IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
Archives
(PRELIMS & MAINS Focus)
Syllabus
- Prelims –Governance
Context: Recently, the Indian Navy announced its plan to organise the ‘Ocean Ring of Yoga’ to commemorate International Yoga Day.
About International Day of Yoga (IDY):-

IMAGE SOURCE: WordPress.com
- The International Day of Yoga (IDY) is celebrated on 21 June, every year.
- June 21 was selected as “Yoga Day” because it is the longest day of the year in the Northern Hemisphere (Summer Solstice).
- It is also considered important in Indian mythology as it marks the start of Yogic science.
- Objective: to inculcate a habit of meditation for the peace of mind and the self-awareness which is necessary to survive in a stress-free environment.
- First Yoga Day celebrations: 2015.
- The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) issued a commemorative coin of 10 rupees, in 2015 to mark the International Day of Yoga.
- UN Postal Administration (UNPA) issued 10 stamps on Asanas in
- UNPA: is the postal agency of the United Nations, which issues postage stamps and postal stationery.
- Theme 2023: Yoga for Vasudhaiva Kutumbakam
Historical Background:-
- The idea of the International Day of Yoga (IDY) was proposed by India during the opening of the 69th session of the United Nations General Assembly (UNGA), held in 2014.
- This proposal was backed by 177 nations, which led the UN to declare June 21 as the “International Day of Yoga.
- The UN proclaimed 21st June as IDY by passing a resolution in December 2014.
- The first Yoga Day celebrations at Rajpath in New Delhi created two Guinness World Records.
- It was the world’s largest yoga session with 35,985 people.
Significance of the Day:-
- It spreads awareness about the practice of yoga.
- Its holistic approach helps maintain physical and mental well-being.
Yoga
- The word ‘yoga’ is derived from Sanskrit and means to join or to unite.
- It symbolizes the union of body and consciousness.
- Yoga is an ancient physical, mental and spiritual practice.
- It originated in India.
- UNESCO put it on the Representative List of the Intangible Cultural Heritage of Humanity in 2016.
- UNESCO List of the Intangible Cultural Heritage of Humanity: includes forms of expression that demonstrate the diversity of intangible heritage and raises awareness of its importance.
- India has 13 intangible heritage including Yoga as a part of this list. (UPSC CSE: UNESCO Heritage Sites in Maharashtra)
Related Initiatives
- M-Yoga App:-The app is a work of collaboration between the World Health Organisation (WHO) and the Ministry of Ayurveda, Yoga & Naturopathy, Unani, Siddha and Homoeopathy (Ministry of AYUSH), Government of India.
- New website for International Day of Yoga (IDY):-This web portal provides all the updated and relevant information relating to the International Day of Yoga.
- Yoga as a sport:-The Ministry of Youth Affairs and Sports, after reviewing the categorization of various Sports disciplines, recognized Yoga as a sports discipline and placed it in the ‘Priority’ category in 2015.
- Common Yoga Protocol:-It is an initiative of the Ministry of AYUSH.
- Vocational Education Courses in Yoga:-The Beauty & Wellness Sector Skill Council (B&WSSC) has vocational education courses in Yoga for CBSE schools.
- Skilling initiatives:-Thousands of candidates have been trained as yoga instructors and trainers through various skilling initiatives like the Pradhan Mantri Kaushal Vikas Yojana (PMKVY).
- PMKVY: it is the flagship scheme of the Ministry of Skill Development and Entrepreneurship.
- Fit India Movement:-Yoga is also a part of the Fit India Movement.
- Fit India Movement: a nationwide campaign that aims at encouraging people to include physical activities and sports in their everyday lives.
Ocean Ring of Yoga
- Ocean Ring of Yoga symbolizes unity and solidarity.
- Organized by: Ministry of Defence and other ministries.
- Implementation: Indian Navy ships deployed in the Indian Ocean Region will be visiting various ports of friendly foreign countries in support of the IDY-23 initiative.
- They will spread the message of ‘Vasudhaiva Kutumbakam’, which is also the theme for IDY 23.
- The Indian Navy has been an ambassador for Yoga across the seas for several years.
