IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
Archives
(PRELIMS & MAINS Focus)
Syllabus
- Prelims – Science and Technology
Context: Recently, a workshop to educate people about Sickle Cell Anaemia Disease was held in New Delhi.
About Sickle Cell Anaemia Disease:-
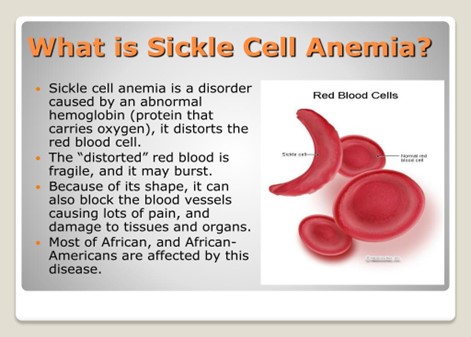
IMAGE SOURCE: SlideServe
- Discovery: in 1910 by James Herrick.
- Sickle cell anaemia is a group of inherited disorders known as sickle cell disease.(UPSC CSE: Rare Diseases)
- It affects the shape of red blood cells.
- Red blood cells: contain haemoglobin, which carries oxygen to all parts of the body.
- Cause: It is transmitted by parents carrying a defective ‘beta globin’ gene.
- Disease condition: under normal conditions, the red blood cells being round and flexible move easily through blood vessels.
- However, in sickle cell anaemia, some of the red blood cells acquire the shape of sickles or crescent moons.
- These sickle cells become rigid and sticky.
- When they travel through small blood vessels, they get stuck and clog the blood flow.
- This can cause pain and other serious health problems such as infection, acute chest syndrome and stroke. . (UPSC CSE: Polio Disease)
- The sickle cells also die early, which causes a constant shortage of red blood cells.
Symptoms:-
- Chronic Anaemia: leading to fatigue, weakness, and paleness.
- Painful episodes (also known as sickle cell crisis): these can cause sudden and intense pain in the bones, chest, back, arms, and legs.
- Delayed growth and puberty.
Mortality rate:-
- Mortality rate refers to the percentage of people with a condition who died within a certain period.
- Sickle cell disease mortality burden is highest in children.
- However, the mortality rate of SCA for children has dropped dramatically over the last few decades.
- A 1975 study indicated a mortality rate of 9.3 per cent for people with SCA under the age of 23.
- However, by 1989, the mortality rate for people with SCA under the age of 20 dropped to 2.6 per cent.
Treatment:-
- Blood Transfusions: These can help relieve anaemia and reduce the risk of pain crises.
- Hydroxyurea: This is a medication that can help reduce the frequency of painful episodes and prevent some of the long-term complications of the disease.
- It can also be treated by bone marrow or stem cell transplantation.
- Bone marrow transplant: a medical treatment that replaces the bone marrow with healthy cells.
- It can be used to treat certain types of cancer, such as leukaemia, myeloma, and lymphoma, and other blood and immune system diseases that affect the bone marrow.
Government initiatives:-
- Ministry of Tribal Affairs: launched a portal wherein people can register themselves, in order to collate all information related to SCA among tribal groups.
- National Health Mission guideline on Hemoglobinopathies: it also identifies “establishing services at the community level for pre-marital and pre-conception screening backed by genetic counselling services” as a strategy for addressing SCA.
- Government released technical operational guidelines: for the prevention and control of hemoglobinopathies in 2016 including sickle cell anaemia.
- Integrated centres: have been established in 22 tribal districts for treatment and diagnosis.
- State Haemoglobinopathy Mission: established in Madhya Pradesh to address the challenges in screening and management of the disease.
- Union Budget 2023-24: the government has announced a mission to eliminate Sickle cell Anemia by 2047.
- Under this universal screening of seven crore people in the age group of 0-40 years in affected tribal areas would be done through collaborative efforts of central ministries and state governments.
