IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
Archives
(PRELIMS & MAINS Focus)
Syllabus
- Prelims –Environment and Ecology and Geography
Context: Recently, the National Green Tribunal (NGT), imposed a penalty of Rs 10 crore on the Kerala government for failing to protect the Vembanad and Ashtamudi lakes.
About Vembanad lake:-
- It is the largest lake in Kerala and the longest Lake in India.
- It is bound by Alappuzha, Kottayam and Ernakulam.
- It has its source in four rivers: Meenachil, Achankovil, Pampa and Manimala.
- It is separated from the Arabian Sea by a narrow barrier island and is a popular backwater stretch in Kerala.
- Vallam Kali (i.e Nehru Trophy Boat Race): a Snake Boat Race held every year in the month of August in Vembanad Lake.
- It was included in the list of wetlands of international importance, as defined by the Ramsar Convention in 2002.
- It is the second-largest Ramsar site in India only after the Sundarbans in West Bengal.
- The Government of India has identified the Vembanad wetland under the National Wetlands Conservation Programme.
- The Kumarakom Bird Sanctuary is located on the east coast of the lake.
- In 2019, Willingdon Island, a seaport was carved out.
About Ashtamudi Lake:-
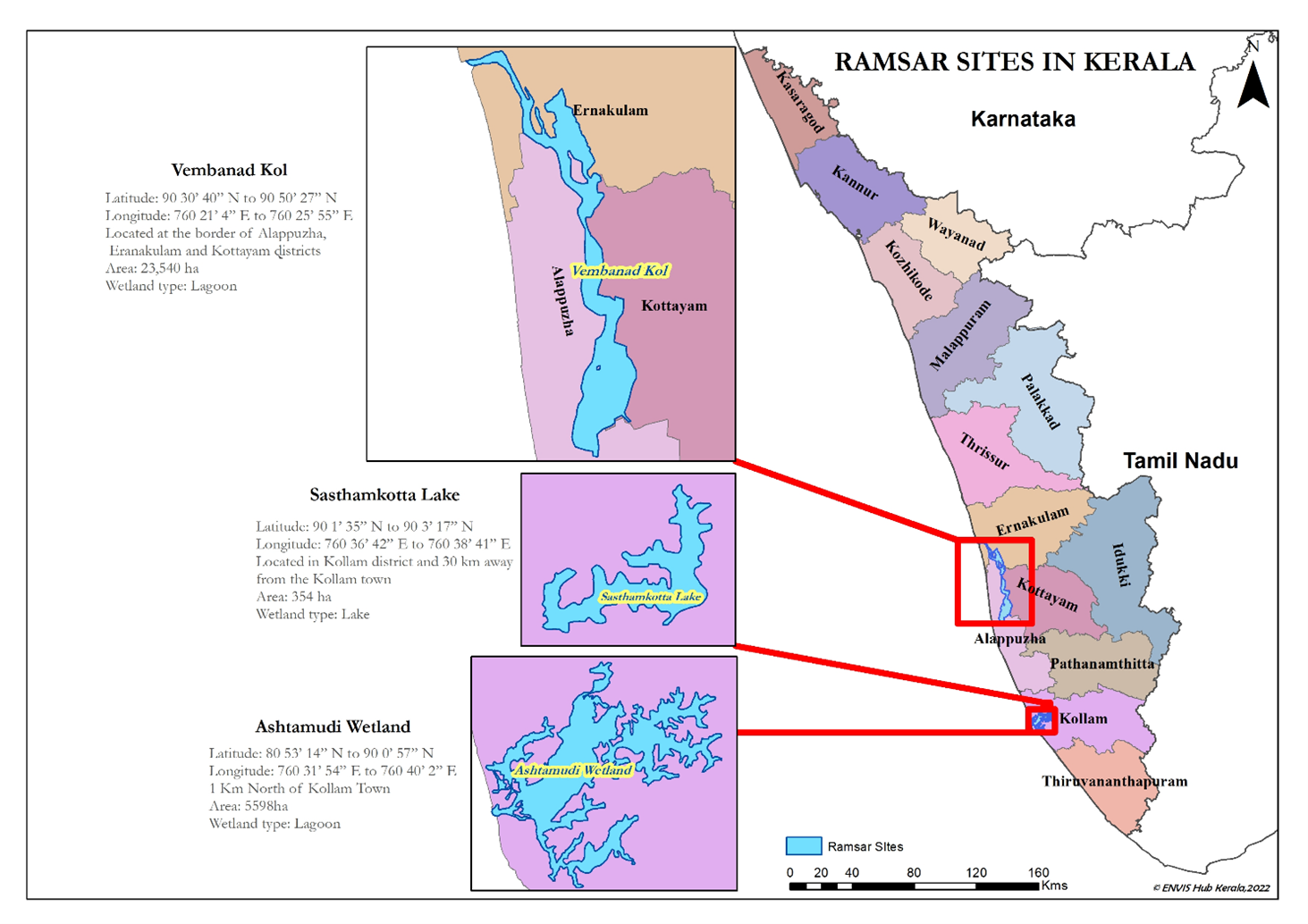
IMAGE SOURCE: http://www.kerenvis.nic.in/WriteReadData/userfiles/ramsar.jpg
- It is a freshwater lake located in the Kollam district of Kerala, a state in southern India.
- It is an extensive estuarine system, the second largest in Kerala State.
- Ashtamudi means ‘eight braids’ in the local Malayalam language.
- It has been recognized as a Ramsar site, a wetland site designated internationally important under the Ramsar Convention.
- The Ramsar Convention: is an international treaty for the conservation and sustainable use of wetlands, and India is a signatory to this treaty.
MUST READ: COP14 of Ramsar Convention on Wetlands
SOURCE: DOWN TO EARTH
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) Consider the following pairs: (2022)
Wetland/Lake: Location
- Hokera Wetland Punjab
- Renuka Wetland Himachal Pradesh
- Rudrasagar Lake Tripura
- Sasthamkotta Tamil Nadu
How many pairs given above are correctly matched?
- Only one pair
- Only two pairs
- Only three pairs
- All four pairs
Q.2) Consider the following statements: (2019)
