IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
Archives
(PRELIMS & MAINS Focus)
Syllabus
- Prelims –Economy
Context: Recent reports suggest that India’s future Lines of Credit (LoCs) to Africa could focus on defence exports to meet the requirements of the continent.
About Lines of Credit (LoCs):-
IMAGE SOURCE: INVESTOPEDIA
- It is a credit facility extended by a bank or any other financial institution that enables the customer to draw the maximum loan amount.
- Lender: it can be given by a bank or any other financial institution.
- Borrower: it can be given to a government, business or individual customer.
- Time limit: the set borrowing limit can be tapped into at any time.
- Transaction Limit: the borrower can take money out until the maximum limit is reached.
- Usage in international relations: it is a soft loan provided on concessional interest rates to developing countries.
- It is not a grant and has to be repaid by the borrowing government.
- Types of credit lines: personal, business, and home equity, among others.
- Advantages: it has built-in flexibility, which is its main advantage.
- Borrowers can request a certain amount, but they do not have to use it all.
- They can tailor their spending from the LOC to their needs.
- They owe interest only on the amount that they draw, not on the entire credit line.
- Disadvantages: high-interest rates, penalties for late payments, and the potential to overspend.
India-Africa Relations:-
IMAGE SOURCE: YourStory
Historical Ties
- India’s trade relations with Africa date back several centuries. (UPSC CSE: India-Africa: Challenges & Way Ahead)
- The presence of Indians in East Africa is documented in the ‘Periplus of the Erythraean Sea’ or Guidebook of the Red Sea by an ancient Greek author written in 60 AD.
- Mahatma Gandhi: he began his political career in South Africa. (UPSC CSE: India and Mahatma Gandhi)
- Non-Alignment Movement (NAM): India was a forerunner as a champion of the interests of the developing countries from Africa among other third-world countries. (UPSC CSE: NAM)
Importance of Africa
- Africa is home to over half a dozen of the fastest-growing countries in the world.
- African continent has a population of over one billion with a combined GDP of 2.5 trillion dollars making it a huge potential market.
- Africa is a resource-rich nation dominated by commodities like crude oil, gas, pulses and lentils, leather, gold and other metals, all of which India lack in sufficient quantities.
- India is seeking diversification of its oil supplies away from the Middle East and Africa can play an important role in India’s energy matrix.
India’s Initiatives in Africa
- India Africa Forum Summit ) is the official platform for African-Indian relations.
- It was launched in 2008.
- India is investing in capacity building providing more than $1 billion in technical assistance and training to personnel under the Indian Technical and Economic Cooperation (ITEC) program.
- ITEC: is the leading capacity-building platform of the Ministry Of External Affairs.
- Instituted in 1964.
- Have trained more than 200,000 officials from 160+ countries in both the civilian and the defence sectors.
- India has invested $100 million in the Pan-African E-Network.
- Objective: to bridge the digital divide in Africa, leveraging its strengths in information technology.
- Indian military academies offer training to military officers from a number of African states.
- Asian Africa Growth Corridor: jointly prepared by Indian and Japanese think tanks.
- The corridor will focus on Developing Cooperation Projects, Quality Infrastructure and Institutional Connectivity, skill enhancement, and People-to-People Partnerships.
MUST READ: Credit in the Economy
SOURCE: THE ECONOMIC TIMES
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) “Rapid Financing Instrument” and “Rapid Credit Facility” are related to the provisions of lending by which of the following: (2022)
- Asian Development Bank
- International Monetary Fund
- United Nations Environment Programme Finance Initiative
- World Bank
Q.2) With reference to the “G20 Common Framework”, consider the following statements: (2022)
- It is an initiative endorsed by the G20 together with the Paris Club.
- It is an initiative to support Low-Income Countries with unsustainable debt.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Syllabus
- Prelims –Geography
Context: Heavy to extremely heavy rainfall was predicted over Kutch, north Gujarat, and south Rajasthan regions recently as Cyclone Biparjoy moved northeastwards.
About Cyclonic Storm Biparjoy:-
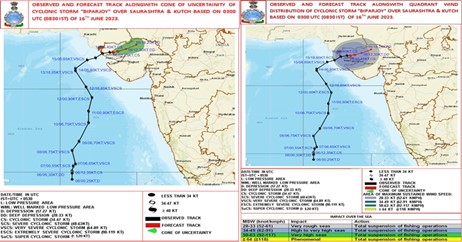
IMAGE SOURCE: AIR
- A deep depression over the southeast Arabian Sea intensified into a cyclonic storm Biparjoy.
