by the countries whose scientists undertake research studies at the North Pole and the South Pole.
- It is a trade and security agreement of the member countries of the Arctic Council.
Q.2) Consider the following statements: (2018)
- The Earth’s magnetic field has reversed every few hundred thousand years
- When the Earth was created more than 4000 million years ago, there was 54% oxygen and no carbon dioxide
- When living organisms originated, they modified the early atmosphere of the Earth
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
Syllabus
Syllabus
- Prelims – Science and Technology
Context : Recently, the European Space Agency highlighted the the need of a universal timekeeping system for the moon .
About MOON TIME ZONE:-
Objective: to streamline contact among the various countries and entities, public and private, that are coordinating trips to and around the moon.
Background:-
- The Moon has its own day and night cycle, which lasts about 29.5 Earth days.
- Currently, the time on the Moon is measured using Universal Time Coordinated (UTC), which is the same timekeeping system used on Earth.
- However, since the Moon’s day is much longer than Earth’s day, it would be difficult to use UTC for day-to-day activities on the Moon.
- To address this issue, scientists and researchers have proposed creating a lunar time zone that would be based on the Moon’s day and night cycle.
BENEFITS:-
- This would make it easier for lunar settlers to keep track of time and coordinate activities.
- Having a lunar time zone would also make it easier for scientists and researchers to conduct experiments and collect data on the Moon.
- It would also help to prevent confusion and errors that could arise from using different timekeeping systems on Earth and the Moon.
CHALLENGES:-
- Time on Earth is precisely tracked by atomic clocks, but synchronizing time on the moon is tricky because clocks run faster there, gaining around 56 microseconds, or millionths of a second, per day.
- It would also be difficult to establish a consistent time zone for the entire Moon, given that the terrain and lighting conditions vary widely across its surface.
- Any timekeeping system on the Moon would need to be able to account for the Moon’s irregular rotation and movement.
About Chandrayaan-1:-
- Chandrayaan-1, India’s first mission to the moon.
- It was launched by the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) in 2008.
- Its collection of sensors included NASA’s Moon Mineralogy Mapper (M3), an imaging spectrometer that supported the finding of water trapped in lunar minerals.
- The orbiter also discharged an impactor that was purposefully sent at the Moon, scattering debris that the science equipment on board, orbiting spacecraft analyzed.
Findings:
- Data from the Mineralogy Mapper (M3), one of the instruments on Chandrayaan-1, indicates the presence of hematite at the lunar poles.
- Hematite -is a mineral which is a form of iron oxide, or rust, produced when iron is exposed to oxygen and water.
- Chandrayaan-1 Moon data indicates that the moon’s poles are home to water that scientists are trying to decipher.
MUST READ : Findings of Chandrayaan-2 and Chandrayaan-3
Source: THE INDIAN EXPRESS
Previous Year Questions
Q.1) Satellites used for telecommunication relays are kept in a geostationary orbit. A satellite is said to be in such an orbit when: (2011)
- The orbit is geosynchronous.
- The orbit is circular,
- The orbit lies in the plane of the Earth’s equator.
- The orbit is at an altitude of 22,236 km.
Select the correct answer using the codes given below:
- 1, 2, and 3 only
- 1, 3, and 4 only
- 2 and 4 only
- 1, 2,3 and 4
Q.2) Which of the following pair is/are correctly matched? (2014)
Spacecraft Purpose
- Cassini-Huygens Orbiting Venus and transmitting data to the Earth
- Messenger Mapping and investigating the Mercury
- Voyager 1 and 2 Exploring the outer solar system
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
- 1 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
Syllabus
- Prelims – Science and Technology
About Adenovirus :-
- The adenoviruses are common pathogens of humans and animals.
- Adenovirus causes wide variety of illness in humans ranging from gastrointestinal infections to common cold.
- The main target for adenoviruses in humans is the respiratory tract.
- Adenovirus are a common cause of viral infections in all age groups.
- There are more than 50 types of adenoviruses that can cause disease in humans.
- Adenovirus is a double-stranded DNA virus .
- Adenoviruses can be transmitted from one infected person to another through physical contact,coughing and sneezing or touching a contaminated object or surface.
- The disease can also be caused by contaminated water or through an infected person’s faeces.
Common symptoms: –
- Respiratory (cough, fever, fast breathing, wheezing, sore throat)
- Pneumonia
- Diarrhea amog others.
MUST READ : Incovacc
Source: THE INDIAN EXPRESS
Previous Year Questions
Q.1) Consider the following statements:
- Adenoviruses have single-stranded DNA genomes whereas retroviruses have double-stranded DNA genomes.
- Common cold is sometimes caused by an adenovirus whereas AIDS is caused by a retrovirus.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct? (2021)
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Q.2) Consider the following: (2021)
- Bacteria
- Fungi
- Virus
Which of the above can be cultured in an artificial/ synthetic medium?