- Under Ramsar Convention, it is mandatory on the part of the Government of India to protect and conserve all the wetlands in the territory of India
- The Wetlands (Conservation and Management) Rules, 2010 were framed by the Government of India based on the recommendations of the Ramsar Convention
- The Wetlands (Conservation and Management) Rules, 2010 also encompass the drainage area or catchment regions of the wetlands as determined by the authority
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 and 2 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
Syllabus
- Prelims –Governance
Context: The implementation of the Scheme for Residential Education for Students in High Schools in Targeted Areas (SHRESHTA) and Support for Marginalised Individuals for Livelihood and Enterprise (SMILE)was reviewed recently.
About Scheme for Residential Education for Students in High Schools in Targeted Areas (SHRESHTA):-
- It is under the Ministry of Social Justice and Empowerment.
- It is a Central Sector Scheme.
- Objective: for the purpose of providing seats for the meritorious SC boys and girls in the best private residential schools in the country.
- Every year, it is expected that about (3000) students would be selected for admission in Class 9 and Class 11 under the scheme.
- Admission will be provided in Class 9 and Class 11 of CBSE-affiliated private schools.
- Selection process: The selection will be done through a transparent mechanism which is known as National Entrance Test for SHRESHTA (NETS).
- It will be conducted by the National Testing Agency (NTA) for admission in classes 9th and 11th.
- NTA: it is a premier, specialist, an autonomous and self-sustained testing organization to conduct entrance examinations for admission/fellowship in higher educational institutions.
- It was established as an independent, autonomous, and self-sustained premier testing organization under the Societies Registration Act (1860) by the Ministry of Education (MoE).
- It is for conducting efficient, transparent, and international standardized tests in order to assess the competency of candidates for admission to premier higher education.
About Support for Marginalised Individuals for Livelihood and Enterprise (SMILE):-
- It is under the Ministry of Social Justice and Empowerment.
- It is a Central Sector scheme.