- Origin: southeast Arabian Sea
- Naming: Bangladesh gave a tropical cyclone the name “Biparjoy,” which is Bengali for “calamity” or “disaster. (UPSC CSE: Naming of Cyclone)
- Cyclone: a low-pressure system that forms over warm waters.
- Usually, a high temperature anywhere means the existence of low-pressure air, and a low temperature means high-pressure wind.
Frequency of Cyclones in the Arabian Sea
- Frequency: It has fewer cyclones compared to the Bay of Bengal.
- This is because the Bay of Bengal is warmer.
- Favorable Month: June
- Factors Influencing Cyclone Formation: Cyclones form due to low-pressure systems over warm waters.
- The Arabian Sea is getting warmer due to climate change, leading to an increase in cyclones. (UPSC CSE: More cyclones in the Arabian Sea)
Tropical Cyclones
- Intense circular storm over warm oceans with low pressure.
- It brings high winds and heavy rain.
- Conditions for formation: Warm sea surface temperatures, anticlockwise rotation of low-level air, favourable atmospheric conditions.
Tropical Cyclones in India:-
- Origin: Tropical cyclones striking India generally originate in the Bay of Bengal.
- Frequency: Cyclones occur in the months of May–June and October–November.
MUST READ: Cyclones forecast
SOURCE: AIR
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) Consider the following statements: (2022)
- High clouds primarily reflect solar radiation and cool the surface of the Earth.
- Low clouds have a high absorption of infrared radiation emanating from the Earth’s surface and thus cause a warming effect.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Q.2) In the northern hemisphere, the longest day of the year normally occurs in the: (2022)
- First half of the month of June
- The second half of the month of June
- The first half of the month of July
- The second half of the month of July
Syllabus
- Prelims –
Context: Recently, the Central Board of Indirect Taxes and Customs (CBIC) released the National Time Release Study (NTRS) 2023 report.
About National Time Release Study (NTRS) 2023 report:-

IMAGE SOURCE: PIB
- The National Time Release Study (NTRS) is a performance measurement tool.
- Published by: Central Board of Indirect Taxes and Customs (CBIC).
- Time period: NTRS 2023 report analyzed data collected during the sample period from January 1 to 7, 2023.
- It serves as an essential tool for assessing the efficiency and effectiveness of customs procedures and regulations related to cargo clearance.
Objectives:-
- Assessing progress towards the targets set in the National Trade Facilitation Action Plan.
- Evaluating the impact of trade facilitative initiatives.
- Identifying challenges hindering the reduction of release time.
- Providing a quantitative measure of cargo release time.
- Presenting port-category-wise average release time for a given year.
Key Findings of NTRS 2023 report:-
- According to the report the average import release time by customs authorities has decreased in 2023 compared to 2022.
- The import release time has declined by 20% for inland container depots (ICDs), 11% for air cargo complexes (ACCs), and 9% for seaports.
- In absolute terms, the import release time for seaports is 85.42 hours, for ICDs is 71.46 hours, for ACCs is 44.16 hours, and for integrated check posts (ICPs) is 31.47 hours.
Central Board of Indirect Taxes and Customs (CBIC)
- The Central Board of Excise and Customs (CBEC) was renamed as the Central Board of Indirect Taxes and Customs (CBIC).
- This renaming happened in 2018 after the roll-out of Goods and Services Tax (GST).
- It is a statutory board under the Central Boards of Revenue Act, 1963 (54 of 1963).
- Ministry: Department of Revenue, Ministry of Finance.
- Composition: Chairman and 6 members in addition to the Chairman.
Functions:-
- It deals with the tasks of formulation of policy concerning levy and collection of customs, central excise duties, Central Goods & Services Tax (CGST) and Integrated GST (IGST). (UPSC CSE: GST)
- The Board is the administrative authority for its subordinate organizations.
- These include Custom Houses, Central Goods and Services Commissionerates and the Central Revenues Control Laboratory.
- It has been actively working towards reducing release time by customs for both imports and exports in order.
