IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
Archives
(PRELIMS & MAINS Focus)
Syllabus
- Prelims –Important Personalities
Context: Recently, a political row erupted following Union Home Minister Amit Shah’s remark that Rabindranath Tagore had composed “national songs” of two countries.
About Rabindranath Tagore:-

IMAGE SOURCE: Tagore wins Nobel Prize (bl. UK)
- Rabindranath Tagore was a Bengali poet, novelist, artist, painter and educational theorist.
- He is credited with composing the National Anthem of India.
- Tagore won the Nobel Prize for Literature in 1913 for his collection Gitanjali.
- He was the first Indian and non-European to receive a Nobel Prize.
- He received the British Knighthood in 1915.
- However, he renounced it in protest against the Jallianwalla Bagh massacre in 1919. (UPSC PRELIMS: Jallianwala Bagh)
- Social Philosophy:-
- He fought against the evils of his society such as poverty, superstition, and untouchability.
- He welcomed Western science and Western beliefs in individual worth, freedom, and democracy.
- Independence movement:-
- He believed that nationalism deteriorated from patriotism to chauvinism.
- He is credited for giving the Mahatma title to Mahatma Gandhi. (UPSC MAINS: Gandhi as a Political thinker and a Social Reformer)
- He strongly protested against the partition of Bengal in 1905.
- He wrote many national songs and attended protest meetings against the decision to partition Bengal.
- Religion:-
- Tagore advocated the religion of humanity.
- Education:-
- In his view, traditional schools imprison children.
- Hence, he started a model school after the ancient hermitage schools of India named Santiniketan (the abode of peace).
- Santiniketan engaged many scholars from across the world, including his English friends, Oxford professor E J Thompson, missionary C F Andrews and Lord Elmhirst.
- He also widened his educational commitment by founding a university – Visva Bharati
- Visva Bharati: promoted an international culture of unity in diversity.
- Literary Contributions:-
- Poems: Manasi (The Ideal One,1890)
- Sonar Tari (The Golden Boat,1894)
- Gitanjali (Song Offerings,1910)
- Gitimalya (Wreath of Songs,1914)
- Balaka (The Flight of Cranes,1916)
- Plays: Raja (1910) [The King of the Dark Chamber],
- Dakghar (The Post Office,1912)
- Achalayatan (The Immovable,1912)
- Muktadhara (The Waterfall,1922)
- Raktakaravi (Red Oleanders,1926)
- Short stories and Novels:
- Gora (1910),
- Ghare-Baire (The Home and the World, 1916) and
- Yogayog (Crosscurrents, 1929)
- Poems: Manasi (The Ideal One,1890)
MUST READ: (Book Review – Gitanjali by Rabindranath Tagore)
SOURCE: THE HINDU
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) Who among the following is associated with ‘Songs from Prison’, a translation of ancient Indian religious lyrics in English? (2021)
- Bal Gangadhar Tilak
- Jawaharlal Nehru
- Mohandas Karamchand Gandhi
- Sarojini Naidu
Q.2) Who among the following was associated as Secretary with Hindu Female School which later came to be known as Bethune Female School? (2021)
- Annie Besant
- Debandranath Tagore
- Ishwar Chandra Vidyasagar
- Sarojini Naidu
Syllabus
- Prelims –Important Institutions
Context: Recently, the Enforcement Directorate conducted a search at gold-backed lender Manappuram Finance.
About Enforcement Directorate:-
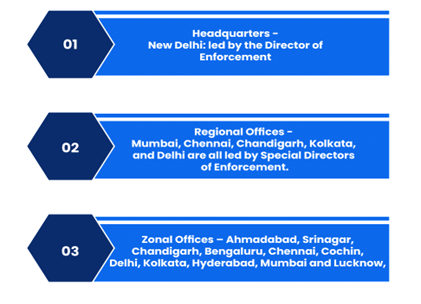
IMAGE SOURCE: Enforcement Directorate (ED) and its Functions – Enterslice
- The Enforcement Directorate is a multi-disciplinary organization founded in 1956.
- It is a law enforcement organization tasked with enforcing economic laws and combating economic crime in India, such as money laundering and foreign exchange irregularities.
- It works under the Department of Revenue, Ministry of Finance.