- This year, Indian Navy is actively supporting the IDY at a global scale as port calls are planned at Chattogram, Bangladesh; Safaga, Egypt; Jakarta, Indonesia; Mombasa, Kenya; Toamasina, Madagascar; Muscat, Oman; Colombo, Sri Lanka; Phuket, Thailand; and Dubai, UAE by IN Ships Kiltan, Chennai, Shivalik, Sunayna, Trishul, Tarkash, Vagir, Sumitra and Brahmaputra respectively.
- The IDY-23 activities by the Indian Naval ships at foreign ports are planned to involve the ship’s crew and personnel from the host country.
MUST READ: New sites added to India’s tentative list of UNESCO world heritage sites
SOURCE: AIR
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) consider the following statements: (2021)
- 21st February is declared International Mother Language Day by UNICEF.
- The demand that Bangla has to be one of the national languages was raised in the Constituent Assembly of Pakistan.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Q.2) Consider the following pairs: (2018)
Crafts Heritage of
- Puthukkuli Shawls Tamil Nadu
- Sujni Embroidery Maharashtra
- Uppada Jamdani saris Karnataka
Which of the pairs given above is /are correct?
- 1 only
- 1 and 2
- 3 only
- 2 and 3
Syllabus
- Prelims –Important Institutions
Context: Recent data released by the Employees Provident Fund Organisation, revealed that it has added 17.20 lakh net members in April this year.
About Employees Provident Fund Organisation:-
- EPFO is one of the World’s largest Social Security Organizations in terms of clientele and the volume of financial transactions undertaken.
- Establishment: 1952.
- Ministry: Ministry of Labour & Employment.
- HQ: New Delhi.
- It is a government organization that manages the provident fund (PF) and pension accounts of member employees.
- Provident fund (PF): it is an investment fund contributed to by employees, employers, and (sometimes) the state, out of which a lump sum is provided to each employee on retirement.
- Functions: It implements the Employees’ Provident Fund and Miscellaneous Provisions Act, 1952.
Historical Background:-
- The Employees’ Provident Fund came into existence with the promulgation of the Employees’ Provident Funds Ordinance in 1951.
- It was later replaced by the Employees’ Provident Funds Act, 1952.
- It is managed by the Employees’ Provident Fund Organization (EPFO).
Objectives:-
- To meet the evolving needs of comprehensive social security in a transparent, contactless, faceless and paperless manner.
- To ensure ease of living for members and pensioners and ease of doing business for employers by leveraging the Government of India’s technology platforms for reaching out to millions.
EPF Scheme of 1952
- It is a mandatory savings scheme under the Employees’ Provident Funds and Miscellaneous Provisions Act, 1952.
- It covers every establishment in which 20 or more persons are employed.
- It also covers certain other establishments which may be notified by the Central Government even if they employ less than 20 persons each.
- The employee has to pay a certain contribution towards the provident fund (PF) and the employer on a monthly basis pays the same amount.
- The employee and the employer contribute to the EPF India scheme on monthly basis in equal proportions of 12% of the basic salary and dearness allowance.
- At the end of retirement or during the service (under some circumstances), the employee gets the lump sum amount including the interest on the PF contributed.
- EPF is a tax-saving instrument that offers relatively higher interest rates on investments.
- Partial withdrawals: allowed for education, marriage, illness and house construction.
MUST READ: National Pension System (NPS)
SOURCE: AIR
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) Consider the following statements: (2022)
- In India, credit rating agencies are regulated by the Reserve Bank of India.
- The rating agency popularly known as ICRA is a public limited company.
- Brickwork Ratings is an Indian credit rating agency.
Which of the statements given above is correct?
- 1 and 2 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
Q.2) With reference to the ‘Banks Board Bureau (BBB)’, which of the following statements is correct? (2022)
- The Governor of RBI is the Chairman of BBB.
- BBB recommends the selection of heads for Public Sector Banks.
- BBB helps Public Sector Banks in developing strategies and capital-raising plans.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
- 1 and 2 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
Syllabus
- Prelims –Geography
Context: Recent reports from the International Centre for Integrated Mountain Development (ICIMOD) suggest that Climate change is severely affecting biodiversity in the Hindu Kush Himalayas region.