MUST READ: Disease Surveillance System
SOURCE: AIR
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) In the context of hereditary diseases, consider the following statements: (2021)
- Passing on mitochondrial diseases from parent to child can be prevented by mitochondrial replacement therapy either before or after in vitro fertilization of the egg.
- A child inherits mitochondrial diseases entirely from the mother and not from the father.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Q.2) Consider the following statements:
- Adenoviruses have single-stranded DNA genomes whereas retroviruses have double-stranded DNA genomes.
- Common cold is sometimes caused by an adenovirus whereas AIDS is caused by a retrovirus.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Syllabus
- Prelims –Science and Technology
Context: Recently, the Drugs Technical Advisory Board (DTAB), recommended banning the manufacture, sale and distribution of Ketoprofen and Aceclofenac.
About Aceclofenac:-
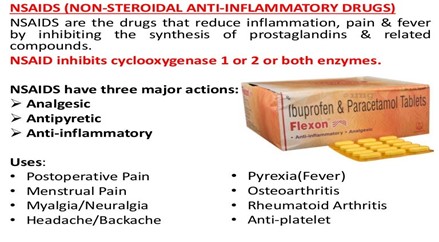
IMAGE SOURCE: SlideShare
- Aceclofenac is an oral non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID).
- NSAID: medications used for reducing pain (analgesic), decreasing fever (antipyretic), preventing blood clots (anti-thrombotic) and decreasing inflammation (anti-inflammatory).
- Uses: to treat non-inflammatory conditions such as migraine, period pain and postoperative pain, and to reduce fever.
- Common NSAIDs: aspirin (such as Disprin), ibuprofen (such as Nurofen) , naproxen (such as Naprosyn), diclofenac (such as Voltaren), celecoxib (such as Celebrex).
- Aceclofenac has anti-inflammatory and analgesic properties.
- Analgesic: medicines used to reduce pain.
- Anti-inflammatory: medicines used to decrease inflammation.
- Working Mechanism: Aceclofenac works by preventing the release of a chemical substance that causes pain and swelling in your body.
- Uses-
- It is used in osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis and ankylosing spondylitis.
- It provides relief from pain, stiffness, and swelling due to various conditions related to the bone and joints.
- It is also used to provide relief from headaches, toothaches, backaches, menstrual pain, sprains, and strains.
- Side effects: dizziness, nausea, vomiting, heartburn, stomach pain, indigestion, and diarrhoea.
Ketoprofen
- Ketoprofen is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) that is used to treat pain or inflammation caused by arthritis.
- Other Uses:-
- It is used to relieve pain, tenderness, swelling and stiffness in conditions such as osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis.
- It is also used to relieve minor aches and pains from headaches, menstrual periods, toothaches, the common cold, fever, muscle aches, backaches, etc.
- Side effects:- Indigestion, Dizziness, Headache, Nausea, Diarrhea, Rash, Abdominal pain etc.
Drugs Technical Advisory Board (DTAB)
- DTAB is a statutory body under the Drugs and Cosmetics Act, 1940.
- It is the highest decision-making body on technical matters related to drugs in the country.
- It is part of the Central Drugs Standard Control Organization (CDSCO)
- CDSCO: is the National Regulatory Authority (NRA) of India.
- It is under the Directorate General of Health Services, Ministry of Health & Family Welfare.
- Ministry: Ministry of Health and Family Welfare.
Functions:-
- It advises the Central Government and the State Governments on technical matters arising out of the administration of the Drugs and Cosmetics Act, of 1940.
- It plays a crucial role in evaluating and assessing various aspects of drug regulation, including drug safety, efficacy, quality, and regulatory policies.
- It examines scientific evidence, conducts reviews, and formulates recommendations based on its expert analysis.