- Headquarters: New Delhi
- The functions of the Directorate include the enforcement of the following Acts:-
- The Prevention of Money Laundering Act, 2002 (PMLA) (UPSC PRELIMS: Prevention of Money Laundering Act (PMLA) 2002)
- The Foreign Exchange Management Act, 1999 (FEMA): A civil law under which ED conducts an investigation into suspected contraventions of foreign exchange laws and regulations. (UPSC PRELIMS: Foreign Exchange Management Act)
- The Foreign Exchange Regulation Act 1973
- Sponsoring Organizations under the 1974 Foreign Exchange Conservation and Smuggling Activity Prevention Act
- The Fugitive Economic Offenders Act, 2018 (FEOA): A law whereby the Directorate is mandated to attach the properties of the fugitive economic offenders who have escaped from India warranting arrest and providing for the confiscation of their properties to the Central Government. (UPSC CSE: Fugitive Economic Offenders)
- Director of Enforcement:-
- Appointed by the central government on the recommendation of a committee chaired by the Central Vigilance Commissioner and members comprising of Vigilance Commissioners, Home Secretary, Secretary DOPT and Revenue Secretary.
- Tenure: up to 5 years.
- Recruitment of other officers:-
- Other officers may be recruited directly from other investigative agencies or indirectly.
- It is made up of representatives from the police, excise, customs, and income tax departments of the Indian Revenue Services (IRS), the Indian Police Services (IPS), and the Indian Administrative Services (IAS).
MUST READ: CBI and ED
SOURCE: THE HINDU
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) Consider the following statements: (2022)
- In India, credit rating agencies are regulated by the Reserve Bank of India.
- The rating agency popularly known as ICRA is a public limited company.
- Brickwork Ratings is an Indian credit rating agency.
Which of the statements given above is correct?
- 1 and 2 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
Q.2) With reference to the ‘Banks Board Bureau (BBB)’, which of the following statements is correct? (2022)
- The Governor of RBI is the Chairman of BBB.
- BBB recommends the selection of heads for Public Sector Banks.
- BBB helps the Public Sector Banks develop strategies and capital raising plans.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
- 1 and 2 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
Syllabus
- Prelims –Important Institutions
Context: Recently, the Geological Survey of India (GSI) denied media reports claiming large lithium reserves being identified in Rajasthan.
About the Geological Survey of India (GSI):-
- The Geological Survey of India (GSI) is a scientific agency of India founded in 1851. (UPSC MAINS: Geological Survey of India )
- It works under the Ministry of Mines.
- Background: It was set up in 1851 primarily to find coal deposits for the Railways.
- It is one of the oldest organisations in the world and the second oldest survey in India after Survey of India. (UPSC PRELIMS: Survey of India)
- Objectives:-
- Conducting geological surveys and studies of India.
- Being the prime provider of basic earth science information to government, industry and the general public, as well as the official participant in steel, coal, metals, cement, power industries and international geoscientific forums.
- Functions: creation and updation of national geoscientific information and mineral resource assessment.
- Headquarters: Kolkata
- It has six regional offices located at Lucknow, Jaipur, Nagpur, Hyderabad, Shillong and Kolkata.
- Important events in the history of the Geological Survey of India:-
- 1821: First Geological Map of parts of India was of the Hyderabad region by Dr H. W. Voysey
- 1840: Museum of Geology established in Calcutta
- 1873: Ram Singh becomes the first Indian to join the Geological Survey of India (as an apprentice)
- 1911: Revised Geological Map of India in 1″= 32 Mile scale was published under H. H. Hayden
- 1921-33: E. H. Pascoe’s “Manual of Geology of India” published in four volumes
- 1951 M. S. Krishnan becomes the first Indian to be a Director of the Geological Survey of India
- 2001: GSI celebrated 150 years
Missions for GSI:-
- Mission I: Baseline Geoscience, Data Collection
- Ground and Marine Surveys
- Remote Sensing and Aerial Surveys
- Mission II: Natural Resource Assessment
- Natural Mineral Resource Assessment
- Natural Energy Mineral Resources
- Mission III: Geoinformatics
- Data Repository and Management, etc
- Publication and Information, Library
- Map, Geoinformatics and Data Integration
- Mission IV: Multidisciplinary Geosciences
- Geotechnical and Geohazards Management
- Climate Change and Eco-Systems, etc
- Fundamental Geosciences and Research
- Mission V: Training And Capacity Building
- Training And Capacity Building
MUST READ: Gold Reserve
SOURCE: THE ECONOMIC TIMES
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) With reference to India, consider the following statements: (2022)
- Monazite is a source of rare earth.