About Hindu Kush Himalayas region:-
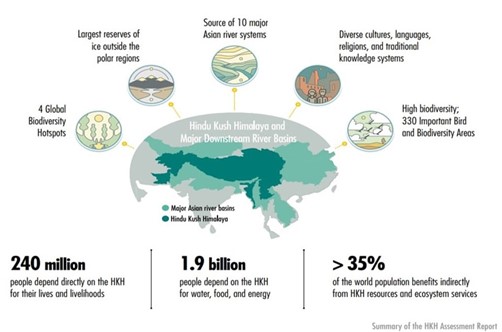
IMAGE SOURCE: THE THIRD POLE
- Hindu Kush is a huge mountain system of Central Asia.
- It spans across Afghanistan, Bangladesh, Bhutan, China, India, Myanmar, Nepal, and Pakistan.
- It is one of the great watersheds of Central Asia.
- It forms a part of the vast Alpine zone that stretches across Eurasia from east to west.
- It runs northeast to southwest and divides the valley of the Amu Darya (the ancient Oxus River) to the north from the Indus River valley to the south.
- To the east the Hindu Kush: lies the Pamir range near the point where the borders of China, Pakistani-controlled Kashmir, and Afghanistan meet.
- On the southwest: it runs through Pakistan and into Afghanistan, finally merging into minor ranges in western Afghanistan.
- The highest peak is Mount Tirich Mir.
- It rises near the Pakistan-Afghanistan border to 25,230 feet (7,690 meters).
- The Third Pole: the region is called ’The Third Pole‘because it stores more snow and ice than anywhere else in the world outside the polar regions.
- It contains some of the world’s highest mountains.
- It is the source of 10 major rivers and forms a formidable global ecological buffer.
- The region contains 1,106 Important Bird Areas (IBAs), covering about 11% of its total area.
- IBA: most important sites for the conservation of birds identified using standard scientific criteria.
Significance:-
- Socioeconomic and cultural diversity: it is home to many different ethnic communities speaking more than 600 languages and many more dialects.
- Ecology: It is endowed with rich natural resources and contains all or part of four global biodiversity hotspots. (UPSC CSE: Mitigating Climate Change)
- These include Himalaya Hotspot, Indo-Burma Hotspot, Mountains of Southwest China and Mountains of Central Asia.
- Local Economy: The mountain resources provide a wide range of ecosystem services and the basis for the livelihoods of the people living in the region.
- Originating Rivers: Many people benefit from the food and energy produced in these river basins that have their origin in the mountains.
Impacts of climate change on Hindu Kush Himalayas region:
- The timing of leaf-fall and fruiting has altered.
- This has led to a decrease in the survival of plants and threatened the vulnerability of species.
- Advanced and delayed flowering of Himalayan rhododendron has been observed in Nepal and nearby HKH region.
- The change in snowfall patterns due to rise in temperatures has resulted in the shifting of the tree line as well.
- Many plant species have shifted upwards at the rate of 11 to 54 meters per decade in the western Himalayan regions of India.
- About 90 per cent of the endemic species in the Sikkim Himalayas have displaced at the rate of 27.53 to 22.04 meters per decade.
- Many species, found in the northwest Himalayas of eastern Ladakh, have moved upwards by about 150 meters above the plant distribution limit.
- 5 per cent of 26 invasive plant species will expand while 25 per cent will contract, thereby threatening biodiversity and food security while causing heavy economic losses.
- An invasive or alien species is an introduced species to an environment that becomes overpopulated and harms its new environment.
- Declining fauna is observed.
- Mammals, insects, microbes, birds, amphibians and fishes are becoming extinct or are experiencing genetic and behavioral changes.
- Himalayan musk deer, golden snub-nosed monkeys and Himalayan grey langurs have already experienced range shifts with declining populations.
- Monocled and king cobras in the Sikkim Himalayas have moved higher from 1,000 meters to 1,700 meters.
- In Pakistan, 14 species of butterflies known to dwell in the Murree hills and neighboring areas are reported to have disappeared.
International Centre for Integrated Mountain Development (ICIMOD)
- ICIMOD is an intergovernmental knowledge and learning center.