- 1 and 2 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 1,2 and 3
Syllabus
- Mains – GS 2 (Governance) and GS 3 (Science and Technology)
Context: The Union government outlined the Digital India Act, 2023 which is a broad overhaul of the decades-old Information Technology Act, 2000.
Main objective of the Digital India Bill:
- The Digital India Bill aims to ensure that the internet in India is open, free from user harm and criminality and that there is an institutional mechanism of accountability.
- The legislation will cover emerging technologies, algorithms of social media platforms, artificial intelligence, and user risks, as well as the diversity of the internet and the regulation of intermediaries.
Provisions under Digital India Act 2023:
Freedom of Expression:
- Social media platforms’ own moderation policies may now be reduced to constitutional protections for freedom of expression and Fundamental speech rights.
- Recent amendment to the IT Rules, 2021 says that platforms must respect users’ free speech rights.
- Three Grievance Appellate Committees have now been established to take up content complaints by social media users.
- These are now likely to be subsumed into the Digital India Act.
Online Safety:
- The Act will cover Artificial Intelligence (AI), Deepfakes, cybercrime, competition issues among internet platforms, and data protection.
- The government put out a draft Digital Personal Data Protection Bill in 2022, which would be one of the four prongs of the Digital India Act, with the National Data Governance Policy and amendments to the Indian Penal Code being others, along with rules formulated under the Digital India Act.
New Adjudicatory Mechanism:
- A new “Adjudicatory Mechanism” for criminal and civil offenses committed online would come into place.
Safe Harbour:
- The government is reconsidering a key aspect of cyberspace — ‘safe harbour’, which is the principle that allows social media platforms to avoid liability for posts made by users.
- The term has been reined in recent years by regulations like the Information Technology (Intermediary Guidelines and Digital Media Ethics Code) Rules, 2021, which require platforms to take down posts when ordered to do so by the government, or when required by law.
Constitutional and legal Protection:
- Fundamental speech rights (Art 19) cannot be violated by any platform.
- However, social media platform’s own moderation policies may violate constitutional protections for freedom of expression.
- There is certainly a case that can be made that weaponization of disinformation is not the same as free speech, and that needs to be addressed.
- IT Rules, 2021: It says that platforms must respect users’ free speech rights.
- Three Grievance Appellate Committees have now been established to take up content complaints by social media users.
- Since the appellate committee portal’s launch, seventeen appeals have already been filed.
The need for a New Act:
- Since the IT Act of 2000 was enacted, there have been many revisions and amendments (IT Act Amendment of 2008, IT Rules 2011).
- However, because the IT Act was originally designed only to protect e-commerce transactions and define cybercrime offenses, it did not deal with the nuances of the current cybersecurity landscape adequately nor did it address data privacy rights.
- Without a complete replacement of the governing digital laws, the IT Act would fail to keep up with the growing sophistication and rate of cyber-attacks.
- The new Digital India Act also envisages to act as catalysts for Indian economy by enabling more innovation, more startups, and at the same time protecting the citizens of India in terms of safety, trust, and accountability.
Way forward
Regulation of hate speech and disinformation on the Internet is a must and intermediaries, including digital news media and social media platforms, have an accountable role to play.
Currently, there are more than 760 million internet users in the country and this is to touch 1.2 billion in coming years. Though the internet is good and aids in connectivity, there are several user harms around it. Therefore, it is essential to bring in laws that will provide new frames on the rights and duties of the citizens and also speaks about the obligation to collect data.
MUST READ: Need for safety on Digital Space
Source: Indian Express
Syllabus
- Mains – GS 2 (International Relations)
Context: The Australian Prime Minister (PM) on his visit, India and Australia signed an Audio-visual co-production agreement. The two Prime Ministers also discussed a range of domains to improve India-Australia relations.
Key highlights of the visit:
- Australia wants to work with India and build a relationship in the areas of culture, economics, and security.
- Both countries signed memorandums of understanding (MoUs) for sports and audio-visual co-production agreements, and they also talked about the terms of reference for the Solar Taskforce between India and Australia.
- India was worried about the damage done to Hindu temples in Australia by people who support the Khalistan government.
- In reply, Australia agreed to protect and keep safe the Indian community in Australia.
Bilateral relations:
Historical Perspective:
- Australia and India for the first time established diplomatic relations in the pre-Independence period, when the Consulate General of India was first opened as a Trade Office in Sydney in 1941.
- India-Australia relations touched a historic low when the Australian Government condemned India’s 1998 nuclear tests.
- In 2014, Australia signed a Uranium supply deal with India, the first of its kind with a country that is a non-signatory to the Nuclear Non-Proliferation Treaty, in recognition of India’s “impeccable” non-proliferation record.
Bilateral Trade:

- India is the 5th largest trade partner of Australia with trade in goods and services at A$ 29 billion representing 3.6% share of the total Australian trade in 2017-18, with export at A$ 8 billion and import at A$ 21 billion.