- Objective: for providing welfare measures to the Transgender community and people engaged in begging.
- It seeks to strengthen and expands the reach of Rights that give necessary legal protection and secured life to the targeted group.
- It keeps in mind the social security required through multiple dimensions of identity, education, medical care, shelter, and occupational opportunities.
- This umbrella scheme would cover several comprehensive measures including welfare measures with a focus extensively on rehabilitation, provision of medical facilities, counselling, education, skill development, economic linkages etc.
- It will work with the support of State Governments/UTs/Local Urban Bodies, Voluntary Organizations, Community-Based Organizations (CBOs) and institutions and others.
- It includes two sub-schemes –
- Comprehensive Rehabilitation for the Welfare of Transgender Persons and
- Comprehensive Rehabilitation of persons engaged in the act of Begging.
Components of Comprehensive Rehabilitation for the Welfare of Transgender Persons:-
- Scholarships for Transgender Students studying in IX and till post-graduation to complete their education.
- Skill Development and Livelihood under the PM-DAKSH scheme.
- Composite Medical Health package in convergence with PM-JAY to support Gender-Reaffirmation surgeries through selected hospitals
- Shelter Homes ‘Garima Greh’, where all the basic facilities (food, clothing, medical support) recreational facilities and skill development opportunities, will be provided.
- Transgender Protection Cell will be set up in each state for monitoring cases of offences and ensuring timely registration, investigation and prosecution.
Components of Comprehensive Rehabilitation of persons engaged in the act of Begging:-
- Survey and Identification of beneficiaries by Implementing Agencies.
- Outreach work will be done to mobilise the persons engaged in begging to avail services available in Shelter Homes.
- Shelter homes will facilitate education for children engaged in the act of Begging.
MUST READ: Education & Nation Building
SOURCE: PIB
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) What is the aim of the programme ‘Unnat Bharat Abhiyan’? (2017)
- Achieving 100% literacy by promoting collaboration between voluntary organizations and the government’s education system and local communities.
- Connecting institutions of higher education with local communities to address development challenges through appropriate technologies.
- Strengthening India’s scientific research institutions in order to make India a scientific and technological power.
- Developing human capital by allocating special funds for health care and education of rural and urban poor, and organizing skill development programmes and vocational training for them.
Q.2) What is the purpose of ‘Vidyanjali Yojana’? (2017)
- To enable famous foreign educational institutions to open their campuses in India.
- To increase the quality of education provided in government schools by taking help from the private sector and the community.
- To encourage voluntary monetary contributions from private individuals and organizations so as to improve the infrastructure facilities for primary and secondary schools.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
- 2 only
- 3 only
- 1 and 2 only
- 2 and 3 only
Syllabus
- Prelims –Governance
Context: Recently, the Government has launched a new Scheme namely, New India Literacy Programme.
About New India Literacy Programme:-

IMAGE SOURCE: Government approves New India Literacy Programme for Financial Years 2022 to 2027 (newsonair.gov.in)
- It is a Centrally Sponsored Scheme.
- The scheme aims to cover a target of five crore non-literates in the age group of 15 years and above.
- It is under the Ministry of Education.
- Implementation: the beneficiaries under the scheme are identified through door-to-door surveys on Mobile Apps by the surveyors in the States and Union Territories.
- The scheme is targeted at all non-literates of age 15 years and above.
- The scheme has five components:-
- Foundational Literacy and Numeracy
- Critical Life Skills (which include, financial literacy, digital literacy, legal literacy, healthcare and awareness, childcare and education, family welfare, etc.)
- Basic Education (includes preparatory (classes 3 – 5), middle (classes 6- 8), and secondary stage (classes 9-12) equivalency)
- Vocational Skills (Skill development will be a part of the continuous learning process for neo-literates to obtain local employment)
- Continuing Education (This includes engaging holistic adult education courses in arts, sciences, technology, culture, sports, and recreation, as well as other topics of interest or use to local learners).
- Formation and involvement of SHGs, Voluntary & User Groups and other community-based organizations may be encouraged. The scheme is to be implemented through volunteerism.