- Established: 1983.
- HQ: Lalitpur, Nepal.
- Objective: it develops and shares research, information, and innovations to empower people in the eight regional member countries of the Hindu Kush-Himalayan region.
- Members: Afghanistan, Bangladesh, Bhutan, China, India, Myanmar, Nepal, and Pakistan.
Functions of ICIMOD:-
- It serve the region through information and knowledge generation.(UPSC CSE: Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC))
- It is involved in sharing to find innovative solutions to critical mountain problems.
- It acts as a bridge between the policies and on-the-ground practices.
- It provides a regional platform where experts, planners, policymakers, and practitioners can exchange ideas and perspectives towards the achievement of sustainable mountain development.
- It facilitates knowledge exchange across the region.
- It helps customize international knowledge and tailor it to the region’s needs.
- It helps to bring regional issues to the global stage.
MUST READ: Water bomb in the Himalayas
SOURCE: DOWN TO EARTH
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) Consider the following pairs: (2022)
Peak Mountains
- Namcha Barwa Garhwal Himalaya
- Nanda Devi Kumaon Himalaya
- Nokrek Sikkim Himalaya
Which of the pairs given above is/are correctly matched?
- 1 and 2
- 2 only
- 1 and 3
- 3 only
Q.2) Consider the following countries: (2022)
- Azerbaijan
- Kyrgyzstan
- Tajikistan
- Uzbekistan
- Turkmenistan
Which of the above has borders with Afghanistan?
- 1, 2 and 5 only
- 1, 2, 3 and 4 only
- 3, 4 and 5 only
- 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5
Syllabus
- Prelims –Geography
Context: Recent reports suggest, that heavy rains, windstorms, and floods threaten the survival and water access of the communities living in the Lake Victoria Basin (LVB), East Africa.
About Lake Victoria Basin (LVB):-
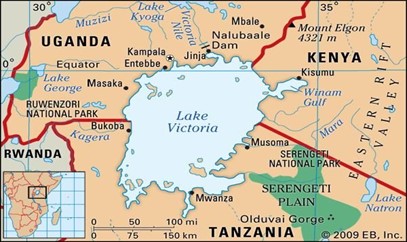
IMAGE SOURCE: Britannica
- The Lake Victoria Basin (LVB) is located in the upper reaches of the Nile River basin. (UPSC CSE: Chilika Lake )
- It comprises one of the world’s greatest complexes of lakes, wetlands, and rivers.
- Catchment area: approximately 194,200 km2.
- It traverses through five East African Countries including Tanzania (44%); Kenya (22%); Uganda (16%); Rwanda (11%) and Burundi (7%).
Significance:-
- The basin plays a major ecological, social and economic role and is central to the development and regional integration of the East Africa Community (EAC).
- It is rich in resources such as fishery, biodiversity, extensive networks of rivers and wetlands, forests, fertile soils, wildlife, minerals, tourism, multimodal transport and communication.
- The basin provides livelihood to locals who directly or indirectly rich natural resources around the basin.
- The basin has huge investment potential.
Lake Victoria
- It is the world’s second-largest
- It is the largest freshwater lake in Africa.
- It is one of the most important landmarks. (UPSC CSE: Managing Water Quality of Lake Victoria)
- It is the chief reservoir of the river Nile.
- Nile: longest river in the world.
- Bordering countries: Kenya (6%), Tanzania (51%) and Uganda (43%).
- Its catchment also touches Burundi and Rwanda.
- It is known for its high level of unique biodiversity.
MUST READ: Lake Sawa
SOURCE: DOWN TO EARTH
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) Which one of the lakes of West Africa has become dry and turned into a desert? (2022)
- Lake Victoria
- Lake Faguibine
- Lake Oguta
- Lake Volta
Q.2) The term “Levant” often heard in the news roughly corresponds to which of the following regions?
- Region along the eastern Mediterranean shores
- The region along North African shores stretches from Egypt to Morocco
- The region along the Persian Gulf and Horn of Africa
- The entire coastal Mediterranean Sea of areas
Syllabus
- Prelims – Important institutions
Context: The National Internet Exchange of India (NIXI) celebrated its 20th Foundation Day recently.