- It carries out the other functions assigned to it by this Act. (UPSC CSE: Medicine Price Control)
MUST READ: iNCOVACC
SOURCE: THE NEW INDIAN EXPRESS
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) Bisphenol A (BPA), a cause of concern, is a structural/key component in the manufacture of which of the following kinds of plastics? (2021)
- Low-density polyethene
- Polycarbonate
- Polyethene terephthalate
- Polyvinyl Chloride
Q.2) “Triclosan” considered harmful when exposed to high levels for a long time, is most likely present in which of the following? (2021)
- Food preservatives
- Fruit ripening substances
- reused plastic containers
- Toiletries
Syllabus
- Prelims –Important Organizations
Context: The Finance Minister recently met the president of the International Fund for Agricultural Development (IFAD) and discussed issues of mutual interest.
About International Fund for Agricultural Development (IFAD):-
- IFAD is an international financial institution and specialized United Nations agency. (UPSC CSE: IFAD)
- It works in the field of poverty eradication in the rural areas of developing countries.
- It provides grants and loans with low interest for allied projects in the related area.
- HQ: Rome, Italy
- Formation: IFAD was created in 1977, as the outcome of the World Food Conference of 1974.
- World Food Conference of 1974: it was organized under United Nations wherein the governments examined the global problem of food production and consumption.
Membership:-
- It has 177 Member States.
- They comprise developing, middle and high-income countries from all regions of the world that are dedicated to eradicating poverty in rural areas.
- Membership in IFAD is open to any State that is a member of the United Nations, any of its specialized agencies or the International Atomic Energy Agency(IAEA). (UPSC CSE: Joint Comprehensive Plan of Action (JCPOA))
- India is a member of IFAD since 1977.
Objectives of the IFAD:-
- To increase the productive capacity of poor people.
- To increase benefits for them from market participation.
- To strengthen the environmental sustainability & climate resilience of their economic activities.
Important Publications:-
- It brings out the Rural Development Report every year.
MUST READ: Poverty
SOURCE: BUSINESSLINE
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) “Rapid Financing Instrument” and “Rapid Credit Facility” are related to the provisions of lending by which of the following: (2022)
- Asian Development Bank
- International Monetary Fund
- United Nations Environment Programme Finance Initiative
- World Bank
Q.2) With reference to Trade-Related Investment Measures (TRIMS), which of the following statements is/are correct? (2020)
- Quantitative restrictions on imports by foreign investors are prohibited.
- They apply to investment measures related to trade in both goods and services.
- They are not concerned with the regulation of foreign investment.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
- 1 and 2 only
- 2 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
Syllabus
- Prelims –Geography
Context: An earthquake of magnitude 6.4 struck the Gulf of California recently, as reported by the European Mediterranean Seismological Centre (EMSC).
About the Gulf of California:-
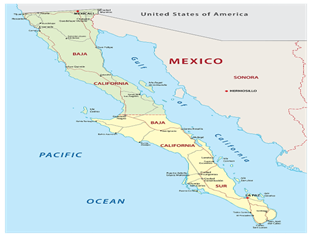
IMAGE SOURCE: WORLDATLAS
- Gulf of California covers an area of 160,000 sq. km.
- Gulf: a body of water that is connected to a sea or ocean and is surrounded or penetrated by land.
- It has a long coastline of approximately 4,000km.
- It is a UNESCO World Heritage Site.
- The Gulf is surrounded by the Mexican states of Sonora, Sinaloa, Baja California, and Baja California Sur.
- The Gulf is divided into two portions.
- It is separated by a narrowing that is marked by the islands of Tiburón and Angel de la Guarda.
- Major ports: La Paz on the Baja California Peninsula and Guaymas on the Mexican mainland are the two major ports that are located along the shores of the Gulf.
- Islands: there are about 37 major islands in the Gulf of California that are mostly located on its western side.
- It is believed that these islands were created due to volcanic eruptions.
- Major islands: the Isla Ángel de la Guarda, Isla Tiburón, Islas Marías, Isla Partida, Islas San Francisco, Isla Coronados, etc.