- Monazite contains thorium.
- Monazite occurs naturally in the entire Indian coastal sands in India.
- In India, Government bodies only can process or export monazite.
Which of the statements given above is correct?
- 1, 2 and 3 only
- 1, 2 and 4 only
- 3 and 4 only
- 1, 2, 3 and 4
Q.2) Consider the following minerals: (2020)
- Bentonite
- Chromite
- Kyanite
- Sillimanite
In India, which of the above is/are officially designated as major minerals?
- 1 and 2 only
- 4 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 2, 3 and 4 only
Syllabus
- Prelims –Environment and Ecology
Context: The United Nations Economic and Social Commission for Asia and the Pacific (ESCAP) recently published a new study on the rising challenges of extreme weather events and natural disasters.
About United Nations Economic and Social Commission for Asia and the Pacific (ESCAP):-

IMAGE SOURCE: About ESCAP | ESCAP (unescap.org)
- The Economic and Social Commission for Asia and the Pacific (ESCAP) is the most inclusive intergovernmental platform in the Asia-Pacific region.
- The United Nations Economic and Social Commission for Asia and the Pacific is the main legislative organ of ESCAP.
- It reports to the Economic and Social Council (ECOSOC) of the UN. (UPSC MAINS: Peacekeeping efforts of UN)
- It provides a forum for all governments of the region to review and discuss economic and social issues and to strengthen regional cooperation.
- The Commission meets annually at the ministerial level.
- It discusses and decides on important issues pertaining to inclusive and sustainable economic and social development in the region, to decide on the recommendations of its subsidiary bodies and of the Executive Secretary.
- It reviews and endorses the proposed strategic framework and programme of work, and makes any other decisions required, in conformity with its terms of reference.
- Members: It has 53 member States and 9 associate members.
- The Commission promotes cooperation in pursuit of solutions to sustainable development challenges.
- ESCAP is one of the five regional commissions of the United Nations. (UPSC MAINS: Reforms in the United Nations (UN))
- Functions:-
- It supports inclusive, resilient and sustainable development in the region by generating action-oriented knowledge.
- It provides technical assistance and capacity-building services in support of national development objectives, regional agreements and the implementation of the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development.
- It also provides support to partners at the national level.
MUST READ: United Nations Institute for Water, Environment and Health (UNU-INWEH)
SOURCE: DOWN TO EARTH
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) The “Common Carbon Metric” supported by UNEP, has been developed for (2021)
- Assessing the carbon footprint of building operations around the world
- Enabling commercial farming entities around the world to enter carbon emission trading
- Enabling governments to assess the overall carbon footprint caused by their countries
- Assessing the overall carbon footprint caused by the use of fossil fuels by the world in a unit of time
Q.2) “R2 Code of Practices” constitute a tool available for promoting the adoption of (2021)
- Environmentally responsible practices in the electronics recycling industry
- Ecological management of ‘’Wetlands of International Importance” under the Ramsar Convention
- Sustainable practices in the cultivation of agricultural crops in degraded lands
- ‘’Environmental Impact Assessment’’ in the exploitation of natural resources
Syllabus
- Prelims –Important Personalities
Context: Maharana Pratap Jayanti was celebrated recently.
About Maharana Pratap:-
- Maharana Pratap, was born in Kumbhalgarh, Rajasthan.
- He was the 13th King of Mewar and the eldest son of Udai Singh II.
- Maharana Udai Singh II: ruled the kingdom of Mewar, with his capital at Chittor.
- Udai Singh II was also a founder of the city of Udaipur (Rajasthan).
Important Events:-
Battle of Haldighati:
- The Battle of Haldighati was fought in 1576.
- It was between Rana Pratap Singh of Mewar and Raja Man Singh of Amber who was the general of the Mughal emperor Akbar. (UPSC PRELIMS: Akbar)
- Maharana Pratap fought a brave war but was defeated by Mughal forces.
- It is said that Maharana Pratap’s loyal horse named Chetak, gave up his life as the Maharana was leaving the battlefield.
- Reconquest:-
- After 1579, Pratap recovered Western Mewar including Kumbhalgarh, Udaipur and Gogunda.
- He also built a new capital, Chavand, near modern Dungarpur.