About the National Internet Exchange of India (NIXI):-
- NIXI is a not-for-profit Organization (NPO) under section 8 of the Companies Act 2013. (UPSC CSE: NIXI)
- NPO: an organization that focuses on a particular social cause, and all the money earned or donated is used in pursuing its objectives and meeting operational costs.
- Established: 2003.
- HQ: New Delhi.
- Ministry: Ministry of Electronics & Information Technology.
- NIXI was set up to increase internet penetration and adoption in India.
- NIXI was established for facilitating various infrastructure aspects to enable the Internet ecosystem to be managed and used by the masses.
- NIXI was set up for peering of Internet Service Providers (ISP) among themselves.
- Peering: the exchange of data directly between internet service providers, rather than via the internet.
Objectives of NIXI:-
- To promote the Internet. (UPSC CSE: India’s National Cyber Security Strategy)
- To set up, when needed, in select location(s)/parts/regions of India Internet Exchanges/Peering Points.
- Internet exchange point (IXP): a network point at which Internet service providers and Content Delivery Networks exchange Internet traffic between their networks.
- To enable effective and efficient routing, peering, transit and exchange of Internet traffic within India.
- Network routing: is the process of selecting a path across one or more networks.
- Peering: the exchange of data directly between internet service providers, rather than via the internet.
- Data transit: carrying of data from one place to another.
- Internet traffic: flow of data within the entire Internet, or in certain network links of its constituent networks.
- To continuously work for enhancing and improving the quality of Internet and Broadband services.
MUST READ: India Internet Governance Forum (IIGF)
SOURCE: PIB
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) Which of the following is/are the aim/aims of the “Digital India” Plan of the Government of India? (2019)
- Formation of India’s own Internet companies like China did.
- Establish a policy framework to encourage overseas multinational corporations that collect Big Data to build their large data centers within our national geographical boundaries.
- Connect many of our villages to the Internet and bring Wi-Fi to many of our schools, public places and major tourist centers.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
- 1 and 2 only
- 3 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
Q.2) In India under cyber insurance for individuals, which of the following benefits are generally covered, in addition to payment for the loss of funds and other benefits? (2020)
- Cost of restoration of the computer system in case of malware disrupting access to one’s computer
- Cost of a new computer if some miscreant willfully damages it, if proved so
- Cost of hiring a specialized consultant to minimize the loss in case of cyber extortion
- Cost of defense in the Court of Law if any third party files a suit
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
- 1, 2 and 4 only
- 1, 3 and 4 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1, 2, 3 and 4
Syllabus
- Prelims –Defense
Context: Multinational Peacekeeping Joint Exercise, Ex Khaan Quest 2023 was held recently.
About Ex Khaan Quest 2023:-
- Ex Khaan Quest 2023 is a 14-day exercise designed to improve interoperability among the participating nation.
- It is a multinational Peacekeeping Joint Exercise.
- Location: Mongolia.
- Participants: participation of military contingents and observers from around 20 countries.
- Sponsored by: Mongolian Armed Forces (MAF) and United States Army Pacific Command (USARPAC).
- The Indian Army is represented by a contingent from the GARHWAL RIFLES.
- Objective: enhancing interoperability of the participating nations, for sharing experience and to train uniformed personnel for the United Nations Peacekeeping Operations (UNPKO).
- The military exercise will enhance the level of defence cooperation between Indian
U.N. Peacekeeping mission
- It is a joint effort between the Department of Peace Operations and the Department of Operational Support,
- It aims to assist host countries to transition from situations of conflict to peace.
- Historical Background: the U.N. began its Peacekeeping efforts in 1948 when it deployed military observers to West Asia.
- Function:N. Peacekeepers provide security as well as political and peacebuilding support to conflict-ridden countries.
- Three basic principles that guide U.N.’s Peacekeeping missions are:
- Consent of the parties.
- Impartiality.
- Non-use of force except in self-defense and defense of the mandate.
India and UN Peacekeeping force:
- Over 200,000 Indians have served in 49 U.N. Peacekeeping missions since 1948.