- Ecology: the waters of the Gulf are home to more than 5,000 species of micro-invertebrates.
- It also supports a high diversity of marine life including more than 900 species of fish along with coral reefs, dolphins, and marine turtles.
European Mediterranean Seismological Centre (EMSC)
- It was founded in 1975.
- The EMSC, acts as the central authority and transmits information immediately to the appropriate international authorities and to the members in order to meet the needs of protection.
Objectives:-
- To establish and operate a system for rapid determination of the European and Mediterranean earthquake epicenters.
- Earthquake epicenter: the point on the earth’s surface vertically above the focus of an earthquake.
- Focus: the place of origin of an earthquake.
- To determine the principal parameters (epicenter, depth, magnitude, focal mechanisms) of major seismic events located within the European-Mediterranean region.
- To collect the data necessary for the operations of the EMSC and make them available to other international, regional or national data centres.
- To encourage scientific cooperation among European and Mediterranean countries in the field of earthquake research.
MUST READ: Oil Spill in the Gulf of Mexico
SOURCE: THE PRINT
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) Consider the following pairs: (2022)
The region often mentioned in the news: Country
- Anatolia Turkey
- Amhara Ethiopia
- Cabo Delgado Spain
- Catalonia Italy
How many pairs given above are correctly matched?
- Only one pair
- Only two pairs
- Only three pairs
- All four pairs
Q.2) Consider the following statements: (2020)
- Jet streams occur in the Northern Hemisphere only.
- Only some cyclones develop an eye.
- The temperature inside the eye of a cyclone is nearly 10°C lesser than that of the surroundings.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 2 only
- 1 and 3 only
Syllabus
- Prelims – International Relations
Context: India and the United States recently unveiled a roadmap for enhanced collaboration in high-technology areas under the Initiative on Critical and Emerging Technology (iCET).
About Initiative on Critical and Emerging Technology (iCET):-
- The iCET is a partnership between India and the US to work together in developing important and new technologies.
- Objective: to increase the technology interaction between the US and India while also potentially adding additional strategic depth and breadth to their growing partnership.
- Areas of collaboration under iCET: quantum computing, semiconductors, 5G and 6G wireless infrastructure, and civilian space projects such as lunar exploration. (UPSC CSE: India-USA: Trade and Climate)
- Supervision: the Prime Minister’s Office in Delhi and the White House in Washington will oversee and direct the iCET.
Significance of iCET for India:-
- Growing convergence of Indian and US interests can help in managing the security, economic, and technological challenges presented by China.
- It can help secure an alternative for India and reduce dependence on Russian military technology.
- It would help boost India’s technological capabilities and provide India with access to cutting-edge technology and expertise in areas that are critical and emerging in nature.
- It will help India’s economic growth by having more business with the US.
- It will help them bring more investment and employment opportunities.
MUST READ: India’s growing defence diplomacy footprint
SOURCE: THE HINDU
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) What is/are the consequence /consequences of a country becoming a member of the ‘Nuclear Suppliers Group’? (2018)
- It will have access to the latest and most efficient nuclear technologies.
- It automatically becomes a member of “The Treaty on the Non-Proliferation of Nuclear Weapons (NPT)”.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Q.2) Consider the following countries : (2018)
- Australia
- Canada
- China
- India
- Japan
- USA
Which of the above are among the ‘free-trade partners’ of ASEAN?
- 1, 2, 4 and 5
- 3, 4, 5 and 6
- 1, 3, 4 and 5
- 2, 3, 4 and 6
Syllabus
- Prelims –Environment and Ecology
Context: Recent reports suggest, that wild orchids of North Bengal are dying at an alarming rate.
About Wild Orchids of North Bengal:-
- Orchids are attractively flowered and colorful plants.
- They are known for their vibrant and intricate flowers. (UPSC CSE: Arunachal to start red-listing of orchids)
- Habitat: they are found in various habitats around the world, including tropical rainforests, mountains, and even deserts.