- The learners will be encouraged to excess the content in local languages in online mode through the DIKSHA platform in NCERT.
- Government/Aided schools registered under UDISE are the units of implementation of the scheme which are run by the State/UT Governments.
- United Information System for Education Plus(UDISE): is one of the largest Management Information Systems on school education.
- It was launched in 2018-2019 to speed up data entry, reduce errors, improve data quality and ease its verification.
MUST READ: Scientific Literacy in India
SOURCE: NEWSONAIR
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) Regarding DigiLocker’, sometimes seen in the news, which of the following statements is/are correct? (2016)
- It is a digital locker system offered by the Government under Digital India Programme.
- It allows you to access your e-documents irrespective of your physical location.
Select the correct answer using the code given below.
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Q.2) SWAYAM’, an initiative of the Government of India, aims at (2016)
- promoting Self-Help Groups in rural areas
- providing financial and technical assistance to young start-up entrepreneurs
- promoting the education and health of adolescent girls
- providing affordable and quality education to the citizens for free
Syllabus
- Prelims –Governance
Context: Recently the top government officials indicated that the PPF, Sukanya Samriddhi Account interest rate hike may remain elusive.
About Sukanya Samriddhi Scheme:-
- It is under the Ministry of Women and Child Development.
- It is a small deposit scheme for girl children, launched as a part of the ‘Beti Bachao Beti Padhao’ campaign.
- Objective: it would fetch an attractive interest rate and provide an income tax rebate.
- Eligibility:-
- Parents or legal guardians can open deposits on behalf of a girl child (including an adopted girl child) for up to 2 daughters aged below 10.
- Minimum of Rs 250 of initial deposit with multiple of Rs 150 thereafter with an annual ceiling of Rs.150000 in a financial year.
- Maximum period up to which deposits can be made 15 years from the date of opening of the account.
- The account shall mature on completion of 21 years from the date of opening of the account or on the marriage of the Account holder whichever is earlier.
- The investments are designated as an EEE (Exempt, Exempt, Exempt) investment.
- This means that the principal invested, the interest earned as well as the maturity amount are tax-free.
About Public Provident Fund (PPF):-
- It is a popular investment scheme with multiple investor-friendly features and associated benefits.
- It is a long-term investment scheme to earn high but stable returns.
- Proper safekeeping of the principal amount is the prime target of individuals opening a PPF account.
- Implementation: When a PPF scheme is opened, the PPF account is scheduled for the applicant where the money is deposited every month and interest is compounded A Public provident fund scheme is ideal for individuals with a low-risk appetite.
- Since this plan is mandated by the government, it is backed up with guaranteed returns to protect the financial needs of the masses in India.
- Further, invested funds in the PPF account are not market-linked either.
- Investors can also undertake the public provident fund regime to diversify their financial and investment portfolios
- Eligibility Criteria:-
- Indian citizens residing in the country are eligible to open a PPF account in his/her name.
- Minors are also allowed to have a Public provident fund account in their name, provided it is operated by their parents.
- Non-residential Indians are not permitted to open a new PPF account.
- However, any existing account in their name remains active till the completion of tenure.
- These accounts cannot be extended for 5 years – a benefit available to Indian residents.
- Interest in a PPF Account:-
- The interest payable on public provident fund schemes is determined by the Central Government of India.
- It aims to provide higher interest than regular accounts maintained by various commercial banks in the country.
- The entire amount redeemed from a PPF account upon completion of maturity is not subject to taxation.
- Loan provisions: these can be done between the third and fifth years of your PPF account.
- The loan amount can be no more than 25% of the second year immediately preceding the loan application year.
- If the first loan is entirely repaid, a second loan can be taken out before the sixth year.
MUST READ: Small savings schemes
SOURCE: THE HINDU
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) Which of the following statements is/are correct regarding the Maternity Benefit Amendment Act, 2017? (2019)
- Pregnant women are entitled to three months of pre-delivery and three months of post-delivery paid leave.
- Enterprises with creches must allow the mother a minimum of six creche visits daily.
- Women with two children get reduced entitlements.