- Currently, approx. 5,581 Indians are part of variousN. Peacekeeping missions. (UPSC CSE: U.N. Peacekeeping Forces)
- 2007: India became the first country to deploy an all-women contingent to a U.N. Peacekeeping mission.
- Issues:-
- Despite its presence in several countries as part of the Peacekeeping missions, India has routinely expressed its displeasure at a similar mission headquartered in Srinagar and Islamabad.
- The United Nations Military Observer Group in India and Pakistan (UNMOGIP) was established in 1949 to supervise the ceasefire between India and Pakistan.
- UNMOGIP has remained in the region to observe hostilities between the neighboring countries.
MUST READ: Need for Reforms in UN
SOURCE: PIB
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) Consider the following pairs: (2020)
International agreement/ set-up Subject
- Alma-Ata Declaration – Healthcare of the people
- Hague Convention – Biological and Chemical Weapons
- Talanoa Dialogue – Global Climate Change
- Under2 Coalition – Child Rights
Which of the pairs given above is/are correctly matched?
- 1 and 2 only
- 4 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 2,3 and 4 only
Q.2) Consider the following statements (2020)
- The value of Indo-Sri Lanka Trade has consistently increased in the last decade.
- Textile and textile articles constitute an important item of trade between India and Bangladesh
- In the last five years, Nepal has been the largest trading partner of India in South Asia
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 and 2 only
- 2 only
- 3 only
- 1,2, and 3
Climate breakdown: the Arctic Ocean could be ice-free by the 2030s
Syllabus
- Mains – GS 3 (Environment)
Context: According to the new study in Nature Communications, the Arctic Ocean could be ice-free in summer by the 2030s, even if we do a good job of reducing emissions between now and then.
About Arctic Region:
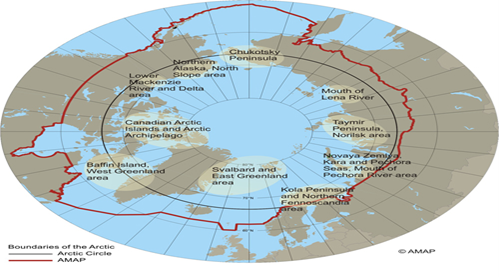
Image source: AMAP
- It is commonly understood to refer to the region above the Arctic Circle, north of latitude 66° 34′ N, which includes the Arctic Ocean with the North Pole at its centre.
- Arctic Council: Eight Arctic States-Canada, Kingdom of Denmark, Finland, Iceland, Norway, Russia, Sweden, and USA form the Arctic Council.
Significance of Arctic Region:
Climate Influence:
- Arctic sea ice plays a crucial role in influencing global climate patterns.
- It reflects sunlight, helping to maintain the earth’s energy balance and cool polar regions.
- Sea ice acts as a barrier, keeping the air cool by separating cold air above from warmer water below.
Biodiversity and Indigenous Communities:
- Changes in sea ice impact biodiversity, particularly mammals like polar bears and walruses.
- Indigenous Arctic populations reliant on sea ice for hunting, breeding, and migration are affected.
Economic Opportunities and Competition:
- Reduced ice cover opens shipping lanes and facilitates access to natural resources in the Arctic.
- This leads to increased competition among countries for influence and resource exploitation in the region.
Resources and inhabitants:
- The Arctic is home to almost four million inhabitants, of which approximately one tenth are considered as indigenous people.
- The Arctic Ocean and its surrounding landmass has been a topic of immense interest and a high-priority area of research among the global scientific fraternity as well as of importance to policy makers.
- The Arctic influences atmospheric, oceanographic and biogeochemical cycles of the earth’s ecosystem.
Mineral Resources:
- The Arctic region has rich deposits of coal, gypsum and diamonds and also substantial reserves of zinc, lead, placer gold and quartz.
- Greenland alone possesses about a quarter of the world’s rare earth reserves.
Hydrocarbons:
- The Arctic also contains a wealth of hydrocarbon resources. India is the third-largest energy-consuming country in the world.
- The Arctic can therefore potentially address India’s energy security needs.
Consequences:
- Weakening of Polar Jet Streams: Diminished sea ice weakens polar jet streams, resulting in rising temperatures and heatwaves in Europe.
- Unseasonal showers in northwest India have also been linked to this weakening.