- Promote ease of doing business and enhance tax collections. (UPSC CSE: Tax-GDP ratio)
MUST READ: International Customs Day, 2023
SOURCE: PIB
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) Which one of the following situations best reflects “Indirect Transfers” often talked about in media recently with reference to India? (2022)
- An Indian company investing in a foreign enterprise and paying taxes to the foreign country on the profits arising out of its investment
- A foreign company investing in India and paying taxes to the country of its base on the profits arising out of its investment
- An Indian company purchases tangible assets in a foreign country and sells such assets after their value increases and transfers the proceeds to India
- A foreign company transfers shares and such shares derive their substantial value from assets located in India
Q.2) Consider the following statements: (2022)
- Tight monetary policy of the US Federal Reserve could lead to capital flight.
- Capital flight may increase the interest cost of firms with existing External Commercial Borrowings (ECBs).
- Devaluation of domestic currency decreases the currency risk associated with ECBS.
Which of the statements given above is correct?
- 1 and 2 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
Syllabus
- Prelims –Science and Technology
Context: Recently, NASA’s Cassini spacecraft discovered ‘phosphorous’, a key element for life, on Saturn’s moon Enceladus.
About Enceladus:-
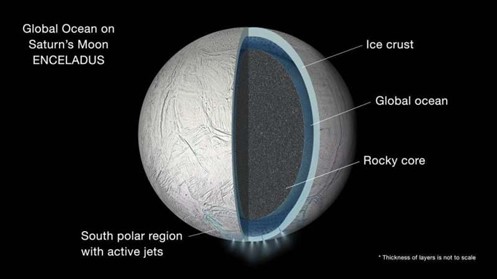
IMAGE SOURCE: phys.org
- Enceladus is the sixth-largest moon of Saturn.
- Discovery: it was discovered in 1789, by the English astronomer William Herschel.
- Origin of the name: it was named for one of the Giants (Gigantes) of Greek mythology.
- Surface features: ranging from old, heavily cratered regions to young, tectonically deformed terrains.
- It is mostly covered by fresh, clean ice, making it one of the most reflective bodies of the Solar System.
- It is the second nearest to the major regular.
- It is the brightest of all moons of Saturn. (UPSC CSE: Methane in the Moons of Saturn)
- It is an active moon that hides a global ocean of liquid salty water beneath its crust. (UPSC CSE: UAE’s Hope Mission)
Major Revelations:-
- 2005: the Cassini spacecraft discovered water-rich plumes venting from the south polar region.
- According to NASA scientists, the plumes are similar in composition to comets.
- 2014: NASA reported that Cassini found evidence for a large south-polar subsurface ocean of liquid water.
- It had a thickness of around 10 km.
- 2021: astronomers reported detecting substantial amounts of methane.
- It could be a possible sign of microbial life, on Enceladus.
Cassini spacecraft
- Launched in 1997 (UPSC CSE: Jupiter and Saturn to be seen in Great Conjunction)
- Launched by: National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA)
- It is an independent agency of the U.S. federal government responsible for the civil space program, aeronautics research, and space research.
- Time Period of mission: It orbited Saturn from 2004 to 2017, circling the planet 294 times.
- It measured the structure of Saturn’s atmosphere and rings, as well as how they interact with the planet’s moons.
- It also discovered six named moons and revealed Enceladus and Titan as promising locations to search for extraterrestrial life.
- Titan: Saturn’s largest moon.
- It is the only moon in the solar system with a substantial atmosphere.
MUST READ: Gaganyaan
SOURCE: HINDUSTAN TIMES
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) The experiment will employ a trio of spacecraft flying in formation in the shape of an equilateral triangle that has sides one million kilometres long, with lasers shining between the craft.” The experiment in question refers to (2020)
- Voyager-2
- New Horizons
- LISA Pathfinder
- Evolved LISA
Q.2) Recently, scientists observed the merger of giant ‘black holes’ billions of light-years away from the Earth. What is the significance of this observation? (2019)
- ‘Higgs boson particles’ were detected.
- ‘Gravitational waves’ were detected.
- Possibility of intergalactic space travel through a ‘wormhole’ was confirmed.
- It enabled the scientists to understand ‘singularity’.