- India has over 1200 species of Orchids ( 388 are endemic to India, out of which 128 are endemic to the Western Ghats)
- Endemic: a plant or animal native and restricted to a certain place.
Protection Status of Wild Orchids of North Bengal:-
CITES: Appendix II
Types of Orchids
Epiphytic Orchids:-
- These are plants growing on another plant including those growing on rock boulders and are often termed lithophytes.
- About 60% of all orchids found in India are epiphytic.
- Their occurrence decreases with an increase in altitude.
Terrestrial Orchids:-
- These are plants growing on land and climbers.
- 447 species in India are terrestrial.
- These grow directly on the soil and are found in large numbers in temperate and alpine regions.
Mycoheterotrophic Orchids:-
- Thes are plants which derive nutrients from mycorrhizal fungi that are attached to the roots of a vascular plant.
Distribution:-
- Himalayan Zone: Richest in orchid species.
- Northeast India: Highest species concentration.
- Western Ghats: High endemism of orchids.
- Highest Number of Orchid Species: Arunachal Pradesh> Sikkim> West Bengal.
Uses:-
- For aesthetic purposes.
- In herbal medicine.
- Vanilla is produced from Vanilla planifolia orchid.
MUST READ: New genus of parasitic flowering plant
SOURCE: DOWN TO EARTH
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) With reference to “Gucchi” sometimes mentioned in the news, consider the following statements: (2022)
- It is a fungus.
- It grows in some Himalayan forest areas.
- It is commercially cultivated in the Himalayan foothills of north-eastern India.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 3 only
- 1 and 2
- 2 and 3
Q.2) Which of the following are nitrogen-fixing plants? (2022)
- Alfalfa
- Amaranth
- Chickpea
- Clover
- Purslane (Kulfa)
- Spinach
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
- 1, 3 and 4 only
- 1, 3, 5 and 6 only
- 2, 4, 5 and 6 only
- 1, 2, 4, 5 and 6
Syllabus
- Prelims – Important Institutions
Context: Recently, Energy Efficiency Services Limited put forward its willingness to support Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises (MSMEs) of Andhra Pradesh.
About Energy Efficiency Services Limited (EESL):-
- Found in 2009.
- Ministry: Ministry of Power. (UPSC CSE: Electricity Production)
- HQ: New Delhi.
- It is a joint venture of four national Public-Sector Undertakings
- NTPC Limited,
- Power Finance Corporation Limited,
- Rural Electrification Corporation Limited and
- POWERGRID Corporation of India Limited.
- Mission: EESL was formed to create and sustain market access to energy-efficient technologies.
- Significance: it is a Super Energy Service Company which enables consumers, industries and governments to effectively manage their energy needs through energy-efficient technologies.
- EESL is implementing the world’s largest energy efficiency portfolio across sectors like lighting, buildings, industry electric mobility, smart metering, agriculture, etc. at an enormous scale.
Objectives:-
- To carry on and promote the business of Energy Efficiency and climate change.
- To act as a resource Centre in the field of Energy Efficiency.
- To take up the activities of Capacity Building.
- Training and other related activities.
- To provide Consultancy Services.
Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises (MSMEs)
- The Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises Development (MSMED) Act, 2006 in terms of which defines micro, small and medium enterprises as under:-
- Enterprises engaged in the manufacture or production, processing or preservation of goods as specified below:
- Microenterprise: where the investment in Plant and Machinery or Equipment does not exceed one crore rupees and turnover does not exceed five crore rupees.
- Small enterprise: where the investment in Plant and Machinery or Equipment does not exceed ten crore rupees and turnover does not exceed fifty crore rupees.
- Medium enterprise: where the investment in Plant and Machinery or Equipment does not exceed fifty crore rupees and turnover does not exceed two hundred and fifty crore rupees.
Significance:-
- They constitute over 90% of total enterprises in most economies.
- They are credited with generating the highest rates of employment growth.