- Melting of Ice: The Greenland ice sheet’s melting contributes to rising sea levels, with a complete melt potentially causing a seven-meter rise.
- Changes in Composition of Sea Water: Warming of the Arctic Ocean and seas, along with changes in salinity and acidification, affects biodiversity, including marine and dependent species.
- Affects Fauna: Increased rainfall due to Arctic amplification affects the availability and accessibility of lichens, leading to starvation and death among Arctic fauna.
- Gaseous Emission: Thawing permafrost releases carbon and methane, greenhouse gases responsible for global warming.
- It may also release long-dormant bacteria and viruses, potentially leading to disease outbreaks.
Impact of Arctic warming on India:
Rising Sea Level:
- According to the World Meteorological Organization’s report, ‘State of Global Climate in 2021’, sea level along the Indian coast is rising faster than the global average rate.
- One of the primary reasons for this rise is the melting of sea ice in the polar regions, especially the Arctic.
Connectivity:
- The Arctic’s ice meltdown and its geographical location will ensure the shortest sea distance between America, Europe and North East Asia.
- This will likely transform the global maritime commerce, presently conducted through the traditional East–West route through the Malacca Strait and Suez Canal.
Monsoons:
- The link between the impact of the changing Arctic and monsoons in India is growing in importance due to the extreme weather events the country faces, and the heavy reliance on rainfall for water and food security.
Geopolitics:
- The melting Arctic ice is also raising the geopolitical temperatures.
- In 2018, China’s White Paper on Arctic policy called itself a ‘Near-Arctic State’.
- The opening of the shipping routes and possibilities of increased resource extraction is leading to the big three—US, China and Russia—and NATO, jockeying for position and influence in the region.
Way Forward:
The temperatures could rise strongly by 2026, resulting in humans going extinct, making it in many respects rather futile to speculate about what will happen beyond 2026. Thus , the right thing to do is to help avoid the worst things from happening, through comprehensive and effective action through a Climate Plan.
Source: The Hindu
Syllabus
- Mains – GS 2 (Governance)
Context: Reports of drugs manufactured in India causing severe harm and dozens of patient deaths from across the world continue to trickle in.
About Indian Pharmaceutical Industry:
- India is the largest provider of generic drugs globally.
- It supplies over 50% of global demand for various vaccines, 40% of generic demand in the US and 25% of all medicine in the UK.
- The Indian pharmaceutical market is estimated at USD 40 billion and pharma companies export another USD 20 billion.
- However, this is a miniscule portion of the USD 1.27-trillion global pharmaceutical market.
- Globally, India ranks 3rd in terms of pharmaceutical production by volume and 14th by value.
- India has more than 30% share in the global generic market but less than 1% share in the new molecular entity space.
- New Molecular Entity: A novel compound that has not previously been approved for use in humans.
- According to the Economic Survey 2021, the domestic market is expected to grow three times in the next decade.
Issues associated with pharma sector in India:
Anaesthetic drugs:
- Latest of the reports is the deaths of two patients in Sri Lanka who were administered Indian-made anaesthetic drugs.
Eye drops:
- Just last month, eye drops manufactured in India had caused eye infection in about 30 patients and blindness in 10 in Sri Lanka.
- While anaesthetic drugs made in India causing deaths are a first in the recent past, eye drops causing infections, blindness and even deaths were reported a few months ago in the United States, with the Atlanta-based Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) finding a highly drug-resistant bacteria in them.
Cough syrups:
- The series of adverse reports against drugs produced in India began last year when the World Health Organization (WHO) linked the deaths of at least 70 children in Gambia from acute kidney injury to cough syrups.
- The culprit ingredient in the syrups was diethylene glycol and ethylene glycol — deadly chemicals used as a cheaper substitute for propylene glycol — that should never have been found in any medicine.
- Soon after the deaths in Gambia, cough syrups made in India and containing the two deadly chemicals killed 18 children in Uzbekistan in December 2022.
- Indian-made cough syrup was again in the news when WHO flagged the contaminated drugs found in the Marshall Islands and Micronesia; the contamination was identified by the Australian regulator.