Select the correct answer using the code given below.
- 1 and 2 only
- 2 only
- 3 only
- 1, 2 and
Q.2) Who among the following can join the National Pension System (NPS)? (2017)
- Resident Indian citizens only
- Persons of age from 21 to 55 only
- All State Government employees joining the services after the state of notification by the respective State Governments
- All Central Government employees including those of Armed Forces joining the services on or after 1st April 2004
Syllabus
- Prelims –Economy
Context: Recent reports suggest that most of EPFO’s equity investments are routed into Nifty 50 stocks, including Adani Enterprises and Adani Ports & SEZ.
About Employees’ Provident Fund Organization (EPFO):-
- The EPFO is under the administrative control of the Ministry of Labour and Employment, Government of India.
- It is one of the World’s largest Social Security Organisations in terms of clientele and the volume of financial transactions undertaken.
- It into existence with the promulgation of the Employees’ Provident Funds Ordinance on the 15th of November 1951.
- It was replaced by the Employees’ Provident Funds Act, of 1952.
- The Employees’ Provident Funds Bill was introduced in the Parliament in the year 1952 as a Bill to provide for the institution of provident funds for employees in factories and other establishments.
- The Act is now referred to as the Employees’ Provident Funds & Miscellaneous Provisions Act, 1952 which extends to the whole of India.
- The Act and Schemes framed there under are administered by a tri-partite Board known as the Central Board of Trustees, Employees’ Provident Fund.
- The Central Board of Trustees :
- It consists of representatives of Government (Both Central and State), Employers, and Employees.
- It administers a contributory provident fund, a pension scheme and an insurance scheme for the workforce engaged in the organized sector in India.
- It is assisted by the Employees’ PF Organization (EPFO), consisting of offices at 138 locations across the country.
- The Organization has a well-equipped training set-up where officers and employees of the Organization as well as Representatives of the Employers and Employees attend sessions for training and seminars.
- Vision: An innovation-driven social security organisation aiming to extend universal coverage and ensure Nirbadh (Seamless and uninterrupted) service delivery to its stakeholders through state-of-the-art technology.
Schemes under EPFO:-
- EPF Scheme 1952
- It provides for the accumulation plus interest upon retirement and death.
- Partial withdrawals are allowed for education, marriage, illness and house construction.
- Pension Scheme 1995 (EPS)
- It provides monthly benefits for superannuation/retirement, disability, survivor, widow(er) and children.
- It provides a minimum pension on disablement.
- It provides past service benefits to participants of the erstwhile Family Pension Scheme, 1971.
- Insurance Scheme 1976 (EDLI)
-
- It provides the benefit in case of the death of an employee who was a member of the scheme at the time of death.
- It provides the benefit amount 20 times the wages.
- Maximum benefit is 6 lakhs.
MUST READ: EPFO’s New Facility on UMANG App started
SOURCE: THE HINDU
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) Regarding ‘Atal Pension Yojana’, which of the following statements is/are correct? (2016)
- It is a minimum guaranteed pension scheme mainly targeted at unorganized sector workers.
- Only one member of a family can join the scheme.
- Same amount of pension is guaranteed for the spouse for life after the subscriber’s death.
Select the correct answer using the code given below.
- 1 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
Q.2) Pradhan Mantri MUDRA Yojana is aimed at (2016)
- bringing the l entrepreneurs into a formal financial system
- providing loans to poor farmers for cultivating particular crops
- providing pensions to old and destitute people
- funding the voluntary organizations involved in the promotion of skill development and employment generation
Syllabus
- Prelims –Geography
Context: Brazilian researchers recently succeeded in taking pictures of the Upward Lightning Phenomenon.
About Upward Lightning Phenomenon:-
- Upward lightning is a phenomenon whereby a self-initiated lightning streak develops from a tall object that travels upward toward an overlaying electrified storm cloud.
- For this to happen, storm electrification and the resulting presence of a cloud charge region are enabling factors.
- The vertical elevation of a tall object accentuates the electric field locally on the ground, resulting in conditions favourable for the initiation of an upward streak (called a leader) from a tall object, which can also develop in response to an electric field change created by a nearby preceding lightning flash.