- He was succeeded by his son Amar Singh, who submitted in 1614 to Emperor Jahangir. (UPSC PRELIMS: Mughal paintings)
MUST READ: Eastern Rajasthan Canal Project (ERCP)
SOURCE: THE ECONOMIC TIMES
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) With reference to medieval India, which one of the following is the correct sequence in ascending order in terms of size? (2020)
- Paragana – Sarkar – Suba
- Sarkar – Paragana – Suba
- Suba – Sarkar – Paragana
- Paragana – Suba – Sarkar
Q.2) Who among the following Mughal Emperors shifted emphasis from illustrated manuscripts to the album and individual portraits? (2018)
- Humayun
- Akbar
- Jahangir
- Shah Jahan
Syllabus
- Prelims –Defence
Context: Indian Navy drones are keeping an eye on China-linked Coco Islands after a top Myanmar military official’s recent visit.
About Coco Islands:-
IMAGE SOURCE: Sri Lanka the heart of the Indian Ocean (heartofindianocean.blogspot.com)
- Coco Islands are a small group of islands located in the Bay of Bengal.
- They are part of the Yangon Region of Myanmar.
- Historical Background:-
- In the early 19th century, the British government in India established a penal colony in the Andaman for the convicts in the Indian subcontinent, and the Coco Islands were a source of food for it.
- The British government had reportedly leased out the islands to the Jadwet family of Burma.
- The leasing of control of the Coco Islands resulted in poor governance of the islands, which made the British government in India transfer its control to the government of Lower Burma in Rangoon.
- In 1882, the islands officially became part of British Burma. (UPSC MAINS: Political Crisis in Myanmar)
- The islands became a self-governing crown colony even after Burma was separated from British India in 1937.
- Great Coco Island, the largest in the group, lies just 55 km from India’s strategic Andaman and Nicobar Islands.
- Coco Islands are geologically an extended division of the Arakan Mountains or Rakhine Mountains.
- They submerge as a chain of islands in the Bay of Bengal for a long stretch and emerge again in the form of the Andaman and Nicobar Islands. (UPSC MAINS: Plate tectonics theory)
- They are part of the same topography as India’s Andaman & Nicobar Islands.
MUST READ: Andaman and Nicobar Gets Large Area Certification
SOURCE: INDIA TODAY
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) Consider the following pairs: (2022)
The region often mentioned in the news: Country
- Anatolia Turkey
- Amhara Ethiopia
- Cabo Delgado Spain
- Catalonia Italy
How many pairs given above are correctly matched?
- Only one pair
- Only two pairs
- Only three pairs
- All four pairs
Q.2) Consider the following pairs : (2018)
Regions sometimes mentioned in news Country
- Catalonia Spain
- Crimea Hungary
- Mindanao Philippines
- Oromia Nigeria
Which of the pairs given above are correctly matched?
- 1, 2 and 3
- 3 and 4 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 2 and 4 only
Syllabus
- Mains – GS 2 (Polity and Governance)
Context: Given the large migrant population in Karnataka, Lokniti-Centre for the Study of Developing Societies conducted a study among the migrant voters of Bengaluru to find out their voting patterns.
About Migrant Worker:
- A migrant worker is a person who migrates within a home country or outside it to pursue work.
- Migrant workers usually do not have the intention to stay permanently in the country or region in which they work.
- In India, Migrant workers usually refer to those who engage in internal migration within the country, often for the purpose of seeking employment.
- Internal migration refers to the movement of people from one place to another within the same country.
Internal migration in India:
- As per census 2011, the total number of internal migrants in India is 36 crore or 37% of the country’s population.
- The Economic Survey pegged the size of the migrant workforce at roughly 20 per cent or over 10 crore in 2016.
- Major origin states of internal migration: Uttar Pradesh, Bihar, Rajasthan, Madhya Pradesh, Jharkhand, and Odisha.
- Major destination states of internal migration: Maharashtra, Delhi, Gujarat, Tamil Nadu, Karnataka, and Punjab.
- Sectoral composition: The share of migrant workers is the highest in the construction sector for females while the highest number of male migrant workers are employed in public services (transport, postal, public administration services) and modern services (financial intermediation, real estate, renting, education, health).
About Remote Voting:
- Any method that enables voters to cast their ballots from locations other than the polling place designated for their registration address is referred to as remote voting.
- Both domestically and internationally may be used as the remote voting location. It includes both non-electronic and electronic voting processes.
- A “Committee of Officers on Domestic Migrants” was established by the Election Commission of India (ECI) earlier to handle this problem.
- A solution in the form of “remote voting” was proposed in the Committee’s 2016 report.