Challenges:
Safety of drugs:
- Except for some customary inspections, the Indian drug regulator has so far failed to institute measures to make sure drugs produced in India for export and domestic use are safe.
Failing the quality tests:
- According to a Central Drugs Standard Control Organization (CDSCO) survey in 2014-2016, about five per cent of Indian drugs, several of them manufactured by large pharma companies, failed the quality test.
- Independent studies suggest that this figure could be much higher.
- The country’s pharma industry has largely been in denial over quality-related concerns expressed by national and international observers.
Costs of production:
- The cost of production in India is 50 percent less than in developed nations, but it is still around 18 percent higher than China.
- This is attributable to raw materials being 25-30 percent costlier, electricity being 20 percent more expensive, and other costs such as financing, logistics, transportation, etc., being 30 percent more expensive.
Regulation of Drugs in India
Drugs and Cosmetics Act, 1940:
- The Act regulates the import, manufacture, and distribution of drugs in India.
- The primary objective of the act is to ensure that the drugs and cosmetics sold in India are safe, effective and conform to state quality standards.
- The Drugs and Cosmetics Act, 1940 was amended by the Drugs & Cosmetics (Amendment) Act, 2008 to provide for more stringent penalties for manufacture and trade of spurious and adulterated drugs.
New Drugs, Medical Devices and Cosmetics Bill, 2022:
- To accommodate changing requirements and encourage the adoption of new technology, the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare released a draft bill in July 2022 to replace the existing Drugs and Cosmetics Act 1940.
- This act governs drug importation, production, and distribution across the country.
Central Drugs Standard Control Organization:
- It is the apex department of the Central Drugs Standard Control Organization (CDSCO) of the Government of India.
- CDSCO is a regulatory body for Indian pharmaceuticals and medical devices.
- It comes under the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare.
Drugs Controller General of India:
- Drugs Controller General of India (DCGI) is the head of department of the Central Drugs Standard Control Organization of the Government of India
- It is responsible for approval of licenses of specified categories of drugs such as blood and blood products, IV fluids, vaccines, and sera in India.
- DCGI also sets standards for manufacturing, sales, import, and distribution of drugs in India.
Way Forward:
- Strengthening the regulatory framework: The government should strengthen the regulatory framework and enforce stricter laws to ensure that the drugs and medicines produced in India meet the required safety and quality standards.
- Increasing inspections and audits: Regular inspections and audits should be conducted at all levels of the pharmaceutical industry to identify and address any potential issues related to the manufacturing process, quality control, and distribution.
- Enhancing transparency and accountability: The government should promote transparency and accountability by making the regulatory process more accessible and understandable to the public and stakeholders.
- This can be done by improving the dissemination of information and conducting public consultations.
- Providing training and capacity building: The government should invest in training and capacity building for regulatory agencies and industry professionals to ensure that they have the necessary skills and knowledge to maintain high standards of drug quality and safety.
- Collaboration with International Bodies: India should collaborate with international bodies like the World Health Organization (WHO) to adopt best practices in drug regulation. This will help ensure that Indian pharmaceutical companies are following global safety and quality standards.
Source: The Hindu
Practice MCQs
Q1) Consider the following statements regarding, Employees’ Provident Fund Organisation:
- It is under the Ministry of Corporate Affairs.
- It was established in 1952.
- It implements the Employees’ Provident Fund and Miscellaneous Provisions Act, 1952.
Which of the above statements is correct?
- 1 and 2 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
Q2) With reference to the Hindukush region, consider the following statements:
- It is called the Third Pole because it stores more snow and ice than anywhere else in the world outside the polar regions.
- The region contains Important Bird Areas (IBAs).
Which of the statements given above is/are incorrect?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Q3) With reference to the Ex Khaan Quest 2023, consider the following statements:
- It is being held in Myanmar.
- India is represented by the Garhwal Rifles.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Comment the answers to the above questions in the comment section below!!
ANSWERS FOR ’ 20th June 2023 – Daily Practice MCQs’ will be updated along with tomorrow’s Daily Current Affairs.st
ANSWERS FOR 9th June – Daily Practice MCQs
Q.1) – b
Q.2) – d
Q.3) – a