- The process is triggered by the development of the stepped leader
- Stepped leader: a channel of negative charge that travels downward in a zigzag pattern from a cloud, nearly invisible to the human eye) travelling to the ground in a millisecond, leading to an intensification of the positive charge on the ground.
- As the streaks of the stepped leader keep streaking towards the ground, the electrical charges between the leader tips and the tops of tall objects on the ground keep on increasing.
- In the due course, these forces cause the air above these tall buildings or towers to ionise and thereby turn more conductive.
- With the negative charge repeatedly moving toward the ground, the channel of air just above the tall objects turns positively charged, which starts streaking upwards and is called an upward streamer.
- In due course, the negatively-charged, downward-moving stepped leader makes contact with one of the developing positively-charged upwards streamers.
- Upward lightning typically has a lower intensity and duration compared to downward lightning.
- It also has a higher frequency of occurrence during thunderstorms
Risks:-
- Upward lightning can cause damage to structures such as buildings and towers by creating an electrical surge that can overload electrical systems and cause fires or explosions.
- Upward lightning can also pose a risk to aviation, particularly for planes that fly close to tall structures during thunderstorms.
- This can cause electromagnetic interference, affecting communication and navigation systems.
Preventions: –
- To prevent damage from upward lightning, lightning rods and other grounding systems can be installed on tall structures to safely dissipate the electrical charge.
- Additionally, electrical equipment and systems can be designed to withstand lightning strikes and power surges.
MUST READ: Lightning
SOURCE: THE INDIAN EXPRESS
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) Consider the following statements: (2022)
- High clouds primarily reflect solar radiation and cool the surface of the Earth.
- Low clouds have a high absorption of infrared radiation emanating from the Earth’s surface and thus cause a warming effect.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Q.2) Consider the following statements: (2021)
- In the tropical zone, the western sections of the oceans are warmer than the eastern sections owing to the influence of trade winds.
- In the temperate Zone, westerlies make the eastern sections of oceans warmer than the western sections
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 and 2
Syllabus
- Prelims –Science and Technology and Environment and Ecology
Context: DNA profiling of 270 captive elephants has been completed recently.
About DNA profiling of Elephant:-
- DNA profiling is a method to differentiate between individuals of the same species using samples of their Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA).
- DNA profiling of elephants was started in August 2022 for Gaj Soochna App.
- This will act as the ‘Adhaar card of captive elephants’.
- Gaj Soochna: this is a mobile application developed to record the details of captive elephants across India.
- The centralized database will include physical and genetic information of every captive elephant individual in the country.
- Gaj Soochna: this is a mobile application developed to record the details of captive elephants across India.
- The DNA profiling process is being carried out in collaboration with the Wildlife Institute of India.
Benefits:-
- The forest officers can identify each elephant and track it.
- Therefore its transfer, which often happens in the case of captive elephants, can be recorded.
- More focus can be put on elephant care with unique information about elephants.
About Project Elephant:-
- It was launched in 1992.
- It is a Centrally-Sponsored Scheme.
- Objective: to protect elephants and improve their habitat and corridors, reduce Human-elephant conflict and ensure their welfare.
- Implementation: Under this project, financial and technical support is given to wildlife management efforts by states for their free-ranging populations of wild Asian Elephants.
- Project elephant is mainly implemented in 16 States.
, Unlike Project Tiger, Project Elephant looks at the welfare and health of captive elephants as well.
Conservation status of Asian Elephant:-
- IUCN: Endangered
- Wildlife (Protection) Act, 1972: Schedule I.
- CITES: Appendix I
MUST READ: Elephant Conservation
SOURCE: THE INDIAN EXPRESS
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) With reference to carbon nanotubes, consider the following statements: (2020)
- They can be used as carriers of drugs and antigens in the human body.
- They can be made into artificial blood capillaries for an injured part of the human body.
- They can be used in biochemical sensors.
Carbon nanotubes are biodegradable.
Which of the statements given above is correct?