Migration and Remote Voting
- Migrant workers across India are often apprehensive about registering themselves as voters in any other State apart from their home State. This is due to various reasons such as
- frequent changes in residence,
- fear of losing property in their home State, and
- their inability or unwillingness to bring their families with them as well.
- The migrants often convey that the locality were not safe for women.
Remote Electronic Voting Machine:
Source: The Hindu
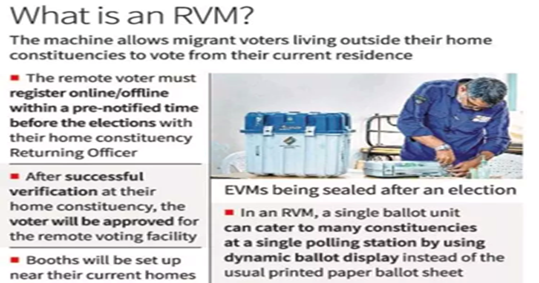
- Remote Electronic Voting Machine (RVM), allows domestic migrants to vote in national and regional elections.
- The EC proposed using this in a State Assembly election as a pilot so internal migrants within a state can cast their ballots.
Features of RVM:
- It is a standalone, non-networked system having the same security features as the existing Indian EVMs and provides the same voting experience to the voter as the EVM.
- The RVM system is essentially a modified version of the existing EVM system.
- A single Ballot Unit (BU) can cater to multiple AC/ PCs at a single polling station by using a dynamic ballot display instead of the usually printed paper ballot sheet on BU.
Significance of RVM:
- Increasing voters’ participation: It will enable a voter, who is listed in constituencies, to exercise voting rights from a single machine.
- Ease of Voting: Migrant voters need not travel to their home district to exercise their voting rights.
- Vibrant Democracy: It will enable approximately 30 crore electors, currently not exercising their franchise, to vote.
- Safety and Security: Remote e-voting machine will be a standalone device which doesn’t need connectivity to operate.
Concerns with RVM:
- Inclusive definition of migrants: Migrants are not a uniform and defined class, with fluid identities, locations and situations.
- Trust Issue: Various countries have already rejected EVMs for paper-based ballots.
- Hacking Probability: RVMs with more technological components are bound to raise further questions.
- Lack of Level Playing Field: Remote voting can theoretically provide an added edge to bigger parties and richer candidates who can campaign across the constituency and beyond.
- Model Code of Conduct: There is no clarity about how Model Code of Conduct will be implemented in the remote constituencies.
Way Forward:
Lakhs of migrants not only have they left their home States, they have also given up on significant rights. While elections are an opportunity for people to exercise their fundamental rights, the votes of migrant voters have been missing for years. While the ECI’s move provides a ray of hope to millions of migrant workers, two crucial priorities ahead are to create awareness about the initiative and ensure transparency.
Source: The Hindu
Syllabus
- Mains – GS 2 (Governance) and GS 3 (Economy)
Context: The ONDC (Open Network for Digital Commerce) is gradually challenging the dominance of Zomato and Swiggy by offering users cheaper prices for the same food items.
About ONDC Project:
Source: The Hindu
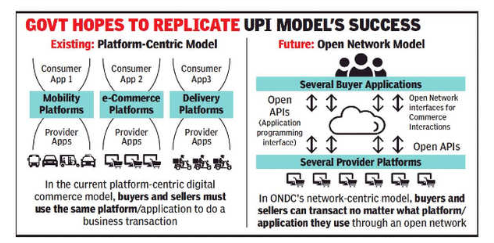
- Open Network for Digital Commerce (ONDC) is an initiative aiming at promoting open networks for all aspects of exchange of goods and services over digital or electronic networks.
- ONDC is to be based on open-sourced methodology, using open specifications and open network protocols independent of any specific platform.
- It is a non-profit initiative of the Department of Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade (DPIIT), Ministry of Commerce.
- Currently, grocery and food items merchants are mostly part of it, but beauty, fashion, personal care products, and electronics, among others, are gradually joining in
- Currently, there are partners like Paytm, Meesho, Magicpin, Mystore, Craftsvilla, and Spice Money, which act as online storefronts, allowing users to order food or any other product from a business listed on the ONDC platform.
Significance of ONDC:
- On ONDC, buyers and sellers may transact irrespective of the fact that they are attached to one specific e-commerce portal.
- This could give a huge booster shot to smaller online retailers and new entrants.