Syllabus
- Prelims –International Relations
Context: The Bay of Bengal Initiative for Multi-Sectoral Technical and Economic Cooperation (BIMSTEC) summit end of this year will adopt a Bangkok Vision 2030 as announced by the Ministry of External Affairs (MEA)recently.
About Bangkok Vision 2030:-
- The Bangkok Vision 2030 was proposed by Thailand.
- Objective: to propel BIMSTEC towards a prosperous, resilient, and open region, fostering sustainable and balanced growth. (UPSC CSE: BIMSTEC)
- Vision: to advance BIMSTEC as a prosperous, resilient, and open region.
- It emphasizes sustainable and balanced growth, adapting to rapid changes in regional and global architecture.
- It aims to further promote BIMSTEC as a region of peace, stability, and economic sustainability.
- The goals are in line with the United Nations’ Sustainable Development Goals and Thailand’s bio-circular-green economic model.
Bay of Bengal Initiative for Multi-Sectoral Technical and Economic Cooperation (BIMSTEC) summit

IMAGE SOURCE: southasiamonitor.org
- It is a regional organization.
- Objective: Creating an enabling environment for the rapid economic development of the sub-region.
- Established: 1997, by the signing of the Bangkok Declaration.
- Member countries: Bangladesh, India, Myanmar, Sri Lanka, Thailand, Bhutan and Nepal.
- Initially, it was formed with four Member States with the acronym ‘BIST-EC’ (Bangladesh, India, Sri Lanka and Thailand Economic Cooperation).
- It became renamed ‘BIMST-EC’ in 1997, following the inclusion of Myanmar.
- With the admission of Nepal and Bhutan in 2004, the name of the grouping was changed to ‘Bay of Bengal Initiative for Multi-Sectoral Technical and Economic Cooperation’ (BIMSTEC).
- Chairmanship of BIMSTEC: rotates according to the alphabetical order of the English names of the Member States.
- Current chair: Thailand.
- Secretariat: Dhaka, Bangladesh.
- It was established during the third BIMSTEC Summit(2014).
MUST READ: BIMSTEC after the Colombo summit
SOURCE: THE HINDU
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) Consider the following pairs: (2020)
International agreement/ set-up Subject
- Alma-Ata Declaration – Healthcare of the people
- Hague Convention – Biological and Chemical Weapons
- Talanoa Dialogue – Global Climate Change
- Under2 Coalition – Child Rights
Which of the pairs given above is/are correctly matched?
- 1 and 2 only
- 4 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 2,3 and 4 only
Q.2) In which one of the following groups are all four countries members of G20? (2020)
- Argentina Mexico, South Africa and Turkey.
- Australia Canada, Malaysia and New Zealand
- Brazil, Iran, Saudi Arabia and Vietnam
- Indonesia Japan Singapore and South Korea
Syllabus
- Prelims –International Relations
Context: Recent reports from the International Energy Agency (IEA) show that India and China bought 80% of Russia’s oil.
About International Energy Agency (IEA):-
IMAGE SOURCE: crudeoilpeak.info
- It is an autonomous Intergovernmental Organisation. (UPSC CSE: IEA)
- Established: in 1974
- HQ: Paris, France.
- Historical Background: it was established in the wake of the oil crisis of 1973-1974, to help its members respond to major disruptions in oil supply.
- Objective: it ensures reliable, affordable and clean energy for its member countries and beyond.
- It focuses on its energy policies which include economic development, energy security and environmental protection.
IEA’s Membership:-
- It has 31 member countries.
- It also includes eight association countries.
Eligibility Criteria:-
- A candidate country to the IEA must be a member country of the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD).
- OECD: an international organisation, founded in 1961 to stimulate economic progress and world trade.
- A candidate country to the IEA must have:
- Crude oil and/or product reserves (Strategic Oil Reserves) equivalent to 90 days of the previous year’s net imports.
- The government must have immediate access (even if it does not own them directly) to use them to address disruptions to the global oil supply.
Major Reports:-
- World Energy Outlook Report.
- World Energy Investment Report.
- World Energy Statistics.
- World Energy Balances.
- Energy Technology Perspectives.
- India Energy Outlook Report.
India and IEA
- 2017: India became an Associate member of IEA.
- 2021: India also inked a Strategic Partnership Agreement with the IEA.
- It aimed to strengthen cooperation in global energy security, stability and sustainability.