- 1 and 2 only
- 2, 3 and 4 only
- 1, 3 and 4 only
- 1, 2, 3 and 4
Q.2) With reference to Indian elephants, consider the following statements (2020)
- The leader of an elephant group is a female
- The maximum gestation period can be 22 months
- An elephant can normally go on calving till the age of 40 years only
- Among the States in India, the highest elephant population is in Kerala
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 and 2 only
- 2 and 4 only
- 3 only
- 1, 3 and 4 only
Syllabus
- Mains – GS 2 (Governance) and GS 3 (Security)
Context: The Union government has extended the Armed Forces (Special) Powers Act (AFSPA) in Arunachal Pradesh and Nagaland and it has been removed from several areas in Northeast India.
About Armed Forces (Special Powers) Act 1958:
Genesis:
- The genesis of the law can be traced to the Armed Forces (Special Powers) Ordinance 1942 which was enacted by the British to subjugate the rebels in the country during the Quit India movement, particularly in Assam and Bengal .
- The law continues to be enforced in its new format as the Armed Forces (Special Powers) Act 1958.
- The need for the law was required in the 1950s when Naga insurgents resorted to large-scale violence.
Provisions
- Under Section 3, the Central Government or the Governor of the State or administrator of the Union Territory can declare the whole or part of the State or Union Territory as a disturbed area.
- An area can be disturbed due to differences or disputes between members of different religious, racial, language or regional groups or castes or communities.
- Section 4 gives the Army powers to search premises and make arrests without warrants, to use force even to the extent of causing death, destroy arms/ammunition dumps, fortifications/shelters/hideouts and to stop, search and seize any vehicle.
- Section 6 stipulates that arrested persons and the seized property are to be made over to the police with the least possible delay.
- Section 7 offers protection of persons acting in good faith in their official capacity.
- The prosecution is permitted only after the sanction of the Central Government.
Need for the AFSPA:
- The Army believes that the AFSPA is extremely necessary to fight domestic insurgency and preserve the nation’s frontiers.
- Protection of members of the armed forces – It is essential to empower members of the military forces whose lives are continuously threatened by rebels and extremists. Its absence would negatively affect morale.
- The Act and Army regulations offer necessary protections, as outlined below: According to Section 5 of the Act, apprehended civilians must be delivered to the closest police station with the “least feasible delay” and a “report of the circumstances that led to the arrest.”
- Effective Counterinsurgency: Strong legislation is required to combat insurgent groups inside the nation, especially in Kashmir and the Northeastern area.
- The presence of proxy groups in troubled regions necessitates the use of extraordinary means to break this connection.
- As the armed services confront asymmetric warfare including raids, ambushes, mines, and explosives, extraordinary abilities are also required.
Arguments against AFSPA:
- Violation of the Human Rights: The exercise of these extraordinary powers by armed forces has often led to allegations of fake encounters and other human rights violations by security forces in disturbed areas while questioning the indefinite imposition of AFSPA in certain states.
- Human rights violations in AFSPA areas are not inquired into and followed by adequate action. Thus, it is against the principle of natural justice.
- Violation of the right to remedy: Section 6 of the Act “immediately takes away, abrogates, frustrates the right to constitutional remedy which has been given in article 32(1) of the Constitution.
- AFSPA was outside the powers granted in the Constitution since it was declaring a state of emergency without following the Constitutional provisions for such a declaration.
- Ineffectiveness of the Act: Critics argue that this act has failed in its objective of restoring normalcy in disturbed areas although being in existence for about 50 years.
Present Status:
- AFSPA now applicable fully only in 31 districts of 4 Northeast states and partially in 12 districts.
- The Act is applicable in the entire state of Jammu and Kashmir and States include Nagaland, Assam, Arunachal Pradesh, Manipur.
Way Forward:
AFSPA is required to counter insurgencies and lack of development in the Northeast region is also a major reason for the insurgency therefore the Government should take urgent steps to create new opportunities for growth and development. However, there needs to be a comprehensive and serious periodical review undertaken by the Centre till the entire North-east is freed from the tentacles of AFSPA.