- However, if mandated, this could be problematic for larger e-commerce companies, which have their own processes and technology deployed for these segments of operations.
- ONDC is expected to digitise the entire value chain, standardise operations, promote inclusion of suppliers, derive efficiency in logistics and enhance value for consumers.
- The platform envisages equal-opportunity participation and is expected to make e-commerce more inclusive and accessible for consumers as they can potentially discover any seller, product or service by using any compatible application/platform, thus increasing their freedom of choice.
- It will enable transactions of any denomination, thus making ONDC a truly ‘open network for democratic commerce’.
- Over the next five years, the ONDC expects to bring on board 90 crore users and 12 lakh sellers on the network, enabling 730 crore additional purchases.
Challenges with ONDC:
- Threat to Local businesses in the long run: The local business will find it extremely challenging to compete with the discounts, sales and other lucrative offers, being offered by prominent e-commerce players which may result in local business being squeezed out of the network in the long run.
- Silent on liability for a bad product: The strategy paper is silent on the issues regarding liability on the network in case consumers faced issues regarding transactions, delivery of substandard products and service.
- No clarity on how existing laws will apply: There is also a lack of clarity on the applicability of the existing e-commerce laws to the network.
Indian e-commerce Industry:
- Growth: The Indian e-commerce industry has been on an upward growth trajectory. The Indian e-commerce market was estimated to be worth over $55 Bn in Gross Merchandise Value in 2021.
- By 2030, it is expected to have an annual gross merchandise value of $350 Bn.
- Factors of Growth: Fuelling e-commerce growth, India is expected to have over 907 million internet users by 2023, which accounts for ~64% of the total population of the country.
- The e-commerce industry in India is growing on levers such as increased smartphone penetration, increased affluence and low data prices, providing impetus for e-retail growth.
- India is the 2nd largest internet market in the world with ~62 billion UPI transactions in 2022.
- Electronics and apparel make up nearly 70 per cent of the e-commerce market, when evaluated against transaction value.
- Other new upcoming categories within e-commerce include ed-tech, hyperlocal and food-tech.
- Gaining Popularity in tier-2 and tier-3 cities: The e-commerce trend is gaining major popularity even in tier-2 and tier– 3 cities as they now make up nearly half of all shoppers and contribute three of every five orders for leading e-retail platforms.
- The average selling price (ASP) in tier-2 and smaller towns is only marginally lower than in tier-1/metro cities.
Way Forward:
ONDC must create consumer trust through robust mechanisms for ensuring redressal of grievances of consumers and enforcing transparent policies for returns, refunds and cancellations.
There needs to be a paradigm shift from an operator-driven monolithic platform-centric model to a facilitator-driven, interoperable decentralized network. The policies should be implemented at the network level.
Source: The Hindu
MUST READ: (UPSC CSE: E-Commerce)
Practice MCQs
Q.1) Consider the following statements regarding the United Nations Economic and Social Commission for Asia and the Pacific (ESCAP):
- It is the most inclusive intergovernmental platform in the Asia-Pacific region.
- It has 75 member States and 15 associate members.
- It reports to the Economic and Social Council (ECOSOC) of the United Nations.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 and 2 only
- 2 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 3 only
Q.2) Consider the following statements regarding the Geological Survey of India (GSI)”
- It is a scientific agency of India founded in 1851.
- It works under the Ministry of Earth Sciences.
- It headquartered in New Delhi
- It aims at creation and updation of national geoscientific information and mineral resource assessment.
Which of the above are correct?
- 1 and 2 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 3 and 4 only
- 1 and 4 only
Q.3) The functions of the Enforcement Directorate in India include the enforcement of the which of the following acts?
- The Prevention of Money Laundering Act, 2002
- The Foreign Exchange Management Act, 1999
- The Fugitive Economic Offenders Act, 2018
- The Conservation of Foreign Exchange and Prevention of Smuggling Activities Act or COFEPOSA 1974
select the correct using the code given below:
- 1 2 and 3 only
- 1 2 and 4 only
- 2 3 and 4 only
- 1 2 3 and 4
Comment the answers to the above questions in the comment section below!!
ANSWERS FOR ’ 10th May 2023 – Daily Practice MCQs’ will be updated along with tomorrow’s Daily Current Affairs.st
ANSWERS FOR 9th May – Daily Practice MCQs
Q.1) – b
Q.2) – d
Q.3) – c