- IEA invited India to become a full Member.
Reason for Offering Membership to India:-
- India is becoming increasingly influential in global energy trends.
- Its in-depth report on India’s energy policies, which was released in January 2020, states that the country’s demand for energy is set to grow rapidly in the coming decades.
- The country’s reliance on fuel imports makes further improving energy security a key priority for the Indian economy.
MUST READ: The Breakthrough Agenda Report 2022
SOURCE: THE INDIAN EXPRESS
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) The term ‘West Taxes Intermediate’, sometimes found in news to a grade of (2020)
- Crude oil
- Bullion
- Rare earth elements
- Uranium
Q.2) Which of the following adopted a law on data protection and privacy for its citizens known as the ‘General Data Protection Regulation’ in April 2016 and started implementation of its form
25th May 2018? (2019)
- Australia
- Canada
- The European Union
- The United States of America
Syllabus
- Prelims –Governance
Context: Recently, the Government launched the Vaishvik Bhartiya Vaigyanik (VAIBHAV) fellowship programme.
About Vaishvik Bhartiya Vaigyanik (VAIBHAV) fellowship programme:-
- This fellowship programme is to foster collaboration and knowledge-sharing between the Indian diaspora scientists and academic institutions in India.
- Starting date: 15th June 2023
- Implementing Agency: Department of Science and Technology (DST), Ministry of Science and Technology.
- Objective: to connect the Indian STEMM (Science, Technology, Engineering, Math and Medicine) diaspora with Indian academic and R&D institutions for collaborative research work leading to sharing of knowledge, wisdom, and best practices in the frontier areas of science & technology.
Implementation:-
- Under this program, 75 selected fellows would be invited to work in 18 identified knowledge verticals.
- 18 verticals include quantum technology, health, pharma, electronics, agriculture, energy, computer sciences, and material sciences amongst others.
Eligibility:–
- The applicant should be a Non-Resident Indian (NRI), Person of Indian Origin (PIO) and Overseas Citizen of India (OCI), currently living abroad.
- The applicant must have obtained a Ph.D/M.D/M.S degree from a recognized University.
- Applicant must be a researcher engaged in an overseas academic / research / industrial organization with a proven track record of research & development working in the top 500 QS World University Ranking.
- Eligibility(for Institutions): Higher Educational Institutions / Universities ranked in the top 200 in NIRF overall rankings and have NAAC ‘A’ grades (3.0 and above) and scientific institutes.
Funding:-
- Fellowship would include a fellowship grant (INR 4,00,000 per month), international and domestic travel, accommodation and contingencies.
SOURCE: PIB
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) Atal Innovation Mission is set up under the (2019)
- Department of Science and Technology
- Ministry of Labour and Employment
- NITI Aayog
- Ministry of Skill Development and Entrepreneurship
Q.2) Which of the following is/are the aim/aims of the “Digital India” Plan of the Government of India? (2018)
- Formation of India’s own Internet companies like China did.
- Establish a policy framework to encourage overseas multinational corporations that collect Big Data to build their large data centres within our national geographical boundaries.
- Connect many of our villages to the Internet and bring Wi-Fi to many of our schools, public places and major tourist centres.
Select the correct answer using the code given below :
- 1 and 2 only
- 3 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
Syllabus
- Mains – GS 2 (Polity and Governance)
Context: The Law Commission recently decided to solicit views from the public on the idea of a uniform civil code.
About Uniform Civil Code(UCC):
- The UCC refers to a common set of laws governing personal matters such as marriage, divorce, adoption, inheritance and succession for all citizens, irrespective of religion.
- Article 44: This Article of the Constitution makes a reference to a UCC and says, “The State shall endeavour to secure for the citizens a uniform civil code throughout the territory of India.”
- This is in the chapter dealing with the Directive Principles of State Policy and is therefore presumed to be advisory in nature.
- Article 37: States that the vision of a Uniform Civil Code (along with other directive principles) is enshrined in the Indian Constitution as a goal towards which the nation should strive, but it isn’t a fundamental right or a Constitutional guarantee.
- One can’t approach the court to demand a UCC. But that doesn’t mean courts can’t opine on the matter.