Source: Indian Express
Syllabus
- Mains – GS 2 (Governance) and GS 3 (Economy)
Context: Recently, the government announced the formation of a committee to monitor the stock of tur dal held by importers, mills, stockists, and traders in order to prevent hoarding and speculation.
- Tur is a long-duration (180 days) pulses variety that is grown in rainfed conditions. It is grown in many states of India including Karnataka, Maharashtra, Uttar Pradesh etc. India meets about 10-12% of its domestic consumption through imports.
About Essential Commodities:
- Essential commodities are not specifically defined in the Essential Commodities Act, 1955, but Section 2(A) of the act underlines that an “essential commodity” means a commodity mentioned in the Schedule of the Act.
- The Union government derives its power to add or remove a commodity specified in the schedule from this act.
- If necessary, the Central Government in consultation with state governments can notify an item as essential.
- Face masks and sanitisers were added to the list on March 13, 2020 in the wake of the COVID-19 outbreak.
- The government can control the production, supply, and distribution of the declared essential commodity and can also impose a stock limit.
About Essential Commodities Act, 1955:
- The Centre has invoked the Essential Commodities Act of 1955 to ask States to monitor and verify the stocks available with such traders.
- Under the EC Act of 1955, if the Central government thinks that it is necessary to maintain or increase supplies of any essential commodity or make it available at fair prices, it can regulate or prohibit the production, supply, distribution and sale of that commodity.
- The Centre has the power to add or remove any commodity in public interest from this list of essential commodities.
The EC (Amendment) Bill 2020:
- It aims to remove fears of private investors of excessive regulatory interference in their business operations.
- The freedom to produce, hold, move, distribute and supply will lead to harnessing economies of scale and attract private sector/foreign direct investment into the agriculture sector.
- It will help drive up investment in cold storages and modernization of the food supply chain.
Issues Related to Essential Commodities Act 1955:
- The Economic Survey 2019-20 highlighted that government intervention under the ECA 1955 often distorted agricultural trade while being totally ineffective in curbing inflation.
- Such intervention does enable opportunities for rent-seeking and harassment.
- Rent-seeking is a term used by economists to describe unproductive income, including from corruption.
- Traders tend to buy far less than their usual capacity and farmers often suffer huge losses during surplus harvests of perishables.
- This led to farmers being unable to get better prices due to lack of investment in cold storage, warehouses, processing and export.
- Owing to these issues, the Parliament passed the Essential Commodities (Amendment) Bill, 2020.
- However, due to farmers’ protest the Government had to repeal this law.
Way Forward:
The ECA 1955 was brought when India was not self-sufficient in food grains production. However, now India has become surplus in most Agri-commodities, and the amendments to the ECA 1955 is an important step by the government to achieve its target of inflation of Agri commodities and ease of doing business in the market.
Source: Financial Express
Practice MCQs
Q.1) Consider the following statements regarding the Employees’ Provident Fund Organization (EPFO):
- It is a statutory organisation
- It is under the administrative control of the Ministry of Labour and Employment.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Q.2) Consider the following statements regarding the Sukanya Samriddhi Scheme:
- It is implemented under the Ministry of Education.
- It is a small deposit scheme for girl children, launched as a part of the ‘Beti Bachao Beti Padhao’ campaign.
- Parents or legal guardians can open deposits on behalf of a girl child (including an adopted girl child) for up to 2 daughters aged below 10.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
- 1 and 2 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 1 2 and 3
Q.3) Consider the following pairs:
Wetland/Lake: Location
- Vembanad lake Tamil Nadu
- Asthamudi Lake Kerala
- Sasthamkotta Lake Karnataka
How many pairs given above are correctly matched?
- Only one pair
- Only two pairs
- Only three pairs
- None
Comment the answers to the above questions in the comment section below!!
ANSWERS FOR ’30th March 2023 – Daily Practice MCQs’ will be updated along with tomorrow’s Daily Current Affairs.st
ANSWERS FOR 29th March – Daily Practice MCQs
Q.1) – c
Q.2) – b
Q.3) – a