- They contribute to a high amount of the overall exports from India. (UPSC CSE: Cross-border Electricity Trade)
- They promote inclusive growth by providing employment opportunities in rural areas, especially to people belonging to weaker sections of society.
- It provides an opportunity for budding entrepreneurs to build creative products boosting business competition and fuel growth.
MUST READ: The Electricity (Amendment) Bill 2022
SOURCE: THE NEW INDIAN EXPRESS
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) In India under cyber insurance for individuals, which of the following benefits are generally covered, in addition to payment for the loss of funds and other benefits? (2020)
- Cost of restoration of the computer system in case of malware disrupting access to one’s computer
- Cost of a new computer if some miscreant willfully damages it, if proved so
- Cost of hiring a specialized consultant to minimize the loss in case of cyber extortion
- Cost of defence in the Court of Law if any third party files a suit
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
- 1, 2 and 4 only
- 1, 3 and 4 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1, 2, 3 and 4
Q.2) What is the purpose of ‘Vidyanjali Yojana’? (2017)
- To enable famous foreign educational institutions to open their campuses in India.
- To increase the quality of education provided in government schools by taking help from the private sector and the community.
- To encourage voluntary monetary contributions from private individuals and organizations so as to improve the infrastructure facilities for primary and secondary schools.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
- 2 only
- 3 only
- 1 and 2 only
- 2 and 3 only
Syllabus
- Mains – GS 2 (Governance)
Context: Recently, the Council of the European Union (EU) adopted a set of recommendations to strengthen action against antimicrobial resistance (AMR).
About one health approach and Antimicrobial resistance (AMR):
- According to World Health Organization, ‘One Health’ is an approach to designing and implementing programmes, policies, legislation and research in which multiple sectors communicate and work together to achieve better public health outcomes.
- Antimicrobial Resistance (AMR) occurs when bacteria, viruses, fungi and parasites change over time and no longer respond to medicines making infections harder to treat and increasing the risk of disease spread, severe illness and death.
- Resistant microbes can pass between animals, plants and food and in the environment.
Emergence and spread of AMR:
- AMR occurs naturally over time, usually through genetic changes.
- Antimicrobial-resistant organisms are found in people, animals, food, plants and the environment (in water, soil and air).
- They can spread from person to person or between people and animals, including from food of animal origin.
- The main drivers include the misuse and overuse of antimicrobials, lack of access to clean water, sanitation and hygiene (WASH), poor infection and disease prevention and control in healthcare facilities and farms, poor access to quality, affordable medicines, vaccines and diagnostics etc.
Significance of One Health in context of rising zoonotic infections:
- Risk of disease: Human populations are growing and expanding into new geographic areas. As a result, more people live in close contact with wild and domestic animals, both livestock and pets.
- Climate change: The earth has experienced changes in climate and land use, such as deforestation and intensive farming practices.
- Disruptions in environmental conditions and habitats can provide new opportunities for diseases to pass to animals.
- Global movement: The movement of people, animals, and animal products has increased from international travel and trade.
- As a result, diseases can spread quickly across borders and around the globe.
- Collaborative effort: Many of the same microbes infect animals and humans, as they share the ecosystems, they live in.
- For instance, rabies in humans is effectively prevented only by targeting the animal source of the virus (for example, by vaccinating dogs).
- Combating disease threat: The areas of work in which a One Health approach is particularly relevant include food safety, the control of zoonosis (diseases that can spread between animals and humans, such as flu, rabies and Rift Valley Fever) and combating antibiotic resistance.
- Information on viral agents: Information on viruses circulating in animals is crucial to the selection of viruses for human vaccines for potential influenza pandemics.
- Well-coordinated approach: Drug-resistant microbes can be transmitted between animals and humans through direct contact between animals and humans or through contaminated food, so to effectively contain it, a well-coordinated approach in humans and in animals is required.