Significance and need of UCC:
- Uniform Principles: Common Code would enable uniform principles to be applied in respect of aspects such as marriage, divorce, succession etc. so that settled principles, safeguards and procedures can be laid down and citizens are not made to struggle due to the conflicts and contradictions in various personal laws.
- Promotion of secularism: One set of laws to govern the personal matters of all citizens irrespective of religion is the cornerstone of true secularism.
- It would help end gender discrimination on religious grounds and strengthen the secular fabric of the nation.
- Protection of Vulnerable and Women’s Rights: It will protect the vulnerable sections of society.
- Women have been denied via personal laws in the name of socio-cultural-religious traditions.
- Therefore UCC could bring all communities together to ensure Women the Right to a dignified life and control over their life as well as body.
- Reduced Discord: if and when the whole population will start following the same laws, chances are there that it would bring more peace in the living and reduce riots.
- Hence, Religious harmony will be created for peaceful living in the country
- Prevents religion-based discrimination: Personal laws differentiate between people on grounds of religion. A unified law having the same provisions regarding marital affairs would provide justice to those who feel discriminated against.
- Ending unjust customs and traditions: A rational common and unified personal law will help eradicate many evil, unjust and irrational customs and traditions prevalent across the communities.
- For example, Law against Manual scavenging. It might have been a custom in the past but in a mature democracy like India, this custom cannot be justified.
- National integration: A common civil code will help the cause of national integration by removing disparate loyalties to laws that have conflicting ideologies.
- Best Practice: While delivering a judgment legitimising the Portuguese Civil Code of 1867, the Supreme Court reportedly described Goa as a “shining example” with a Uniform Civil Code.
- Remove vote bank politics: Opting the UCC will remove the religious nexus of the Political system in which voters are divided on the basis of religion, caste etc.
- Eases Administration: UCC would make it easy to administer the huge population base of India.
- Global practice of UCC: Almost all Muslim nations like Morocco, Pakistan etc. have been following the UCC.
Arguments Against UCC:
- Hampering diversity and multiculturalism: Indian society has a unique identity in the form of being diverse and multicultural, and unified law might do away with these unique characteristics of this nation.
- Violation of fundamental rights: Religious bodies oppose a uniform civil code on the ground that it would be interference in religious affairs which would violate fundamental rights guaranteed under Article 25 of the constitution.
- May lead to communal unrest: It would be a tyranny to the minority and when implemented could bring a lot of unrest in the country.
- The All India Muslim Personal Law Board stated that the laws pertaining to marriage and inheritance were part of religious injunctions for ages.
Constitution of the 22nd Law Commission: The Commission is headed by former Karnataka High Court Chief Justice Rituraj Awasthi.
Functions:
- The Commission, among other things, shall “identify laws which are no longer needed or relevant and can be immediately repealed; examine the existing laws in the light of Directive Principles of State Policy and suggest ways of improvement and reform.
- suggest such legislations as might be necessary to implement the Directive Principles and to attain the objectives set out in the Preamble of the Constitution”; and “revise the Central Acts of general importance so as to simplify them and remove anomalies, ambiguities and inequities”.
- The Commission is also looking into several significant issues like
- Implementation of a Uniform Civil Code (UCC).
- Holding of simultaneous elections.
- The 22nd Commission has claimed that years have elapsed since similar views were sought by the previous panel on UCC, and that a fresh effort was needed to garner varied opinions.
- According to critics, the Law Commission’s decision to solicit views from the public on the idea of a uniform civil code appears to be a political initiative aimed at bringing the potentially divisive issue under focus.
Way Forward:
The goal of a UCC should ideally be reached in piecemeal manner, like the recent amendment on the age of marriage. Government need to balance the aims of the Constitution dealing with the aspects of valuing and preserving the rich heritage of composite culture and renouncing practices that are derogatory to the dignity of people especially women.
Source: The Hindu
Syllabus
- Mains – GS 3 (Economy)
Context: Recently, the World Bank released its latest Migration and Development Brief.
About Remittance:
- It denotes a sum of money sent by one party to another. These days, the term describes the money sent by someone working abroad to their family back home.
- In the case of India, the largest sources of remittances have been from Indians working in the Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC) countries (UAE, Bahrain, Saudi Arabia, Oman, Qatar, Kuwait), and the U.S./U.K.
Major Highlights:
- The remittance flows are expected to reach $840 billion in 2023 for the world.