Defence:
- AUSINDEX: The first-ever Bilateral Maritime Exercise, AUSINDEX, was conducted in Visakhapatnam (Bay of Bengal) in September 2015.
- Exercise Pitch Black: In 2018, the Indian Air Force participated for the first time in the Exercise Pitch Black in Australia.
- Exercise of the Australian Navy: INS Sahyadri participated in Kakadu, the biennial exercise of the Australian Navy held in 2018, in which 27 nations participated.
- AUSTRAHIND: The 4th edition of AUSTRAHIND (Special Forces of Army Exercise) was held in recently.
- Joint military exercises: In 2023, India, Japan, and the US will all take part in the “Malabar” exercises, which will be held in Australia.
- India has been invited to join the Talisman Sabre exercises in 2023.
Multilateral Cooperation:
- Both are members of the Quad, Commonwealth, Indian Ocean Rim Association (IORA), ASEAN Regional Forum, Asia Pacific Partnership on Climate and Clean Development, and have participated in the East Asia Summits.
- Both countries have also been cooperating as members of the Five Interested Parties (FIP) in the World Trade Organization context.
- Australia is an important player in Asia Pacific Economic Cooperation (APEC) and supports India’s membership of the organisation.
Cooperation on Clean Energy:
- In February 2022, countries signed a Letter of Intent on New and Renewable Energy for cooperation to reduce the cost of renewable energy technologies, including ultra low-cost solar and clean hydrogen.
- India announced Australian Dollars(AUD) 10 million for Pacific Island Countries under the International Solar Alliance (ISA).
- Both the countries committed to USD 5.8 million to the three-year India-Australia Critical Minerals Investment Partnership.
Indian Diaspora:
- The Indian community in Australia continues to grow in size and importance, with a population of nearly half seven lakhs.
- India is now the third-largest source of immigrants to Australia, after the UK and New Zealand and the largest source of skilled professionals for Australia.
- There is a constant flow of students and tourists from India.
Challenges in India-Australia Relations:
- China’s Discontent: China is unhappy with the growing security cooperation between Australia and India.
- The Chinese government responded to the Quadrilateral dialogue by issuing formal diplomatic protests to its members, calling it “Asian NATO”.
- India’s stand on the Russia-Ukraine crisis: Australia has criticized the Russian invasion of Ukraine and sided with the U.S. and western countries.
- However, India has refrained from criticizing Russia over the issue. This can create differences in bilateral discourse and the functioning of QUAD.
- Coal mine controversy: There was controversy over the Adani coal mine project in Australia, with some activists protesting against it, which created a strain in the relationship between the two countries.
- Visa issues: There have been concerns over visa restrictions for Indian students and professionals seeking to work in Australia.
- No Free Trade Agreement: Both nations have been interacting and communicating with each other for decades but have failed to create a consensus on a Free trade agreement.
- Lack of Uranium Supply: The progress on uranium supply has been very low, despite efforts from both sides. In 2017, Australia had sent its first uranium shipment to India but that was cited as “a small sample of uranium” transferred “purely for testing purposes”.
- Violence with Indian Diaspora: Attacks on Indian Diaspora and temples in the recent past by Khalistan supporters have been an issue of strain.
Way Forward:
On the whole, The India–Australia strategic partnership has seen impressive advancements in the last few years, but its potential and promise are yet to be fully realised. Hence, the need of dedicated attention and political leadership from both capitals to become more than a work in progress going forward.
MUST READ: India-Australia Critical Minerals Investment Partnership
Source: Indian Express
Practice MCQs
Q.1) Which of the following recently released the Landslide Atlas of India?
- Ministry of Home Affairs
- NITI Aayog
- Ministry of Earth Sciences
- National Remote Sensing Centre, ISRO
Q.2) Consider the following statements regarding Subhash Chandra Bose Aapda Prabandhan Puraskar:
- It is an award to recognize and honor the invaluable contribution and selfless service rendered by individuals and organizations in India in the field of Science and Technology.
- The award is administered by the National Disaster Management Authority under the Ministry of Home Affairs.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Q.3) Consider the following statements regarding the National Platform for Disaster Risk Reduction (NPDRR):
- It is chaired by the Prime Minister of India
- It is a statutory body
- The Vice-Chairman of, the National Disaster Management Authority acts as the Vice-Chairperson of the NPDRR.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 and 2 only
- 2 only
- 3 only
- 1 and 3 only
Comment the answers to the above questions in the comment section below!!
ANSWERS FOR ’13th March 2023 – Daily Practice MCQs’ will be updated along with tomorrow’s Daily Current Affairs.st
ANSWERS FOR 11th March 2023 – Daily Practice MCQs
Q.1) – d
Q.2) – b
Q.3) – d