EU’s action to combat antimicrobial resistance:
Combating AMR in a One Health approach:
- The commission submitted the proposal for a recommendation on stepping up EU actions to combat AMR in a One Health approach.
- These recommendations were part of a proposal submitted by the European Commission to the European Council.
Focussing on the health of humans, animals and the environment:
- It recommended the prudent use of antimicrobials such as antibiotics in human and animal health for reducing the risk of microorganisms becoming resistant to medical intervention.
The proposal included a series of actions to:
- Strengthen national action plans against antimicrobial resistance.
- Reinforce surveillance and monitoring of AMR and antimicrobial consumption (AMC).
- Strengthen infection prevention and control as well as antimicrobial stewardship and prudent use of antimicrobials.
- Recommend targets for AMC and AMR in human health.
The target:
Surveillance and monitoring:
- The targets called for closing existing surveillance and monitoring gaps and ensuring the completeness of data, including real-time information.
- It also includes timely access to data on both AMR and AMC at all levels, like the community, hospitals and long-term care facilities.
Reducing the consumption of antibiotics:
- Reducing the total consumption of antibiotics in humans by 20 percent in the Union compared with the baseline year of 2019 is also another target.
- This would be applicable for the community and hospital sectors combined, including in long-term care facilities and in home-care settings.
AWaRe classification of WHO:
- The member states must also ensure that at least 65 percent of the total consumption of antibiotics in humans belongs to the access group of antibiotics as defined in the AWaRe classification of the World Health Organization.
Measures Taken to Rising Anti-Microbial Resistance in India:
- National programme on AMR containment: It was launched during the 12th FYP in 2012-17
- National Action Plan on Antimicrobial Resistance (NAP-AMR): It has a focus on the One Health approach and was launched on 19th April 2017 with the aim of involving various stakeholders ministries/departments.
- AMR Surveillance Network: ICMR has established the AMR surveillance and research network (AMRSN) in 2013, to generate evidence and capture trends and patterns of drug resistant infections in the country.
- AMR Research and International Collaboration: ICMR has taken initiatives to develop new drugs /medicines through international collaborations in order to strengthen medical research in AMR.
- India’s National Action Plan for containment of AMR: It focuses on an integrated One Health approach and involves coordination at the state, national and international levels.
Way Forward:
Therefore successful public health interventions require the cooperation of human, animal, and environmental health partners. Professionals in human health, animal health, environment and other areas of expertise need to communicate, collaborate on, and coordinate activities. By promoting collaboration across all sectors, a One Health approach can achieve the best health outcomes for people, animals, and plants in a shared environment.
Source: DTE
Syllabus
- Mains – GS 2 (International Relations)
Context: India and the United States recently unveiled a roadmap for enhanced collaboration in high-technology areas which focuses on addressing regulatory barriers and aligning export controls for smoother trade and “deeper cooperation” in critical areas.
About India – USA Relations:
Bilateral engagement:
- India and the United States enjoy a comprehensive global strategic partnership covering almost all areas of human endeavour, driven by shared democratic values, convergence of interests on a range of issues, and vibrant people-to-people contacts.
- Regular exchanges at the leadership-level have been an integral element of the expanding bilateral engagement.
- Despite COVID-19 pandemic, India-U.S. cooperation witnessed intense engagement under various bilateral dialogue mechanisms in a wide range of areas including defence, security, health, trade, economic, science & technology, energy and people-to-people ties.
Defence and Security:
- India-US defence cooperation is based on “New Framework for India US Defence Cooperation”, which was renewed for a period of ten years in 2015.
- In 2016, the defence relationship was designated as a Major Defence Partnership (MDP).
- Bilateral military exercises and defence exchanges are important aspects of deepening military-to-military cooperation.
QUAD:
- The four Quad partners (India, Japan, United States & Australia) first formed a “Core Group” in 2004, to swiftly mobilise aid during the joint response to the 2004 Tsunami. Since 2017, Quad engagements have increased and intensified.