- In 2024, the remittances growth rate globally is projected to increase to 0% in 2024, increasing inflows by $18 billion.
- Region Wise: The growth of remittances is likely to be the highest in Latin America and the Caribbean (forecast of 3.3%), as the labour market in the US continues to be strong.
- Remittance growth is expected to be the lowest in South Asia (0.3%), mainly because of the high base in 2022 along with slowing demand for highly skilled IT workers in the US and Europe.
- Remittance flows to the six South Asian countries will also be limited by demand for migrants in the GCC countries where declining oil prices are expected to slow growth from 5.3% in 2022 to 3% in 2023.
- Remittance flows to low- and middle-income countries (LMICs) are expected to moderate to 1.4% in 2023, resulting in total inflows of $656 billion.
- The top sources of remittances for India: Almost 36% of India’s remittances are from the high-skilled and largely high-tech Indian migrants in three high-income destinations — the US, the United Kingdom, and Singapore.
- The post-pandemic recovery led to a tight labour market in these regions, and wage hikes boosted remittances.
Significance of Remittances:
- In the aftermath of the Covid-19 pandemic, remittances are being viewed as a critical financial inflow, and an important source of foreign exchange for several countries including those in South Asia.
- Remittances are highly complementary to government cash transfers and essential to households during times of need.
- Remittances have become a financial lifeline in many economies through the pandemic and will become even more so in the foreseeable future.
Challenges:
- Slower growth in OECD economies — especially in the high-tech sector in the United States that could affect the demand for information technology (IT) workers and lead to a diversion of formal remittances toward informal money transfer channels — is likely to impact the flow of remittances this year.
- Slowing demand for migrants in the GCC countries and weak balance-of-payments conditions and exchange controls are expected to divert remittances to informal money transfer channels in Pakistan, Bangladesh, and Sri Lanka.
- The projected decline in GDP growth from 2.8% in 2022 to approximately 1.0% in 2023 and 2024 will erode many of the employment and income gains that East Asia’s high-skilled migrants reaped in 2022, dampening remittance flows to the region in 2023.
- Lower fuel prices in 2023 will further dampen demand for migrants in the GCC countries, reducing remittance flows to East Asia and the Pacific Islands.
- In Europe and Central Asia, the growth in remittances is expected to fall to 1% due to a high base effect, lingering weakness in flows to Ukraine and Russia, and a weaker Russian Ruble against the US dollar.
Suggestive measures:
- Recognize the complexity and the increasing necessity of cross-border movements.
- Distinguish between various types of movements to identify appropriate policy responses.
- Maximize net gains when people bring skills and attributes that strongly match the needs of their destination society—for them, their countries of destination, and their countries of origin.
- Provide international protection to refuges in a manner that can be sustained, financially and socially—because most refugee situations last many years.
- There is a pressing need to improve relevant data collection systems.
- India can attract more NRI money with modern fintech tools such as the UPI linkages which prove faster and cheaper than the traditional money transfer systems such as the SWIFT.
Source: Indian Express
Practice MCQs
Q1) Consider the following regarding, International Energy Agency (IEA):
- India became an associate member of IEA in 2020.
- It was established in 1974.
- Its Headquarters are in Montreal, Canada.
Select the correct answer using the code given below
- 1 and 2 only
- 2 only
- 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
Q2) Consider the following regarding, Vaishvik Bhartiya Vaigyanik (VAIBHAV) fellowships programme.
- The fellowship would include a fellowship grant (INR 4,00,000 per month).
- It is under the Ministry of Education.
- It is a collaboration of Indian diaspora scientists and academic institutions in India.
Select the correct answer using the code given below
- 1 and 3 only
- 2 only
- 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
Q3) Consider the following regarding, Enceladus:
- It is the moon of Jupiter.
- It was discovered by the Juno mission.
- It was named for one of the Giants (Gigantes) of Greek mythology.
Select the correct answer using the code given below
- 1 and 2 only
- 2 only
- 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
Comment the answers to the above questions in the comment section below!!
ANSWERS FOR ’ 17th June 2023 – Daily Practice MCQs’ will be updated along with tomorrow’s Daily Current Affairs.st
ANSWERS FOR 16th June – Daily Practice MCQs
Q.1) – d
Q.2) – a
Q.3) -c