Counter Terrorism Cooperation:
- Cooperation in counter-terrorism has seen considerable progress with information exchange, operational cooperation and sharing of counterterrorism technology and equipment.
- India-U.S. Joint Working Group on Counter-Terrorism oversees the expanding CT cooperation.
Trade and Economic Relations:
- The rapidly expanding trade and commercial linkages form an important component of the multi-faceted partnership between India and the United States.
- The U.S. is India’s second largest trading partner and a major destination for our exports of goods and services.
- Bilateral trade in goods and services stood at US$ 146 billion in 2019.
- During the financial year 2020-21, India received the highest ever foreign direct investment amounting to USD 81.72 billion, as per data published by the Ministry of Commerce and Industry, Government of India.
- The US replaced Mauritius as the second largest source of foreign direct investment into India during 2020-21 with inflows of USD 13.82 billion.
- The US is one of the top 5 investment destinations for Indian FDI.
Education partnership:
- It is an important pillar of India-US ties and both the countries share strong linkages and history of higher education collaborations.
- The United States Educational Foundation in India (USEFI) was set up after a bilateral agreement on education exchange was signed between India and the US on February 2, 1950
Indian Diaspora:
- About 4.2 million Indian Americans/Indian origin people reside in the US. The Indian Americans [3.18 million] constitute the third largest Asian ethnic group in the US.
Challenges between India-US relations:
- Trade: Recently India and US confronted each other regarding tariffs and protectionist policies.
- US has continuously accused India of high tariffs and India have accused USA of restriction to US markets and high tariffs on Indian products.
- Intellectual Property Rights: US has continuously criticised India for its IPR policies. It has accused India of acting against Intellectual properties of major companies especially pharmaceutical over generic drugs.
- Continuous support to Pakistan: Although US has reduced support to Pakistan, it has still provided monetary support to Pakistan.
- In February 2016, the Obama administration notified the US Congress that it intended to provide Pakistan eight nuclear-capable F-16 fighters and assorted military goods including eight despite strong reservations from US lawmakers regarding the transfer of any nuclear weapons capable platforms to Pakistan.
- Relations with Russia: Russia has always supported India in international platform. It helped India to develop its defence capabilities.
- In 2018, India inked the historic agreement worth with Russia to procure four S-400 surface-to-air missile defence system, the most powerful missile defence system in the world ignoring America’s CAATSA act.
- Relations with Iran: US has put sanctions on Iran due to its nuclear development. India has strategic interest in Iran to buy oil.
- The United States threatened India with sanctions over India’s decision to buy oil from Iran.
- But recently it exempted India from sanctions that allowed India to buy oil from Iran.
Way Forward:
It appears highly likely that in strategic, political, security, defence and economic terms, relations between India and the USA will continue their upward trajectory under the present leadership. Impact of USA’s relations with Pakistan over India is likely to be beneficial and positive. Geopolitical manoeuvres can have significant impact on India-USA relations; however, it would remain to be multi-faceted and an “indispensable partnership”.
Source: The Hindu
Practice MCQs
Q.1) In the context of the International Fund for Agricultural Development (IFAD), consider the following statements:
- India is not a member of IFAD.
- IFAD was created in 1977.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Q.2) In the context of Aceclofenac, consider the following statements:
- It is a pain killer.
- Indigestion and diarrhoea are one of its side effects.
Which of the statements given above is/are incorrect?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Q.3) In the context of Energy Efficiency Services Limited (EESL )consider the following statements:
- It works under the Ministry of Power.
- Its headquarters are in Mumbai.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Comment the answers to the above questions in the comment section below!!
ANSWERS FOR ’ 20th June 2023 – Daily Practice MCQs’ will be updated along with tomorrow’s Daily Current Affairs.st
ANSWERS FOR 9th June – Daily Practice MCQs
Q.1) – b
Q.2) – b
Q.3) -d











